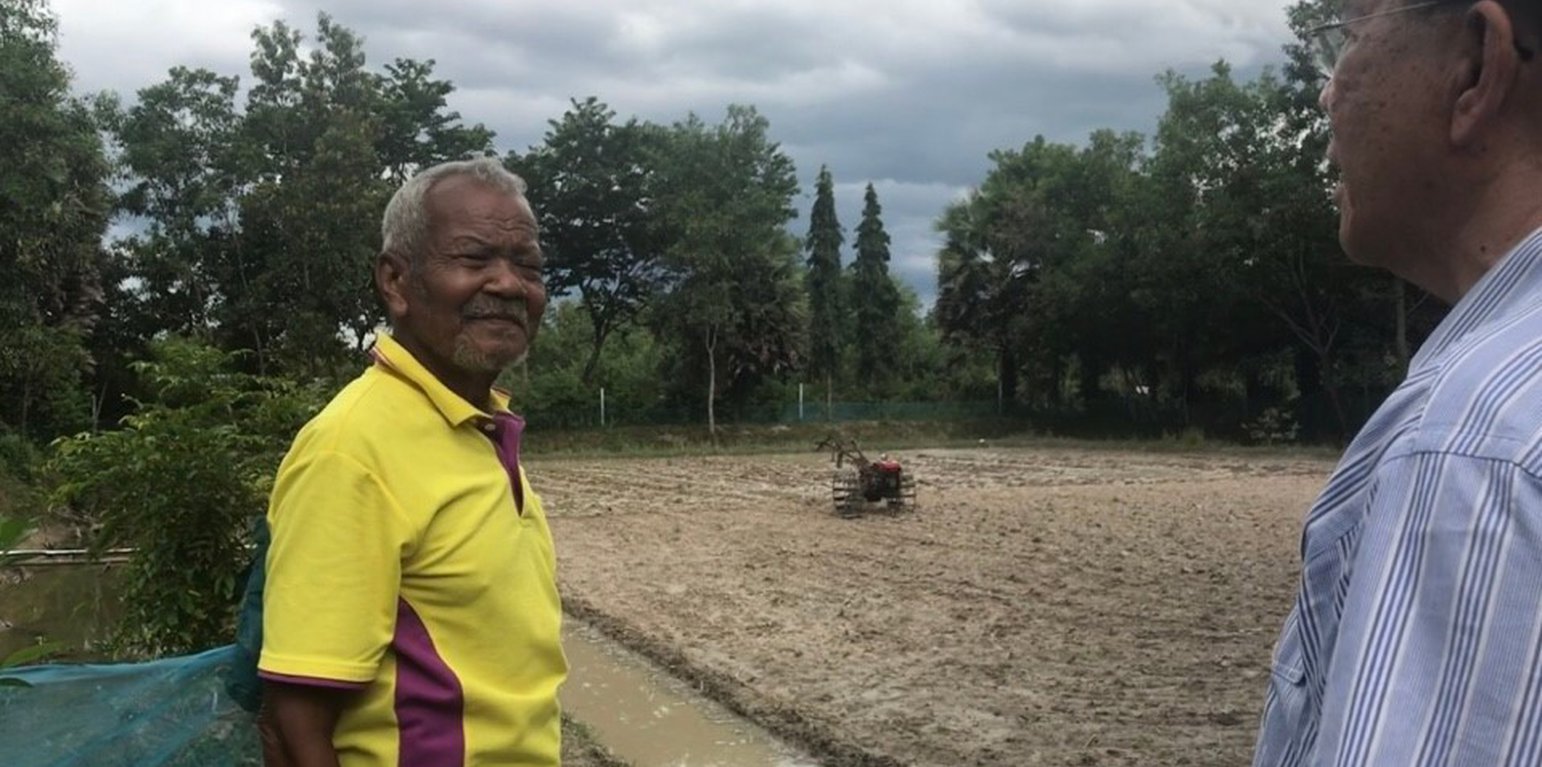




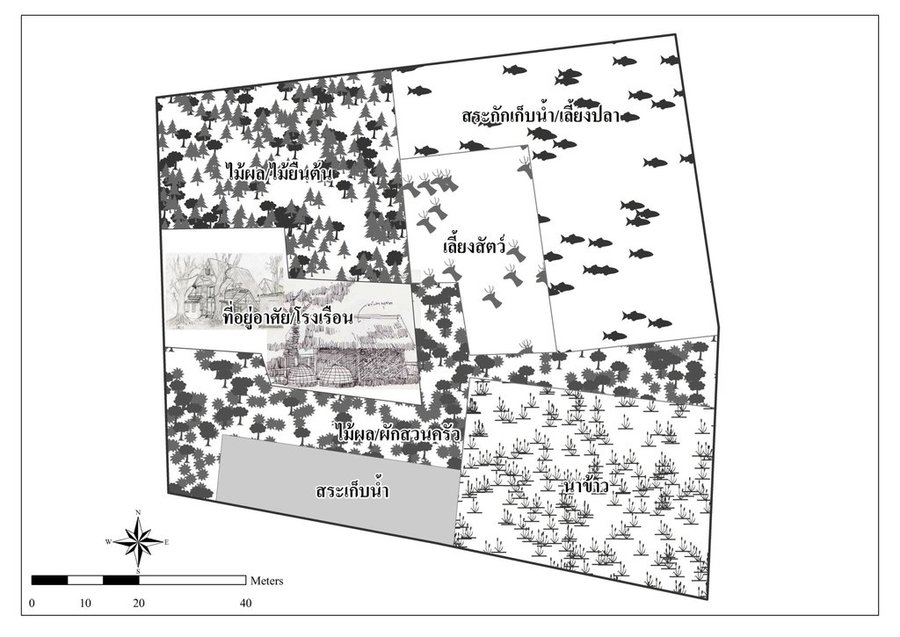
The new theory of agriculture is the application of improved mixed farming systems to poor farmers with smallholdings - for example in Chang Sai sub-district, Phra Phrom district, Nakhon Si Thammarat province, Thailand. The most important concept underlying the new theory of farming is efficient allocation of land to serve the different needs of farm households. This includes paddy fields, farm ponds for water and fish, and cash crops, fruit trees, and trees for farm income, plus a residential area. It's goal is solving the problem of shortage of land and water resources, which is a very serious problem in Thailand, in order to help smallholder farmers make a living. Apart from the fact that the size of the farm and water resources are the limiting factors in this area, the land is also degraded by both natural and human activities. The area is classified as sand dunes with low to very low soil fertility where farmers mostly grow the same crops continuously. This results in high risk of fluctuations in the amount of production - and insufficient food crop production for household consumption. Therefore, land allocation for agriculture under the concept of the new theory of agriculture is the appropriate use of resources in small-scale areas for optimal benefits and increases in household incomes. Nowadays, farmers in adjacent areas are realizing the benefits obtained from land allocation, and they have formed a group to improve the use of their small-scale holdings for optimal benefits.
The new agricultural theory was initiated by His Majesty the Late King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand to provide help for farmers with small-scale farms. For land allocation, the land is divided into 4 parts. Part 1 is designated for a pond to store rainwater during the rainy season and to supply water to grow crops in the dry season as well as for raising aquatic animals (fish, field crabs) and plants (such as morning glory, water mimosa, etc.). Part 2 is set aside for rice cultivation during the rainy season as the daily staple in households throughout the year, which cuts down on expenses and allows the farmers to be self-reliant. Part 3 is used for growing fruit trees, perennials, vegetables, and field crops for daily consumption. If there is any surplus from consumption, it can be sold. Part 4 is used for dwellings, animal husbandry, roads and other structures - including barns, strawstacks, compost, houses, mushroom nurseries, stalls, flowering-plants, ornamental plants, home-grown vegetables in backyard gardens. The proportion of the area in each section can be adjusted for either increase or decrease depending on the conditions of each location and the necessity of farmers who make use of the area, but it is usually 30:30:30:10.
الموقع: Chang Sai sub-district, Phra Phrom district, Nakhon Si Thammarat province, تايلاند
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها: موقع واحد
انتشار التقنية: يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟: كلا
تاريخ التنفيذ: 2010
نوع التقديم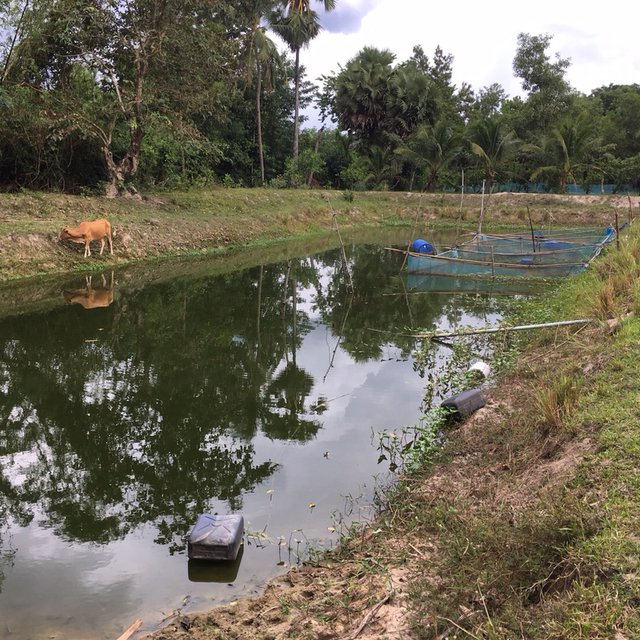










| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (Baht) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (Baht) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Cultivation | days | 60,0 | 300,0 | 18000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Hiring tractors for pond construction | ponds | 3,0 | 16000,0 | 48000,0 | 70,0 |
| المواد النباتية | |||||
| Seeds | Kilogram | 300,0 | 10,0 | 3000,0 | |
| Seedlings | Plants | 100,0 | 50,0 | 5000,0 | 80,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| Compost | Ton | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 50,0 |
| مواد البناء | |||||
| Roof tiles | each | 240,0 | 60,0 | 14400,0 | |
| Cement | bags | 8,0 | 100,0 | 800,0 | |
| Sand and rocks | ton | 1,0 | 1650,0 | 1650,0 | |
| Pillars | each | 12,0 | 100,0 | 1200,0 | |
| غير ذلك | |||||
| Fishes and crabs | each | 2500,0 | 1,0 | 2500,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 97'050.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 2'940.91 | ||||
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (Baht) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (Baht) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Cultivation | days | 260,0 | 300,0 | 78000,0 | 100,0 |
| Cultivation | days | 260,0 | 300,0 | 78000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| Compost | ton | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 50,0 |
| غير ذلك | |||||
| Fishes and crabs | each | 5000,0 | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 30,0 |
| Feeding | month | 9,0 | 5000,0 | 45000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 208'500.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 6'318.18 | ||||
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 100
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 500
Considering from rice production in 1 rai
As farmers allocate the land to different types of crop, they can evaluate the suitable types of crops for the markets and climatic conditions
Rainwater can be collected in the ponds and this can be a supply for cultivation during the dry season
The knowledge about SLM comes through the support of the government agencies
Application of compost in the farm leads to an increase in soil organic matter
Earthworms, Birds, Bees, Cicada, and Varanus.
Agrichemical products are not applied to the farmland, resulting in less soil contamination to environment