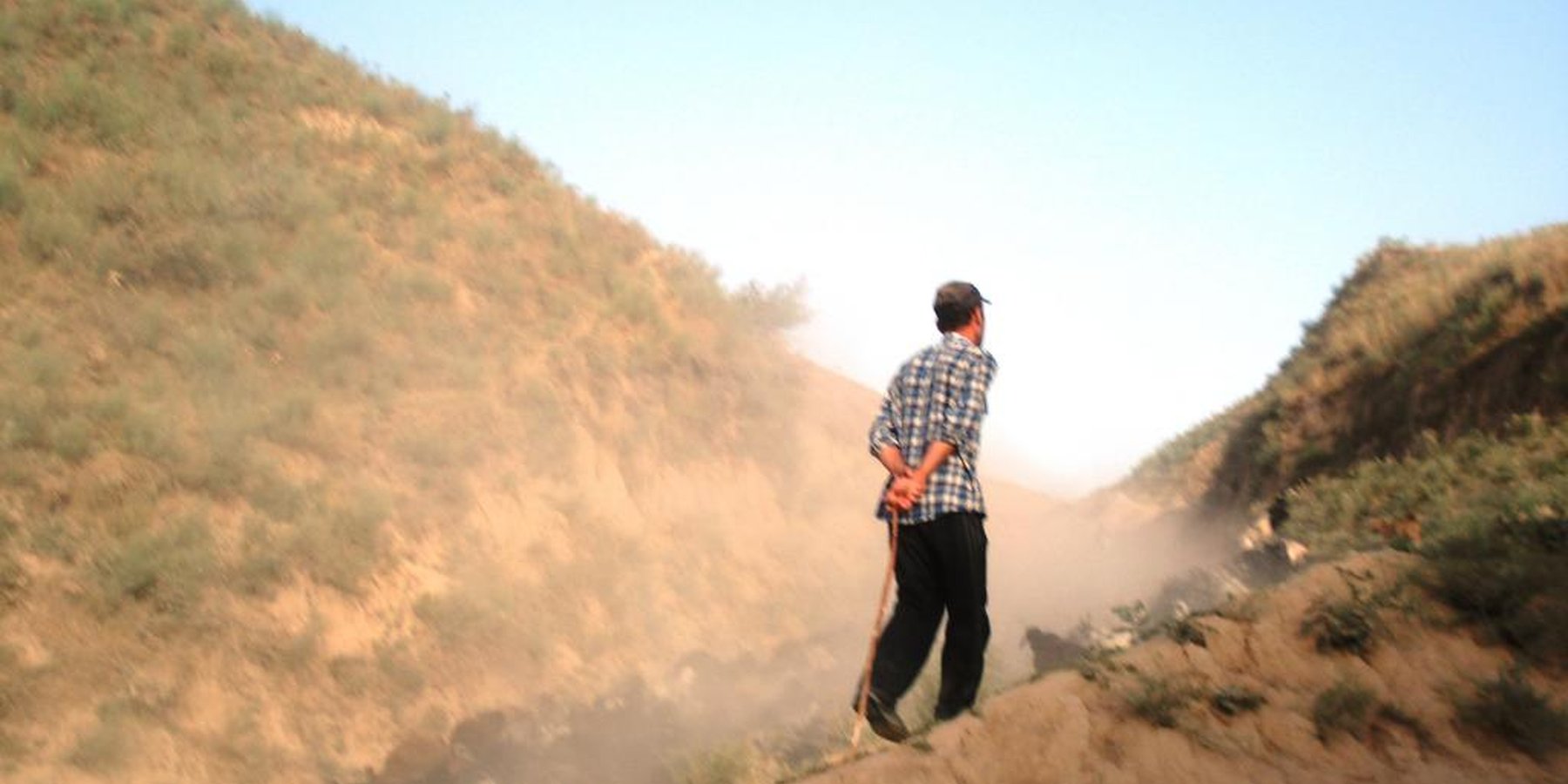
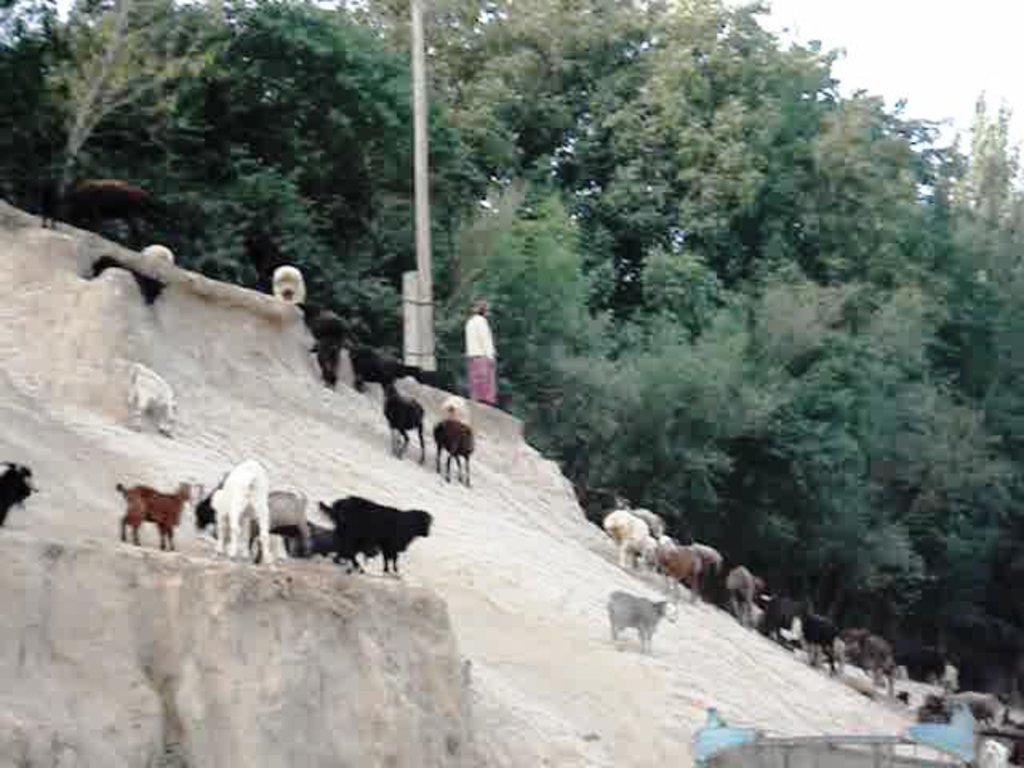
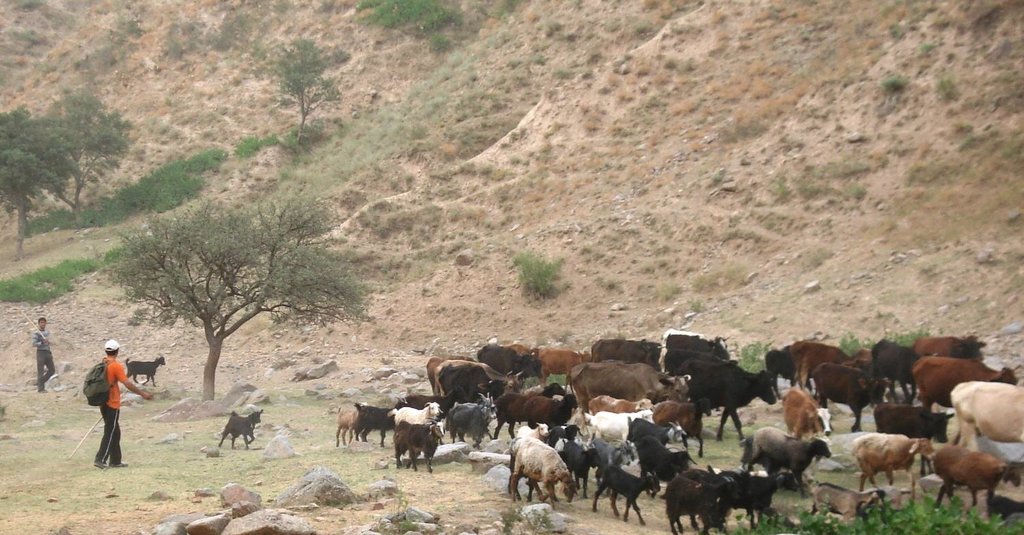
Common village herding [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Christian Wirz
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Navbati Poda (succession of herders)
approaches_2656 - طاجيكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
15/08/2008
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
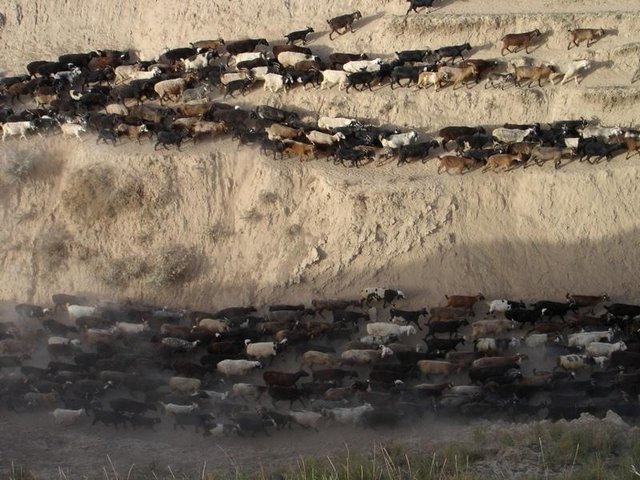

Daily grazing of village-herds [طاجيكستان]
Rotational grazing on village pastures with heavy pressure with daily to weekly change of grazing places.
- جامع المعلومات: Christian Wirz
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
Village herding system with daily alternation of the herders including each household in a monthly turnus.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
Aims / objectives: The herding system has to be easy and little labour-intensive, because children are the main workforce. It is a collective system and thus requires the participation of all households with families: For instance in the village Karsang with 141 households (not all having livestock) and two village herds, each family has to send monthly one child for herding or pay if it does not have workforce. In addition, always at least one adult has to accompany the herd. This means that children of big families only rarely miss school whereas those from small families miss more frequently. The final objective is to nourish animals maximally so they need a minimum of costly hay and concentrated feed (in terms of labour respectively in financial terms).
Methods: Children and adults are taught by the elders, the parents and the village land use committee how the rotation works: They should not stay at one place longer than three days, they should not chase the animals which otherwise lose energy unnecessarily and they shall not lose animals. Children not obeying are punished. In case of lost animals different approaches exist: Mostly the family of the herder who was responsible for the herd on the respective day reaches an agreement with the tenant's family.The village committee or elders can also arbitrate.
Stages of implementation: It is difficult to say when this system first emerged. A land user says that during Soviet Union there were village herds with a fix herder or an alternation like nowadays and, parallely, wealthy people had their own herd with a paid herder. During civil war only a few rich villagers kept animals and only at the beginning of the 2000s collective herding reemerged.
Role of stakeholders: The implementation of herding is a matter of each family's participation. The collaboration of the villagers with institutions is especially important in questions of taxes. In most villages the households pay per capita animal taxes. In order to improve SLM the land use committee on district level and the forest administration (as far as the village has such pastures) together with the local representants of the ecology commission advise the land use committees of each village to take the appropriate measures. And these talk with the herders to influence their comportment. A teacher from the local land use committee says that a lot is said about SLM, but little is effectively done.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Region of Republican Subordination
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Faizabad
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
1920
2.7 نوع النهج
- تقليدي/أصلي
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Maximal nutrition of livestock with child labour.)
In animal husbandry the semi-monetary value of livestock is important. Therefore, 'everyone would like to have more animals', says a land user. At the same time agricultural population has other activities such as the cultivation of kitchen-gardens and of cropland. And labour shortage is omnipresent, with many young men staying in Russia for work. In these multistrategies efforts for herding must be minimised which is best possible if children are sent as herders.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The approach needed and needs to be compatible with the traditionally sedentary culture and with the new employment and income sources in local economy: be it the work as a taxi-driver or selling vegetables on the local market. Today herding has to be especially cheap (finance, labour) because there is a multitude of preferences how to invest resources: building a (better) house, buying a mobile phone and a car or enabling (higher) education of children.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- معيق
Keeping animals is expensive because you have to nourish them (see costs of technology).
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The use of comparatively cheap grazing land of the former collective farms that is under village administration and contracts with forest administration for cheaper land are the solution.
الإطار المؤسساتي
- معيق
If the defined herding system is not respected, cover is damaged, especially trees. And institutions have little authority in implementation, partly because of their own corruption.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Implementation is based on the households: They do not only send their children for herding, but they also punish them if they treat animals badly.
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: The fact that a great part of grassland of former collective farms has not yet been attributed to farmers' associations makes it possible for everyone to use them. The only disadvantage in the eyes of land users is that they have to pay rent fees for this land.
عبء العمل، توفر القوى العاملة
- معيق
It is difficult to find labour force that is able to walk to the pastures with the animals, because many young men are in Russia.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Children are cheap and mobile.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
ny people with animals participate in collective herding. Especially poor families cannot afford professional herding.
There are both boys and girls working as herders. Among adults, men more often working as herders than women.
The role of women is traditionally associated with domestic work and kitchen gardens.
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون
Different institutions: land use committees, forest administration, committee for ecology.
- المعلمون / أطفال المدارس / الطلاب
إذا كان هناك العديد من الأطراف المعنية، قم بالإشارة إلى الوكالة الرائدة:
Mainly land users supported by SLM specialists
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | التعبئة الذاتية | Initiatation and planning was organised among villagers. They based themselves on experiences from Soviet times and from before. |
| التخطيط | غير موجود | |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | Recently the institutions mentioned have become more important. |
| الرصد/التقييم | غير موجود | |
| Research | غير موجود |
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- مستخدمو الأراضي وحدهم (المبادرة الذاتية)
اشرح:
Animal husbandry is chosen as an important strategy because it provides for higher levels of self-sufficiency.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Even if the methods are somehow prescribed by land use committees, herders themselves finally decide on the herding strategy.
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
كلا
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
كلا
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by other through observations; indicators: Local land use committees go to the pastures in spring to decide whether soils are dry enough and gr
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Land users control if their animals are fat and if they give milk. Otherwise they might not send the
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
كلا
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- < 2000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (Meetings of administration with leaders.): 20.0%; local community / land user(s) (Organising herding: low costs.): 80.0%
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- تطوعي
التعليقات:
Herding is not rewarded by anyone. But if a family does not respect its obligations (monthly sending a herder) it has to pay compensation.
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Especially poor population could profit from cheap communal pastures and thus afford keeping livestock.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
It can be assumed that this somehow logical solution of herding for settled people (not like in other Central Asian countries) emerged as a part of self-sufficient strategies during USSR. Similar herding patterns might though have existed already before USSR, according to local experts.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Compared to a situation without private livestock this is clearly an improvement in terms of
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
By increasing self-sufficiency it did contribute to better nutrition of rural households with livestock than of many people in town who have to buy meat (which is expensive).
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
Little SLM is contained in the approach of common herding. But if there is motivation to implement S
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- غير مؤكد
إذا كان الجواب لا أو غير متأكد، حدد ذلك وعلق عليه:
On the one hand decreasing productivity of pastures threatens their daily use by big herds. On the other hand the increasing consciousness of leaders about degradation might make herding more expensive (animal taxes) and not affordable for everyone anymore.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| This form of herding is not conflictive: all people can afford it and everyone contributes to it by sending an own family member for herding. And, if a herder loses a villager's animal, the villager knows that he will also be a herder and might lose an animal, too. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The institutions - be it elders or the land committee - must implement the technology.) |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Common herding has a strong social component as it makes herders cooperate in order to maintain reputation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Projects in Muminabad proposed by the village with a professional herder elected in a village meeting ) |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The dependance upon children rather hinders the implementation of SLM, according to some land users. Children prefer to play rather than to respect rules about herding, says for example a teacher. And he adds that also adults do not always respect the established rules and that nobody controls effective implementation of the technology. | It is difficult to find adult herders. One village - Chujamar - decided to engage a professional herder, who would lead the cows to the pastures separately. Because cows cannot be lead only by children like little animals, according to the chief of that village. The villagers pay around 2$ per cow and season for herding. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Land users mention that implementation is difficult with herders (often children) that lack the necessary knowledge to implement SLM. | It is difficult to abolish child labour. But, by completing the herders' team with at least one professional, paid herder, progress in SLM would be possible perhaps. And making pastures a subject in school might help to araise awareness about SLM. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Daily grazing of village-herds [طاجيكستان]
Rotational grazing on village pastures with heavy pressure with daily to weekly change of grazing places.
- جامع المعلومات: Christian Wirz
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية