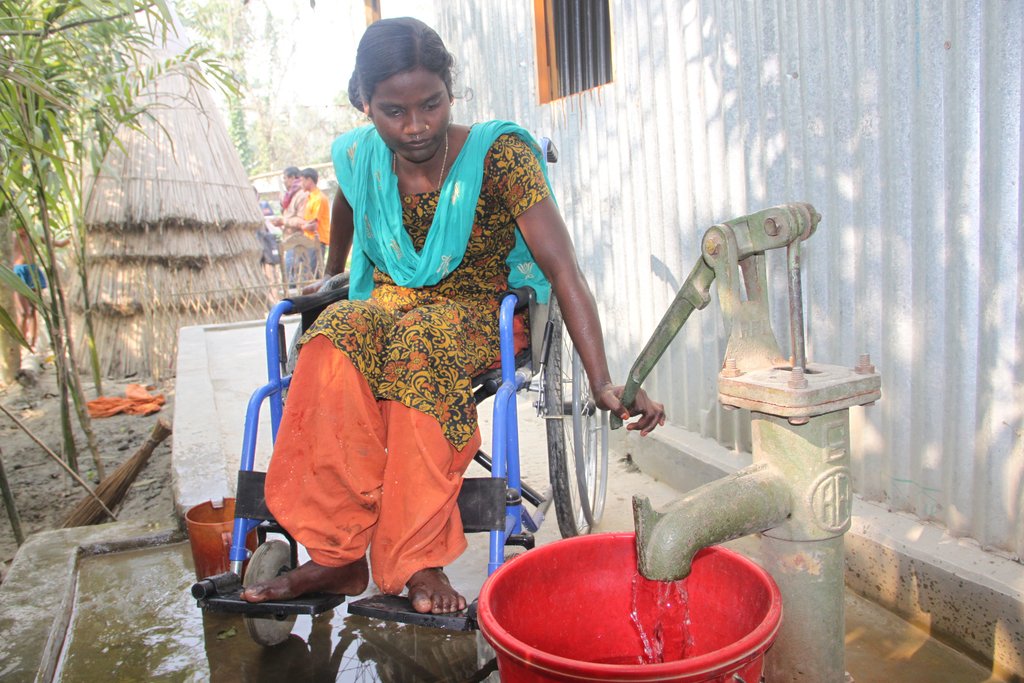Disability inclusive Disaster Risk Reduction [بنغلاديش]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Subir Saha
- المحررون: Subir Saha, Manuel Rothe
- المُراجع: Alexandra Gavilano
Protibondhita Bandhob Durjog Jhuki Rash
approaches_2001 - بنغلاديش
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
DRR specialist:
Islam Shahidul
+8801733143435
shahidulpls@yahoo.com
Centre for Disability in Development (CDD)
Gaibandha
بنغلاديش
DRR specialist:
Dey Ashutosh
880-2-9887251 / +8801787662993
ashutosh.dey@cbm.org
CBM
Country Coordination Office CBM International H # 12 (GF) R # 2/A, Block-F Banani, Dhaka-1213
بنغلاديش
DRR Specialist:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Christoffel Blindenmission (CBM) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
09/11/2016
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
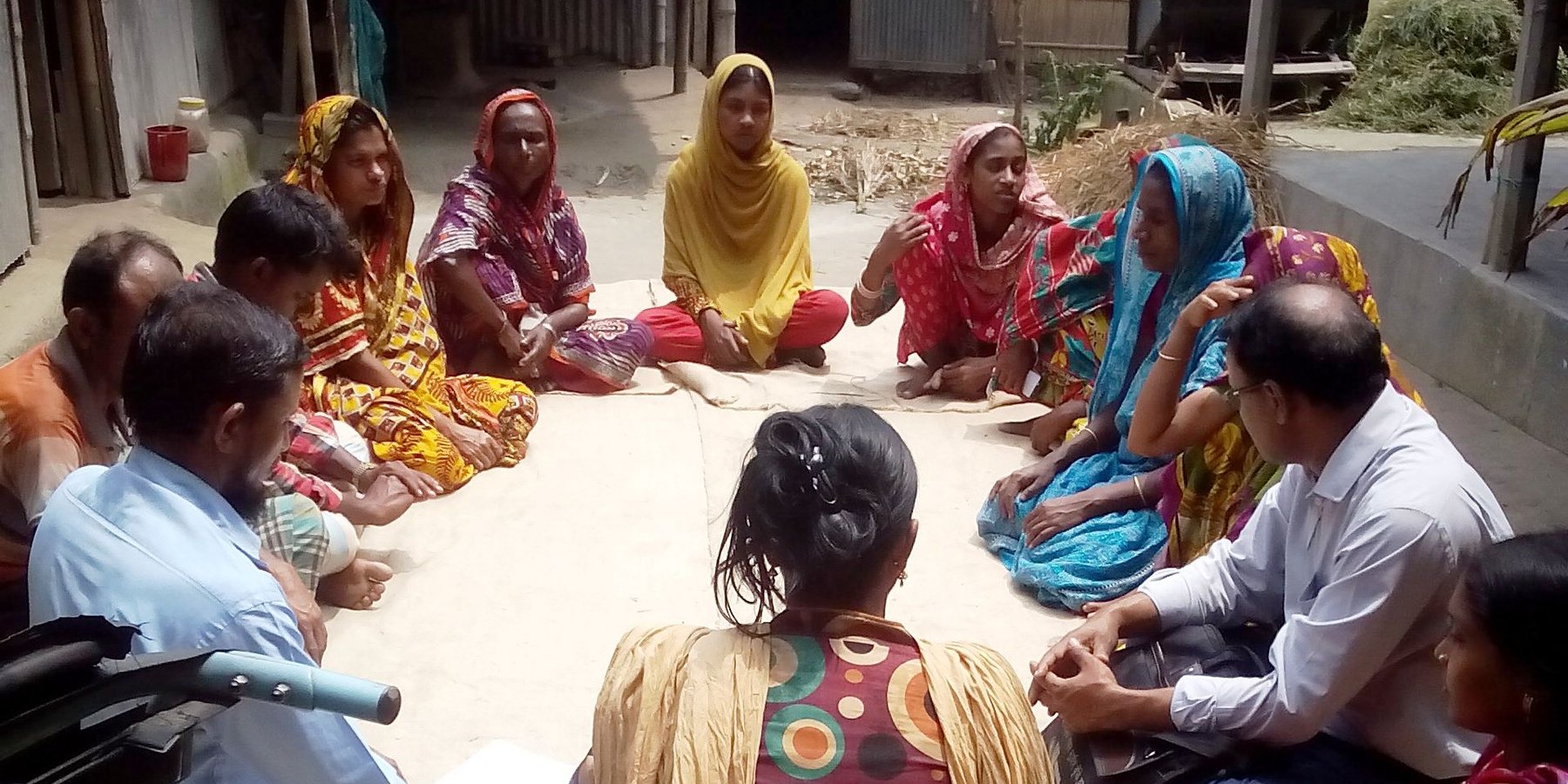
The disability inclusive approach is centered around the meaningful contribution and leadership of persons with disabilties during the entire project management cycle, from the planning stage to the evaluation of the impact of a project. It contributes to empowering them to overcome social exclusion and recognizes their needs and priorities as persons who are disproportionally at risk of disaster.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
The main charactistic and central feature of the approach is that persons with disabilties can actively and meaningfully participate in, contribute to and benefit from sustainable land management/disaster risk reduction activities. The implementing organization needs to invest sufficient time and financial ressources into the formation and strenthening of self-representation groups of persons with disabilities and support their active engagement with the local government and the wider community to address the physical and attitudinal barriers that hinder their full participation in the project and society in general.
The aim is twofold: On the one hand, the participation of persons with disabitities ensures that their needs and priorities are fully taken into account in the project design and implementation, to ensure that they can benefit equally from it. On the other hand, it contributes to reducing barriers beyond the project and empowers them to demand their rights in other areas of human development, like education, health or livelihood.
The main stages of disability inclusion in the implementation of a SLM/DRR technology are:
1) Formation of self-help groups for persons with disabilities,
2) trainings and other capacity development activities for the groups, including rights awareness sessions and organizational management trainings,
3) set up the collaboration between the groups and the local government and with other members of the community,
4) participation of persons with disabilities/group members in the planning phase to decide on the technology and adapt the technology to universal design standards, which takes into account their needs and the needs of other groups with other specific accessiblity needs, like the elderly or pregnant women,
5) persons with disabilities (together with other land users) support the introduction of the technology (including the construction activities) by providing manual labor and supervision functions
6) full handover of the technology to land users, ensuring Joint ownership includes persons with disabilities, and provision of trainings for self-maintenance,
7) participation of persons with disabilties in the evaluation of the impact of the technology, sharing of lessons and good practices and continuous advocacy for community development and for the rights of persons with disabilties.
Experience from Bangladesh shows that what the land users, including persons with disabilties, like about the approach is: The strong community engagement, the empowerment and increased status of persons with disabilities, the collaboration between persons with disabilities and persons without disability, and the adaptation of existing technology to fit the needs of persons with disability.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
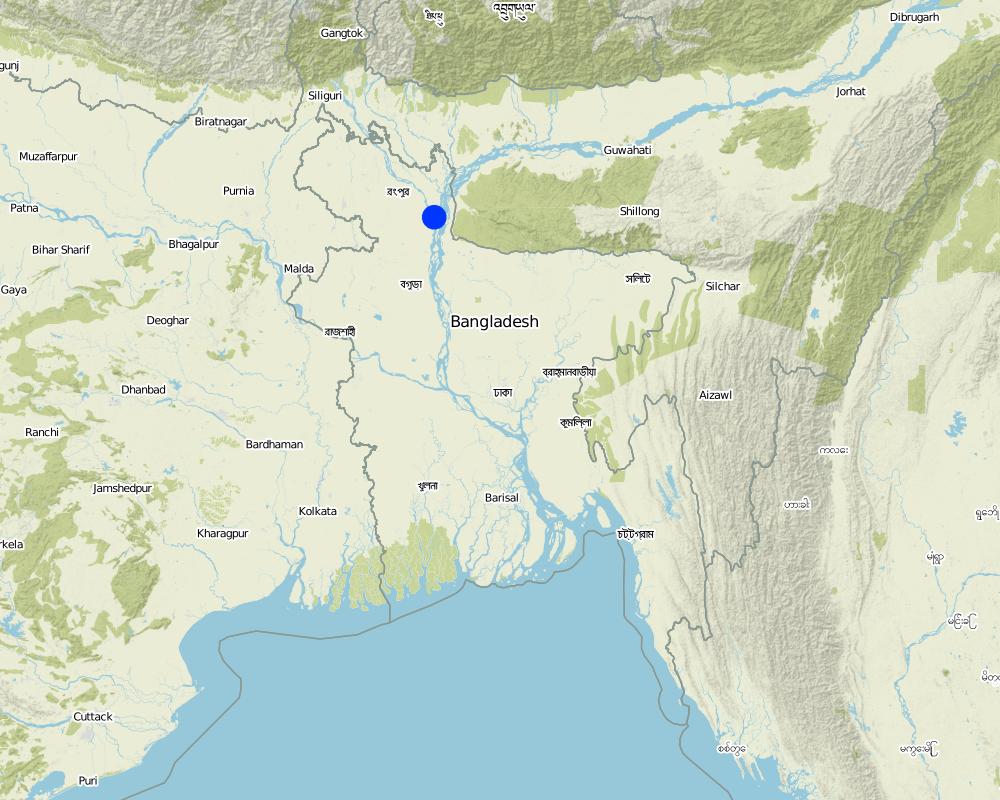
بنغلاديش
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Gaibandha District
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Horipur Union, Sundargonj Sub district
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
2015
سنة الإنهاء (إذا لم يعد النهج مطبقًا):
2016
التعليقات:
Project "Disability inclusive, flood resilient cluster village" implemented from December 2015 to September 2016.
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
To empower persons with disabilities to meaningfully participate in, contribute to and benefit from the implementation of an SLM/DRR technology.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
المعايير والقيم الاجتماعية /الثقافية/ الدينية
- معيق
The social stigma and exclusion, that persons with disabilities experience in rural Bangladesh, was a challenge for the project. Persons with disabilities are sometimes believed to be incapable of contributing anything meaningful to society and village life. Some community members did not want to associate with persons with disabilities. This required an extra effort to ensure the participation of the wider community in the project and it required sustained advocacy and awareness raising for the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities.
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- تمكين/تمكيني
The financial resources for the implementation of the technology and the extra ressources needed to ensure disability inclusion, were readily available because the technology was widely and positively recognized by the community and by donors.
الإطار المؤسساتي
- تمكين/تمكيني
The institutional environment was overwhelmingly supportive of the implementation of the project. The local Union Council government, schools, mosques and other civil society organizations were in favor of the technology and approach and supported the implementation.
التعاون/التنسيق بين الجهات الفاعلة
- تمكين/تمكيني
Beneficiaries/land users were selected in a participative process, involving the whole community. The process was transparent and inclusive. It was a foundation for the smooth collaboration with beneficiaries and other involved stakeholders later on.
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
To ensure joint ownership of beneficiaries of the land on which the SLM/DRR Technology was implemented, an exchange of land was needed. Due to the remoteness and scarce population of the implementation area in rural Bangladesh, a cooperative local government and a manageable legal framework this was easy to achieve.
A deep-rooted tube well was installed for water access of the land users. Water use rights were also easy to acquire.
السياسات
- تمكين/تمكيني
No specific policies existed, which significantly affected the implementation of the technology.
حوكمة الأراضي (صنع القرار والتنفيذ والإنفاذ)
- تمكين/تمكيني
Land ownership was recognized by the local government and land governance was controlled by land owners.
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- تمكين/تمكيني
Indigenous knowledge about SLM was enabling for the implementation of the technology. Technical expertise by the implementing organization (NGO) was available.
الأسواق (لشراء المدخلات وبيع المنتجات) والأسعار
- تمكين/تمكيني
Inputs for construction and planting were locally available at reasonable prices.
عبء العمل، توفر القوى العاملة
- تمكين/تمكيني
During the lean season manpower was abundant in the area, but it was scarce during the planting season. The workload for the implementation of the technology was manageable and could easily be provided by land users themselves.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
The land users include 10 families who jointly own and inhabit the land of the cluster village.
Land users were closely engaged in the implementation of the technology by participating in decision making processes, informing the design of the technology and contributing to the construction process.
- المنظمات المجتمعية
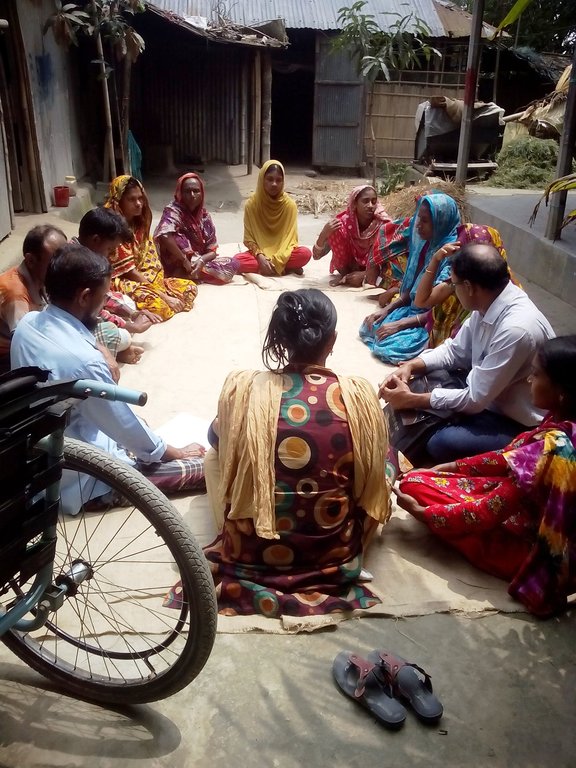
Self-help (self-representation) groups of persons with disabilities are informal community based groups of 15 persons with different types of disabilities (physical-, sensory- and mental disabilities).
The group is closely engaged in the implementation of the technology. It participates in decision making processes, informs the design of the technology, contributes to the construction process, is engaged in the evaluation of the technology and the sharing of learnings about it to the wider community.
The group also provides benefits for its members by supporting them with everyday challenges, which can be of economic, legal or social nature, and promotes the rights of all persons with disabilities in the community.
- منظمة غير حكومية
The implementing NGOs included an international and a local organization in partnership (CBM and CDD).
CDD was responsible for the overall management of project implementation and the collaboration with other involved local stakeholders. CBM provided training and technical support.
- الحكومة المحلية
The Union Parishad government is the lowest level of local government.
