Minimum Water Use [تركيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Mehmet Zengin
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2424 - تركيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Selcuk, Faculty of Agriculture (University of Selcuk, Faculty of Agriculture) - تركيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
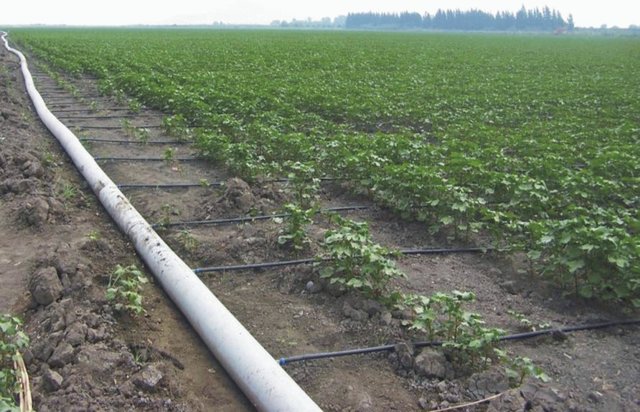

Drip irrigation [تركيا]
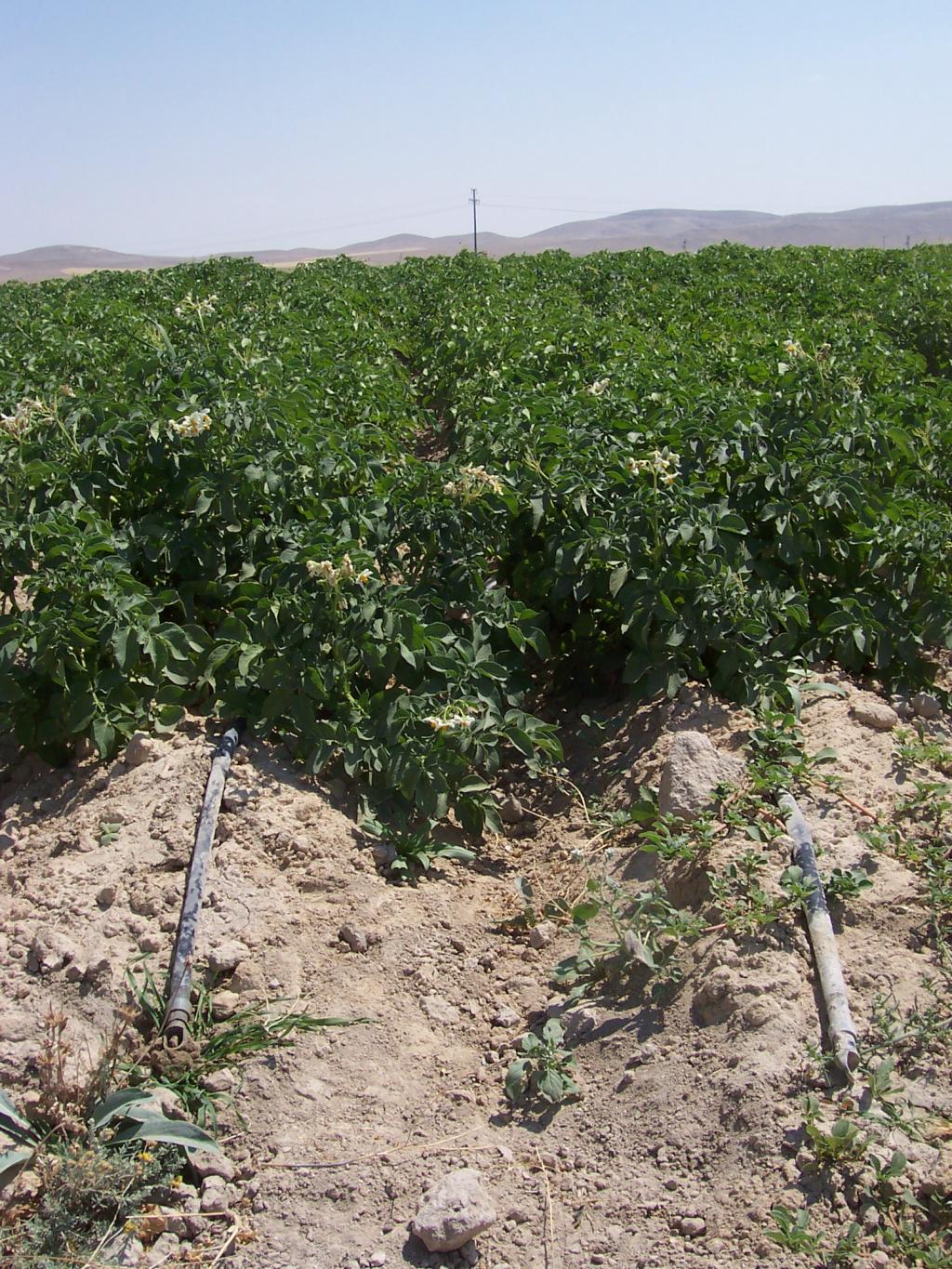
Drip irrigation is a method designed for minimum use of water and labour for the optimum irrigation of plants in arid and semi-arid regions.
- جامع المعلومات: Faruk Ocakoglu
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
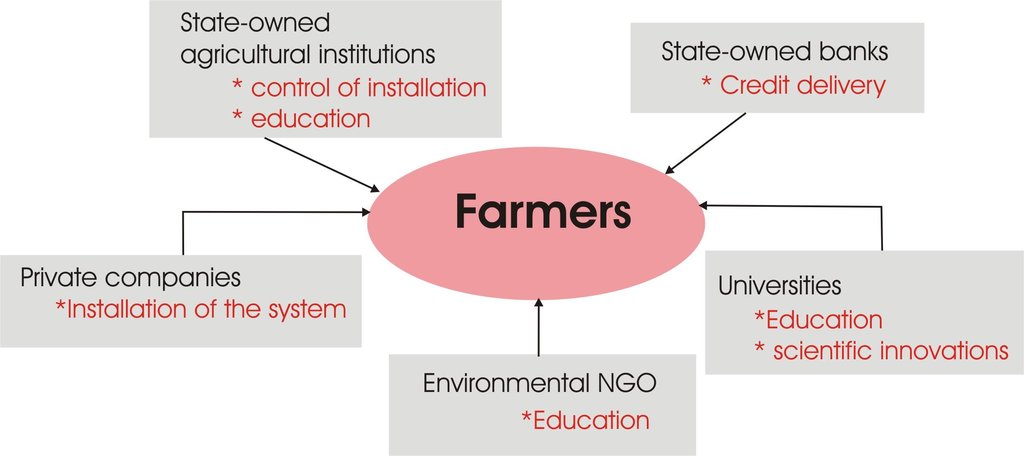
Instead of flow irrigation that requires high water consumption and causes excessive evaporation, water can be transported in pipes till crop's body and can be given slowly under controlled conditions. The approach is brought to farmers by state institutions as well as banks, and education for the scientific background, installation and usage of the technology is provided by state-owned companies
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
Aims / objectives: To inform the farmers who use water in their crops about minimum water use, effective water use, in order to conserve underground water resources in semi-arid regions. The basic stress of the approach is to demonstrate the advantages of drip irrigation in terms of croping, soil preservation and particularly the water preservation.
Methods: To convey water by means of pipes until the crop roote zone and distribute water in a controlled manner by using valves. This method facilitates also the use of chemical fertilisers.
Stages of implementation: The methods of drip irrigation system will be tought in detail to land users. Measure addresses to the benefits of minimum water use by field demonstrations. Information is delivered to the farmers in winter and the other studies are caried out in spring and summer.
Role of stakeholders: Actually drip irrigation plans are done by private companies and there is significant financial support from state companies. The role of stakeholders are limited with the eagerness to follow approach and to use suitable crop types.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
تركيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Konya
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Karapınar
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
2004
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Drip irrigation system, irrigation, minimum water.)
To conserve the underground water, inform the farmers about the mechanisms of saving water by minimum irrigation, showing them advantage of this irrigation and then create a demand among farmers towards drip irrigation and build a robust structure between controlling authorities, knowlegde supplying units (such as universities) and financial sector.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Drought and decreasing level of underground water. Lack of technical knowledge on drip irrigation tecniques and lack of existing budget to promote these techniques.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- معيق
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: Existing fields belong to individual farmers but they are highly fragmented due to inheritence.
- معيق
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- معيق
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون
- الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار)
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | غير موجود | |
| التخطيط | سلبي | Planning is done by authorised private companies. |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | Implementation is done in colloboration with private companies and individual land owners. There is significant credit supports from the state for implementation of approach. |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | Monitoring and evaluation is done by land owners themselves. |
| Research | غير موجود |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي بشكل أساسي، بعد التشاور مع مستخدمي الأراضي
اشرح:
Decision is taken from top to bottom, mainly fueled with favorable agricultural credits organised by the state. Some large scale agricultural farms can build the minimum water use system by themselves without any technical and financial help from the state.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- موظفون ميدانيون/ مستشارون
شكل التدريب:
- مناطق العرض
المواضيع المغطاة:
They watched minimum irrigation water use technique with demonstrations.
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- نعم، باعتدال
حدد المستوى (المستويات) التي تم فيها تعزيز أو إنشاء المؤسسات:
- محلي
حدد نوع الدعم:
- بناء القدرات/التدريب
اعط مزيدا من التفاصيل:
Local state experts control the installation to be sure that it is done accordingly the plan, and universities and local state institutions help in education of farmers on the benefits and way of installation of the approach.
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by government, other through observations; indicators: extension experts and universities made the observations.
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations
There were many changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: As the advantages (technical as well as financial) of the approach become clear by monitoring activites though discontinous, the new irrigation teqniques is adopted by increasingly more farmers.
There were many changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Technology does not change too much but its adoption rate increases.
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- علم الايكولوجيا
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
Research was carried out on station
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- 1,000000-100،000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government: 90.0%; other: 10.0%
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- معدات
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| الآلات | ممول بالكامل | |
| أدوات | ممول بالكامل | Hand tools |
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- الغذاء مقابل العمل
التعليقات:
Normally, installation of the irrigation system is done by the specialised componies with speciel equipments. Farmers only help them voluntarily.
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Drip irrgation system affected positively minimum water use.
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
This group is not economically strong to install the approach, for this reason its benefits to this group is small.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسن في مسائل حيازة الأراضي / حقوق المستخدمين التي أعاقت تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Small size of individual crop fields hinders the approach and and its implementation. The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. By gatering together of these small fields might ease the application of technique in the future.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Man power significantly decreased in irrigation. But the basic improvement is on the water save and crop yield increase.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
- زيادة الربح (القدرة)، وتحسين نسبة التكلفة إلى العائد
reducing significantly the energy usage for pumping water.
- انخفاض عبء العمل
irrigation in this way is quite easy.
- المدفوعات/ الإعانات
Credits are low interest and long term.
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Drip irrigation system is very easy and energy costs are low. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: More long term credit will increase the application of approach.) |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Minimum water use conserve water sources. It positively affects crop yields and quality. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Training, demonstration and giving credit to farmers while begining to set up drip irrigation. ) |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Drip irrigation system is expensive. They have no enough techniqual knowledge on the sytem in drought regions. | By receiving bank credit at the begining and crop market values must be high. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| First investment expenses are high in drip irrigation system. Farmers do not know completely water use techniques. | By the training and demonstrations |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Drip irrigation [تركيا]
Drip irrigation is a method designed for minimum use of water and labour for the optimum irrigation of plants in arid and semi-arid regions.
- جامع المعلومات: Faruk Ocakoglu
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية