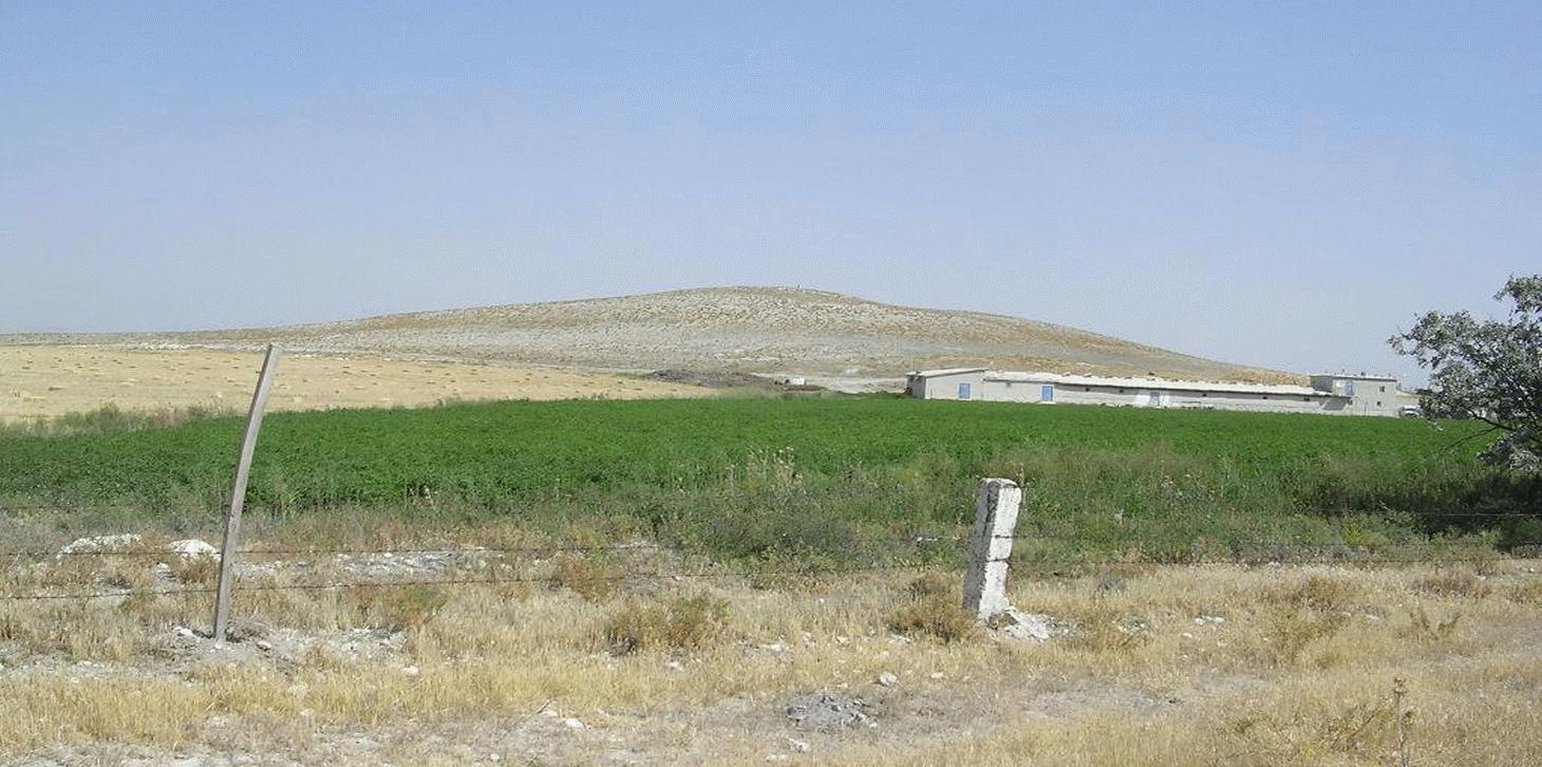




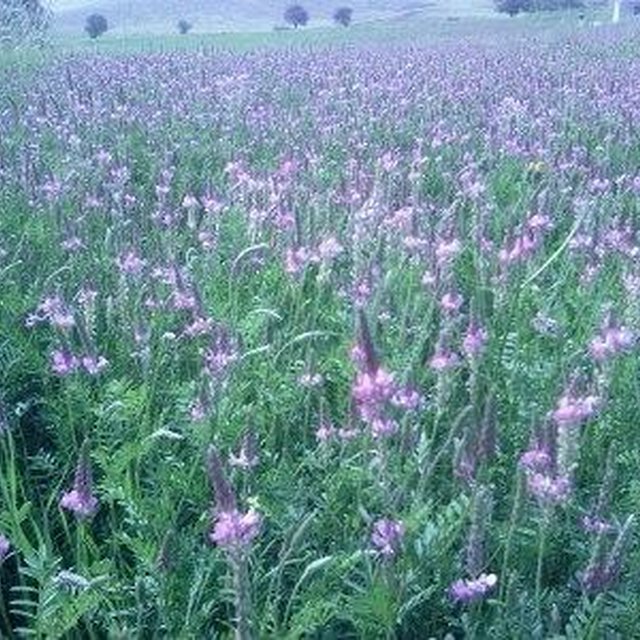
Fodder crops (maize, alfalfa, sainfoin, common vetch, triticale, oat, fodder beet, wheat and barley) are grown for hay production for livestock feeding. Growing fodder crops is a part of sustainable agriculture. The soil is protected in dry farming areas by covering the soil surface and leguminous fodder species (alfalfa, sainfoin, common vetch), which increases the soil fertility by nitrogen fixation. Applying the technology does not require extra inputs different from other agricultural crops. All that is needed is to identify a crop rotation plan including fodder production and regular agricultural crops.
Purpose of the Technology: Different fodder crops (legumineous and gramineous plants) are produced to feed the farmers’ own livestock. By enabling widespread and dense surface cover, It helps both in dry farming and irrigated areas to protect the soil from water and wind erosion.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Usually the soil is first ploughed. Soil cultivation machinery (tractor, disc plough, wide-sweep cultivator, disc harrow, fertilizer and seed drill) is used to prepare the soil for cultivation, to fertilize the soil and to sow the seeds. After seeding and growing of the crops, special machinery is used for harvesting.
Natural / human environment: Farmers who produce both livestock and field crops in particular can use this technology and get an improved benefit. They can increase income and at the same time protect their soil.
الموقع: Keskin Watershed, Eskişehir, تركيا
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها:
انتشار التقنية: منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة (approx. 100-10 كم2)
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
تاريخ التنفيذ: منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
نوع التقديم








| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (YTL) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (YTL) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| معدات | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 50.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 38.46 | ||||
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (YTL) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (YTL) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Ploughing | ha | 1,0 | 175,0 | 175,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 75,0 |
| Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Irrigation | ha | 1,0 | 280,0 | 280,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 1'200.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 923.08 | ||||
20 % increase
75% increase
75% increase
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
20% increase
Imncreased 40%
increased 30%
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 25%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50%
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 10%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 15%