The Union Parishad government managed land ownership and approved construction projects.
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | تفاعلي | Land users contributed to the initial situation analysis and joined self-help groups for persons with disabilities. |
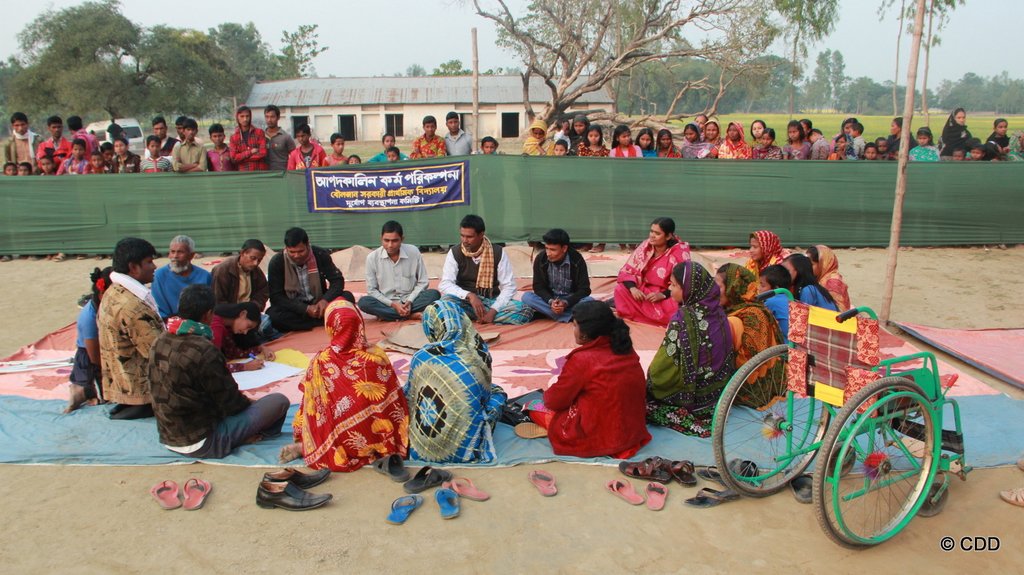
| التخطيط | تفاعلي | Land users, and in particular those who are persons with disabilities, participated in all planning and decision making processes related to the design and introduction of the technology, including the selection of the land. |
| التنفيذ | الدعم الخارجي | Land users engaged in the construction of the technology by providing paid and unpaid labor. |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | The land users monitored the implementation process and gave feedback to the implementing NGOs when changes were needed. Land users participated in the evaluation of the technology and the approach and contributed to the dissemination of good practices and learnings. |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
الوصف:
Not available.
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- جميع الجهات الفاعلة ذات الصلة، كجزء من نهج تشاركي
اشرح:
The cluster village technology was known to the community before the implementation. The technology was suggested by the implementing NGOs to the community, which supported its implementation. The technology was adapted to fit the needs of persons with disabilities based on the decisions of land users with technical support of the implementing NGOs.
حدد على أي أساس تم اتخاذ القرارات:
- تقييم المعرفة الموثقة جيدًا بشأن الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي(اتخاذ القرارات القائمة على الأدلة)
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
- موظفون ميدانيون/ مستشارون
إذا كان ذلك على صلة، حدد الجنس والعمر والوضع والعرق وما إلى ذلك.
10 males and 15 females, aged between 18 to 55. Three were persons with disabilities. Most of them were daily laborers and share croppers.
شكل التدريب:
- في العمل
- مناطق العرض
- دورات
المواضيع المغطاة:
On the job training and demonstration on the construction and maintenance of the technology. Training to self-help groups for persons with disabilities on the rights of persons with disabilities, the use and benefits of the technology for persons with disabilities and the management of self-help groups.
التعليقات:
Training Subjects were: 1) Group dynamics and Development, 2) Disability inclusive DRR 3) Tree plantation and Vegetable Gardening using organic fertilizer 4) Government safety nets and Rights of the persons with disabilities.
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
- construction/implementation of technology
وصف/تعليقات:
The implementing NGOs provided detailed technical support to land users on the adaptation of the technology to the needs of persons with disabilities, following the standards of universal design.
