Improving terraces with farmers [النيبال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Madhav Dhakal
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Laura Ebneter
Kisansangai gara sudhar (Nepali)
approaches_2549 - النيبال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - النيبال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
Participatory action research with multiple stakeholders for the demonstration and extension of improved rainfed hill terraces in Nepal
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
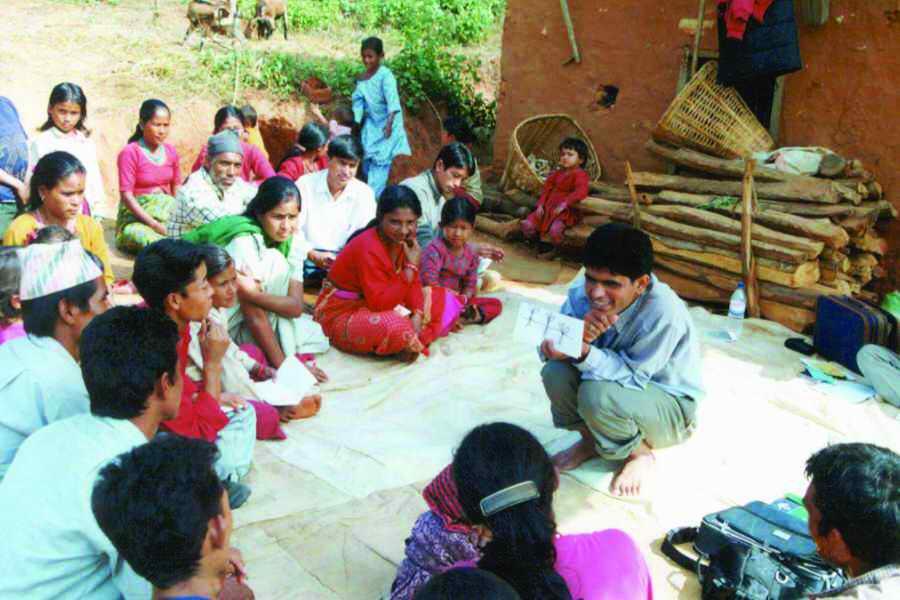
The traditional farming practices employed on steep sloping land in Kubinde village in Nepal's midhills led to soil and water erosion and low crop and fodder yields. The People and Resource Dynamics in Mountain Watersheds of the Hindu Kush- Himalayas Project (PARDYP) started work in 2001, with a small group of farmers from this village (who were also members of the local forest user group) and the Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management to identify and test an integrated approach for addressing these constraints. The approach taken was an improved hill terrace for rainfed conditions consisting of structural and vegetative measures. The aim was to demonstrate and test the technologies' potential for overcoming constraints related to farming sloping agricultural land. The specific objectives were, in association with the local farmers, to design a technology that solved soi erosion problems on sloping agricultural lands whilst at the same time increasing the land's nutrient conservation and production capacity. The local line agency office of the Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management was involved in developing the technology to make use of their experiences and to come up with a validated technology that the department could use in its own programmes.
Before implementing the terrace improvement work in Kubinde village, a terrace improvement committee was formed made up of local farmers. The awareness activities began in January 2001. Committee members were trained on subwatershed management and were taken to the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development’s (ICIMOD) Demonstration and Training Centre at Godavari and another ICIMOD site to show them potential soil and water conservation technologies including improved terraces. After the technologies were implemented, a number of farmer exchange, interaction and monitoring programmes were held to assess the technology and to promote it. Indicators were developed for monitoring the activity.
About half of the costs were covered by the participating farmers and the rest by PARDYP. The other incentives were training and extension, allowances for participants, national expert honoraria, and training material such as audio-visual facilities. These were all provided by PARDYP with the help of the line agency.
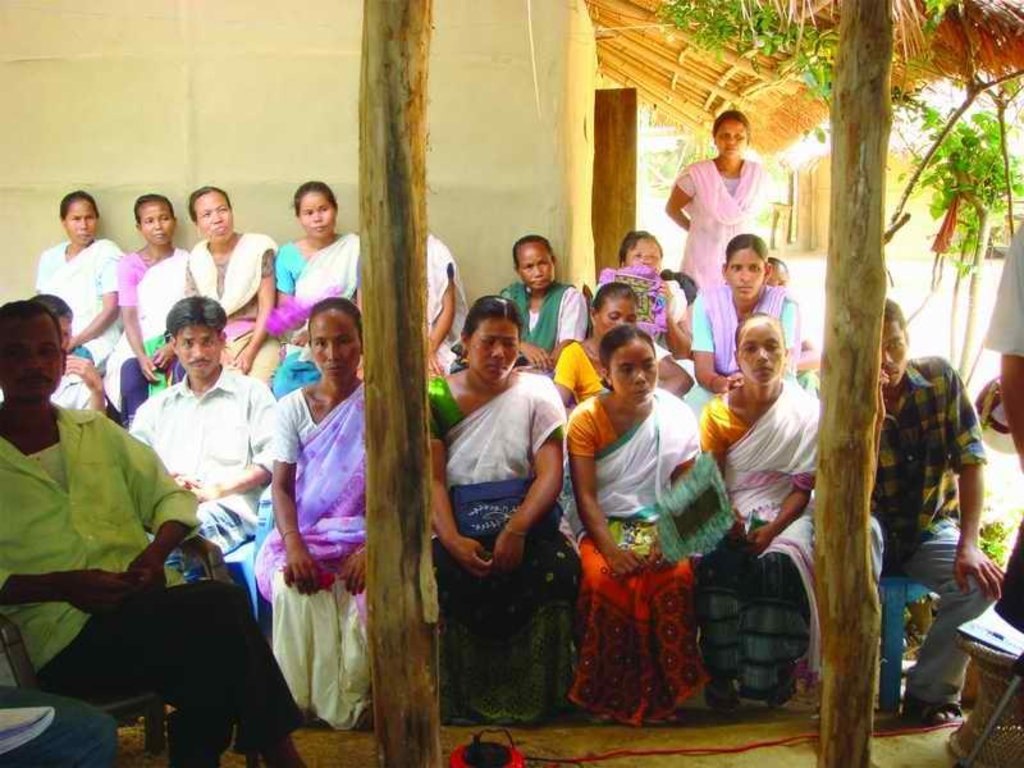
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
النيبال
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
kavre Palanchok/ Kubinde village, Jhikhu Khola watershed
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
سنة الإنهاء (إذا لم يعد النهج مطبقًا):
2005
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
Local farmers collectively solving problems by identifying and using the most appropriate local solutions. Local farmers designing, testing, and disseminating alternative technologies adapted to local conditions. Strengthening joint learning by farmers and development actors
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Weak institutional collaboration for addressing 1) poor soil fertility and land productivity; 2) soil and nutrient loss and excessive water runoff from sloping agricultural land; and 3) fodder scarcity. Lack of on-farm research for developing technologies that attend to farmers' needs.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- معيق
Government incentives are lacking
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The technology is cost effective.
الإطار المؤسساتي
- معيق
Lack of coordination among land users
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Terrace improvementuser group formed
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: Because of private land ownership, there were no conflicts and hence the technology for deissmeination was well maintained.
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- معيق
It is not a priority area of line agencies
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The appraoch relies on farmer adoption
غير ذلك
- معيق
lack of awareness
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Trainings , discussions and field visits
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
Men and women land users worked equally
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون
- المعلمون / أطفال المدارس / الطلاب
- منظمة غير حكومية
- الحكومة المحلية
- الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار)
- health volunteers
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | سلبي | Group discussion; organised with local forest user group; selection of members for training and tours (12 men and 11 women); formation of terrace improvement committee. |
| التخطيط | تفاعلي | group discussion; survey , site selection , fodder / grass species selection |
| التنفيذ | التعبئة الذاتية | Terracing activities: measurement, soil excavation, and retaining wall construction |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | Done in a participatory way involving individual farmers, project staff, and Department of Soil Conservation staff |
| Research | سلبي | Assessing performance of planted grasses and advantages and disadvantages of technology |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي بشكل أساسي، بعد التشاور مع مستخدمي الأراضي
اشرح:
The package was initially offered by researchers and later modified and implemented by land users.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. The landusers are more familiar with their land's capacity and charcteristics.
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
- extensionists/trainers, teachers, school children/students, politicians/decision makers, Health volu
شكل التدريب:
- من مزارع إلى مزارع
- مناطق العرض
- دورات
شكل التدريب:
- Audio vidual learning
المواضيع المغطاة:
Importance of Soil and Water conservation in local level, concept of sub watershed management, activities in other parts of a country regarding SLM, etc.
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
وصف/تعليقات:
Name of method used for advisory service: Demnstration/extension of improved terrace technology;
Key elements: Participatory Action Research, Trainigs and Farmer to Farmer visits, Particpatory monitoring and evaluation; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: projects own extension structure and agents, government's existing extension system; Extension staff: project employees, govt. staff and farmers. 2) Target groups for extension: land users, technicians/SLM specialists; Activities: Farmer to farmer exchange, demonstration, trainings; Invited to trainigs, field visits
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Various extension service agencies have secured funding for SLM programmes.
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- لا
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: plant heigth, biomass production, usefulness of grass/fodder species
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: views about technology
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: species selection, change of agricultural practices
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: changes in crop yields and patterns and the value of the land
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: survey, on-site verifications
land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: survey, number of land users applying for SWC
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: maintenance of terraces and hedgerows
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: New ideas have been generated but strategies to implement them are yet to be in place.
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: New varieties of grass, fruit and fodder species have been introduced
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- علم الاجتماع
- علم الايكولوجيا
- تكنولوجيا
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
Sociology: Looking at scaling up process; Ecology: Looking at the impacts of the technology at subwatershed level; Technology: development process.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- < 2000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: national non-government (SDC, IDRC, ICIMOD): 65.0%; local community / land user(s) (Terrace improvement committee): 35.0%
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- زراعة
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| بذور | ممول بالكامل | |
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- مدفوع نقدا
التعليقات:
About 50% of total labour costs were met by land users.
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Area expanded , about 100 percent of previously improved terraces was expanded. New variety of grass/ fodder species has been adopted..
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The project's aim was not to promote the approach but the technology. However, similar appraches are followed by other programs as well from before; such as the District Soil Conservation Offices.
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
increased production (grain and biomass) due to moisture and nutrient conervation
- زيادة الربح (القدرة)، وتحسين نسبة التكلفة إلى العائد
Increased land prize
- انخفاض عبء العمل
fodder/ grass availability ( near to house)
- تحسينات جماليية
greenary throughout the season due to fodder and grass species.
- environmental consciousness, moral, health
less soil erosion from the land
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، صف كيف:
More than 60% of the total improved terraces in Kubinde village were built by the land users themselves. Widespread rapid adoption did not happen in other villages due to financial and labour limitations. Land users of Kubinde village continue to maintain the improved terraces.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Technical knowledge and confidence increased from the training and field visits, interactions, and experience sharing (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Such activities should be continued by incorporating other new ideas) |
| The approach led to the development of a team spirit among farmers (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: As above) |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The approach is based on building the capacity of farmers (both men and women) by involving multiple stakeholders in the development and adoption of the technology. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Approach should be to strengthen land users' involvement in SWC activities) |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Due to the conflict, which was on-going at the time, follow-up after a year of implementing technology was not possible and the monitoring was not done. This resulted in the adoption of the technology by other farmers not being carried out properly with, for example, farmers not maintaining the hedgerows as recommended. Also, the new terraces were not as good as they should have been. | The technical experts need to visit the sites and identify gaps and encourage farmers to 'fill them'. For example, the benefit of hedgerow management needs to be demonstrated. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Mathema, P. (2003) Watershed Management in South Asia. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Department of soil conservation, Nepal
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية