



The main features of the approach:
•Empower farmers to become self-sufficient in managing their lands under Conservation Agriculture through education, awareness raising with a focus on transferring knowledge, skills and tools to improve crop production, increase food security, and incomes of rural communities.
•Promote the transition from traditional farming to modern systems based on minimal soil treatment, diversified crop production, stubble retention and direct seeding by building capacity.
•Facilitate positive change by leveraging the strengths and capabilities of different partners to transfer skills, knowledge and resources to farmers and communities interested in active CA adoption.
In Kazakhstan the most of crop management experiences and education in universities emphasized conventional tillage based production systems. Changing minds to accept crop management practices based on the principles of Conservation Agriculture is one of the biggest constraint of CA adoption. Farmers are ready to change their mind set if they are knowledgeable, well informed and see the benefits of CA-based crop management practices in their fields. The approach is based on awareness raising, training of farmers and farmer testing of CA technology in close collaboration with specialists from international and local institutions. An active dialogue with farmers, knowledge and technology dissemination are built on participation of qualified specialists/experts who are part of the management team of each farm and are able to efficiently test and adapt new technologies to the local conditions. CA is a complex approach and system, it implies changes in a number of technological components of the existing traditional systems of agriculture. It is necessary to change two basic paradigms: the paradigm of soil tillage and the paradigm of linear knowledge flow.
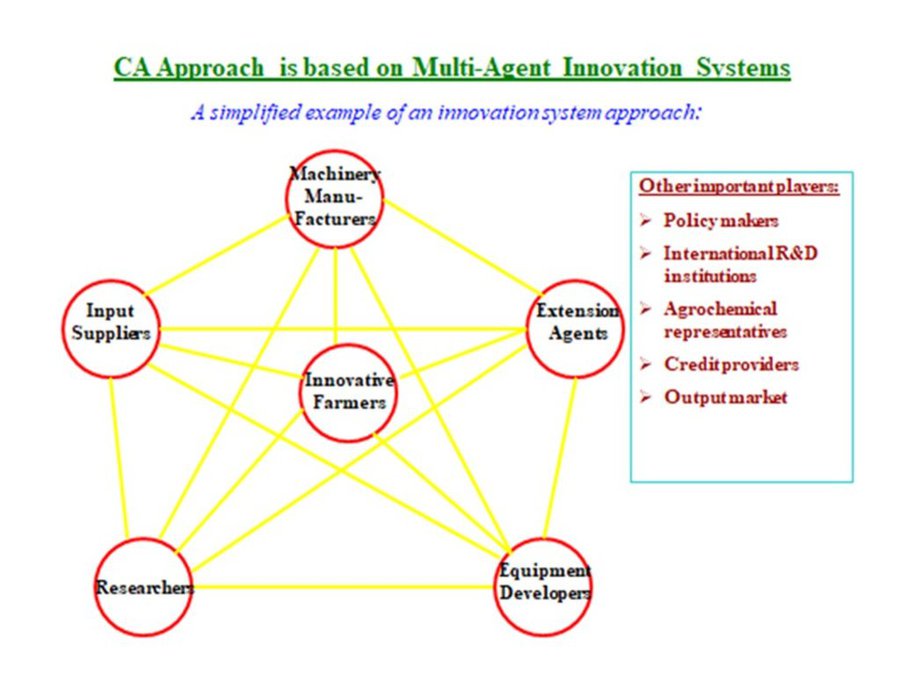
Many agricultural research and extension systems are based on a linear model of knowledge flow, with new knowledge being developed in research organizations, passed on to agricultural extension agents who in turn pass on the new knowledge and information to farmers. While this model may be applied to simple technology, it does not always effectively work with complex technologies, especially when research institutes do not have the capacity to develop functional packages of multiple technological components for all farmer situations. Innovative approaches on the basis of complex technologies are needed in adaptation, system development process and promotion. Innovative approach (platforms) are based on networks of multiple agents, including farmers-innovators and decision-makers, all utilizing their own knowledge, external information and policy support to help overcome problems and develop functional systems for local farming conditions and farmer circumstances.