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- نعم، باعتدال
حدد المستوى (المستويات) التي تم فيها تعزيز أو إنشاء المؤسسات:
- محلي
صف المؤسسة والأدوار والمسؤوليات والأعضاء وما إلى ذلك.
Local self-help groups and their APEX body (umbrella group) at Union level were strengthened. Their roles of the self-help groups were to establish a mutual support network, raise awareness among group members of disability rights and development issues, pool ressources and give individual persons with disabilities a greater political voice. The APEX body gave the groups contact points beyond their immediate community and gave further weight to their political voice.
حدد نوع الدعم:
- مالي
- بناء القدرات/التدريب
- معدات
اعط مزيدا من التفاصيل:
To strengthen self-help groups, they were provided with, 1) awarness- and skill development trainings, 2) financial support for climate resilient income generation through agricultural and non-agricultural activities, and 3) assistive devices.
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
A participatory monitoring and evaluation system was implemented with support of the self-help groups for persons with disabilties.
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، فهل من المقصود استخدام هذه الوثائق للمراقبة والتقييم؟:
كلا
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
كلا
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
أشر إلى ميزانية النهج السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي بالدولار الأمريكي:
218702,00
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- 1,000000-100،000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
The annual budget includes the total funds used for the introduction of the technology. Funds were provided through the implementing NGOs CBM and CDD, with the support of a private donor from Germany.
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد نوع (أنواع) الدعم والشروط والمزودين:
Land users received a daily fee for the labor provided for the introduction of the technology. The NGOs also provided most material input for the technology, including soil, sand, seeds, seedlings, grass, trees, ramp, water and sanitation facilties.
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- عمالة
| إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|
| ممول جزئيا | Labor provided by land users for certain construction actvities was compensated with a daily fee. |
- معدات
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| الآلات | ممول بالكامل | Rent of sand extravation machine was funded by the project. |
| أدوات | ممول بالكامل | Tools for construction activities was provided to land users by the project. |
- زراعة
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| بذور | ممول بالكامل | Seeds and seedlings for the homestead garden was provided by the project. |
| أسمدة | ممول جزئيا | The facility for composting organic fertilizer was provided by the project. |
| Plants | ممول بالكامل | Deep-rooted fruit trees and grass turfing was provided by the project. |
- بناء
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| خشب | ممول جزئيا | Wood for fencing for the homestead vegetable garden in front of all houses and a flood resilient cow sheds in the village was provided by the project. |
| Soil | ممول بالكامل | The purchase of soil for the raising of land was funded by the project. |
- بنى تحتية
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| طرق | ممول جزئيا | Construction material for barrier free connections to all houses in the village was funded by the project. |
| Ramp | ممول بالكامل | A ramp, connecting the cluster village with the road was funded by the project. |
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- مدفوع نقدا
التعليقات:
A daily fee of 300 Taka was provided for labor inputs by the land users.
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
5.5 حوافز أو وسائل أخرى
هل تم استخدام حوافز أو أدوات أخرى لتشجيع تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين وتحسين مشاركة الأطراف المعنية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The approach is based on the empowerment of land users, in particularly those who are persons with disabilites. It ensured participation of persons with disablities who would otherwise be isolated and excluded.
هل مكّن النهج من اتخاذ القرارات المبنية على الأدلة؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The project supported land users with the implementation and use of the technology.
هل نجح النهج في تحسين التنسيق والتنفيذ الفعال من حيث التكلفة لأنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The coordination among land users has improved and actions of land management have become more cost effective.
هل نجح النهج في تعبئة/تحسين الوصول إلى الموارد المالية لتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين معرفة وقدرات مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Land users were provided with trainings and demonstrations about the implementation and use of the technology.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين معرفة وقدرات الأطراف المعنية الأخرى؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The local goverment, other members of the community and other non-governmental organizations took note of the technology and sensitization about the rights and needs of persons with disabilties increased.
هل ساهم النهج في بناء/تعزيز المؤسسات والتعاون بين الأطراف المعنية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The approach strengthened the collaboration between the local government and self-help groups of persons with disabilities.
هل ساهم النهج في التخفيف من حدة الصراعات؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Joint decision making and the resolution of conflicts among land users improved through the joint managment of the land.
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The approach empowered persons with disabilities and other land users, who all belonged to economically marginalized groups. Their social and economic status greatly improved.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين المساواة بين الجنسين وتمكين النساء والفتيات؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Land user participation in the implementation of the technology always included men and women. Self-help groups for persons with disabilities, which were formed and strengthened by the project, always included around 50% women. Meaningful participation by women in group meetings was promoted by the implementing NGOs.
هل شجع النهج الشباب/الجيل القادم من مستخدمي الأراضي على الانخراط في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The technology was of of high interest for youth clubs, high school students and other young people in the community and many voiced the intention of replicating it in the future.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسن في مسائل حيازة الأراضي / حقوق المستخدمين التي أعاقت تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
هل أدى هذا النهج إلى تحسين الأمن الغذائي / تحسين التغذية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The technology improved food security and nutrition through the introduction of fruit tree plantation and a homestead vegetable garden.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين الوصول إلى الأسواق؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The construction of a ramp for road access allows wheelchair users and other persons with limited mobility to better access local markets.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين الوصول إلى المياه والصرف الصحي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The technology improved water access through the drilling of a deep bore hole water source for common water access and the construction of barrier free household latrines.
هل أدى النهج إلى استخدام طاقة/ مصادر طاقة أكثر استدامة؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The technology lead to more sustainable energy use through the provision of household based mini solar systems.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين قدرة مستخدمي الأراضي على التكيف مع التغيرات المناخية/الظواهر المناخية المتطرفة والتخفيف من الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The technology offers a safe and accessible space for housing, fruit and vegetable cultivation and livestock shelter. It greatly improved the capacity of land users to adapt to the increasing occurence and intensity of monsoon floods.
هل أدى النهج إلى توفير فرص عمل ودخل؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The technology improved income opportunities through the introduction of a flood resilient fruit tree plantation and homestead vegetable garden. Part of the harvest can be sold on the market.
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
Vegetable production and fruit production increased and is more flood resilient.
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
Soil erosion and land degradation in the custer village reduced.
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
Reduction of disaster risk was the main motivating factor for land users. The cluster village is a flood-resilient safe-place providing shelter for the whole community, including their livestock, during flood season.
- انخفاض عبء العمل
Household works and household based income generating activities have become easier to organize because of the safety and reliable energy supply that the cluster village provides.
- الانتماء إلى حركة/ مشروع/ مجموعة/ شبكات
Joint ownership of the cluster village by land users, who all belonged to an economically marginalized part of the community (daily laborers and share-croppers) and the formation of self-help groups for persons with disabilities, have greatly improved social cohesion among land users.
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- غير مؤكد
إذا كان الجواب لا أو غير متأكد، حدد ذلك وعلق عليه:
The maintenance of the cluster village (including grass turfing, tree plantation, vegetable garden, solar panels, water and sanitation facilities) is currently managed by land users themselves . Long-term sustainability cannot be evaluated yet.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Land users greatly apprechiate the empowerment and social cohesion that the approach enabled. Decisions are taken together and conflicts in the village can be mitigated. The Cluster Village has become a safe space and meeting point for the whole community. |
| The Cluster Village is fully inclusive of persons with disabilities (inclusion in decision making processes and social activities and fully accessible infrastructure), which is something that land users are proud of because it is the first such set-up in the community and is apprechiated as a model by others. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Meaningful participation and of persons with disabilities in project implementation has a signaling effect beyond the project and fosters sensitization of the local government and wider community for more inclusive community development and principles of universal design. |
| Formation of self-help groups of persons with disabilities and their active engagement with the wider community on community development issues, which go beyond the rights and needs of persons with disabilites, lead to empowerment and geater social inclusion of persons with disabilities. |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Technical knowledge gap when it comes to the maintenance of the technology and the continuous dependence on external support. | Invest sufficient ressources in trainings and capacity building and emphasis and formalize the transfer of ownership of the technology to land users. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Formation and strenthening of self-help groups of persons with disabilties to the level where they are sustainable and able to make significant contributions to the projects and community development and demand their rights, takes significant ressources with regard to time and funds invested. | Strong committment of the implementing organization to inclusive programming and sufficient internal capacity building. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
6
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
10
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
5
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Disability inclusive disaster risk managment, CBM, 2013
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.cbm.org/article/downloads/54741/Disability_Inclusive_Disaster_Risk_Management.pdf
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية