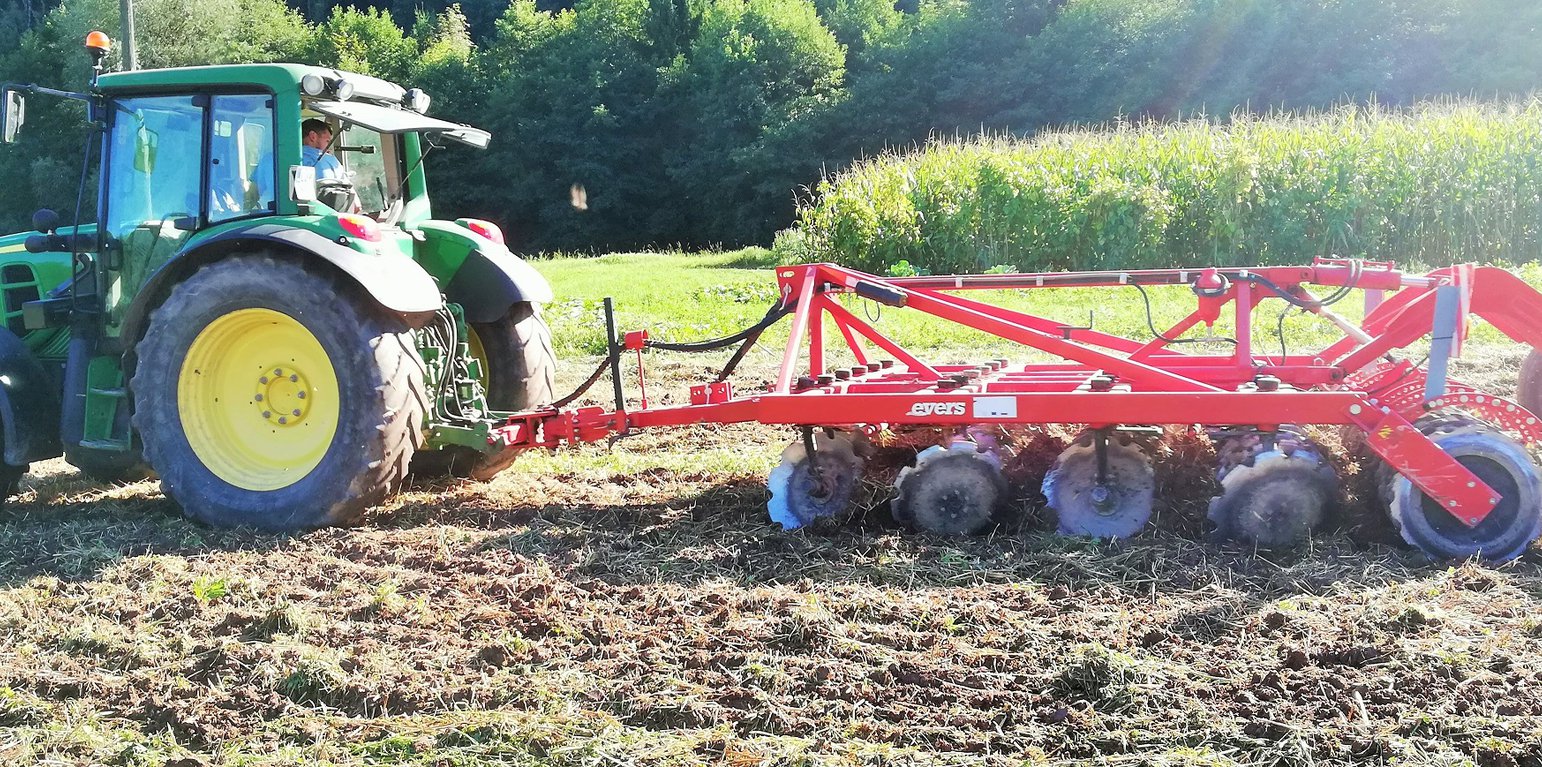




1. The technology of conservational tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) is applied in flatlands around the Municipality of Vrhnika with an average altitude of 290 m.a.s.l. Average annual precipitation is 1400 mm. The area is characterized with often stormy precipitation events and occasional summer droughts. A farmer applies this technology on various soil types from silty loam to silty clay Gleysol to organic Histosol soils (peat). Soils in the area are generally moderately deep to deep with medium soil organic matter (Gleysol) of 3-7% or with a high share of organic matter (Histosol) of >20% (Ljubljana moors). The area has good availability of surface water and groundwater of good drinking quality. Gleysol areas are drained (drainage systems) to prevent floods to enable cultivation. Histosol areas are drained (open-channel drainage systems) to enable arable crop production. However, due to high groundwater and many surface water sources, certain areas are regularly flooded during flood events mostly in late autumn, winter and spring. Salinity is not a problem due to high precipitation and leaching. Farmer practices rotational agriculture. Less than 5% of income coming from off-farm activities. The examined farm household has an average wealth and is fully mechanized/motorized. the farm has good access to services and infrastructure. The examined farm is medium in scale with land partly owned by the land user and partly leased from other private owners.The general biodiversity of the area is medium on Gleysols to high on Histosol where nature protection Landscape Park of Ljubljansko Barje (The Ljubljana Moors Landscape Park) is located.
Part of the farmers land parcels is located inside boundaries of Krajinski park Ljubljansko barje /Ljubljana Moor Landscape park. Park takes a lot of actions to secure peat soils. This almost 16,000 hectares large lowland marshy plain is marked by an interminable mosaic of grasslands, broadleaf woodlands, fields, ditches and hedges.
The farmer decided to abandon conventional ploughing technology and to start with conservational tillage technology when he noticed that the organic layer of peat soils in these areas started to become thinner. Farmer introduced this technology to preserve peat soils of Ljubljana Moors on his parcels in 2015. With ploughing, peat was mixed and decomposing - mineralise. In 18th-century peat layers of up to 2m depth were exploited for the same use as firewood. Only shallow layers of peat soil (up to 1 m) are still covering agricultural areas. As peat is a source of fertility farmers are seeking ways of preserving it. Farmer Anton Mrzlikar took a lead and started with conservational tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till).
Video https://vimeo.com/97415985 presents the effects of conservational tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) on soil stability. This is a simulation of abundant summer rain and its impact on the tilled soils in terms of water infiltration capacity and erodibility. The result of this simulation is presented very clearly. It shows the difference between long-term conventional versus conservation tillage (mulch-till). Conventional tillage ploughs the top 25-28 cm of the soil at least once or twice a year. The soil is inverted, its structure breaks down and the surface is left bare. The first raindrops break the structural aggregates causing soil surface siltation and blockage of the soil pores. Thus vertical water flow is blocked and redirected as surface runoff, causing distinct erosion. If fertilizers and pesticides are used, the water flow will transport them, along with the soil particles, to surface waters where they cause pollution or surface ponding on the fields. This leads to an uneven distribution of substances across the field surface.
In conservation tillage (mulch-till), a shallow, 10 cm layer of topsoil is mixed with organic residues which are thus retained near and on the surface. In this way, soil structure is reinforced with good soil water infiltration and absorption. Despite heavy rainfall, the soils do not show any signs of erosion. There is no surface flow. Water drains into the soil vertical flow where it is available to the plants.
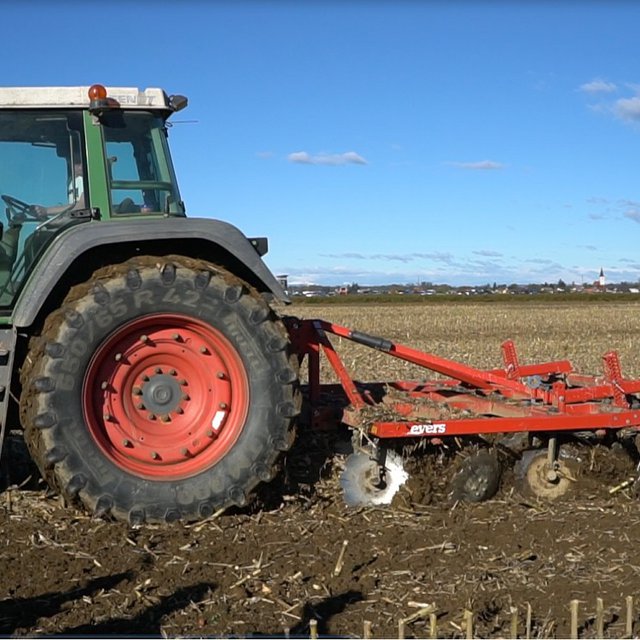
2. The farmer usees of 4-row-disk harrow tillage machinery (vario-disc) on arable fields for all crop types. When cultivating fields he crosses fields 1 - 2 times (depends on soil moisture). Every few years he uses chisels to break and shatters (aerate) the soils (depends on crop type - cereals and drought years). After main/first crop he seeds various cover crops (if fodder is needed they harvested it otherwise is used for green manure). He uses manure 30-40 t/ha. He applies typical dairy cow farm rotation (cereals/maize/soya/grass-clover mix). Cover crops are classified as rapes, cereals, oats, grass-clover, grass.
3. The main function is an increase of organic matter, retain water, increase soil biodiversity, stabilise soil structure in the soils and reduce water erosion, as well as reduce energy consumption and costs. This leads to better (1) productivity due to nutrients slow-release, (2) better water holding capacity and (3) decreased soil compaction threat. The technology was introduced to prevent decomposition of organic matter on Ljubljana moor peat soils.
4. Major inputs needed to establish is to change machinery and to gain new knowledge and experiences. They had to buy 4-row disc harrows, chisels plough and new seeders (maize). Seeding machines for cereals and oilseed rape are hired from other farmers. It is important that soils are covered all year round. Soils must be dry when cultivated.
5. The benefits are (1) increase in soil organic matter, (2) increase soil water holding capacity, (3) to maintain soil productivity, (4) increase in yields quantity and quality, (5) reduce energy consumption, (6) reduce workload - 3-4 times less time used for cultivation, (7) reduce costs.
6. Land users like (1) reduced workload and energy consumption, (2) positive impact on soil fertility and stability, (3) preserves organic matter - decrease peat soils decomposition, (4) as soils need to be covered all the time they produce more feed for cows, (5) smooths surface fields, (6) with disc harrow is easy to till soils even when residues are present on fields, (7) less soil compaction
Land users dislike: (1) investment cost for new machinery are high, (2) time to change in doing things and practice, (3) on clay soils (Gleysol) surface ponding is occurring, (4) soils need to be drier for tilling in comparison to ploughing.
الموقع: Podlipa, Vrhnika. This specific farmer applies this technology on Ljubljansko barje, othewise is applied all over Slovenia, Central Slovenia, سلوفينيا
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها: 10 - 100 موقع
انتشار التقنية: يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟: نعم
تاريخ التنفيذ: 2015; منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
نوع التقديم






| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (EUR) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (EUR) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| معدات | |||||
| chisel plow material (home made) | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 6500,0 | 6500,0 | 100,0 |
| seeder fo cover crops | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 50,0 |
| seeder for maize | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 7500,0 | 7500,0 | 50,0 |
| 4-row disk harrow | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 23000,0 | 23000,0 | 50,0 |
| sprayer | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 12,5 | 12,5 | 25,0 |
| GPS navigation | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| hire seeder for cereals | EUR/ha | 15,0 | 50,0 | 750,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 42'762.5 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 47'513.89 | ||||
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (EUR) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (EUR) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Maintenance of 4-disc harrow | hour | 6,0 | 6,25 | 37,5 | 100,0 |
| Maintenance of Spayer | hour | 6,0 | 6,25 | 37,5 | 100,0 |
| Maintenance of seeder for maize | hour | 4,0 | 6,25 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Maintenance of seeder for cover crops | hour | 1,0 | 6,25 | 6,25 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Lubricant cartridge for4-disc harrow | cartridge | 18,0 | 5,0 | 90,0 | 100,0 |
| Nozzels for Spayer | nozzel | 20,0 | 4,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Lubricant cartridge for seeder for maize | cartridge | 4,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Lubricant cartridge for seeder for cover crops | cartridge | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 301.25 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 334.72 | ||||
It increased due to the fact that soil has to be covered at all times (grass, clover, cover crops) to retain soil moisture and prevent soil erosion and to provide an optimal living condition for soil life (fauna, flora). Previously the land was left bare after harvesting cereals until autumn or even spring.
Due to more fodder, the farmer managed to increase the number of livestock (dairy cows).
Due to the fact that soils are not ploughed anymore, a farmer has in wet years (more precipitation in a short period of time, especially in the springtime) problems on organic marshland and clay gley soils being fully saturated. This causes a reduction in the germination of seeds and weaker growth of plants due to hypoxia.
More different types of cover crops in production. Some are used as nitrogen fixators or for loosening the soils with deep rots.
The land management simplified due to fewer machines needed and less time need for land cultivation and soil preparation.
Less petrol nedeed for land cultivation.
More livestock means more income.
Workload decreased due to abandoning of ploughing.
The farmer observed positive impacts and seeks for more knowledge on this topic to improve its practice.
Difficult to quantify. An increase in soil organic matter has an impact on CO2 sequestration.