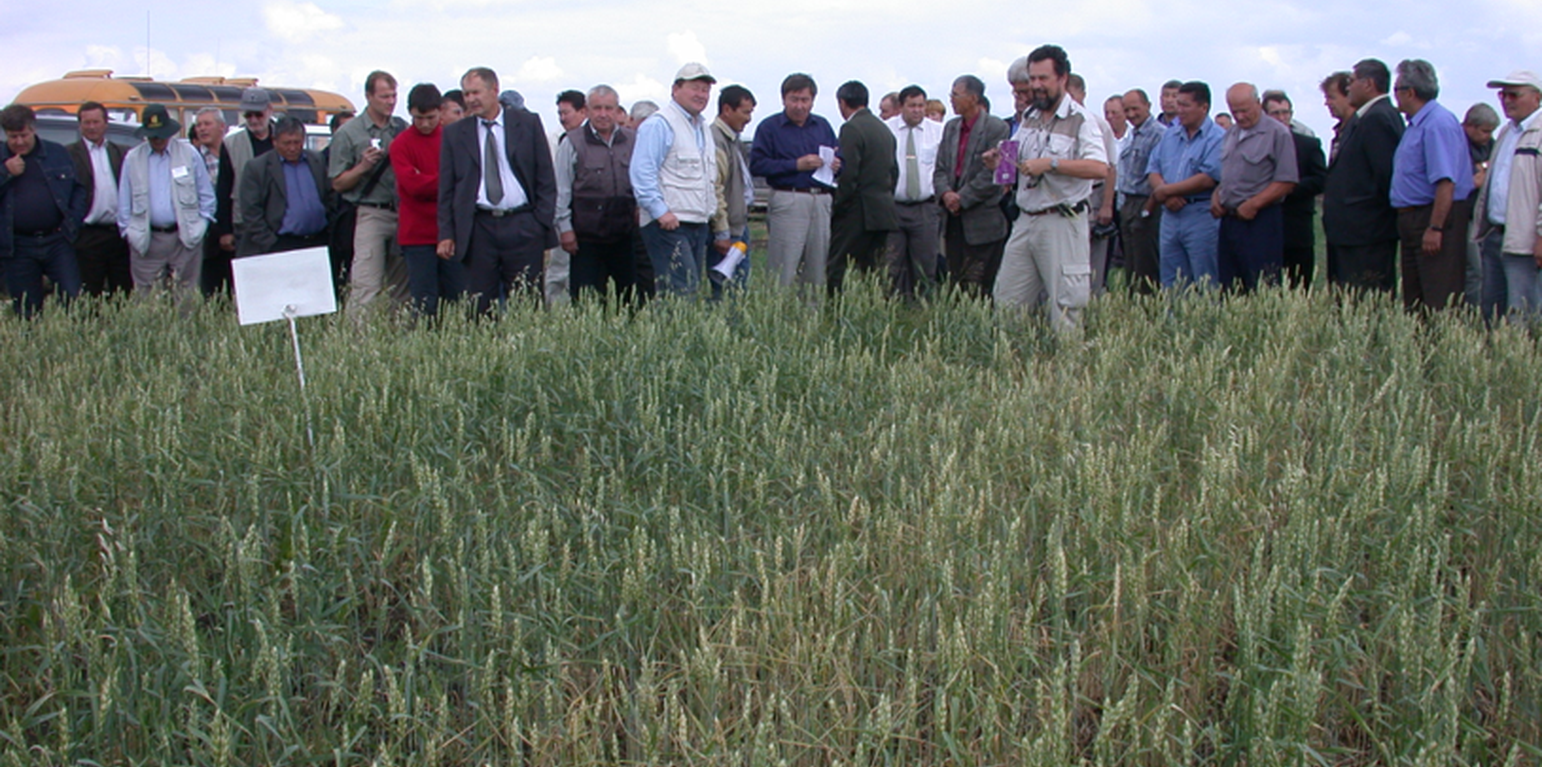
The target farmers as well as farmers of the neighbouring farming community were trained on-the-job on key topics of CA such as diversified cropping systems, chemical fallow, minimum/no-tillage, direct seeding, and snow and residue management. Altogether four training workshops were carried out. In each session international and national experts trained about 30 farmers. Conservation Agriculture study tour to USA (Washington State, Idaho State) and Canada (Saskatchewan Province) was organized. Public awareness and also training on CA-technology also were generated through six field days and seminars bringing together farmers, stakeholders, policy-makers and researchers to observe and discuss key field demonstrations.
Large-scale adoption of Conservation Agriculture (zero/minimum soil tillage, leaving crop residues in the fields, direct seeding with narrow chisel and disk openers, permanent bed-planting and furrow irrigation, etc.) were initiated by the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and FAO in 2002. Thanks to the joint efforts of national scientists and farmers, international organizations (CIMMYT, FAO, ICARDA, World Bank, UNDP, USAID, etc.), support by the state and government bodies, the areas under no-till have been increasing from virtually none in 2002 to an estimated area of 3 000 000 ha in 2019.
الموقع: Northern Kazakhstan: Akmola and North Kazakhstan regions (provinces), كازاخستان
تاريخ البدء: 2002
سنة الإنهاء: 2004
نوع النهج

| ما هي الجهات المعنية / الكيانات المنفذة التي شاركت في النهج؟ | حدد الأطراف المعنيين | وصف أدوار الأطراف المعنية |
| مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية | 1) A.Darynov, “Daryn” Farm, Valikhanovo village, Zharkainsky district, Akmola region, Kazakhstan 2) M.Sagimbayev, “Dostyk06” Farm, Astrahanovka village, Astrahanskyi district, Akmola region, Kazakhstan 3) V.Surayev, “Surayev” Farm, Vishnevka village, Arshalinskyi district, Akmola region, Kazakhstan 4) V.Cherezdanov, “Cherezdanov” Farm, Smirnovo village, Akkayinskii district, Northern Kazakhstan region, Kazakhstan | Coordination of field works, adoption at the farm |
| متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون | 1) Dr.M.Matyushkov, Research and Production Center of Grain Farming, Shortandy, Akmola region, adviser in agriculture equipment 2) Dr.I.Vasko, Research and Production Center of Grain Farming, Shortandy, Akmola region, adviser in agronomy and economics | 1) Adoption of CA equipment at farms 2) Assessment of CA technology effectiveness |
| الباحثون | 1) Dr.A.Bektemirov, Research and Production Center of Grain Farming, Shortandy, Akmola region, consultant on soil science 2) Dr.A.Kenjebekov, Research and Production Center of Grain Farming, Shortandy, Akmola region, consultant on agronomy | 1) Soil investigations and analysis 2) Agronomy research and analysis |
| الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار) | Prof.K.Elemesov, Ministry of Agriculture of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Head of Science Department, National Project Coordinator | Coordination of the CA adoption project on behalf of the government of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
| منظمة دولية | 1) Dr.Th,Bachmann, FAO Specialist on Agronomy 2) Dr.Th.Friedrich, FAO Specialist on Engineering 3) Prof. M.Karabayev, CIMMYT Representative in Kazakhstan | 1) Consultations on agronomy issues of the CA technology adoption 2) Consultations on engineering issues of the CA technology adoption 3) The Project Leader |
| Foreign organization | Prof. L. Makus, Professor of Economics, Idaho State University, USA | Economic research and assessment of CA adoption at farms |
Conservation Agriculture Innovative approach (platform) is based on networks of multiple agents, including farmers-innovators and decision-makers, all utilizing their own knowledge, external information and policy support to help overcome problems and develop functional systems for local farming conditions and farmer сircumstances
وقد تم اتخاذ القرارات من قبل
تم اتخاذ القرارات بناء على
“Conservation Agriculture for rainfed crop production”, “Conservation Agriculture for irrigated crop production”
Technology and economics research were carried out by two main national research institutes: 1) Kazakh Research and Production Center for Grain Farming, Shortandy settl., Akmola region (province); 2) Kazakh Research Institute for Farming and Crop Production, Almalybak settl., Almaty region (province).
Land-users and decision-makers are convinced to adopt and promote CA as key element of the agriculture system in the country
The approach helped land users to clearly understand all components and stages of CA, to follow and abide main requirements for the technology introduction and maintenance.
CA adoption and promotion implies participation of multiple agents the approach suggested ways to effective coordination and implementation of SLM
The approach enabled farmers and national specialists to recognize as perspective, economically and ecologically profitable of Conservation Agriculture based on no-till and direct seeding systems.
Yield of spring wheat under CA, in average, 50 to 60% higher in comparison with the conventional technologies.
The advantages of CA are especially evident in the years of drought, that is extremely important for Kazakhstani soil-climate conditions (called as “Area of Risk Farming”)