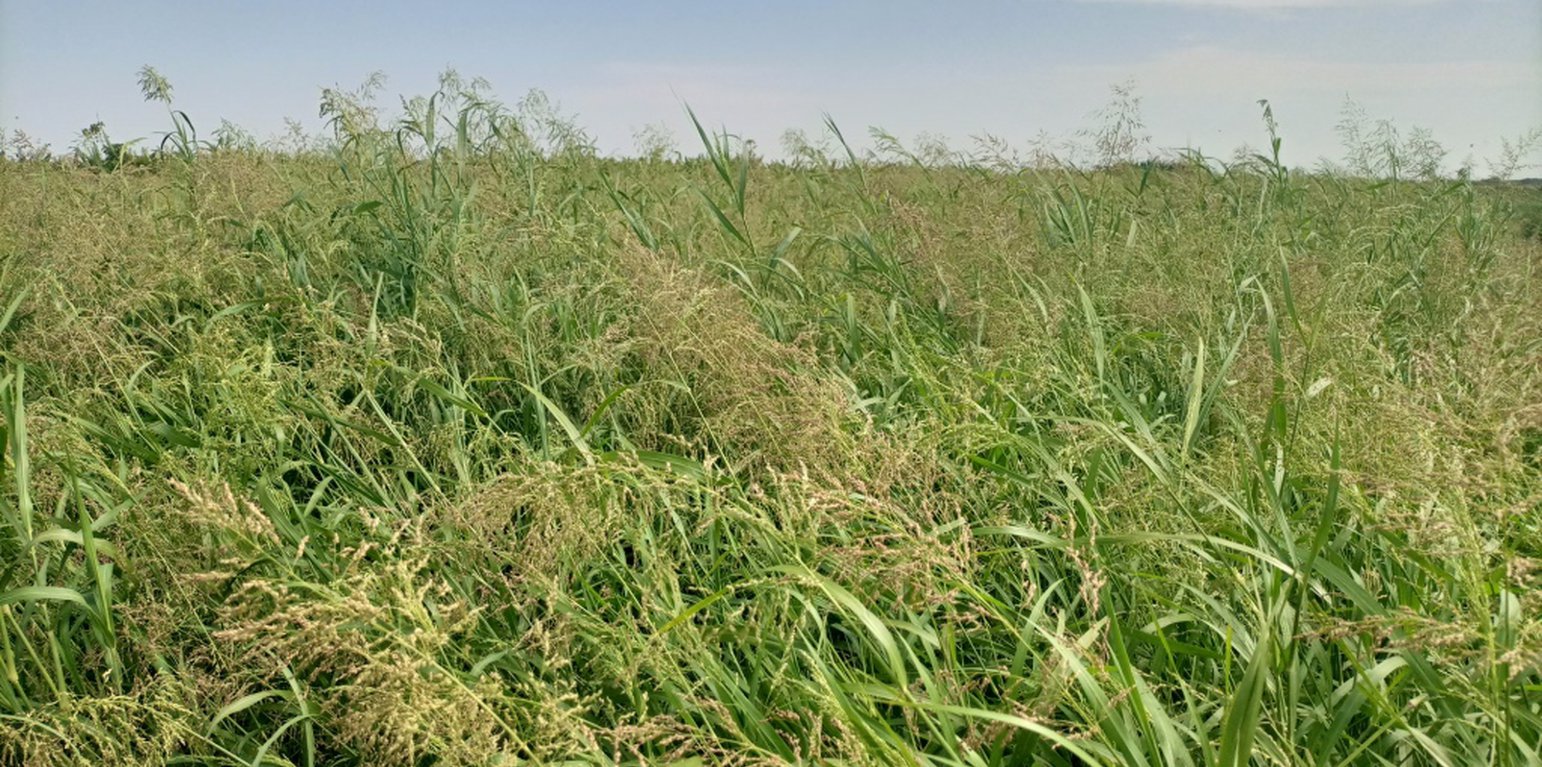




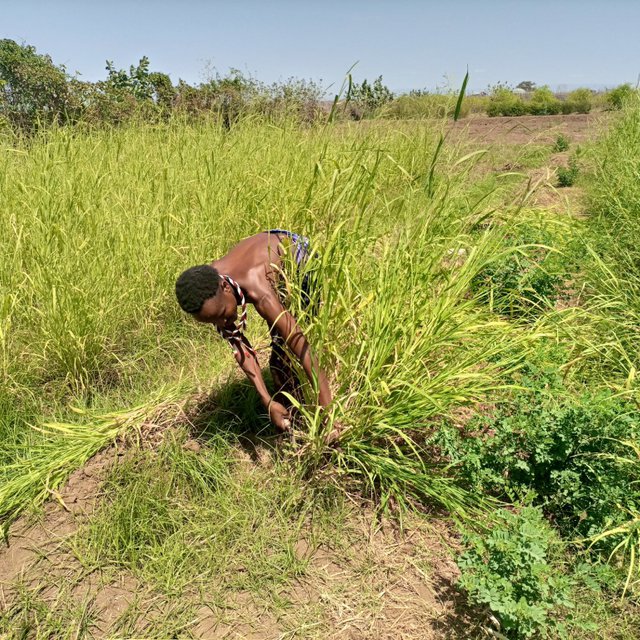
Irrigated fodder production is carried out by pastoralist groups in arid areas of South Omo. Among a number of fodder grasses, Panicum coloratum is a fast-growing species. Panicum is grown as livestock fodder, particularly for the dry season when feed availability is in short supply. It mitigates the issues of recurrent livestock feed shortages which are becoming worse with climate change. Also, growing fodder grass allows resource-poor pastoralist communities to generate income from the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. Irrigating at least twice a week, good weed management, and fertilization ensure sustained production.
In Dassenech district of Southwest Ethiopia, Panicum’s annual fresh biomass and dry matter production potential is over 63 and 18 tons/ha, respectively. It can reach its first harvest after about 60 days and subsequently can be harvested every 45 days. Panicum germinates and establishes readily on any soil type under both irrigated and rainfed conditions. It is also drought tolerant and resilient to climate variability, and does particularly well on alluvial soils with high fertility. Panicum is mainly used for grazing, but it is also suitable for cut-and-carry feeding systems. Each member of the pastoralist group grows panicum on 0.04 ha of land. In the flood lowlands of the Omo River basin, panicum is known for tolerating periodic flooding, salinity, & disease.
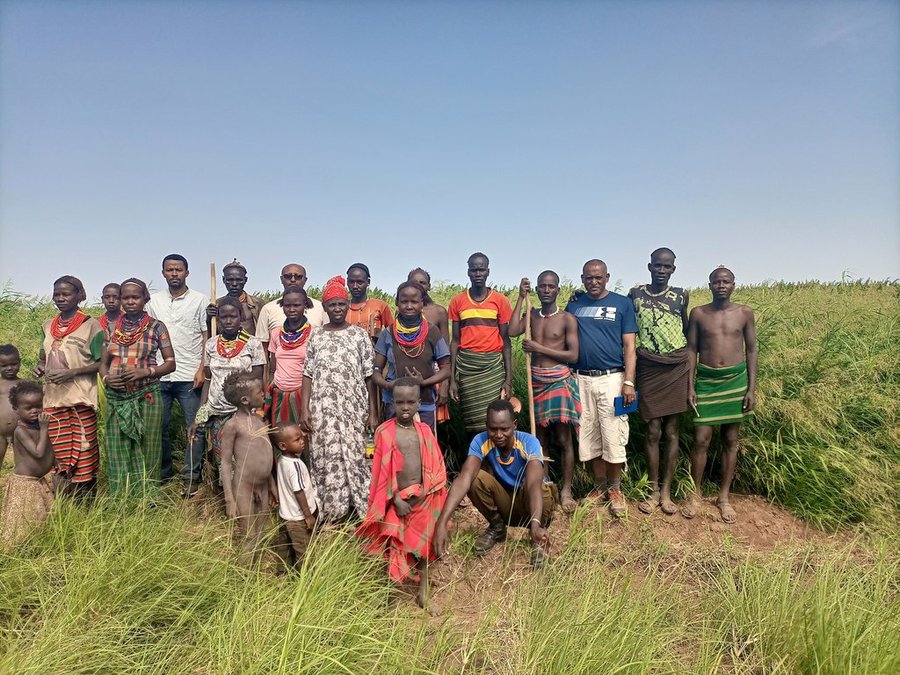
Previously, the land users were unfamiliar with this particular grass and its associated management practices. Also, irrigating on a regular schedule and keeping the grass free from roaming animals adds a work burden to the pastoralist community. However, the Resilience in Pastoral Areas (RIPA) project has introduced and familiarized the community with fodder production and management practices. The project also assists in linking the output to sustainable market. In this regard, the contribution of the RIPA project of the International Development Enterprises (iDE) is immense. The pastoralists appreciate their livestock’s access to year-round feed, as well as the generation of income from the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. Fodder production also creates year-round employment opportunity. However, the community's reliance on government and civic organization support for land preparation and access to irrigation water (conveyance services) might be considered a threat to ensuring sustainability of fodder development by the pastoralist groups.
الموقع: Omorate, Dassenech., Southern Nations, Nationalities and People Region (SNNPR)., أثيوبيا
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها: 2- 10 مواقع
انتشار التقنية: يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟: كلا
تاريخ التنفيذ: 2021
نوع التقديم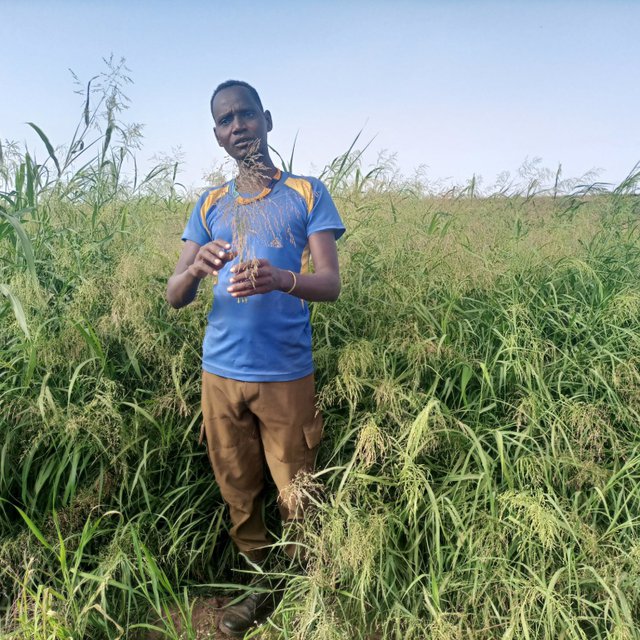



| الصنف | العدد |
| الماعز | 12 |
| الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو) | 8 |
| الجمال | 1 |
| الأغنام | 9 |





| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (Ethiopian Birr (ETB)) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (Ethiopian Birr (ETB)) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Clearing and land preparation | PDs | 12,0 | 200,0 | 2400,0 | 50,0 |
| Planting/sowing | PDs | 5,0 | 100,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Irrigating the farm | PDs | 14,0 | 200,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| Weeding (twice a season) | PDs | 10,0 | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Spade | Pcs | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | |
| Hoes | Pcs | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | |||||
| Seed | kg | 4,0 | 300,0 | 1200,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| NSP | kg | 50,0 | 50,0 | 2500,0 | |
| غير ذلك | |||||
| Seed collection, drying and cleaning | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Harvesting and hay making | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 15'200.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 284.44 | ||||
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (Ethiopian Birr (ETB)) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (Ethiopian Birr (ETB)) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Cleaning irrigation ditch | PDs | 5,0 | 200,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Irrigating the farm | PDs | 12,0 | 200,0 | 2400,0 | 100,0 |
| Weeding (at least twice during the growing season) | PDs | 10,0 | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Seed collection, drying and cleaning | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Harvesting and hay making | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| NSP Fertilizers | kg | 50,0 | 50,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 10'900.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 203.97 | ||||
Access to facility and the services is mainly to those pastoralist community who are residing closer to the Omorate, the woreda capital.
Access to irrigation water increase the fodder production throughout the year.
As the alluvial soil around the river bank is suitable for Panicum, it increases the quality of fodder.
Increase in livestock production is related to the availability of feed/fodder.
Access to irrigation water highly reduced risk of production failure.
Panicum as perennial fodder increases ground cover throughout the year and contributes to land management from wind erosion in the dry land areas.
As Panicum is harvested at least six times a year post reaching the first maturity, farm income is significantly increases.
Income can be generated from the sale of fresh fodder, hay and seeds.
Irrigated fodder production needs intensive management practices. Panicum is perennial fodder that remain on the field all year round. So, irrigating, weeding and looking after the farm... increases the workload.
As it permanently covers the ground, it has high likelihoods of reducing surface runoff.
Improve water drainage.
Decreases surface evaporation but not transpiration.
The farm remains covered by perennial grass. Irrigating the farm also favor the regrowth of other wild species.
Above ground biomass is highly increased as described in the description section.
Reduced with increased management practices. Invasive alien species such as Prosopis juliflora is less common in this part of the River basin.
Animal diversity correlates with fodder availability.
It reduces the impacts of drought on livestock by providing access to adequate feeds throughout the year.
As Panicum increase ground cover and store the carbon above and below the soil surface, it reduces the emission of the carbon.
It breaks the velocity of wind in the lowland, one of the main issues.
Slightly ameliorate the micro-climate of the area.
It is expected that downstream flooding is reduced as the perennial fodder crop cover the ground throughout the year.
Permanent ground cover expected to increase the filtering capacity.
It has expected positive effects of reducing wind transportation.
As perennial crops cover the ground and absorb the carbon, it has an inevitable positive effects on reducing carbon emission.