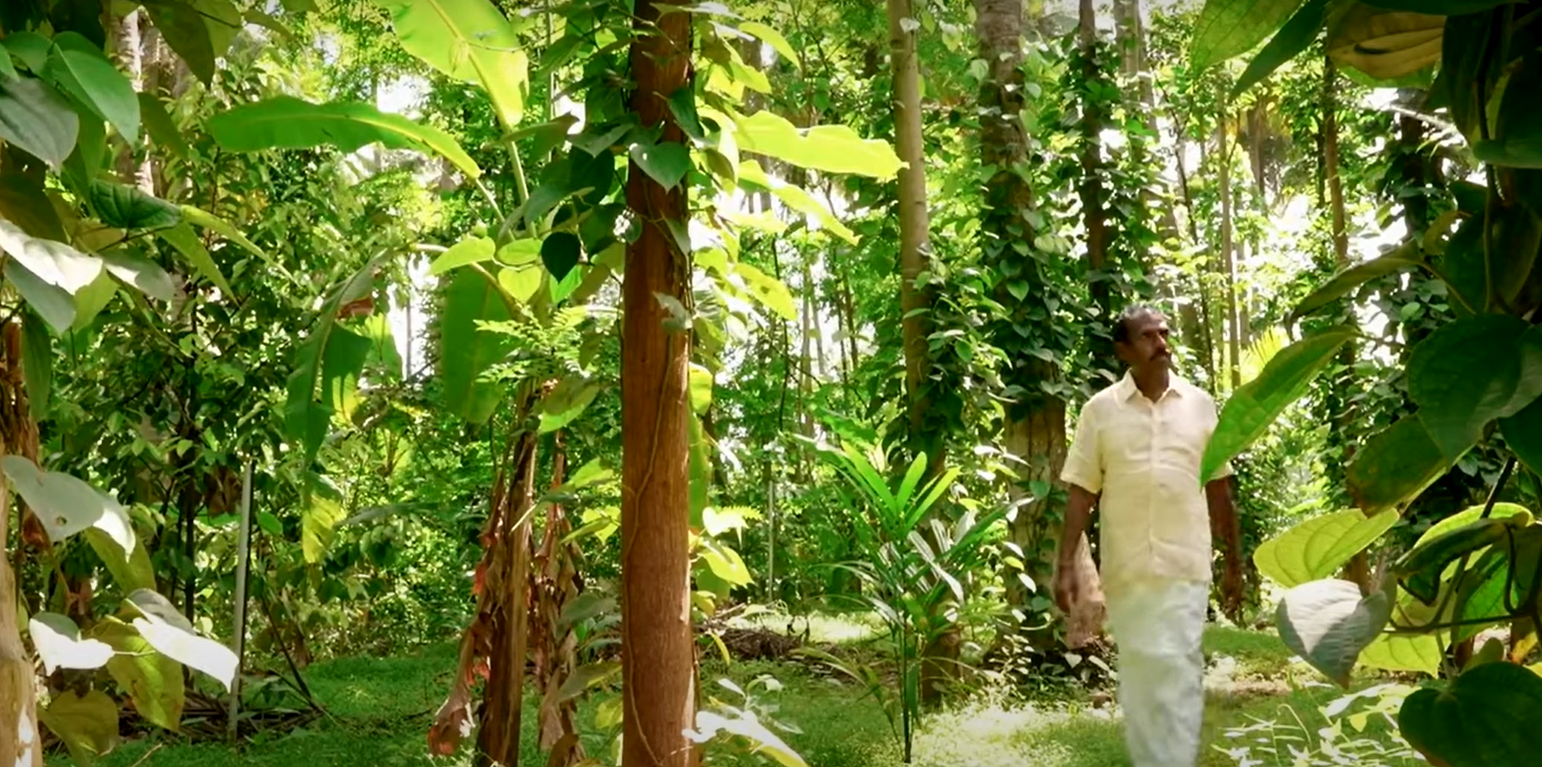




Transforming a monocrop coconut farm into a resilient food forest can sustainably enhance soil health, biodiversity, and productivity while reducing labour and external input requirements. This demonstrates the potential to increase yields and provide long-term economic and ecological stability for farmers. Experience was gained from implementation in 2008 on a monocrop coconut farm in Pollachi, Tamil Nadu. The stages were as follows:
1) Rainwater management: Trenches were dug throughout the farm to retain rainwater and prevent runoff, thus enhancing soil moisture. This was critical given the limited rainfall in the region. A drip irrigation system was installed for efficient watering.
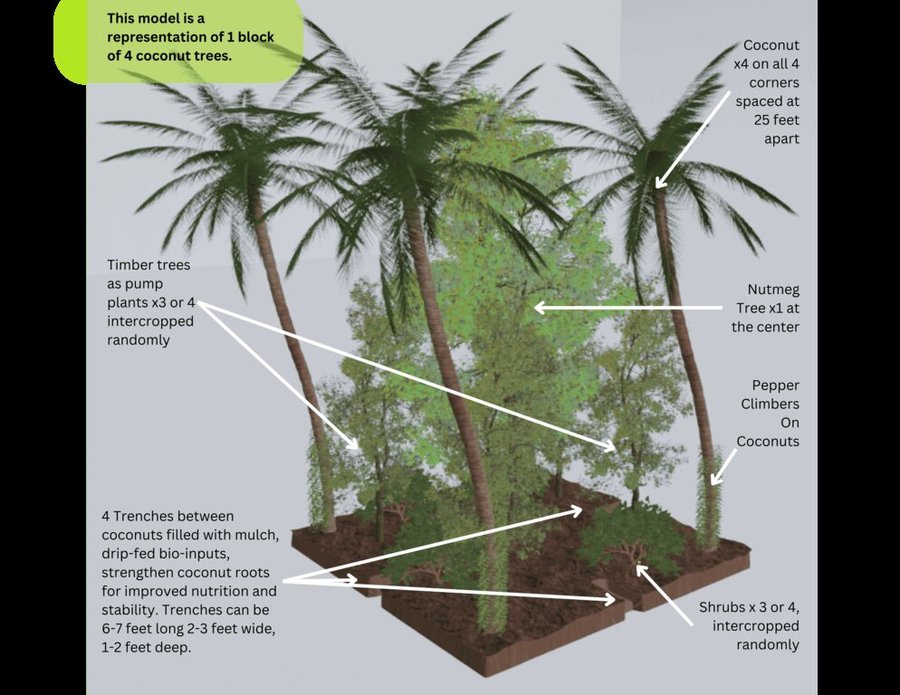
2) Plant diversity: Various crops were introduced. Nutmeg, intercropped among coconut trees, provides 3 - 4 times the income of coconuts after 15 to 20 years. Timber trees extract micronutrients from deeper soil layers via deep tap roots: micronutrients are concentrated in the leaves which are used as mulch to enrich the soil nutrient profile. Banana and papaya provided early income, shade for plants, and added biomass. This diversity also ensures a steady income, reducing dependency on external markets.
3) Biomass and soil fertility improvement: Fast-growing crops were planted to generate additional biomass. Leaves were pruned and added to the water-retaining trenches as mulch. Nitrogen-fixing plants were cultivated extensively to improve soil fertility, eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers.
4) Mulch and bio-input application: Mulch in the trenches was decomposed by the bio-inputs from Cows (Earlier 2, now 1) applied via drip lines, which increased soil organic matter through enhanced microbial decomposition. The irrigation and sprinklers were used judiciously to achieve soil moisture rather than over-watering, as trees primarily needed stable moisture conditions.
5) Minimal maintenance approach: After establishing this system, the farm required minimal maintenance. There was no need for tilling, weeding, or other intensive practices, just monitoring of, and maintaining, moisture levels. This low-maintenance approach reduces farmers’ workloads and improves their quality of life.
6) Enhanced biodiversity and pest management: To further enhance biodiversity, flowering plants to attract pollinators and predatory insects can be planted along the farm's boundaries - though this was not done at this particular site. Nonetheless, the increased biodiversity already fostered here brought in earthworms, birds, and beneficial insects for natural pest management.
After 12 years of minimal maintenance, soil organic matter content increased from 0.5% to 3.36%, and both production quantity and quality increased. The farm retained high soil moisture despite periods of low rainfall. Land users liked the use of minimal inputs, crop diversification as a financial safety net, and the visible impact on soil health and yield, as well as the increase in land value. There was initial fear about time and money invested and doubts about the feasibility of a technology that challenged the status quo of the region. Digging trenches and planting saplings were physically demanding. The initial pest pressure was also a concern before a stable ecosystem was established. The transformation of this coconut monoculture into a diverse food forest has demonstrated a sustainable model of enhanced resilience, productivity, and biodiversity. This model can be replicated across similar regions to help minimize labor and improve farmers’ livelihoods while restoring land and ecosystems.
الموقع: Pollachi, Tamil Nadu, الهند
عدد مواقع تنفيذ التقنيةالتي تم تحليلها: موقع واحد
انتشار التقنية: يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟: كلا
تاريخ التنفيذ: منذ 10-50 سنة
نوع التقديم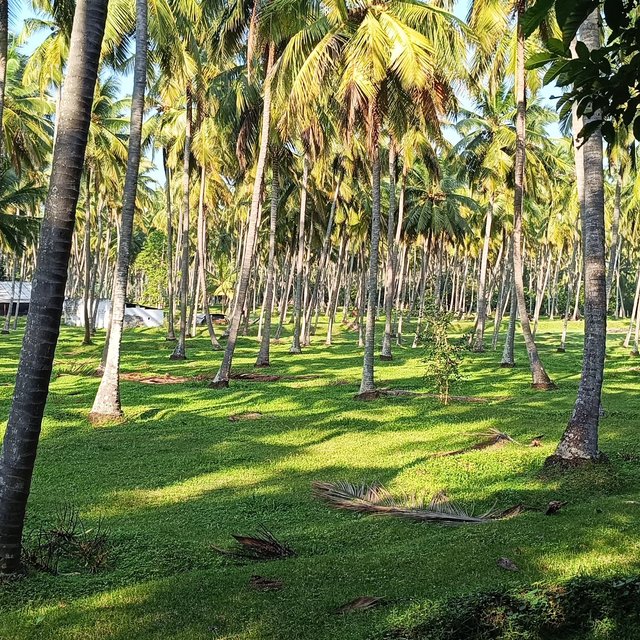











| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (INR) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (INR) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Trench Digging | machine-hours | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Tree Planting | person-days | 75,0 | 600,0 | 45000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Farm Tools | lump sum | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| Irrigation Setup | lump sum | 1,0 | 100000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Pruning Machine | units | 1,0 | 25000,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | |||||
| Timber Saplings | units | 5500,0 | 3,0 | 16500,0 | 100,0 |
| Nutmeg Saplings | units | 1000,0 | 20,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| Pepper Saplings | units | 1000,0 | 40,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fruit Trees | units | 500,0 | 100,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| Organic Manure | load | 10,0 | 1500,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| Organic Pest Repellants | lump sum | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | |||||
| Fencing Irrigation | lump sum | 1,0 | 200000,0 | 200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Bio-Input Preparation Unit | lump sum | 1,0 | 200000,0 | 200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Pipes and Valves | lump sum | 1,0 | 530000,0 | 530000,0 | 100,0 |
| Tool Shed | lump sum | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| Worker Shed | lump sum | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | |||||
| Farm Animals | units | 5,0 | 20000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fodder | annual | 1,0 | 25000,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1'606'500.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 19'109.08 | ||||
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة (INR) | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل (INR) | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي |
| العمالة | |||||
| Pruning, mulching, replanting | person-days | 100,0 | 600,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| Harvesting | person-days | 300,0 | 600,0 | 180000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | |||||
| Tools for pruning fencing checks | lump sum | 1,0 | 10000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Irrigation system maintenance | lump sum | 1,0 | 10000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fencing maintenance | lump sum | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | |||||
| Replacement seedlings | pieces | 50,0 | 30,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | |||||
| Preparing organic bio-inputs via irrigation system | lump sum | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | |||||
| Fencing materials for repair | lump sum | 1,0 | 8000,0 | 8000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | |||||
| Cow Care and Fodder | kg | 5,0 | 5000,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 319'500.0 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 3'800.4 | ||||
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 110
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 160
Coconuts were small in size and fewer in number when the farm was bought. After 6-7 years, the counts increased from 110 per tree per year to 160 and size increased 150% on average.
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: Not so tasty
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: Taste is the best compared to surrounding many farms.
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 50-60%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0%
The risk of production failure has come down to 0% as there is no pest and disease attack. The coconuts yield continuously throughout the year.
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 1
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 3
From just one crop to 2 main crops, pepper as a sub-main crop and a variety of fruits for self consumption.
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 60%
Coconuts occupied approximately 40% area in terms of canopy. Now in addition to that there is nutmeg which occupies another 20%. Rest of the area is for timber and other supporting crops not included here.
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 24/7
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 1 Day a Week
Farmer before this owner spent hours in weeding, application of inputs and pesticide, burning of crop residue, harvesting coconuts. Now the whole farm needs 2 labour to collect fallen coconuts and turn on the irrigation switches and valves. The farmer comes to visit the farm once a week for monitoring.
Earlier the bore wells would run only for a couple of hours and then the water would dry out. Now it fulfills the irrigation requirement without interruption.
Demand for water has drastically come down as the SOC content in the soil has risen.
There is no expense in any agricultural input apart from maintenance of 2-3 cows. The entire system is automatic. The slurry from the cowshed goes into the tank which supplies input through a venturi to the drip irrigaton system.
Farm income has gone up significantly owing to the high yields, multiple crops, better prices, low cultivation and management costs.
Incomes are coming from sale of coconuts, nutmeg and pepper. Coconut oil is also extracted now by the farmer and sold at a high premium price.
The drudgery of mainting a monocrop and all the works associalted with conventional agriculture is eliminated by 95%. The only workload is to pick up the fallen coconuts and harvest nutmeg and pepper.
The health of the owner and the consumers is greatly benefitted owing to the absense of harmful chemicals and pesticides in the produce.
This model is a great source of wisdom about tree-based regenerative agriculture which can counter land degradation. It has all the necessary components of how to convert dirt into soil.
Soil moisture is maintained as high levels except for summers when its a little low due to the intense heat this region faces.
Soil compaction has reduced because of the heavy penetraton of tree roots, improved SOC and biological activity in the soil.
It is evident from the yields that there is a very resilient process of nutrient cycling happening in the farm compared to what was happening earlier.
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 0.5
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 3.36
The SOC level have increased continously and is still increasing because of the leaf litter that is added continuously throughout the year.
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي: 90%
Vegetation cover in the form of trees, shrubs, perennial crops and pepper has shown dramatic increase.
Addition of 3 times the number of trees has increased the above ground biomass multiple times.
The farm is now a home for more than 100 species of plants compared to just one when it was bought.
There is an absolute balance in the farm ecosystem with no species going out of control. There are no significant weeds as the soil ecosystem and shade doesn't support the common invasive species found in the region.
Minor farm animals are seen. Since its not a large area, enough diversity has not been established.
There are no harmful species for which the farmer needs to worry about. All species are beneficaial in some way or the other.
Multi layer multi crop system allows various different habitat for a variety of species. Here from high coconut to rich soil undergrond has a habitat diversity of semi-forest which was not present earlier.
The farmer says he doesn't know what are pests now which was not the case earlier. Earlier his coconuts would be continously be harmed by something or the other.
The impact of drought is not significant in this farm because of the green cover, soil moisture, high water tables, year-round water availability and overall resiliance of the system. All other conventional farms face enormous hardship during droughts.
This system is carbon negative as there is no use of chemicals or fossil fuels needed to run any operation except the transportation of coconuts to the markets.
The micro-climate is the most tangible change that anyone visiting the farm is able to relish. The coolness inside the farm is completely mood-changing for someone who is entering from outside. It leaves people wanting to live here or create such a place for themselves. Its an oasis in a desert.
It is assumed that as the groundwater table in the site has increased, it would definitely have some effect of the neighboring sites.