Tugai forest management through village committees [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Firdavs Faizulloev
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
approaches_2441 - طاجيكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Abdurakhimov Najmiddin
najmiddin.abdurakhimov@undp.org
National Expert on Forestry, UNDP
Shaartuz Area Office, 2 Ziyodaliev Street, Shaartuz
طاجيكستان
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Sustainable Land Management - Multicountry Capacity Building (CACILM - MCB) - قرغيزستاناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
United Nations Development Program (United Nations Development Program) - طاجيكستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
13/04/2011
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
The described approach facilitates the establishment of contracts between village committees and local authorities for decentralised management of Tugai forest areas on State Reserve Land.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
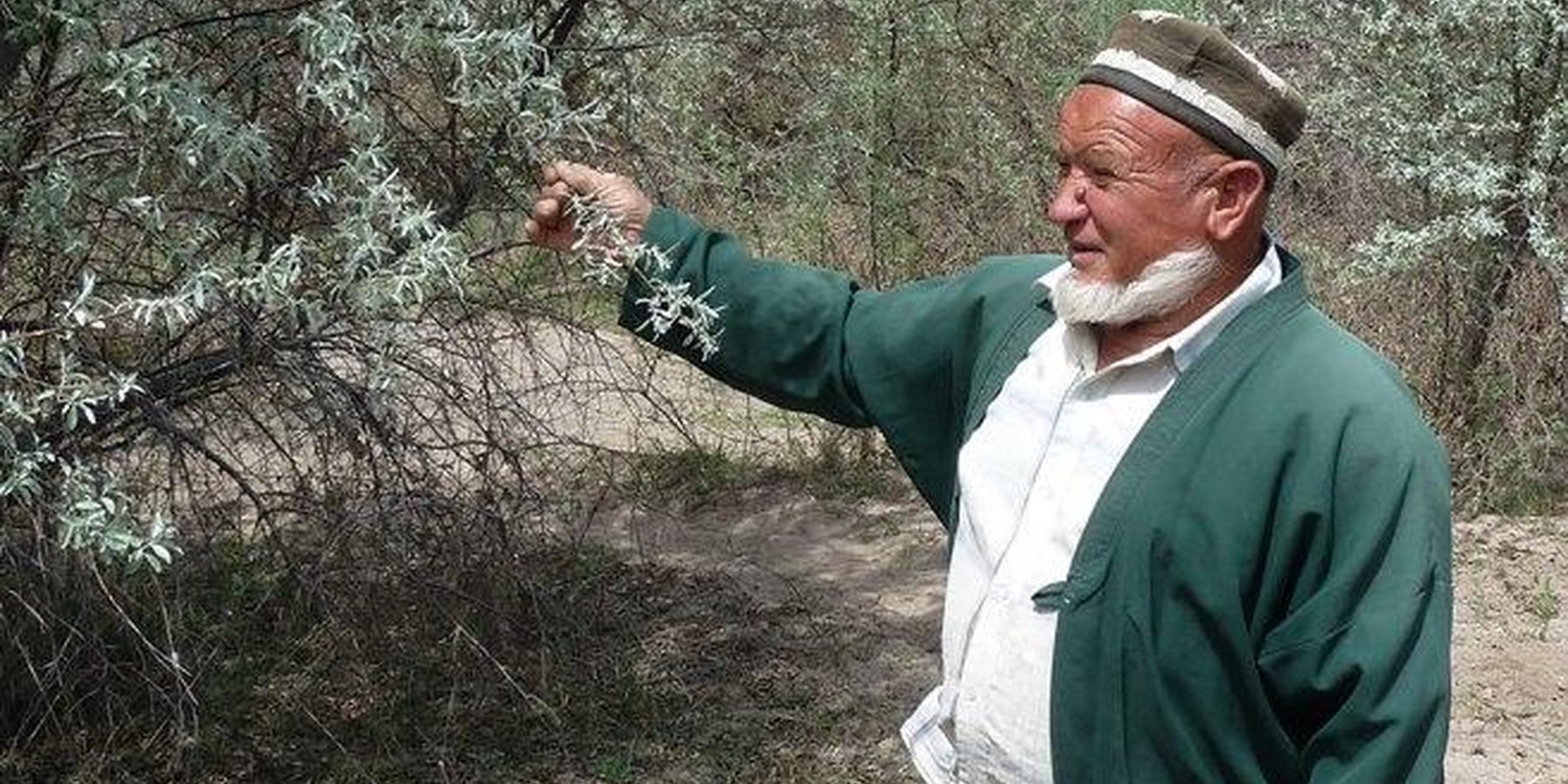
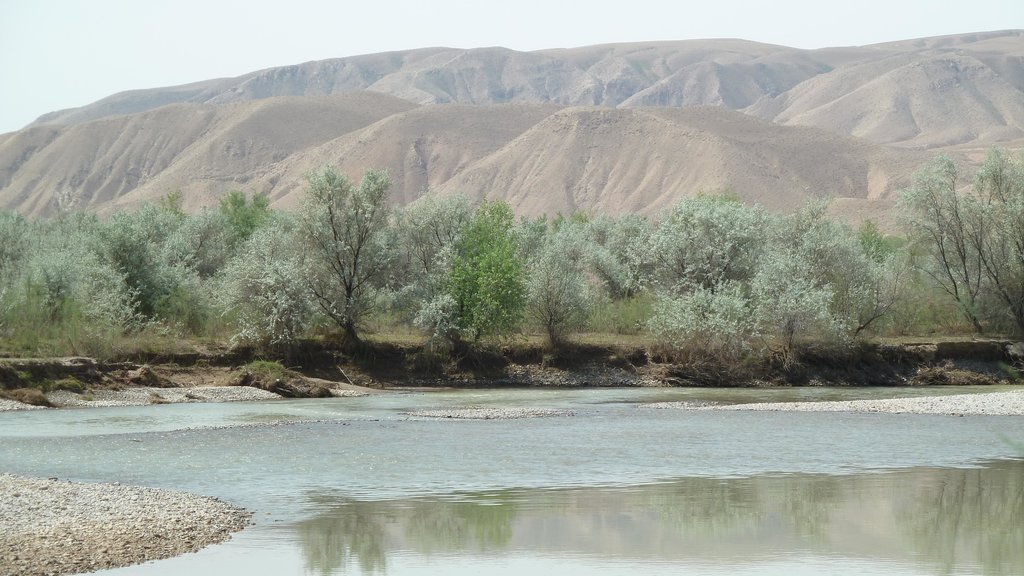
Aims / objectives: Tugai forests are riparian forest ecosystems situated in the continental, winter-cold deserts of Central Asia. These flood plain forests are severely threatened by overexploitation for fire wood and by overgrazing. The 253 ha of Tugai forest in Nuri Vakhsh Jamoat along the Vakhsh river in southern Tajikstan were suffering due to their de facto status as open access resources. The district environmental department that was supposed to monitor the forest was unable to effectively carry out this work. Therefore the UNDP project on “Demonstrating Local Responses to Combating Land Degradation and Improving Sustainable Land Management in SW Tajikistan” saw the protection of this Tugai forest as a priority and engaged with local land users to help protect the forest.
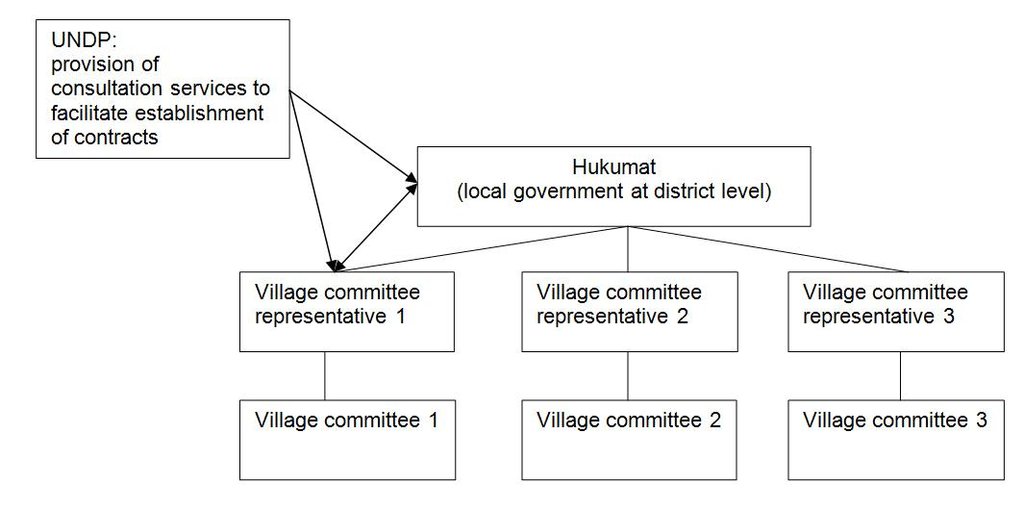
Methods: UNDP project representatives held discussions with forest users living in villages next to to the Tugai forests, regarding the establishment of community-based forest management institutions. UNDP proposed that these institutions enter into agreement with the Hukumat (local district-level government) to protect and exclusively use well defined forest areas on nearby State Reserve Land.
Stages of implementation: As a first step, UNDP obtained permission from the Hukumat to conduct sanitary felling of dry and infected trees, to help improve the forest structure under supervision of the Jamoat (local municipality-level government). The removed tree material was distributed to schools and hospitals as fire wood. Next, a leasehold agreement was formed between a representative of each of the three village committees and the Hukumat. These leasehold agreements covered a total of 126 ha out of 253 ha of Tugai forest existing in the area and they are valid for five years. The remaining forest area, which is not under an agreement, is not threatened as it is situated on an island in the middle of a strong stream that cannot be crossed. The committee has to pay about or 1.73 USD / ha of leased forest land as a tax to the district. The tax paid is collected from contributions by members of the villages who pay for each head of cattle that they send for grazing at a cost of 1 USD / head of cattle.
Role of stakeholders: The village committees are headed by one representative who is responsible for regulating access to the forest plots. The local Jamoat supervises the activities carried out by the village committees on their respective plots. UNDP provides consulting services for the process of establishing contracts between village committees and the local authorities and is carrying out regular monitoring of the forest management activities.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khatlon
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Nuri Vakhsh Jamoat
التعليقات:
Total area of Tugai is 253 ha, of which 126 ha are under leasehold agreement (approach). The rest is still open access, but is not threatened as it is situated in the middle of a strong stream and cattle cannot access it to graze.
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
2009
سنة الإنهاء (إذا لم يعد النهج مطبقًا):
2011
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (regulation of access for herders)
The main aim of the approach is to help prevent the degradation of Tugai forest, and the disappeareance of this threatened ecosystem, while giving the local population the chance to manage and use it in a sustainable way.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: uncontrolled access and degradation of Tugai forest, overgrazing, cutting of trees, no firewood resources available
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
المعايير والقيم الاجتماعية /الثقافية/ الدينية
- معيق
lack of local level structures enabling collaboration between village organisations and Jamoat or Hukumat
Treatment through the SLM Approach: UNDP assistance and consulting to improve collaboration and enabling the establishment of leasehold agreements
الإطار المؤسساتي
- معيق
no implementation of control and punishment measures regarding the overexploitation of Tugai forest
Treatment through the SLM Approach: clearly defined rights and responsibilities for forest users and village and local government institutions
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: As the land is classified as State Reserve Land, and is under the control of the forestry department within the Hukumat, the establishment of an agreement between village organisations and the Hukumat was possible.
- معيق
no defined forest use or management rights and responsibilities
Treatment through the SLM Approach: user agreement between village committees and district administration
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- معيق
overgrazing and overexploitation of Tugai forest for firewood
Treatment through the SLM Approach: the forest leasehold agreement defines that no cutting of trees is allowed during the first 5 years, apart from sanitary felling, and grazing is limited to a certain number of cattle
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
Representative of village committee and village committees
Village committees were all represented by men.
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون
UNDP consultants
International experts designed the broad structure/framework of the approach, but the specific agreements were designed by village representatives, Hukumat, and the UNDP consultant.
- الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار)
District administration
- منظمة دولية
UNDP
إذا كان هناك العديد من الأطراف المعنية، قم بالإشارة إلى الوكالة الرائدة:
UNDP
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | غير موجود | Consultants from UNDP initiated the approach and started discussions with villages next to the forest |
| التخطيط | غير موجود | |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | establishment of village committees, managing access for livestock herders |
| الرصد/التقييم | غير موجود | monthly monitoring through UNDP consultant |
| Research | غير موجود |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
الوصف:
UNDP facilitates the process of establishing contracts between village organisations and the Hukumat for decentralised forest management.
المؤلف:
Julie Zähringer (Baumackerstr. 51)
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- مستخدمو الأراضي بشكل أساسي، بدعم من متخصصي الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
اشرح:
As technology in this case we understand the implementation of the forest leasehold agreements.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. As technology in this case we understand the implementation of the forest leasehold agreements.
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
شكل التدريب:
- اجتماعات عامة
المواضيع المغطاة:
forest conservation, sustainable grazing management, sanitary cutting
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
وصف/تعليقات:
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; The forest leasehold agreements were established for a duration of 5 years. After this, the Hukumat should be in an adequate position to renew or adjust those agreements if necessary.
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- نعم، باعتدال
حدد المستوى (المستويات) التي تم فيها تعزيز أو إنشاء المؤسسات:
- محلي
حدد نوع الدعم:
- بناء القدرات/التدريب
اعط مزيدا من التفاصيل:
Jamoat
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: plant and bird species, number of cases connected with illegal cutting of trees
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: visual assessment of rehabilitation of grass, bushes and trees, number of wild animals and birds
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- علم الايكولوجيا
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
Studies about presence of plant and bird species
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (UNDP): 100.0%
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
كلا
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- زراعة
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| ممول بالكامل | seeds for riverbank afforestation | |
- غير ذلك
| غير ذلك(حدد) | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| costs associated with training and meetings | ممول بالكامل |
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- تطوعي
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
5.5 حوافز أو وسائل أخرى
هل تم استخدام حوافز أو أدوات أخرى لتشجيع تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Jamoat
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
protection of biodiversity, improved fodder availability
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
the experience has not yet been disseminated
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
improved pasture quality within the forest plots and high aesthetic value of the forest
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- القواعد واللوائح (الغرامات) / الإنفاذ
- الوعي البيئي
- تحسينات جماليية
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، صف كيف:
The land users should now be in a position to renew contracts with the Hukumat.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Protection of plant and animal diversity |
| Increasing the capacity of the community on legal issues |
| Aesthetic value of the beauty of this landscape - quote from land user responsible for a 41 ha forest plot 'Every morning when I open the window and I see the beautiful landscape of the Tugai forest I feel happy' |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Protection of a highly endangered ecosystem, while allowing for improvement of grazing for local herders |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| no tenure security as the government could sell off the land at any time | issue land user certificates |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية