The 4-Wheels Approach for sustainable scaling [تونس]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Joren Verbist
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
approaches_6885 - تونس
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
Agricultural Economist:
Aymen Frija
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
تونس
Specialist on Economics and Participatory Methods:
Idoudi Zied
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
تونس
Agricultural Innovation Specialist:
Rudiger Udo
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
تونس
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiativeاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - لبنان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
2022
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

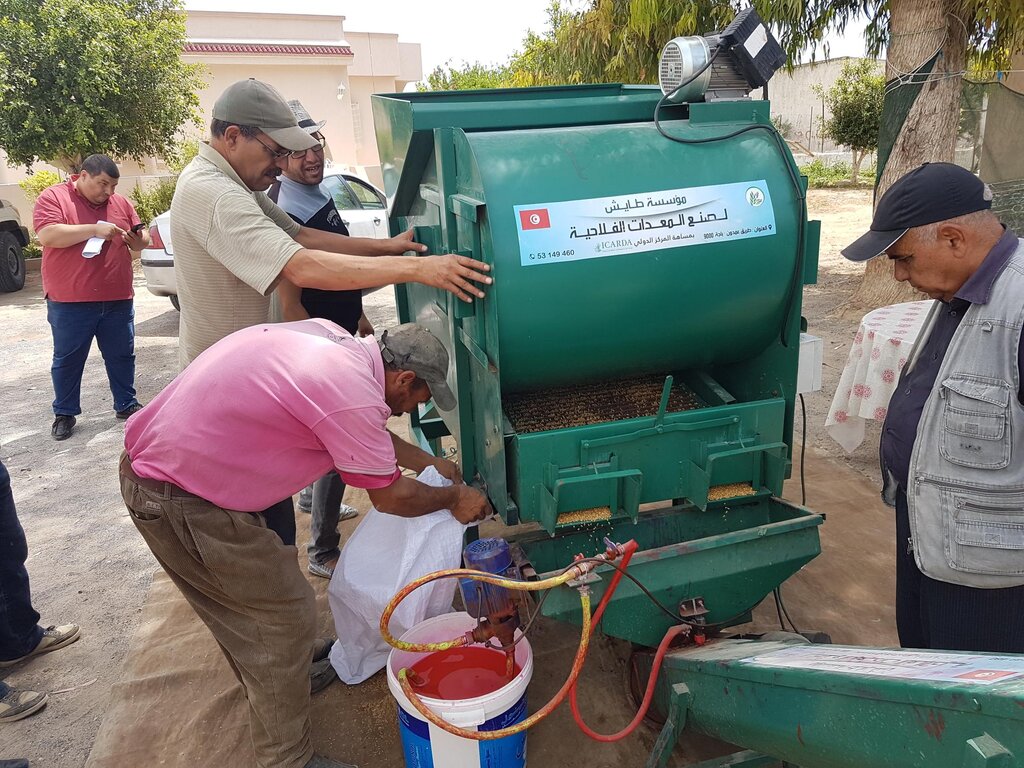
Small-Scale Seed Cleaning Unit [تونس]
The mobile seed cleaning machine improves the livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Tunisia by significantly enhancing seed quality, increasing crop production, reducing workload and costs, and promoting local value chains and social cohesion.
- جامع المعلومات: Joren Verbist

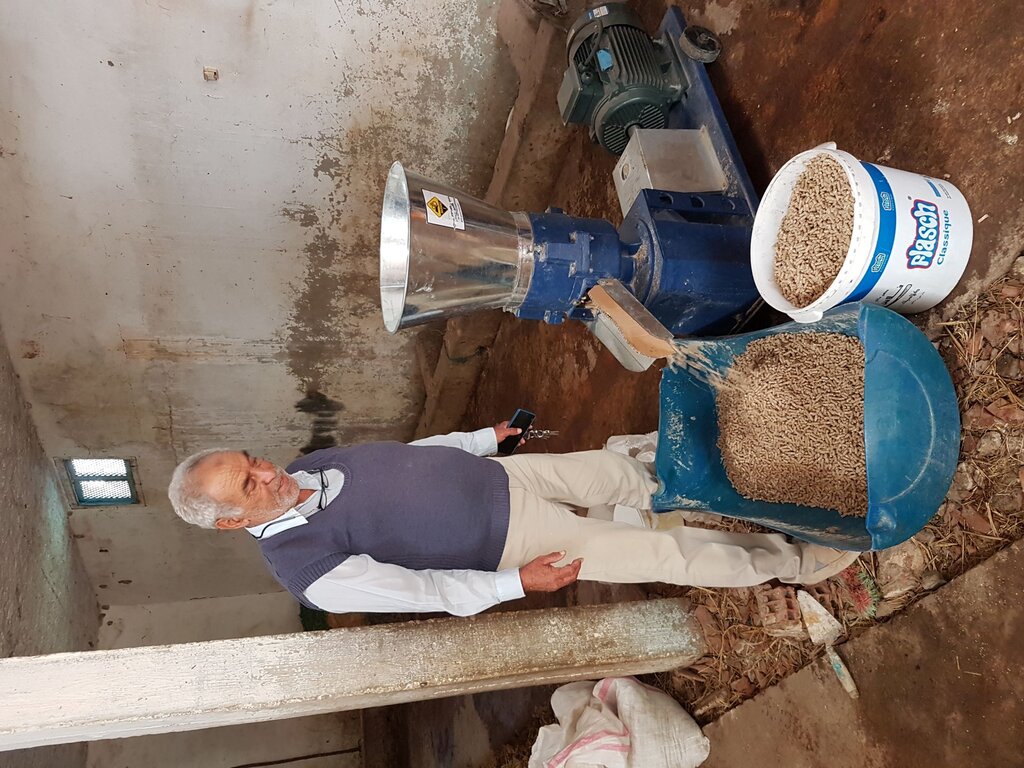
Small-Scale Nutrient-Dense Pellet Production [تونس]
Compressing agro-industrial by-products produces nutrient-dense livestock feed pellets that can compete with expensive and imported alternatives. This innovation consists of a small-scale compressor or "pelletizer" and formulae to create feed pellets of sufficient quality with locally available inputs.
- جامع المعلومات: Joren Verbist
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
The 4-Wheels Approach addresses the challenge of slow adoption of agricultural innovations among smallholder farmers by establishing Knowledge Hubs and partnerships with diverse stakeholders. The focus is on income-generating technologies and essential factors behind successful scaling up of innovations, ultimately driving agricultural modernization and sustainability.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
The challenge of low and slow adoption of innovations from agricultural research by smallholder farmers is difficult, complex, and is impeding the progress of agricultural modernization in many developing countries. This issue has negative consequences on farm productivity and farmers' livelihoods. Furthermore, it influences the outcomes of investments made by both national and international agricultural research and development initiatives. The problem is exacerbated by evolving climatic and social conditions, which makes more urgent the need for systemic transformation and modernization to enhance food production - while ensuring sustainability.
To confront this challenge of low rates of scaling up and adoption, the International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA) introduced and validated the “4-Wheels Approach” in countries where ICARDA is active, including Algeria and Tunisia. Among other innovations, two types of machinery are being scaled up this way: (a) the pelletizer (which creates feed pellets from by-products) and (b) the seed cleaning machine (for mechanical seed cleaning, substantially reducing workload). Both technologies have been documented in WOCAT’s global database.
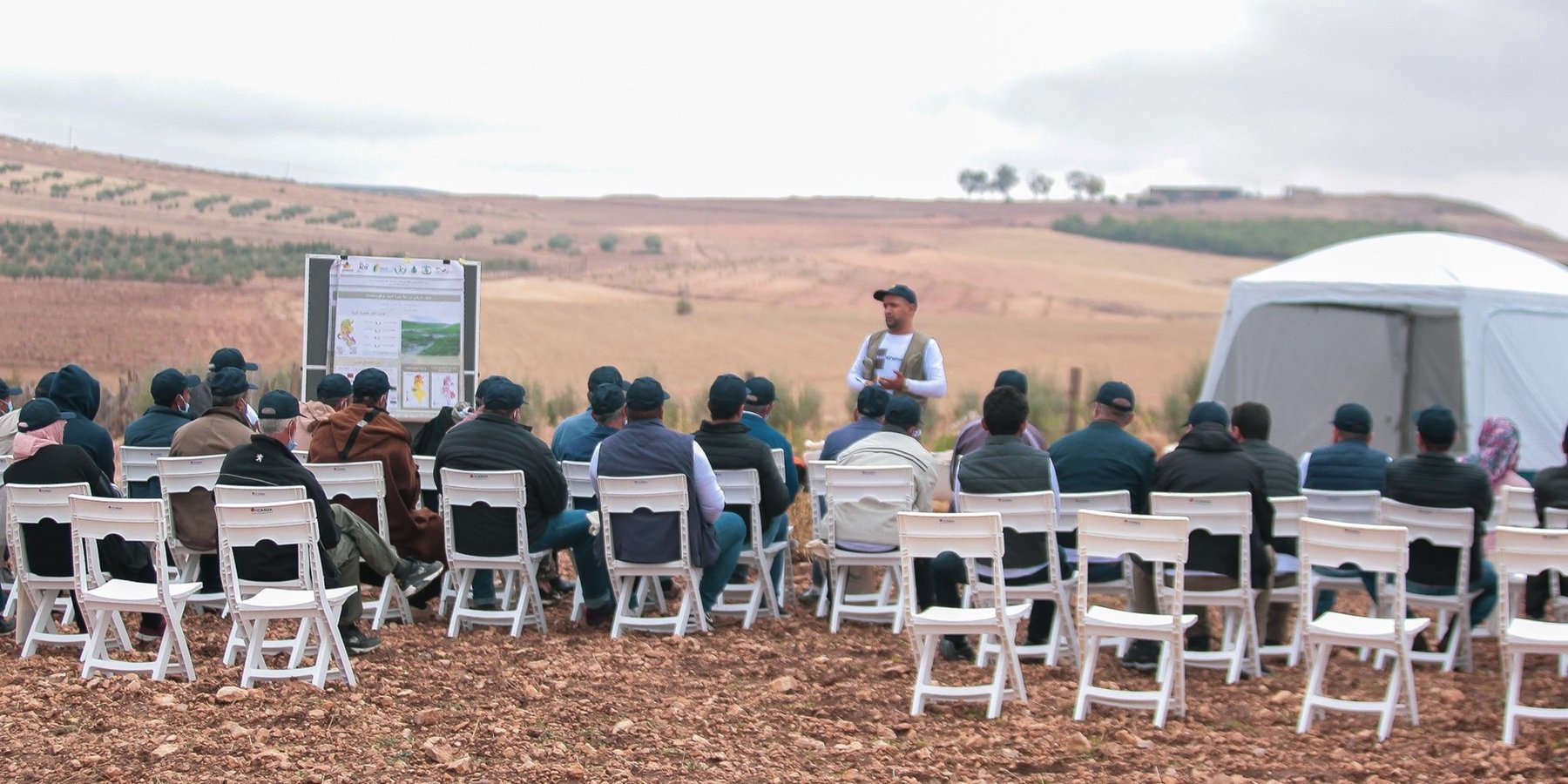
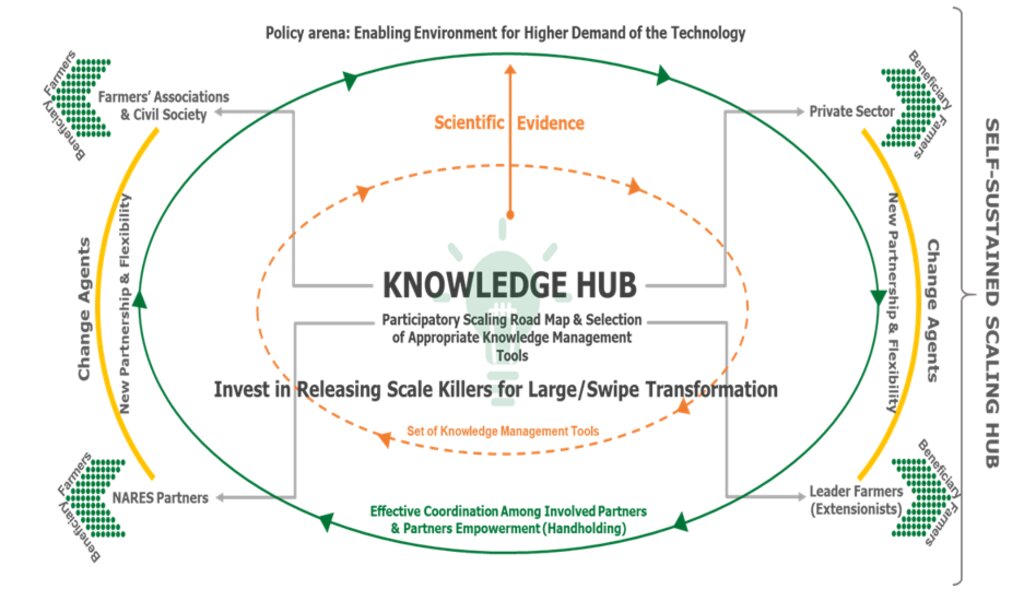
The 4-Wheels Approach is built upon Knowledge Hubs and dynamic partnerships. Knowledge Hubs encompass physical structures, such as (informal) training centres, which usually belong to local farmers’ associations and cooperatives. The purpose of these hubs is to refine and disseminate knowledge locally in a self-sustained way, potentially through established partnerships with key local and regional stakeholders and scaling partners. Four categories of stakeholders, also referred to as change-agents and facilitators of technology dissemination, are identified: i) farmers’ groups and various other local associations, ii) civil society (including non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and the private sector), iii) national public development partners, and iv) lead farmers and extensionists, all of whom play a pivotal role in holding the key knowledge about the technology and spreading it locally. Consequently, these Knowledge Hubs serve to further adapt and mainstream technical knowledge through intermediary beneficiaries (also called proxies or “ambassadors” of the technology), who in turn facilitate dissemination to the ultimate users and beneficiaries, namely the farmers. Viewing the approach’s scaling and Knowledge Hubs through this lens underscores the necessity of investing in continuous and comprehensive networking, which doesn’t overlook any of the possible and relevant scaling partners.
The implementation of the 4-Wheels Approach via Knowledge Hubs and collaborative partnerships has emerged as a compelling strategy for challenges in the uptake of agricultural innovations, fostering a sustainable pathway towards modernization, and thus uplifting the well-being of smallholder farmers in developing areas. The concepts of 4-Wheels Approach and Knowledge Hubs are closely related and interlinked/integrated. The participation of the four types of partners who are engaged through the 4-Wheels Approach within the Knowledge Hub activities allows them to better understand, participate and advocate for relevant local innovations. The 4-Wheels Approach ensures the concentrated involvement of scaling partners of different background within the same landscape, and thus efforts to engage innovation actors become more fruitful by being more accessible and inclusive.
Acknowledgement: This research was funded by the CLCA project (funded by IFAD), PROSOL (funded by GIZ), and OneCGIAR initiative on agroecology. All of the previous projects and initiatives are implemented and coordinated by the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA). The projects partnered with national partners including the OEP (Office de l’elevage et des pâturages) for the training of the cooperatives, as well as Tunisia’s National Agricultural Research Institute (Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique en Tunisi, INRAT) and the National Institute of Field Crops (Institut National des Grands Cultures, INGC) which selected the cooperatives, and the Regional Department for Agricultural Development (Commissariat Regional de Développement Agricole, CRDA) which facilitated the access to farmers communities and creation of knowledge hubs. We would like to thank all partners for their contributions and collaboration.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
تونس
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي لبدء النهج:
منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The aim of this approach is to achieve sustainable scaling and foster greater adoption of innovations. This is pursued through the establishment of Knowledge Hubs (as spaces of innovation) where, the formation of partnerships (based on the 4-Wheels Approach), and the research into viable business models is carefully and step-wise implemented (in reference list see the protocol for implementation in Frija & Idoudi 2020).
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- معيق
A minimum of financial resources are needed to create and establish the knowledge hub in the form of informal training center at the cooperative and farmers association level. These fees aims at creating a local space for the community which can be “pedagogically” relevant for further exchange, discussions, trainings, and joint decision making by the community. Such spaces are material investments which can partly enhance the social capital and support the process of building collective cognitive capacity of farmers.
الإطار المؤسساتي
- معيق
The 4-Wheels Approach supports the process of technology transfers in countries where there is a lack of connections and collaboration between research and development. Under such institutional conditions where extension services are low and unavailable, and where research programs are disconnected from the real concrete problems and development bottlenecks, the 4-Wheels approach can be instrumental to leverage the public investments in technology transfers by creating local performing knowledge hubs which would remain sustainable thanks to the mobilization of all relevant innovation and scaling partners (as identified in the 4-wheel partners typology – see above
التعاون/التنسيق بين الجهات الفاعلة
- تمكين/تمكيني
This was rather enabling as different actors like OEP (livestock agency) on the regional level as well as national level were always willing to collaborate with ICARDA and the different beneficiary communities of our different projects (listed in the acknowledgement). This is also especially relevant given that the early technologies for which we built and started piloting the concept of knowledge hubs and partnership for scaling were focusing on forage crops and forage mixtures . Also INRAT was happy to collaborate in the development of the concepts and to also facilitate the overall process of partners mobilization, including collaboration with private actor such as forage seeds companies, pelletizer or seed cleaning manufacturers etc
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- تمكين/تمكيني
Technical support was guaranteed by OEP, INRAT and ICARDA and private actor. The whole idea of these partners is to generate knowledge through experimentation and demonstration, and sustain it through capacity development and partnership/networking. Communities and particularly farmers associations were key in this regards as these are supposed to be the main holders of knowledge after the project ending. The whole process of creation of KHs aims at enhancing and sustaining knowledge about key agricultural practices and technologies locally, thus making it more inclusive and accessible.
الأسواق (لشراء المدخلات وبيع المنتجات) والأسعار
- تمكين/تمكيني
Theoretically, markets and prices are not key aspects since we are talking about knowledge. Currently, the problem is about access to lacking knowledge by smallholder farmers and is not about “price of the knowledge” or who is paying for it. However, scaling of KH themselves would involve the development of a business model in which “payment for knowledge” would be key for its scaling and sustainability.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
Farmer Cooperatives
Farmers communities, cooperatives and members are asked to engage into the participatory innovation process by defining their needs, problems, and helping to identify possible affordable solutions. They are also asked to offer a space of concentration where the overall R4D teams can meet, interact and discuss. This space is meant to be sustainable and will be used by the cooperative after the end of the project.
- الباحثون
INRAT and OEP
Researchers are asked to facilitate the whole process of community engagement and Knowledge Hub installation. They are also asked to install some local experiments which can provide more contextual knowledge about technologies benefits and impact in specific localities. Researchers are also asked to design and facilitate appropriate networking event thus connecting the cooperatives with all relevant public and private actors who are operating for the considered technologies of the Knowledge Hub.
- القطاع الخاص
Manufacturer of the seed cleaning unit and Importer of the Pelletizer machine
Private sector in general, supports the communities with some capacity development activities in case they are providers of the technology to be scaled (object of the Knowledge Hubs).
They also ensure good affordable and reliable access of farmers of the community to the relevant technologies object of the hub.
In this case, they did: design and produce, or import machine; train farmers in use and maintenance; perform after sale services
- منظمة دولية
ICARDA
Lead and coordination; installation of the hub, facilitation between research and development actors; organize training and demonstration
إذا كان هناك العديد من الأطراف المعنية، قم بالإشارة إلى الوكالة الرائدة:
ICARDA
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | غير موجود | ICARDA and OEP led discussion with the importer and manufacturer. |
| التخطيط | غير موجود | Discussion between ICARDA, OEP, GIZ, INGC, to identify potential beneficiaries of the machines. |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | ICARDA and OEP discussed with farmer cooperatives their interests in the machines. ICARDA, OEP, and manufacture produced and distributed the machines. Financial contribution of the farmer cooperation was requested to foster ownership. |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | ICARDA and OEP visits the farmer cooperatives every three months to collect business data, see if the machine operates correctly, and to identify constraints. |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
الوصف:
The 4-Wheels Approach for effective partnership for scaling
المؤلف:
Aymen Frija, Zied Idoudi. (18/12/2020). Self-Sustained “Scaling Hubs” for Agricultural Technologies: Defnition of Concepts, Protocols, and Implementation. (ICARDA)
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي بمفردهم
اشرح:
ICARDA and partners investigated relevant and suitable technologies. Essential was that the business model is self-sustaining.
حدد على أي أساس تم اتخاذ القرارات:
- تقييم المعرفة الموثقة جيدًا بشأن الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي(اتخاذ القرارات القائمة على الأدلة)
- نتائج البحوث
- خبرة وآراء شخصية(غير موثقة)
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
إذا كان ذلك على صلة، حدد الجنس والعمر والوضع والعرق وما إلى ذلك.
Farmers of the cooperation were trained
شكل التدريب:
- في العمل
- مناطق العرض
- اجتماعات عامة
- دورات
المواضيع المغطاة:
The use of the machinery, their maintenance and recipes for pellets
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- نعم، باعتدال
حدد المستوى (المستويات) التي تم فيها تعزيز أو إنشاء المؤسسات:
- محلي
صف المؤسسة والأدوار والمسؤوليات والأعضاء وما إلى ذلك.
Farmer cooperation and knowledge hubs were established. The rationale is that because the machines are economically viable on their own, the cooperation will keep on sharing the knowledge using the hubs.
حدد نوع الدعم:
- بناء القدرات/التدريب
- معدات
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
By monitoring certain indicators, such as the number of beneficiaries, pellets produced, seed cleaned, etc. In addition, ICARDA is frequently visiting the hubs to see progress and solve problems that occurred.
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، فهل من المقصود استخدام هذه الوثائق للمراقبة والتقييم؟:
نعم
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- علم الاجتماع
- الاقتصاد / التسويق
- علم الايكولوجيا
- تكنولوجيا
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- 100,000-10,000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
This includes the machines and trainings.
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد نوع (أنواع) الدعم والشروط والمزودين:
The land users, organized in farmer cooperation, were supported with machinery
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- معدات
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| الآلات | ممول جزئيا | The farmer cooperatives made a financial contribution. |
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
5.5 حوافز أو وسائل أخرى
هل تم استخدام حوافز أو أدوات أخرى لتشجيع تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين وتحسين مشاركة الأطراف المعنية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Land users were empowered because the machines strengthen the cooperatives.
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين معرفة وقدرات مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Farmers received training on how to operate and maintain the machinery, but they are still struggling with the optimal recipes for the pellets.
هل ساهم النهج في بناء/تعزيز المؤسسات والتعاون بين الأطراف المعنية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The projects was a successful collaboration between many different organization. Its success has strengthen the relations.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين المساواة بين الجنسين وتمكين النساء والفتيات؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Conventionally, the cleaning of seeds was done by hand by women and children. The use of machinery has substantially lowered their workload.
هل أدى هذا النهج إلى تحسين الأمن الغذائي / تحسين التغذية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The use of the machinery lead to improved food security.
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
- زيادة الربح (القدرة)، وتحسين نسبة التكلفة إلى العائد
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- انخفاض عبء العمل
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، صف كيف:
The machines on their self are economically viable.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Seed Cleaning Unit: better seeds, improves yield, higher income, less workload |
| Feed Pelletizer: use of agricultural by-products, cheap compound feed, less workload |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Major strength of the 4-Wheels approach is the aspect of the collaboration, between private actor (machine manufacturer or importer), farmer organization, lead farmer of the organization, OEP (extension), INRAT (research for composition). This multi-actor collaboration is key of the 4-wheel approach and key of the success of the scaling of the two technologies |
| Seed Cleaning Unit: better seeds, improves yield, higher income, less workload |
| Feed Pelletizer: use of agricultural by-products, cheap compound feed, less workload |
| The 4-Wheels Approach ensures ownership over the machinery while building capacity |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Feed Pelletizer: Farmers still don’t know the optimum mixture of ingredients to produce pellets for each region and categories of animals (sheep / cow / camel). | Intense collaboration with agricultural research |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| A risk of the approach is the sustainability. It is not sure (yet) if and how the knowledge hub will continue once there is no more support from ICARDA and (national) partners. |
The theoretical idea is that through the income generation with these machines they (farmer organization) will continue training others and sharing their knowledge. But this theory needs to be validated and proven. |
| Seed Cleaning Unit: quite expensive for a small scale farmer (7,000 US$ nowadays) | To buy the unit as a farmer organization (cooperation) and use it by many farmers |
| The Feed Pelletizer can be expensive for individual small scale farmer, availability of spare parts of pelletizing machine only in Tunis (access problem), needs available by-products (they are only seasonable), need access to subsidized barley and wheat bran to produce at competitive prices. Farmer organizations have no quota for subsidized barley and wheat bran, only individual farmers to a limited amount and feed enterprises | To use the feed pelletizer as a group to reduce costs per farmer; transform cooperative into a feed processing enterprise as they have access to subsidized barley and wheat bran |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Aymen Frija, Zied Idoudi. (18/12/2020). Self-Sustained “Scaling Hubs” for Agricultural Technologies: Definition of Concepts, Protocols, and Implementation. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12248
العنوان/الوصف:
Mourad Rekik, Aymen Frija, Zied Idoudi, Santiago López Ridaura, Nasreddine Louahdi, Boubaker Dhehibi, Dina Najjar, Udo Rudiger, Enrico Bonaiuti, Laura Becker, Zohra Djender Ghallem, Hatem Cheikh M'hamed, Mina Devkota Wasti, Barbara Rischkowsky. (11/3/2021). Use of Conservation Agriculture in Crop-Livestock Systems (CLCA) in the Drylands for Enhanced Water Use Efficiency, Soil Fertility and Productivity in NEN and LAC Countries – Progress Highlights: Year (3) - April 2020 to March 2021. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/12703
العنوان/الوصف:
Aymen Frija, Zied Idoudi, Udo Rudiger, Jebali Oussama, Hatem Cheikh M'hamed, Haithem Bahri, Boubaker Dhehibi, Mourad Rekik, Imen Hemissi, Salah Ben Youssef, Khouloud Chetoui, Mounir Louhaichi, Mouldi Gamoun, Asma Souissi. (6/12/2022). Soil Protection and Rehabilitation of Degraded Soil for Food Security – ProSol: Towards the Effective Scaling of Soil and Water Conservation Technologies under Different Agroecosystems in North and Central West Tunisia – SWC@Scale/ProSol: Technical Progress Report/ January – August 2022. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/67835
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Small-Scale Seed Cleaning Unit [تونس]
The mobile seed cleaning machine improves the livelihoods of smallholder farmers in Tunisia by significantly enhancing seed quality, increasing crop production, reducing workload and costs, and promoting local value chains and social cohesion.
- جامع المعلومات: Joren Verbist

Small-Scale Nutrient-Dense Pellet Production [تونس]
Compressing agro-industrial by-products produces nutrient-dense livestock feed pellets that can compete with expensive and imported alternatives. This innovation consists of a small-scale compressor or "pelletizer" and formulae to create feed pellets of sufficient quality with locally available inputs.
- جامع المعلومات: Joren Verbist
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية