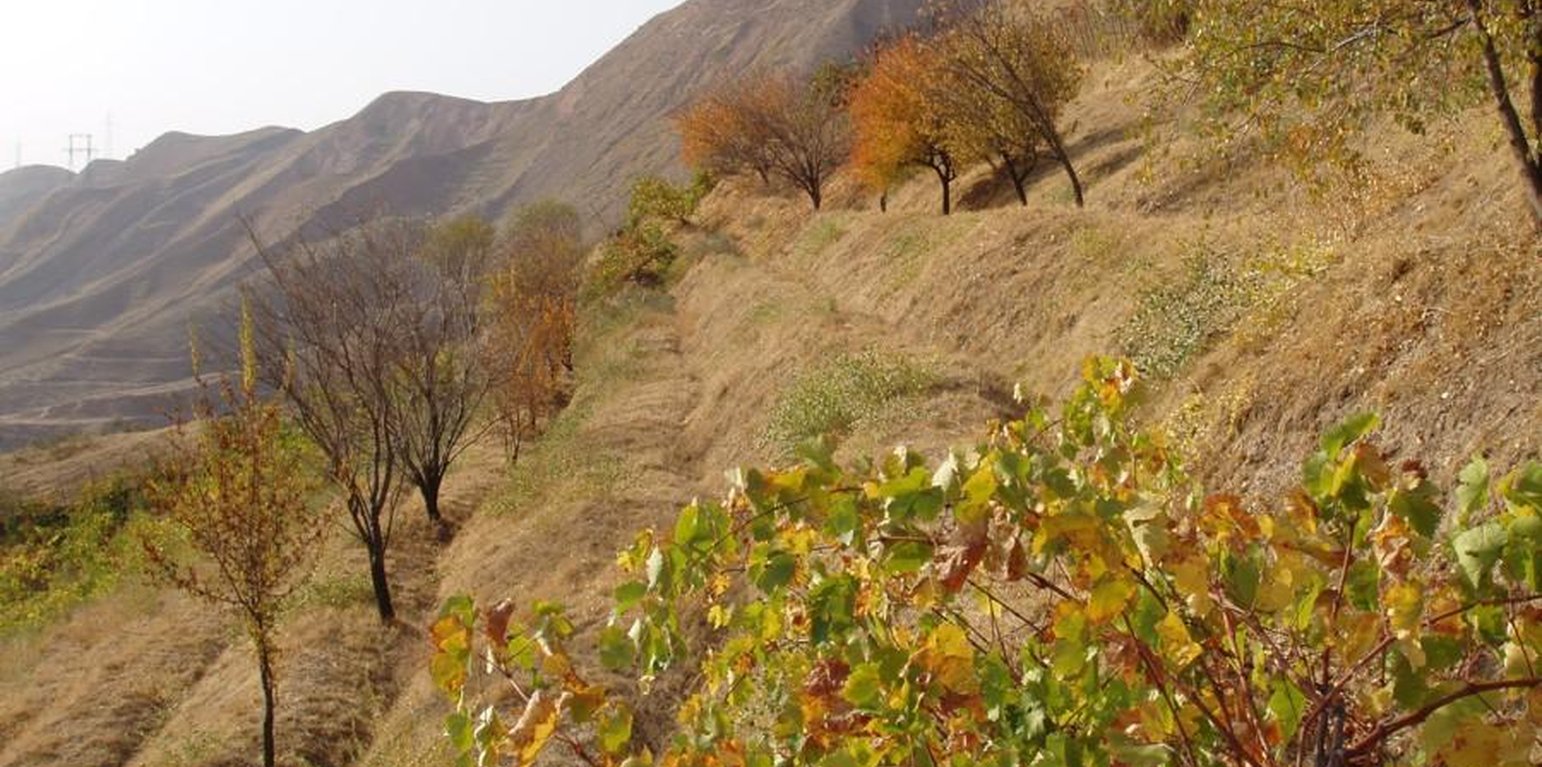




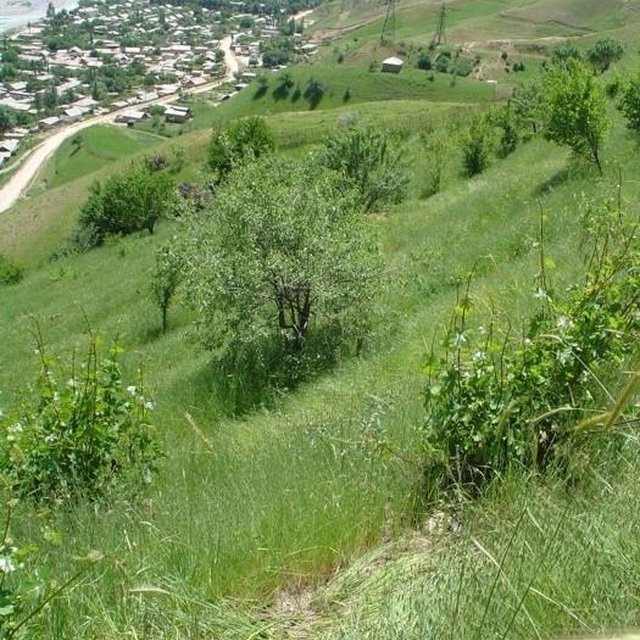
In the Varzob valley of Tajikistan, slopes of around 30% are used communally, and are heavily overgrazed. This has led to a reduction in vegetation cover, to soil compaction, and to severe sheet and rill erosion. In 1982, one innovative land user began to set up half a hectare vineyard/fruit plot with intensive grass/fodder production for cut-and-carry and also a separate section above for hay making - by his own initiative. By the application of various conservation measures, within five years an area exposed to severe water erosion was converted into an area of sustainable use. Fodder and fruits are now flourishing and the natural resources of soil and water are conserved more effectively.
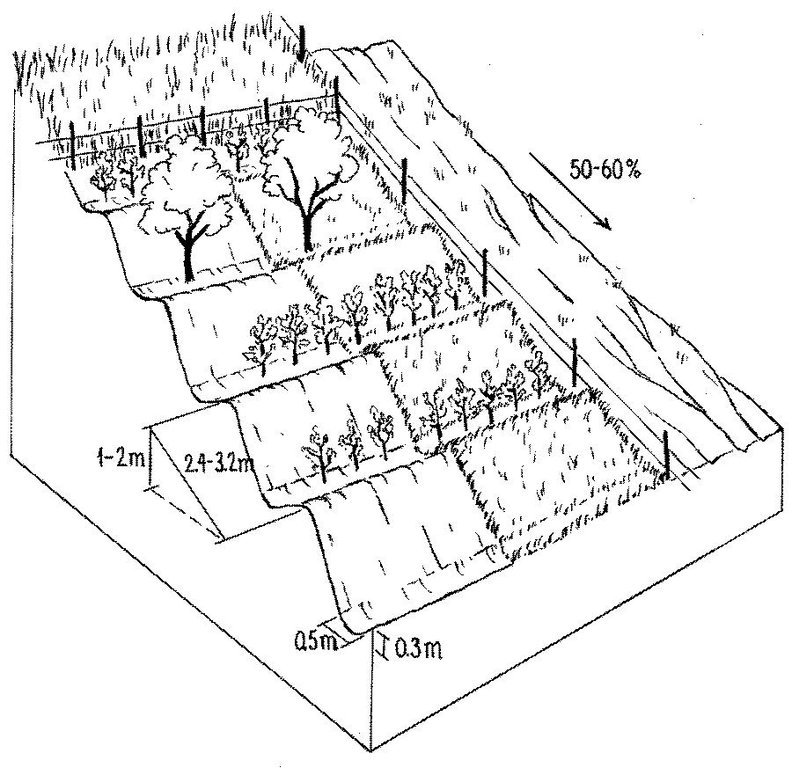
Purpose of the Technology: The start of the process was fencing of the plot to keep out animals. Scrap metal and other materials from a machinery depot were used to build a 1.5 m high fence. To harvest and hold runoff water from the hillside for grapes and fruit trees, narrow backsloping terraces were constructed, each with a water retention ditch along the contour. During the initial phase, the terraces did not harvest enough water for establishment of the seedlings. So water for supplementary irrigation was carried to the plot by donkeys in old inner tubes from car tyres. Manure is applied to the plot to improve soil fertility. The manure is collected on the high pastures where the herders graze their animals during summer. The total amount of manure applied to the plot so far amounts to about 3 t/ha over 20 years.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of such a plot is very demanding in terms of manpower. However within 5-6 years the system becomes self-sustaining and the productivity of the land is improved several times over. Following this positive experience, other households in the area have adopted the technology spontaneously, and today about 15 ha of degraded grazing land in the Varzob valley have been converted into productive fruit gardens.
Natural / human environment: For the innovator, his most valuable fruits are grapes, followed by apricots, almonds and plums. He has also successfully grown mulberry, pomegranate and cherry trees. Not all the seedlings survive: the farmer considers a 40% survival rate of grape vines to be reasonable. The fruit harvest is mainly used for home consumption. However, in a good year the table grapes and apricots are sold on the market. The hay harvest, from naturally regenerated grasses and fodder plants between the fruits amounts on average to 0.2 t/ha/year. The pruned branches from the vines are collected and used as firewood.
The establishment of such a plot is very demanding in terms of manpower. However within 5-6 years the system becomes self-sustaining and the productivity of the land is improved several times over. Following this positive experience, other households in the area have adopted the technology spontaneously, and today about 15 ha of degraded grazing land in the Varzob valley have been converted into productive fruit gardens.
الموقع: Varzob, Tajikistan, طاجيكستان
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها:
انتشار التقنية:
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
تاريخ التنفيذ: منذ 10-50 سنة
نوع التقديم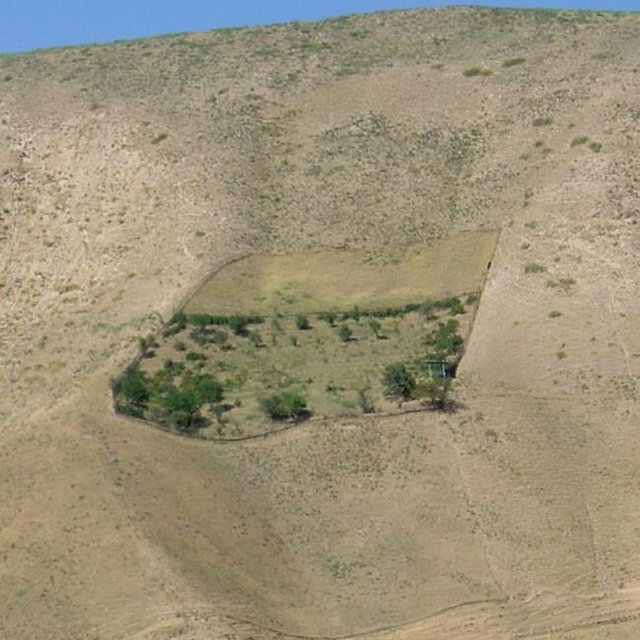











| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (دولار أمريكي USD) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (دولار أمريكي USD) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Planting/Fencing/Constructing | ha | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | |||||
| seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 99,0 |
| grape vines | ha | 1,0 | 1500,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| manure | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 2'690.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 2'690.0 | ||||
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (دولار أمريكي USD) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (دولار أمريكي USD) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Irrigation/manuring/keeping in good repair | ha | 1,0 | 180,0 | 180,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | |||||
| Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Grape vines (replacment) | ha | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| manure | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 570.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 570.0 | ||||
for manure application
high labour input needed for establishment and recurrent irrigation
terrace construction requires collaboration with relatives and friend
in the beginning conflicts due to jealousy, loss of community grazing land and fear of landslides caused by water retention on sloping loess areas
poorly maintained terraces may lead to increased erosion (medium (20-50%))
conserved area is too small to have significant impact