Evaluation of the System of Rice Intensification through participatory research and development [النيبال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Madhav Dhakal
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Sahabhagitamulak anusandhan ra bikas dwara dhan uttpadan bridhhi garne tarika ko mulyankan (Nepali)
approaches_2550 - النيبال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - النيبال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

System of Rice Intensification [النيبال]
A method for increasing the productivity of rice by changing the management of plants, soil, water, and nutrients.
- جامع المعلومات: Madhav Dhakal
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
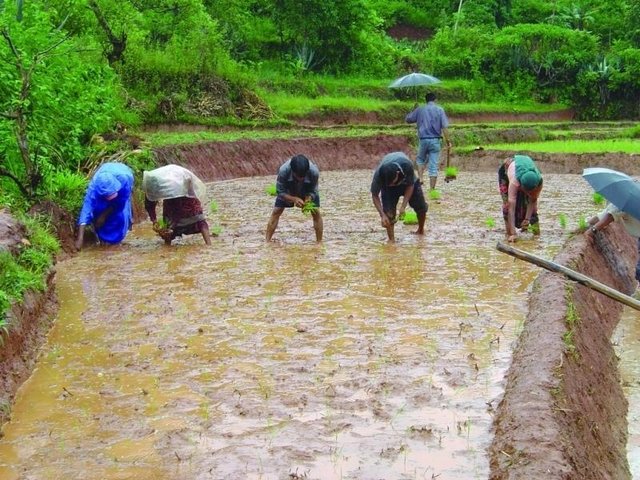
Conducting participatory action research with farmers and district level line agencies for demonstrating, disseminating and scaling up SRI
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
Aims / objectives: PARDYP pilot tested SRI in the Spice Crop Development Centre (SCDC) at Tamaghat, Kavrepalanchok in 2002. The positive results led the technique to be tried out in 25 farmer’s fields in 2004 to evaluate whether SRI was technically feasible in the Himalayan middle mountains. Based on farmers’ interests and to promote SRI systematically, PARDYP organised interaction programmes between farmers who had and had not used SRI, village level group discussions, farmer-to-farmer visits and farmer-led on-site monitoring and evaluation in 2002, 2003 and 2004.
Methods: In 2005, the emphasis shifted to carrying out research with groups of farmers in a more systematic way and participatory rural appraisal methods and tools were used. The approach was called the SRI farmer field school (FFS) approach. Lead farmers (13 male and 6 female) were trained as SRI trainers and then facilitated village level farmer field schools for testing and promoting SRI. In 2005, SRI farmer field schools were run in 15 villages for about 100 farmers. Each school carried out hands-on training sessions to help farmers understand (1) the basic concepts of SRI and its practices, (2) methods for comparing traditional practices with SRI, and (3) how to observe, analyse and present findings more systematically. Monitoring and evaluation gathered both men’s and women’s perceptions. This also helped establish an informal farmer-learning network in the watershed. Village level discussions, farmer visits, and interaction with staff from the district agriculture offices continued. At the end of the on-farm experiments, a district level farmer’s day was organised to share the experiences gained.
Other important information: To promote wider understanding of the action research and encourage farmers to continue developing and adapting SRI, the project disseminated information about SRI through information, education and communication (IEC) materials aimed at community-level users, and a multi-media package on a CD ROM for the global audience and Nepali policy-makers and administrators. A national exchange workshop was held to share experiences from across the country on the use of SRI.
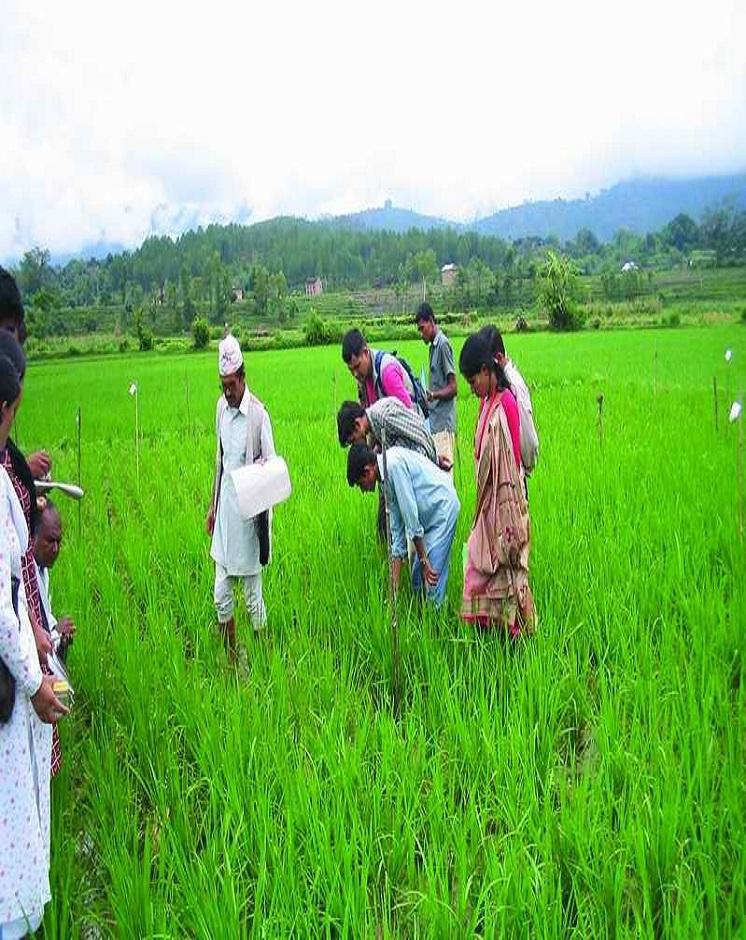
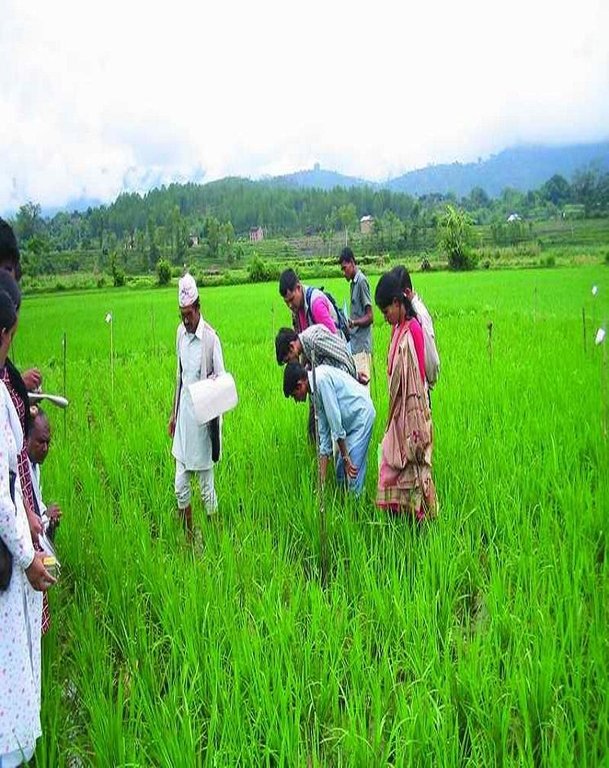
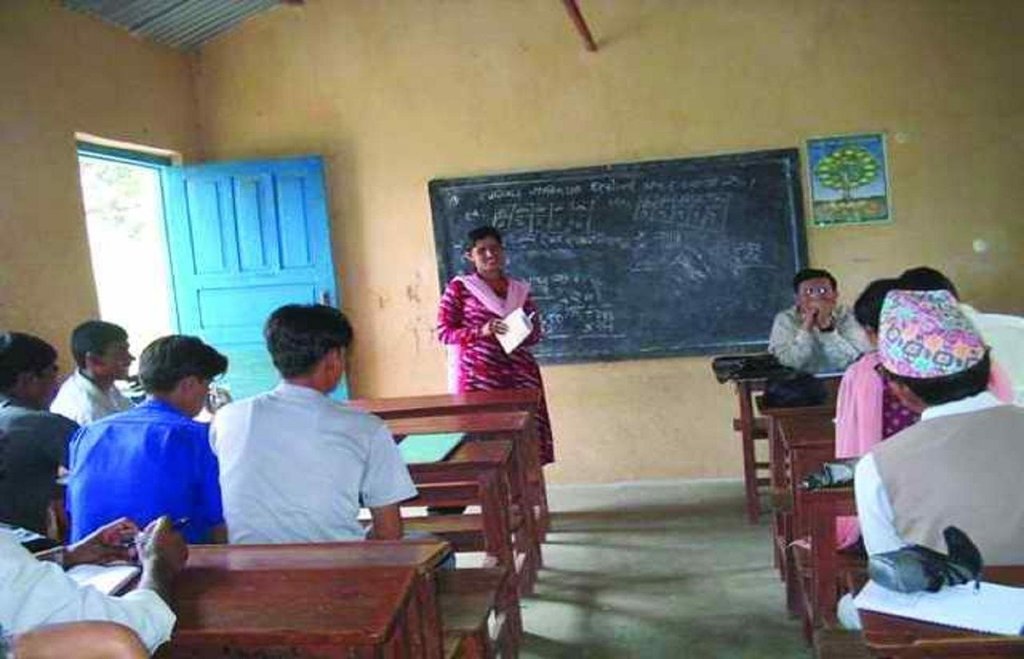
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
النيبال
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Kavrepalanchowk/ Jhikhu Khola watershed
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
سنة الإنهاء (إذا لم يعد النهج مطبقًا):
2005
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Rice cultivation, watersaving, agronomic innovation)
- To demonstrate and evaluate the innovative SRI technique under local conditions with land users' participation. - To inform farmers about the basic concepts, associated principles, and technical know-how related to SRI. - To share knowledge gained on SRI with a wider audience. - To scale up the innovation across larger areas
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - Lack of systematic on-farm research for developing a technology that takes into account farmers' needs. - Weak institutional collaboration for technology development, dissemination and scaling up. - Poor soil fertility, limited crop production, and poor irrigation facilities
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- معيق
Government incentives lacking
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The innovation is cost effective and doesn't need additional inputs
الإطار المؤسساتي
- معيق
Lack of cordination among land users
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Informal SRI farmers network established with trained human resources.
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The individual land use rights helped in implementing the technology as there were no conflicts among land users.
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- معيق
It is not a priority area of line agencies
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Sharing of technical know how with concerned stakeholders
غير ذلك
- معيق
lack of awareness
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Trainings, group discussions , field visits
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
Spices Crop Development Centre and farmer groups
Women are generally busy with in-house work. There was only 30 % women participation. Initially SRI was demonstrated onindividual farmers' field. Working land users were mainly men (about 30 percent were women), villlage level groups were formed.
- منظمة غير حكومية
PARDYP project
- الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار)
- منظمة دولية
إذا كان هناك العديد من الأطراف المعنية، قم بالإشارة إلى الوكالة الرائدة:
Concept and orientation - national specialists and implementation of the approach jointly with land users.
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | سلبي | public meetings; First year's on-station demonstration with results shared at public meetings |
| التخطيط | تفاعلي | public meetings; Public meetings organised in different villages; villagers selected lead farmers for the training, and orientation meeting held to plan activities |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | responsibility for major steps; Farmers themselves implemented the activities; the project facilitated the research and arranged logistics |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | Measurements, observations and reporting were carried out once a week. At the end of the project, results were evaluated through interviews using questionnaires. Public meeting organised to share results with district level stakeholders |
| Research | تفاعلي | On-farm and on-station research conducted; information from research station collected by technicians; farmers themselves collected information from their fields |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
الوصف:
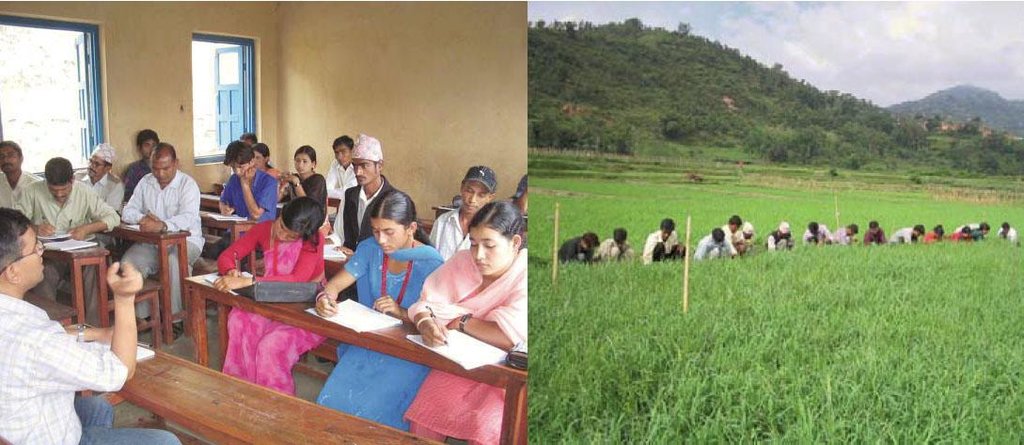
left: Public meeting: an orientation meeting to plan and implement SRI activities. Right: Lead farmers in the demonstration field – an activity of a farmer field school.
المؤلف:
Madhav Dhakal
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي بشكل أساسي، بعد التشاور مع مستخدمي الأراضي
اشرح:
SRI is being tested in many countries in Asia and rest of the world with proven benefits. Project staff shared SRI principles and methods with the watershed-farmers, few of them came forward and tested it to observe the performance in the local condition.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. It was tested first at a research station to build confidence of project staff and surrounding villagers, and was then taken to interested farmers' fields
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
- موظفون ميدانيون/ مستشارون
شكل التدريب:
- من مزارع إلى مزارع
- مناطق العرض
- اجتماعات عامة
- دورات
المواضيع المغطاة:
The principles associated with SRI, participatory research procedures, and farmers' concerns (men and women).
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
وصف/تعليقات:
Name of method used for advisory service: Farmer - to - Farmer Extension of SRI; Key elements: Use of local farmers as facilitators, Farmer - to - farmer visits, Public meetings , national workshop; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: projects own extension structure and agents; Extension staff: specifically hired project employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: trainings, group discussions, farm visits
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Large number of farmers can now implement SRI with confidence, there are 15 local trainers who can train many farmers, which insures the continuation of SRI activities .
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- لا
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: soil condition and irrigation facilities
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: number of tillers, tiller height, climatic conditions
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: preference for rice varieties
economic / production aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: grain and biomass production, cost of production
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements; indicators: area of SRI cultivation
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: frequency of farm visits and record keeping
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: training management by farmer field school management sub-committees
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
- Comparision between traditional and SRI methods
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
Participatory research at the farmer field schools was a key element of the approach. The schools compared the inputs and outputs of the traditional and SRI methods including the differences in grain and biomass production, the costs and benefits, and the advantages and disadvantages.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- 10,0000-2,000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (SDC, IDRC, ICIMOD): 90.0%; other (Jhikhu Khola farmers): 10.0%
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- زراعة
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| بذور | on- station and on- farm demonstration sites only | |
| أسمدة | on- station and on- farm demonstration sites only | |
| Biocides | on- station and on- farm demonstration sites only | |
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- تطوعي
التعليقات:
Farmers worked either as a trainee or as a volunteer.
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The approach has helped participating farmers to improve soil and water management. They started to apply the recommended dose of chemical fertiliser and improved farmyard manure. The frequency of irrigation was reduced and there were less cases of terrace-riser failure caused by stagnant water. The
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
A similar approach was used to promote SRI by a few projects in the same district.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Through better management of rice crop
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
Increased (nearly doubled) production
- زيادة الربح (القدرة)، وتحسين نسبة التكلفة إلى العائد
Increased production with same or little less cost input
- الوعي البيئي
Improved land and water management
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، صف كيف:
About 35 local land users had adopted the SRI method and previous adopters were continuing to use SRI method. However, some more time may be required for its wider adoption.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Through farmer-to-farmer fi eld visits, farmers had an opportunity to observe others' fi elds and see the performance of SRI in different locations and conditions. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such visits as farmers learn much more from farm visits and from sharing experiences with other farmers.) |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Lead farmers served as key resource persons in the village-level farmer field schools. Data from test plots were analyzed by farmers on a weekly basis. This was very effective for promoting the sustainability of SRI. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Encourage district level agriculture offi ces to use the skills of lead farmers as resource persons to expand SRI in their districts.) |
| Action research was conducted through farmer field schools and lead farmers were trained in training of trainers programmes. These served as platforms for farmers to share their immediate concerns. Besides analysing and presenting, farmers' skills were also developed. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Implement the farmers fi eld school approach during technology implementation to build confi dence of land users and empower them in soil and water conservation.) |
| Participatory methods and tools were applied repeatedly. Farmer visits and village level group discussions were very effective for evaluating SRI. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Use participatory tools and methods widely during the technology implementing period) |
| Action research was conducted with farmer groups and individual households. The group approach was more systematic and helped to build confidence of land users in the technology (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: It should be maintained and continued on a regular basis to strengthen land users' involvement) |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| A long dry spell meant that the SRI observation plot could not be established near to the lead farmers' fi eld school site, and only 15 facilitators were able to establish observation plots in their villages. | This was due to natural causes (late arrival of monsoon), it can be improved easily if monsoon arrives on time. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Agro-ecosystem analysis, as used at the farmer fi eld schools, became a time-consuming process as participants had to spend much time in preparing presentations. | Pre-planning and pre-preparation of presentation format should reduce the time length |
| Women's participation in the village level workshops was poor (2% at one location and 5% at another) | Encourage women to participate, and adapt programmes to suit their interests. |
| Due to time limits, not all SRI adopters' opinions and experiences could be covered during interaction workshops. The scattered farmer field schools (distance-wise) and the diffi cult political situation meant that exchange visits could not be organised for all schools. | Allocate enough time for such programmes |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Dhakal, M.P. (2005) Farmers' Evaluation of System of Rice Intensifi cation in Middle Mountains of Nepal.Cornell International Institute for Food, Agriculture, and Development (CIIFAD)ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. KathmanduIRRI - International Rice Research Institute.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ICIMOD, SRI.URL: http://ciifad.cornell.edu/sri/countries/nepal/index.htmlICIMODwww.irri.org.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ICIMOD
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
IRRI - International Rice Research Institute.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
www.irri.org.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

System of Rice Intensification [النيبال]
A method for increasing the productivity of rice by changing the management of plants, soil, water, and nutrients.
- جامع المعلومات: Madhav Dhakal
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية