Participatory Cost Benefit Analysis for Energy Efficiency Measures [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: shane stevenson
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
approaches_2442 - طاجيكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Pochoev Mirzo
992 44 601 55 05
CAMP Kuhiston
Dushanbe
طاجيكستان
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership (CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership) - قرغيزستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
25/04/2011
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
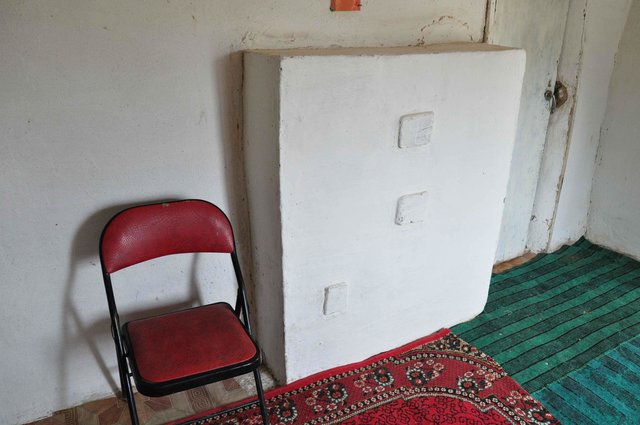

Two Room Stove [طاجيكستان]
A brick stove that is built into the existing internal wall, that will heat the two rooms and can be used for cooking.
- جامع المعلومات: shane stevenson

Energy efficiency measures to increase the application of … [طاجيكستان]
The implementation of several low cost energy efficiency measures to reduce the amount of organic material used as fuel within rural households.
- جامع المعلومات: Daler Domullojonov
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
The use of a cost benefit analysis approach to assess the financial and natural resource needs for energy consumption at community level, and further attribute costs to SLM practices to meet this need, and subsequently improve rural livelihoods.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
Aims / objectives: To collate quantitative data on the amount of energy used within the community in terms of financial expenditure and natural resource use. Through the use of a participatory workshop the attendees determine which natural resources are being utilised, in the form of wood, bush and organic materials. The objective is to use this quantitative data to encourage through cost benefit demonstrations, the implementation of Sustainable Land Management technologies to reduce the amount of natural resources exploited, and the expenditure on energy consumption.
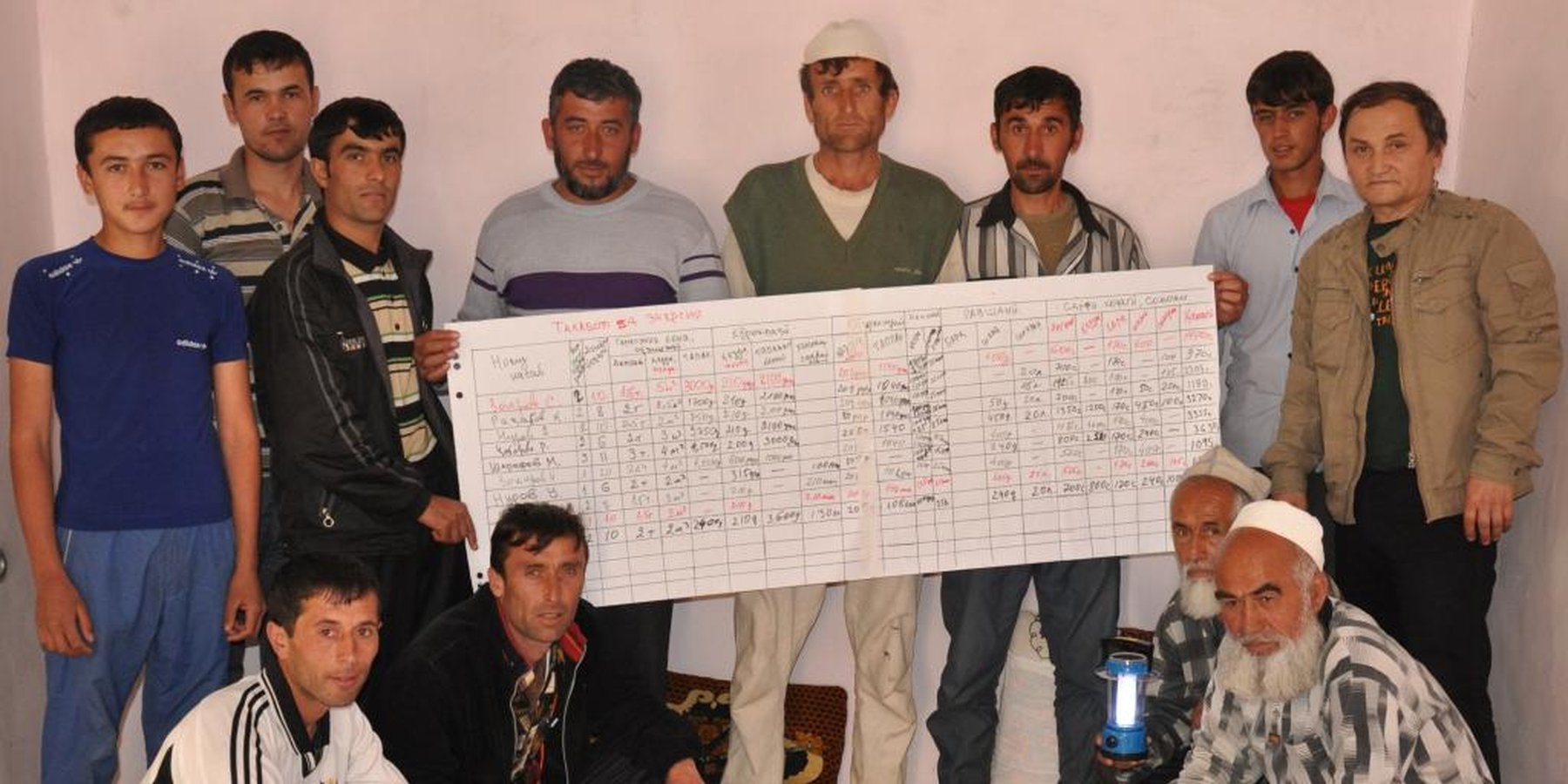
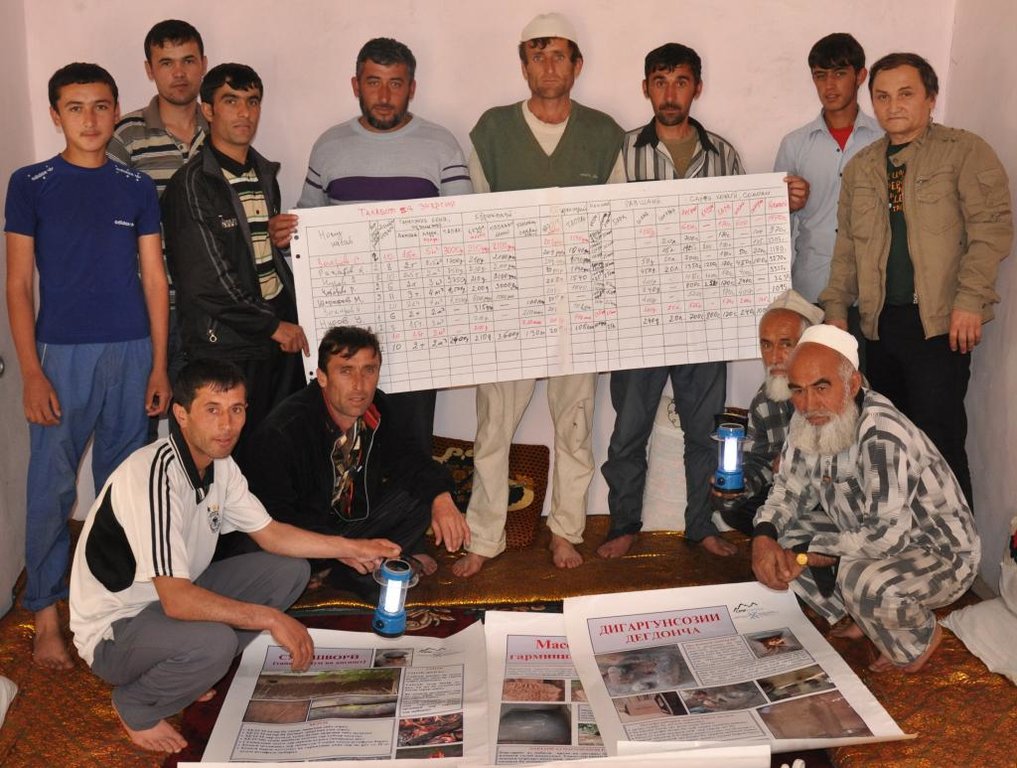
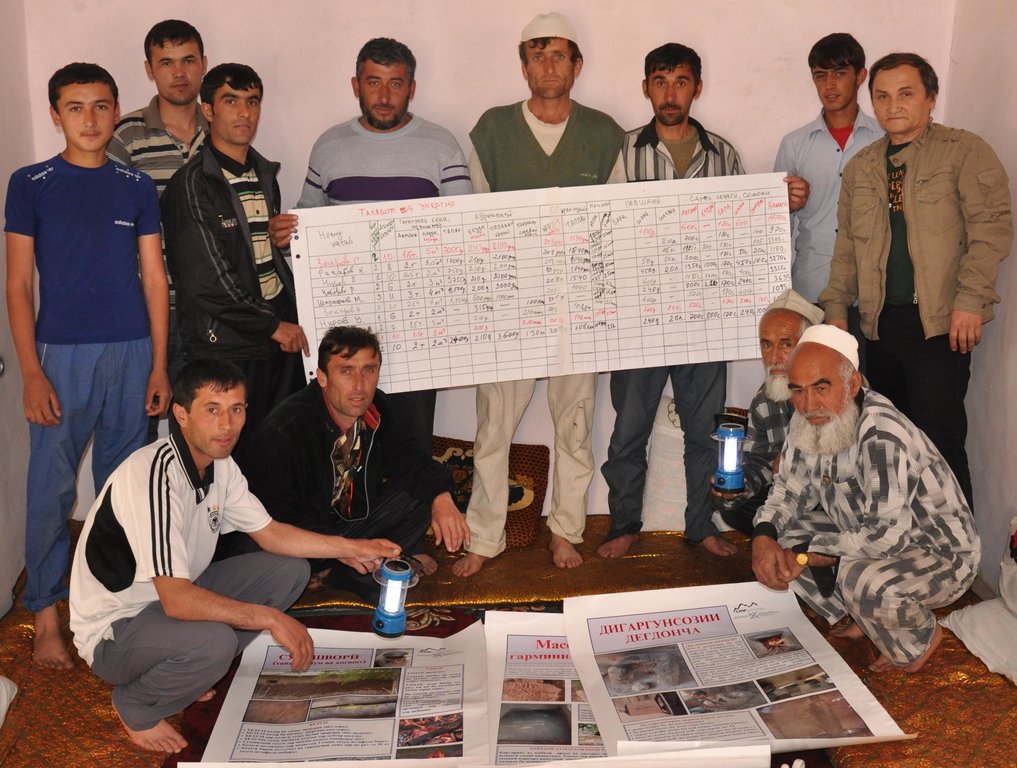
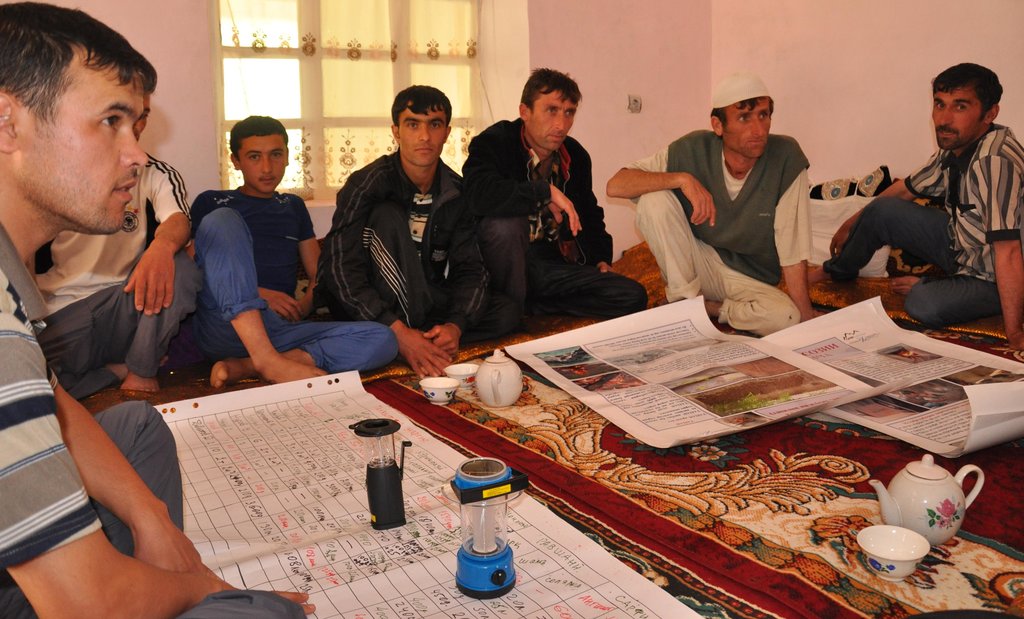
Methods: An energy specialist organises a community based workshop with up to 15 participants. In the 2-3hr workshop the participants complete, under guidance, a pre prepared flip chart on energy use (electric, tapak, wood, coal, brush). The information is collected in financial expenditure and weight. Once the energy assessment is completed a subsequent discussion is encouraged on how to more effectively meet this need at a community level. The moderator also takes this oppoprtunity to demonstrate several technologies including solar lights, improved stove design, thermal insulation, and the development of energy forests. The information is collated and used as a baseline assessment for evaluation of implemented technologies.
Stages of implementation: The stages of implementation are relatively straight forward. First you must select the community that you wish to work in, and inform a community mobiliser, in this case the head of the village that you wish to conduct a 2-3 hr workshop for up to 15 participants, and that the participants must be the person in the households who is responsible (or has knowledge of) the energy use within the household. The moderator prepares a flip chart with a table of fuel types used in the village and uses this as the basis of the workshop to extract information on energy use within the community. Once the information is collated, a discussion is encouraged to review the information and devise means by which this amount can be reduced. The moderator then takes this opportunity to demonstrate several low cost energy efficiency measures that may appeal to the community.
Role of stakeholders: The community are expected to attend the workshop, engage in active discussions on their energy use and ways in which it can be reduced. The workshop needs to be supported by the local government, this provides gravitas, and a platform to launch the approach in other communities. The final stakeholder is the implementer, in this case a local NGO who organises the workshop, demonstrates the technologies and provides ongoing support during the implementation of the technologies.
Other important information: It is important to understand the spending habits of the participants, if they are used to spending on a day to day basis and not used to financial planning, it is important to recognise this fact in the implementation of the technology.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
RRS
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Nurobod, Shaftuti Bolo
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
2011
سنة الإنهاء (إذا لم يعد النهج مطبقًا):
2012
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Energy Conservation)
There were two main objectives to this approach, the first was to raise awareness on energy use with respect to types of energy, cost and accessibility, and to use this as a platform for encouraging the implementation of low cost energy efficiency measures in the community. The second was to collate baseline data to allow an assessment of how the implemented technologies impacted on energy (and by association natural resources) use and how the expenditure and amounts were reduced in real terms.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: This approach was designed to make the participants evaluate and assess the amount of money, time and effort that goes into meeting their energy needs. It is also a clear and precise way to collate information on the amount of natural resources that are been used to meet this need. These natural resources can be in the form on bushes, wood, dung, cotton sticks etc. These resources are being redirected from other purposes such as construction, but also as natural fertilisers, mulch and compost. This directly impacts on agricultural production, household finance and ultimately livelihoods. The reduction in resource use can reduce the risk of conflicts between villages, and reduce pressure on natural resources allowing them to rejuvenate, and increase soil fertility and quality.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
المعايير والقيم الاجتماعية /الثقافية/ الدينية
- معيق
Rural communities emerging from the soviet system have very low business awareness. Even when there are seemingly obvious savings to be made in finance and natural resources there is a lack of appreciation of the potential savings that could be made.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Discussion on the issue of savings in time, money and resources helps promote better understanding. The concept of pay back had to be repeatedly explained.
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
- معيق
عبء العمل، توفر القوى العاملة
- معيق
There are times of year when the village participants are otherwise distracted by sowing seeds, harvesting, Ramadan etc.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The most effective time would be at the end of the winter period when resources are scarce, money constraints are more apparent and energy use is a household priority issue.
غير ذلك
- معيق
In many of the households the men are working away in Russia. This leaves the women in charge of the household, however, many of the energy costs are organised by the men before they leave or on their return.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Many of the labour migrant leave in the springtime, therefore it would be more effective to organise the workshops at the end of the winter before they leave.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
A representative from each household in the community was involved.
Women hold a traditional role in the society and did not participate in the workshops. The men pay all the bills and see their role as that of the provider for the family.
The entire village suffers from mass labour migration, with nearly all households reliant upon remittances from Russia.
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون
International support and finance was provided for this approach, however, the questionnaire was developed in collaboration between national and international staff to ensure relevance and applicability to the context.
- منظمة غير حكومية
CAMP Kuhiston
إذا كان هناك العديد من الأطراف المعنية، قم بالإشارة إلى الوكالة الرائدة:
CAMP Kuhiston
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | غير موجود | |
| التخطيط | غير موجود | |
| التنفيذ | التعبئة الذاتية | they were active in the participation in the workshops and the collation of data. |
| الرصد/التقييم | الدعم الخارجي | Active in providing follow-up data to evaluate the success of the project. |
| Research | غير موجود |
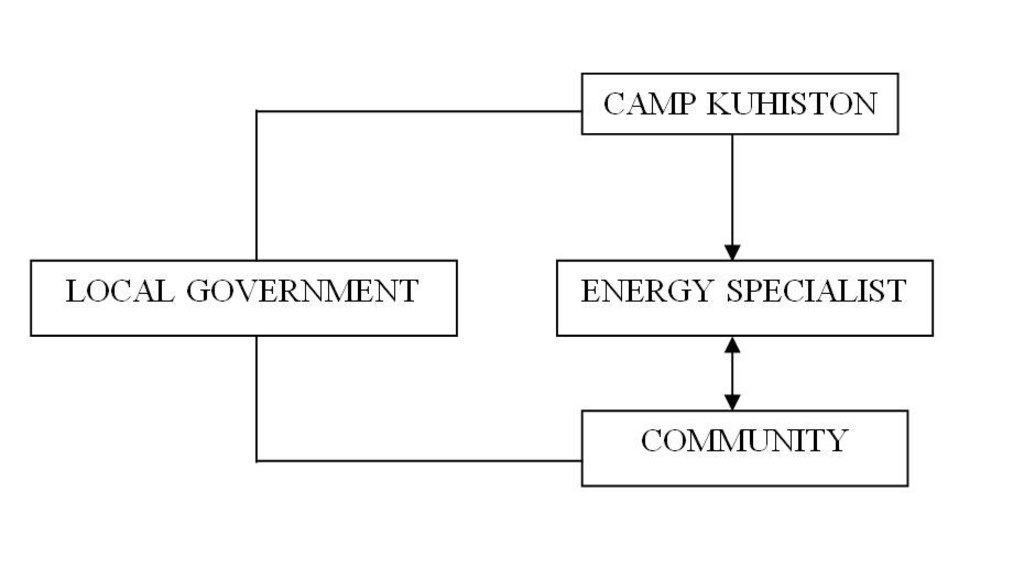
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
الوصف:
The project employs an energy specialist to conduct a participatory workshop. The process is supported by the local government.
المؤلف:
S. Stevenson (CAMP Kuhiston, Dushanbe)
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- مستخدمو الأراضي بشكل أساسي، بدعم من متخصصي الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
اشرح:
The participants are presented with a range of potential energy efficiency technologies such as stove adaptation, thermal insulation by experts, however, it is the participants decision as to which technologies are the most appropriate for their communtiy, and how they can implemented.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. One technology involved the adaptation of traditional cooking stoves; demonstrations were provided however, the mechanisms for securing the materials and ensuring the entire village implemented the technology were up to the discretion of the participants.
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
إذا كان ذلك على صلة، حدد الجنس والعمر والوضع والعرق وما إلى ذلك.
The initial training was for all the households in the village, however, only the men attended due to the religious and cultural position of the region.
شكل التدريب:
- دورات
المواضيع المغطاة:
The training included raising awareness on stove adaptation, indoor two room stove construction, solar power, and low cost thermal insulation for rooms.
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
كلا
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- نعم، باعتدال
حدد المستوى (المستويات) التي تم فيها تعزيز أو إنشاء المؤسسات:
- محلي
حدد نوع الدعم:
- مالي
اعط مزيدا من التفاصيل:
The Jephcott Foundation financed local NGO CAMP Kuhiston to implement the approach.
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Observations of participants understanding of economic benefits.
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by None through observations; indicators: international staff monitor the set up of the workshops and levels of participation.
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The timing of the workshops (i.e the time of year) will be changed to the end of the winter when energy use is more of a priority issue, e.g. cold weather, poor electric supply, lack of easily accessible natural resources
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- علم الاجتماع
- الاقتصاد / التسويق
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
CAMP Kuhiston collated data on energy usage and by association natural resource use. In addition to the participatory workshop CAMP conducted a household questionnaire to assess the suitability of different energy efficiency technologies, and the social vulnerability of the inhabitants, to identify the most effective households to implement energy saving activities.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- < 2000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government (Jephcott Foundation, UK): 100.0%
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
كلا
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- معدات
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| Posters and stationery | ممول بالكامل | |
- بناء
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| Metal sheets, demonstration material | ممول بالكامل | |
التعليقات:
Metal sheets and some other basic materials were provided for the demonstration adaptation of the outdoor cooking stoves.
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
5.5 حوافز أو وسائل أخرى
هل تم استخدام حوافز أو أدوات أخرى لتشجيع تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
The Jephcott Foundation financed local NGO CAMP Kuhiston to implement the approach.
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The extent to which it will reduce the amount and type of natural resource use will be re assessed at the end of the project. It is estimated that there will be a 20% reduction.
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The approach was implemented in a socially disadvantaged area.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The stove adaptation should lead to a 10-20% reduction in natural resources used for cooking, and the solar lights could make a $100/year saving.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
It should help reduce spending on energy, dependence on natural resources, and increase the amount of organic materials for agricultural purposes.
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الربح (القدرة)، وتحسين نسبة التكلفة إلى العائد
The approach is designed to highlight to households how much of their income they spend on energy.
- الوجاهة والضغط الاجتماعي/التماسك الاجتماعي
Social pressure ensured all the households participated.
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
Improvement in living conditions and saving of finance and natural resources.
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- غير مؤكد
إذا كان الجواب لا أو غير متأكد، حدد ذلك وعلق عليه:
The participants will be encouraged to re-assess their natural resource use in the following year, and hopefully instigate their own measures to tackle the issue.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Quick and simple way to put an economic cost on fuel use. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The approach needs minimal resources and is relatively easy to implement. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: It would be easy to replicate and easy to teach others how to undertake the approach.) |
| It makes participants evaluate what they need to run their households, and puts an economic and natural resource value on the process. |
| It helps focus the participants on how much time, effort and money are being used to run their household. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: To follow up, to see how effective the implementation of the technologies was in reducing their energy needs.) |
| The scope of the level of participation is flexible and can be adapted to the contexts. It allows for direct comparison for before and after the implementation of the technology. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: It could be further developed to put an economic value on SLM technologies.) |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| It requires participants to have good quality data available to be effective. | Complete follow up visits to households to check data quality. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Two Room Stove [طاجيكستان]
A brick stove that is built into the existing internal wall, that will heat the two rooms and can be used for cooking.
- جامع المعلومات: shane stevenson

Energy efficiency measures to increase the application of … [طاجيكستان]
The implementation of several low cost energy efficiency measures to reduce the amount of organic material used as fuel within rural households.
- جامع المعلومات: Daler Domullojonov
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية