Promoting Farmer Innovation [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: William Critchley
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2412 - كينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
The PFI approach seeks to build on technical initiatives - innovation in the local context - developed by farmers themselves in dry/marginal areas where the conventional approach of transfer of technology from research to extension agents and then on to farmers has so often failed.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
Aims / objectives: The objective of PFI is to stimulate technical innovation, in the field of land management, by farmers. The approach basically comprises indentifying, validating and documenting local innovations/initiatives. Simple monitoring and evaluation systems are set up amongst those innovative farmers who are willing to co-operate. Through contact with researchers, extra value is added to these techniques where possible.
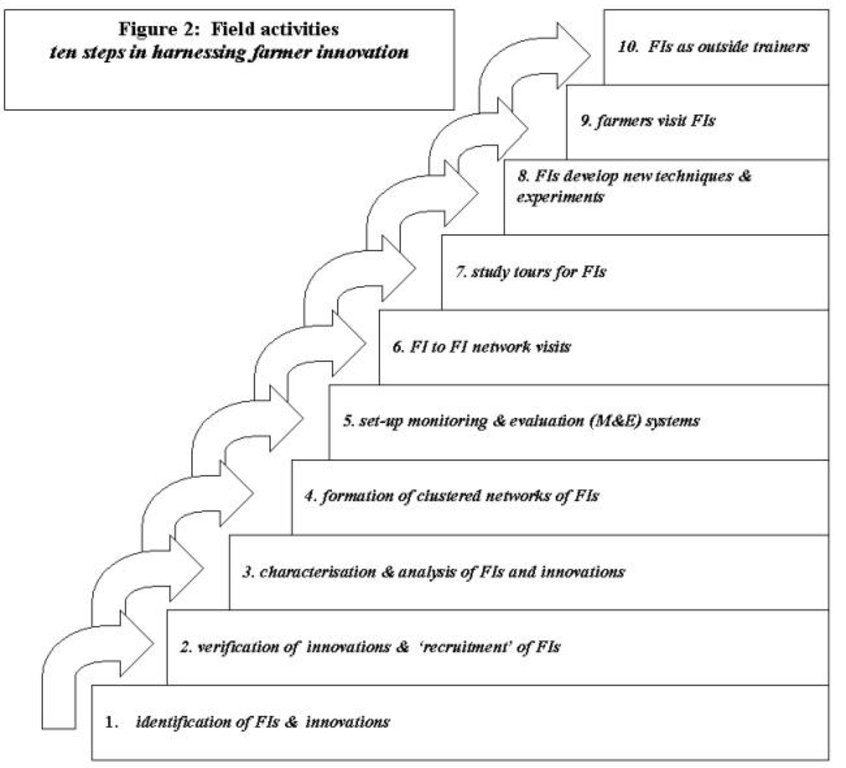
Methods: Farmer innovators are brought together to share Ideas. Finally, best-bet technologies, in other words thos that are considered to be good enough to be sharedd, are disseminated through farmer-to-farmer extension. This takes two forms. First, farmers are brought to visit the innovators in their farms. Secondly, farmer innovators are used as teachers/trainers to visit groups of farmers - including FAO's farmer field schools in some cases. Only in this second form of extension is an allowance payable to the innovator. A ten-step field activity methodology has been developed.
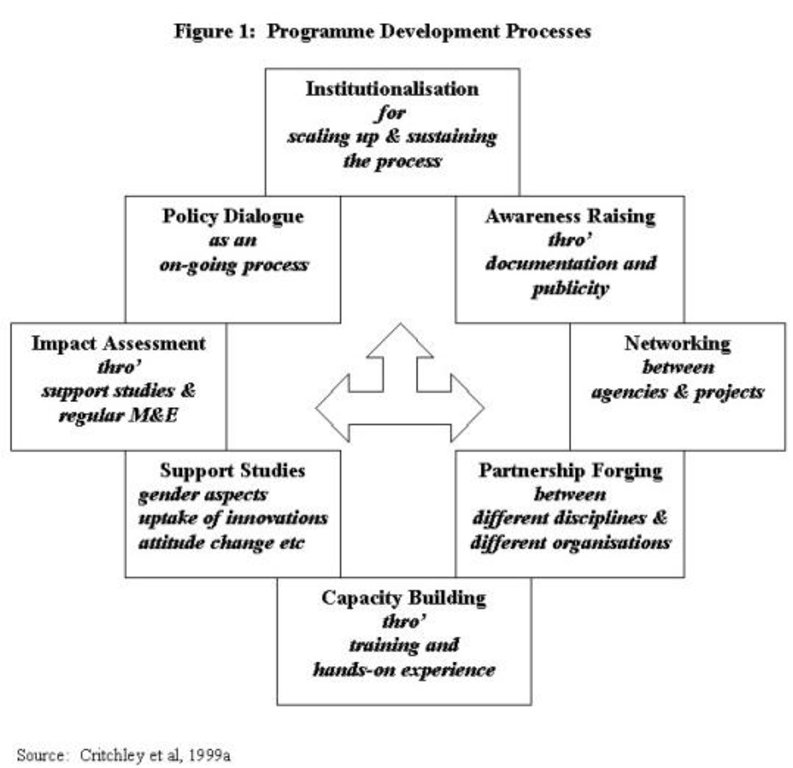
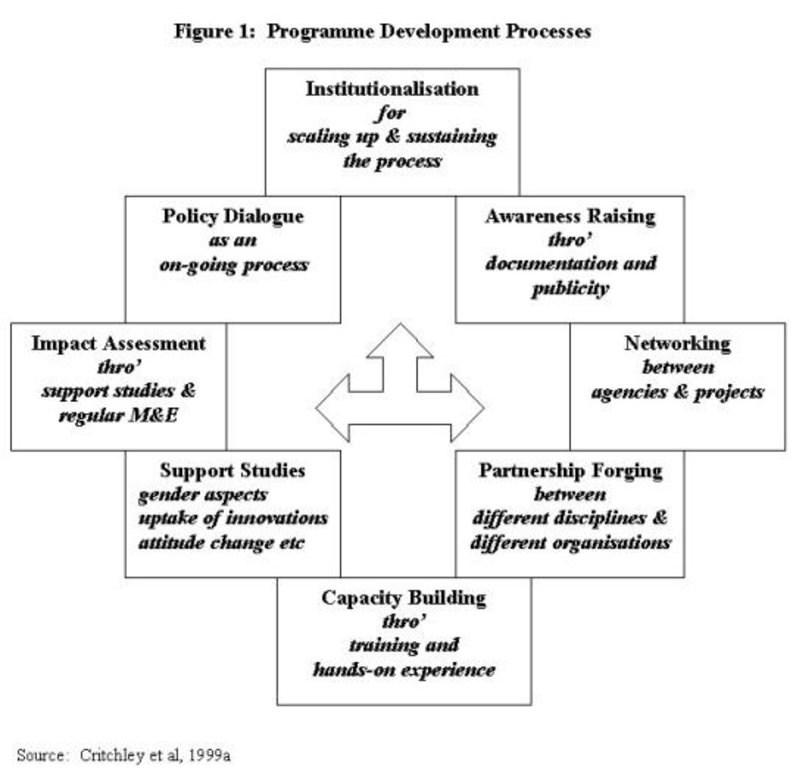
Role of stakeholders: At programme level, there is capacity building of in-line extension and research staff, who are the main outside actors in the programme. In each of the countries the approach has been implemented through a government ministry and with NGOs in the field. The principle, and practice, is not to create seperate project enclaves, but to work through existing personnel, sharing buildings and vehicles that are already operational in the area. A programme development process methodological framework shows how the ultimate goal of institutionalisation can be achieved. PFI's first phase, completed in 2000, was financed by the Government of The Netherlands, through UNDP, and was active in Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda.
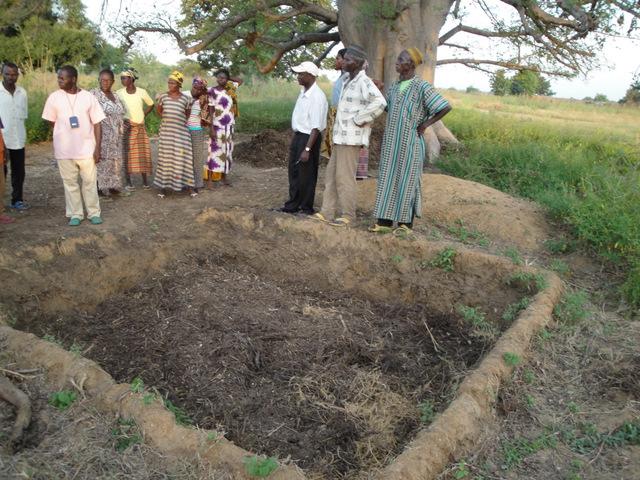
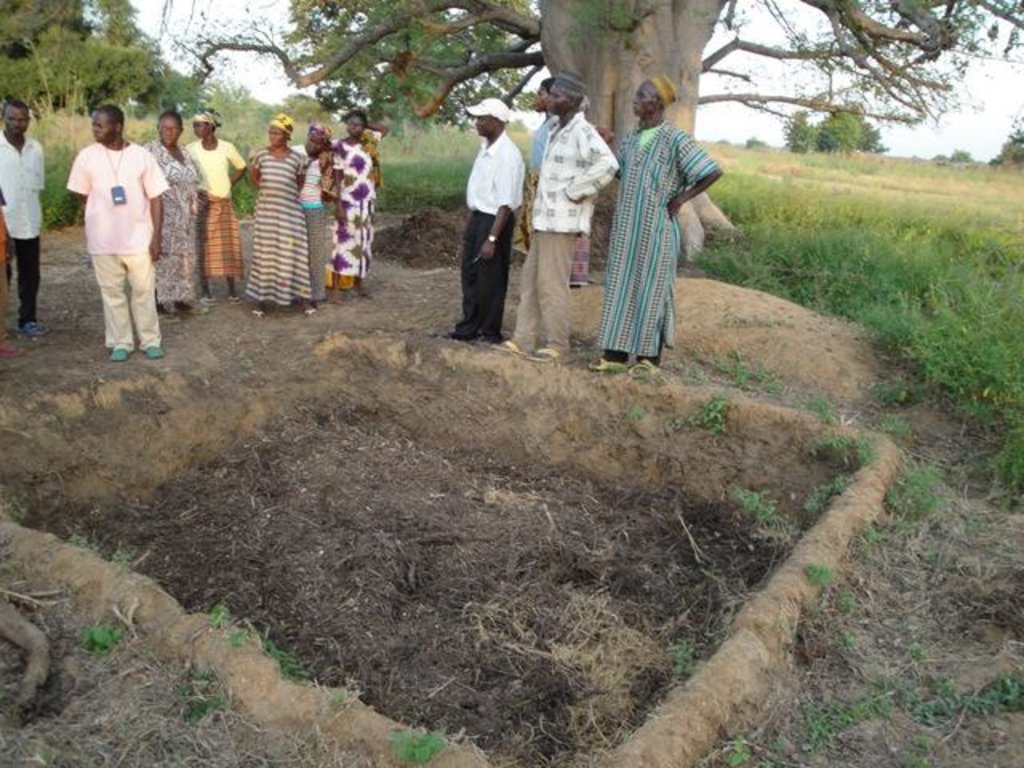
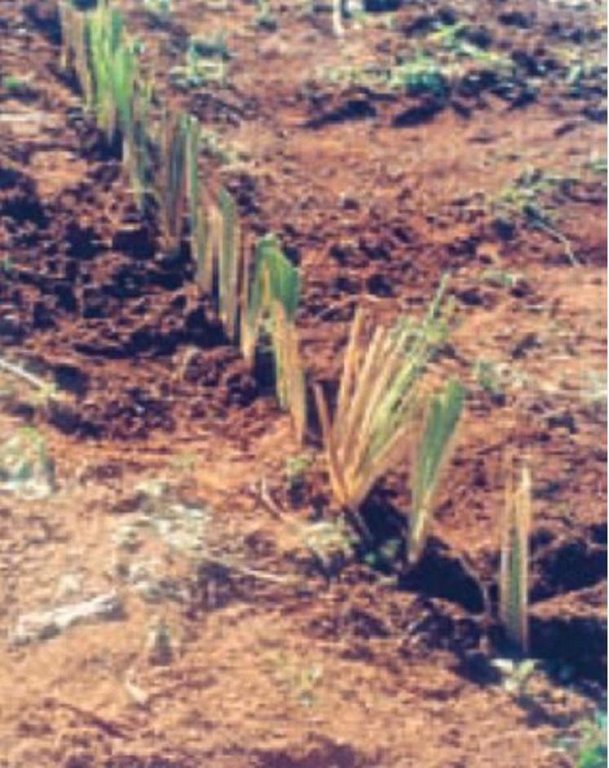
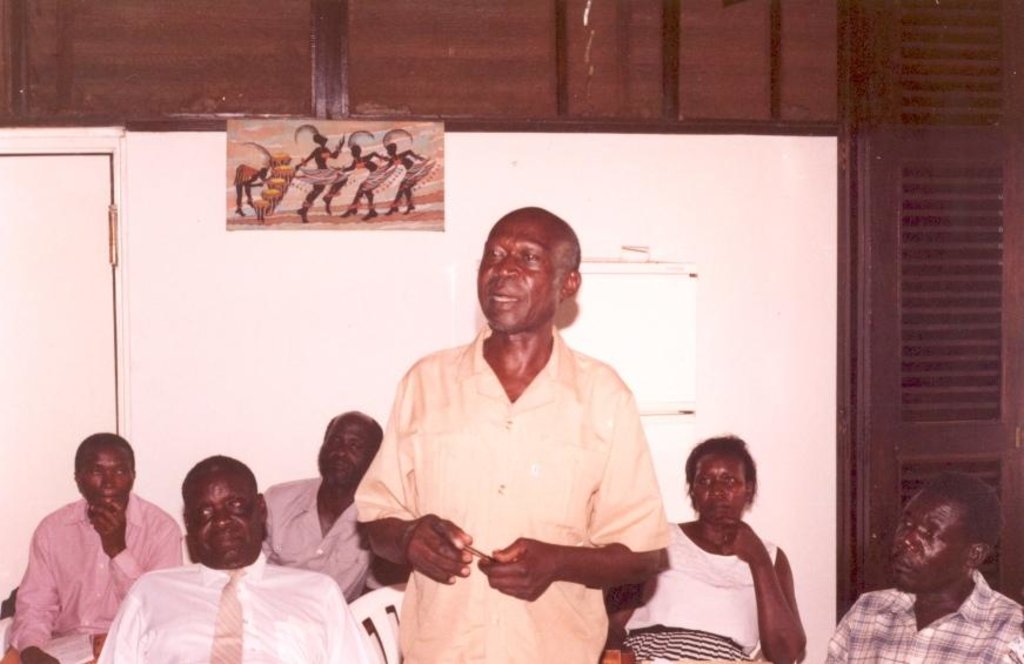
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Mwingi District
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
1996
سنة الإنهاء (إذا لم يعد النهج مطبقًا):
2000
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (better land husbandry practices (eg animal husbandry/ crop selection))
Improve rural livelihoods through an increase in the rate of diffusion and appropriate SLM/water harvesting technologies, promotion of farmer-farmer exchange, capacity building of farmers and supporting organisations, promotion of policy dialogue
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Poor supply of relevant recommendations from research for small-scale farmers in marginal areas, poor delivery of SLM technologies to farmers, lack of motivation of research and extension staff, isolation of promising innovative SLM ideas which address low crop yields, land degradation and poverty, lack of exchange of innovative knowledge.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
الإطار المؤسساتي
- معيق
lack of motivation of research and extension institutions
Treatment through the SLM Approach: bringing them together with farmer innovators
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- معيق
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation access to land for women was a problem that inhibited women to innovate
غير ذلك
- معيق
spread of knowledge and ideas
Treatment through the SLM Approach: networking of farmers (+extension staff and researchers)
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
Existing groups of land users
Men tend to 'volunteer' themselves as innovators and to ignore their wives. This led to (1) gender studies and (2) gender sensitisation workshops to try to overcome the problem(s)
- الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار)
International specialists in collaboration with/ after discussions with national specialists and land users
- منظمة دولية
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | سلبي | public meetings, interviews/questionnaires, workshops/seminars, rapid/participatory rural appraisal |
| التخطيط | تفاعلي | rapid/participatory rural appraisal, interviews/questionnaires, workshops/seminars, public meetings, |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | Mainly: responsibility for minor steps; partly: responsibility for major steps |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | Mainly: public meetings, measurements/observations; partly: workshop/seminars; |
| Research | تفاعلي | Mainly: public meetings, measurements/observations; partly: workshop/seminars; |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- مستخدمو الأراضي بشكل أساسي، بدعم من متخصصي الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
اشرح:
land user driven (bottom-up). farmers developed the technologies; field staff selected them
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. land user driven (bottom-up).
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
- SWC specialists, extensionists/trainer
شكل التدريب:
- من مزارع إلى مزارع
- اجتماعات عامة
- دورات
المواضيع المغطاة:
1. Training in presentation skills for farmer innovators 2. Facilitation of field days where innovators/ extension staff could present jointly (so farmers trained thereby)
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
وصف/تعليقات:
Name of method used for advisory service: 'Farmer Innovation Approach'; Key elements: Identify Fis, Form networks of FIs groups which meet, Bring farmers to see 'best-bet' innovations; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system, non-governmental agency 2) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system, non-governmental agency; Extension staff: mainly government employees
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- نعم، باعتدال
حدد المستوى (المستويات) التي تم فيها تعزيز أو إنشاء المؤسسات:
- محلي
حدد نوع الدعم:
- بناء القدرات/التدريب
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored
technical aspects were regular monitored
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored
economic / production aspects were regular monitored
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: e.g. Better integration with government services/ system for technical backstopping and extension
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- تكنولوجيا
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
research was slow to begin activities in this phase but supposed to be a key pillar in this farmer/ research/ extension linkage
Research was carried out on-farm
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- 1,000000-100،000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (Dutch Government): 60.0%; government (national): 20.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 20.0%
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- زراعة
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| بذور | ممول جزئيا | |
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- تطوعي
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Innovative land husbandry technologies of other farmers
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسن في مسائل حيازة الأراضي / حقوق المستخدمين التي أعاقت تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Gender sensitisation training may have helped The problem is unlikely to be overcome in the near future.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
1. GTZ in Kenya are adopting the PFI approach widely; 2. FAO's farmer field schools are joining hands with PFI in Kenya 3. INADES Tanzania adopted the approach 4. Several organisations in Uganda have expressed an interest
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- غير مؤكد
إذا كان الجواب لا أو غير متأكد، حدد ذلك وعلق عليه:
There may be some groups of farmers who will continue to meet and exchange ideas but this approach basically depends on a continuation (long term) of the farmer/ extension/ research interaction
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Gives them confidence |
| Offers them new and viable ideas from their peers |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Builds on local ideas (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: institutionalise the approach!) |
| Revitalises the extension service |
| Is attractive at all levels |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Research reluctant to respond to farmers' agenda | effort to convince researchers of benefits of joint research with farmers. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Depends on individual flexibility and commitment, does not follow the conventional institutional chain of command | training in skills and methodologies. |
| Sometimes confers too much prestige on a particular group of favoured farmers | rotate farmers who are the focus of attention. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Promoting Farmer Innovation (1999) Critchley et alVideo (same name)
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
RELMA, Nairobiditto
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية