Community based reforestation initiatives to restore degraded forest and rangeland [أفغانستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Mohammad Aslam Hasand
- المحررون: Megha bajaj, Afghanistan Safi, Mohammad Arif
- المراجعون: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
د ټولنې پر مټ د بيا رغنيز نوښت له لارې د تخريب شوي ځنګل او څړځای رغول
approaches_7470 - أفغانستان
- Community based reforestation initiative to restore degraded forest and rangeland.: 6 مارس، 2025 (inactive)
- Community based reforestation initiative to restore degraded forest and rangeland.: 24 مارس، 2025 (inactive)
- Community based reforestation initiative to restore degraded forest and rangeland.: 2 مايو، 2025 (inactive)
- Community based reforestation initiatives to restore degraded forest and rangeland: 7 مايو، 2025 (public)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
مستخدم الأرض:
Haleem Bakhtawer Khan
0765983451
bakhtawerkhan.halim@gmail.com
Sapari Forest and Rangeland Management Association
Sapari, Sabari, Khost, Afghanistan
أفغانستان
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in Afghanistanاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - أفغانستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
15/12/2024
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
Community-driven reforestation initiative that involves awareness-raising, capacity building, feasibility analysis, and collaboration among various stakeholders to address land degradation and promote sustainable forest and rangeland management
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
The main aim of this approach is to contribute to ecosystem restoration, biodiversity conservation and carbon sequestration through community awareness-raising, consultation and capacity building, feasibility analysis, site selection as well as resources mobilization for reforestation initiatives in Khost, Afghanistan.
This community driven initiative emerged, bringing together land users, forest and rangeland management associations, environmental experts, specialists and policymakers from various departments like Provincial Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock, National Environment Projection Agency, District Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock to heal the land, restore the forests, and rebuild the connection between people and nature.
The first step was to understand the root causes of degradation, followed by a detailed assessment to identify areas most in need of intervention. Priority was given to barren land stripped by erosion, degraded forests areas, and nutrient-depleted soils. The community incorporated traditional ecological knowledge shared by local elders, who recalled periods when the valley supported dense vegetation and thriving ecosystems. This was combined with modern ecological practices to develop a comprehensive restoration plan that balanced traditional knowledge with scientific innovation. The approach ensures awareness raising of the rural community, and knowledge and information enhancement on restoration of degraded forest and rangeland through reforestation initiatives in Khost, Afghanistan.
Specific objectives of the approach are:
1. To enhance the knowledge and awareness of rural communities in Khost, Afghanistan on restoring degraded forests and rangelands, including through public awareness, campaigns, community mobilization, consultations, and feasibility assessments, and mobilizing resources.
2. Involve key stakeholders actively in restoration, including Provincial Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (PAIL), Provincial National Environmental Protection Agency (NEPA), District Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock department (DAIL), Forest and Rangeland Management Association (FM/RM Association).
3. To enhance the capacity of Forest and Rangeland Management Association (FM/RM Associations) and local communities for effective restoration of degraded forests and rangelands through reforestation initiatives in Khost, Afghanistan.
4. To restore degraded forests and rangelands by enhancing knowledge, skills, and resources for sustainable management. This includes empowering the FM/RM Associations by improving its members’ understanding, skills, capacity, and active participation in conservation and restoration efforts.
5. To restore habitat for strengthening biodiversity conservation.
2.3 صور عن النهج
ملاحظات عامة بخصوص الصور:
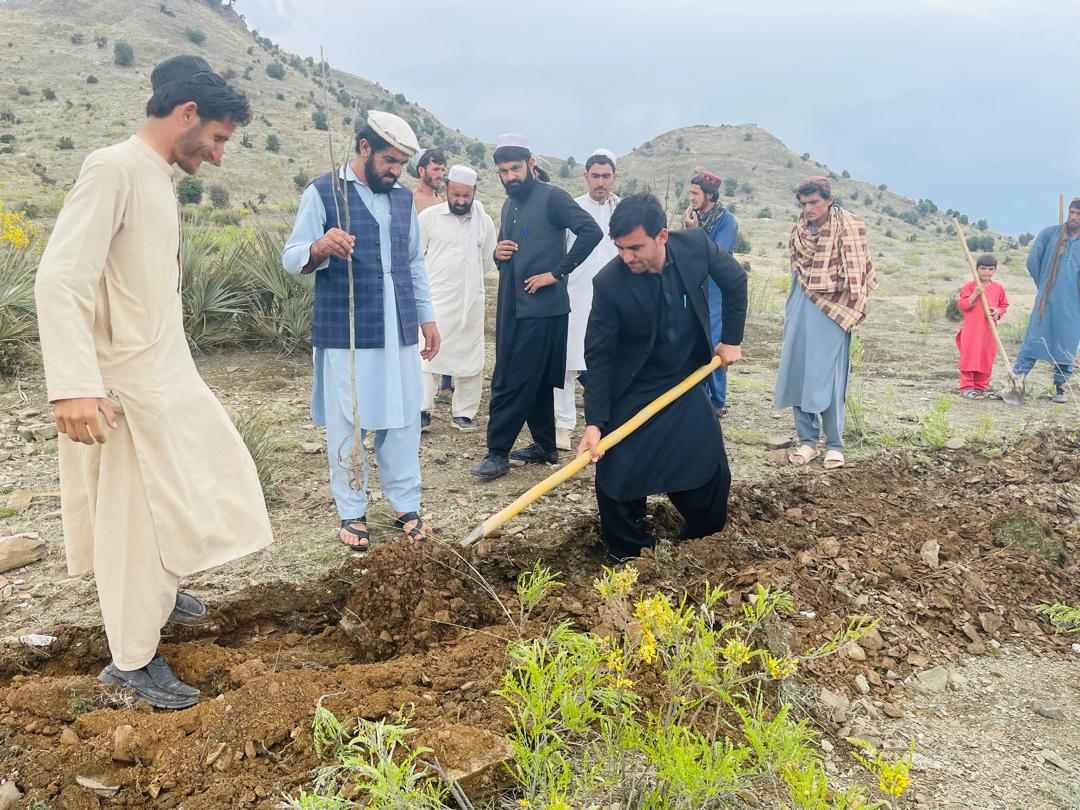
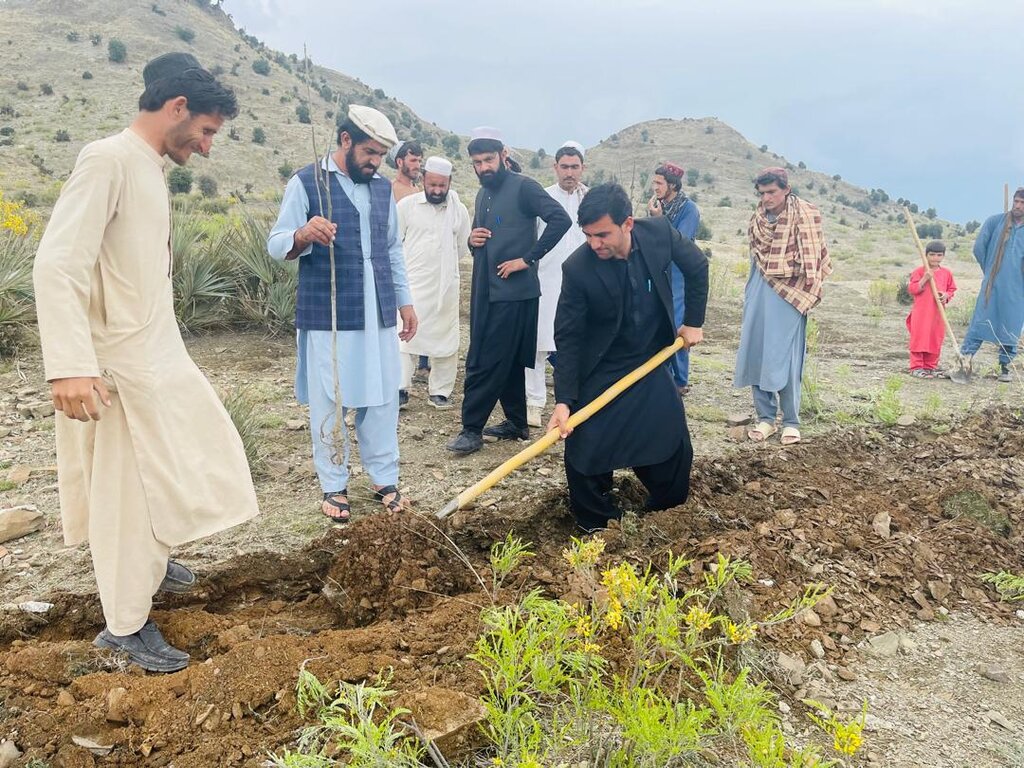
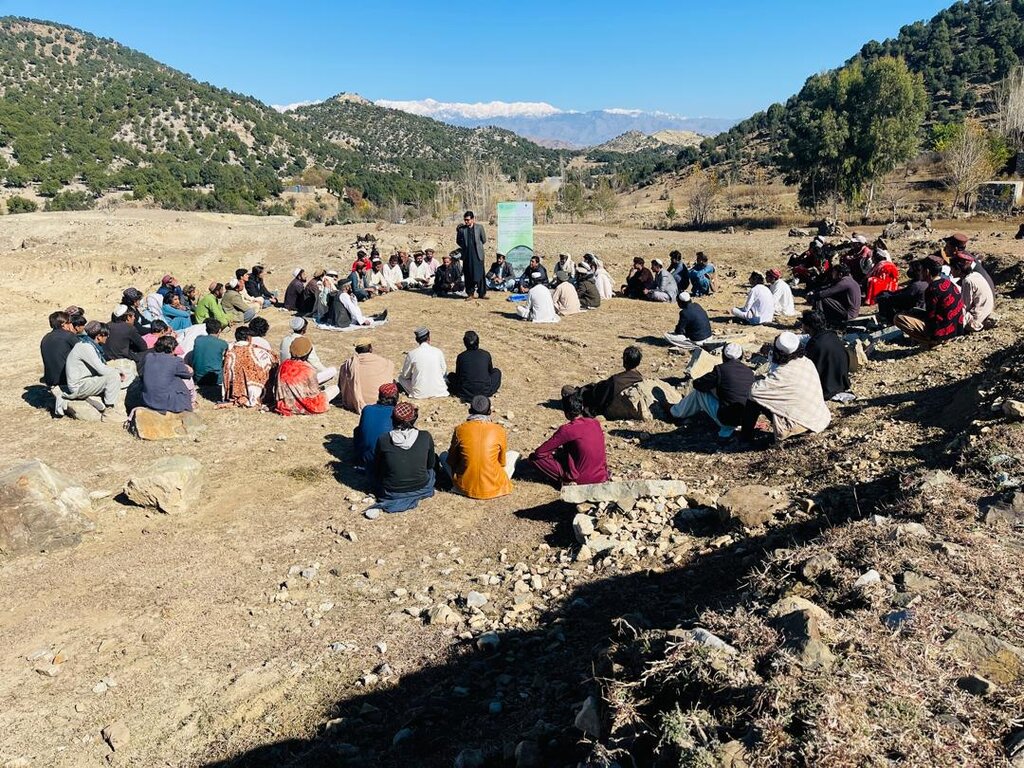
Public awareness and community mobilization – engaging local communities, tribal elders, and stakeholders in decision-making, social participation as well as capacity building – training communities on sustainable practices and policy enforcement.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
أفغانستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khost
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Sapari forest, Sabari district, Khost, Afghanistan
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
2023
سنة الإنهاء (إذا لم يعد النهج مطبقًا):
2026
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
To enhance the capacity of FM/RM Associations and local communities for adopting the technology on restoration of degraded forests and rangelands through reforestation initiatives in Khost.
-To restore habitat for strengthening biodiversity conservation.
-To promote the conversion of unproductive lands to productive lands.
-To empower local communities to replicate and scale up similar initiatives.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
المعايير والقيم الاجتماعية /الثقافية/ الدينية
- تمكين/تمكيني
Social gathering, social participation for sapling plantation, information sharing among community members.
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- تمكين/تمكيني
There is availability and access to financial resource and services, because all the financial support is directly transferred to community.
الإطار المؤسساتي
- تمكين/تمكيني
FM/RM Associations are established to improve forest and rangeland management.
التعاون/التنسيق بين الجهات الفاعلة
- تمكين/تمكيني
Other projects are collaborating with FM/RM Associations due to their status as a legal entity
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- معيق
The legal framework for land tenure and land and water use rights exists; they are, however, not properly implemented.
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- تمكين/تمكيني
Community members have access to SLM knowledge through awareness raising, training and workshops offered
عبء العمل، توفر القوى العاملة
- تمكين/تمكيني
Workload of FM/RM Associations during plantation campaign, protection and general management.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
Local community and farmers
Land users, local community members: Mobilizations, awareness, social participation as well as self-contribution.
- المنظمات المجتمعية
Forest and Rangeland Management Associations (FM/RM Associations)
FM/RM Associations: decision making, awareness, mobilization, capacity building and social structure for self and in kind contribution.
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون
FAO specialist
Technical assistance
- القطاع الخاص
Construction company
Construction, mechanical work and installation of system in including facilitation
- الحكومة المحلية
Provincial Agriculture and Livestock (PAIL), District Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock (DAIL), National Environment Protection Agency (NEPA)
Facilitation for the implementation of project
- منظمة دولية
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations)
Implementation of the GEF-funded project and technical assistance
إذا كان هناك العديد من الأطراف المعنية، قم بالإشارة إلى الوكالة الرائدة:
UNFAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations)
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | التعبئة الذاتية | FM/RM Association: mobilization, awareness raising and general management through social participation. |
| التخطيط | تفاعلي | FM/RM Association: jointly with community by developing of Community Based Natural Resources Management (CBNRM) plan. |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | FM/RM Association: jointly with community provided labour, facilitation, coordination and consultation as well as supporting all the activities during implementation period as self and community in kind contribution. |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | FM/RM Association: members are key stakeholders of the participatory monitoring and evaluation process. |
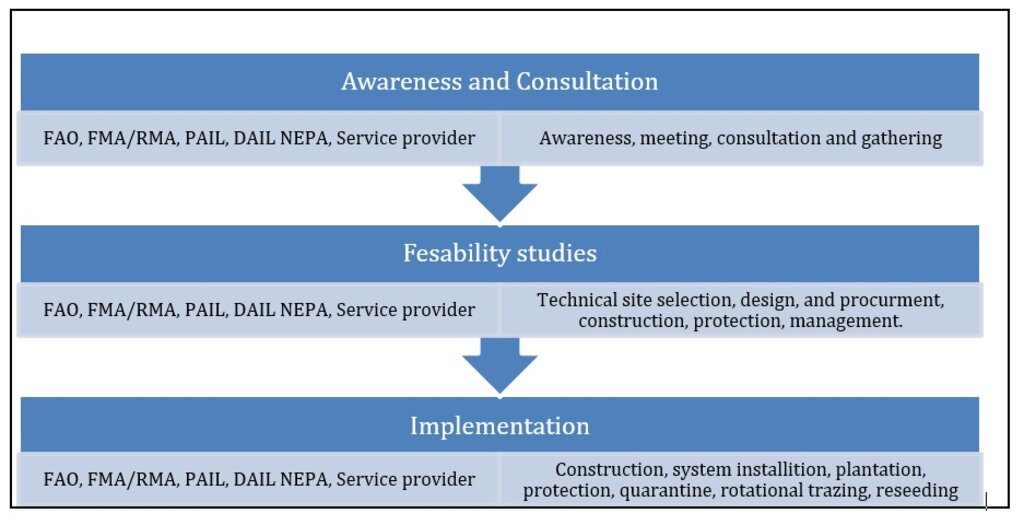
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
الوصف:
"The Restoration of Degraded Forest and Rangeland Approach" focuses on reviving degraded forest, rangeland and generally ecosystems through sustainable reforestation initiatives. This approach involves: Identifying degraded areas and developing restoration initiatives, involving local communities in decision-making and capacity-building, planting native species, improving soil health, and adopting sustainable land management techniques, regularly assessing progress, addressing challenges, and ensuring long-term sustainability.
This integrated approach helps restore forest and rangeland, biodiversity, improve water retention, prevent soil erosion, and enhance local livelihoods.
Acronyms and Key Concepts:
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)
Provincial Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock (PAIL)
District Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock (DAIL)
Forest and Rangeland Management Association (FM/RM Association)
Service providers are referred to different construction and logistics’ companies and contractors.
المؤلف:
Mohammad Aslam Hasand
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- جميع الجهات الفاعلة ذات الصلة، كجزء من نهج تشاركي
اشرح:
It was a participatory feasibility study that involved joint decision making
حدد على أي أساس تم اتخاذ القرارات:
- تقييم المعرفة الموثقة جيدًا بشأن الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي(اتخاذ القرارات القائمة على الأدلة)
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
- موظفون ميدانيون/ مستشارون
شكل التدريب:
- في العمل
- من مزارع إلى مزارع
- اجتماعات عامة
المواضيع المغطاة:
SLM/SFM practices, awareness, mobilization, quarantine, rotational grazing, biodiversity conservation, climate change, CBNRM plan, participatory moinotoring, operation of the system and general management of natural resources.
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
وصف/تعليقات:
Operating the irrigation system, sapling transplantation, quarantine, rotational grazing and general management.
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- نعم، باعتدال
حدد المستوى (المستويات) التي تم فيها تعزيز أو إنشاء المؤسسات:
- محلي
صف المؤسسة والأدوار والمسؤوليات والأعضاء وما إلى ذلك.
FM/RM Association
حدد نوع الدعم:
- مالي
- بناء القدرات/التدريب
- معدات
اعط مزيدا من التفاصيل:
Signed LoA for implementation and cost contribution, on site awareness raising, social mobilization, holding gathering and workshops and provided construction materials and tools for nursery establishment.
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
FM/RM Association has the responsibility to perform monitoring of all activities in Sapari forest of Sabari district of Khost province.
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، فهل من المقصود استخدام هذه الوثائق للمراقبة والتقييم؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
Monitoring is a part of the Community-based NRM plan.
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
كلا
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- 100,000-10,000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Financial support is provided by the FAO-GEF project and in-kind contributions are from the community. In-kind contribution covers providing physical space or facilities to support the project, coordination, consultation and general facilitation, and human resources for restoration, patrolling, quarantine, and other community relevant activities. Hence, 80 percent of the financial support is provided by the FAO-GEF project and 20 percent by the community (as in-kind support).
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد نوع (أنواع) الدعم والشروط والمزودين:
Technical support and livelihood packages including solar cooker, chopper machine, dairy toolkit, walnut cracker, construction material for reservoirs (cement, sand, stone, pipes), material for nursery establishment and saplings were provided.
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- غير موجود
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- تطوعي
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
5.5 حوافز أو وسائل أخرى
هل تم استخدام حوافز أو أدوات أخرى لتشجيع تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Training workshops and other capacity building programmes, field day tour, social gathering as well as site visits by communities.
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين وتحسين مشاركة الأطراف المعنية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Capacity building, empowering of Forest and rangeland management associations (FM/RM Associations)
هل مكّن النهج من اتخاذ القرارات المبنية على الأدلة؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Monitoring and participatory assessment skills were improved under the approach allowing to assess results and impacts and collecting evidence for decision-making
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Consultation meetings, workshops, training, on job practical work and capacity building for better implementation of the technology.
هل نجح النهج في تحسين التنسيق والتنفيذ الفعال من حيث التكلفة لأنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
FM/RM Associations and local community contribution, particularly providing of labour during plantation campaigns, protection and maintenance.
هل نجح النهج في تعبئة/تحسين الوصول إلى الموارد المالية لتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Financial resources accessed according to the terms specified in the LoA.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين معرفة وقدرات مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
FAO technical staff conducted various trainings, workshop as well as awareness raising session regarding improving of land users’ capacity for better implementation of the SLM.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين معرفة وقدرات الأطراف المعنية الأخرى؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Local governmental institutions like provicial and district Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock (PAIL/DAIL) departements,FM/RM Associations and local community knowledge has been improved on SLM/SFM.
هل ساهم النهج في بناء/تعزيز المؤسسات والتعاون بين الأطراف المعنية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Collaboration among FM/RM Associations, local community, governmental institutions and other stakeholders has been strengthened.
هل ساهم النهج في التخفيف من حدة الصراعات؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
FM/RM Associations and local community facilitated implementation of the project on communal land as well as mitigated all sort of conflicts regarding protection, quarantine, rotational grazing and other sections.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين المساواة بين الجنسين وتمكين النساء والفتيات؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Women were actively involved in all project activities; some livelihood programs have been targeted at women and girls.
هل شجع النهج الشباب/الجيل القادم من مستخدمي الأراضي على الانخراط في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Through awareness raising, workshop, training, farmer field schools, brochures and other visibility materials encouraged young people or next generation to engage in SLM.
Awareness raising sessions, trainings and workshops enhanced the knowledge of Forest and Rangeland Management Association (FMA/RMA) members and local community regarding sustainable of natural resource management.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين قدرة مستخدمي الأراضي على التكيف مع التغيرات المناخية/الظواهر المناخية المتطرفة والتخفيف من الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Improved water harvesting, controlled land degradation, planted saplings, prevented flood splash and water erosion which improved land users’ resilience to climatic changes/extremes and disaster.
هل أدى النهج إلى توفير فرص عمل ودخل؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Short employment created for local community.
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
Increased production of fodder from trees and grasses.
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
Improved soil cover reduces water-induced erosion, helping to preserve soil fertility. Water harvesting captures surface runoff for irrigation and contributes to groundwater recharge.
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- انخفاض عبء العمل
Through active social participation.
- القواعد واللوائح (الغرامات) / الإنفاذ
Enforcement of customary roles and regulations among the community, enhance tribal and traditional structures for facilitation and implementation of the technology.
- تعزيز المعرفة والمهارات في مجال الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
The consciousness of local community has been enhanced regarding SLM.
- التخفيف من حدة الصراع
The establishment of FM/RM Associations helped mitigate conflicts and facilitated smoother project implementation.
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، صف كيف:
Land users can sustain these efforts because their capacity has been strengthened, they have a sense of local ownership, and adaptive tribal management systems are in place, ensuring the long-term benefits of restoration for future generations.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Awareness, consciousness and knowledge on natural resources management of communities enhanced through workshops and trainings. |
| Increased availability of natural resources for better livelihoods of communities. |
| With increased community contribution, local efforts will support the protection and sustainable management of resources even after external support ends. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| This approach revives ecosystems by reintroducing native plant and animal species, supporting increased biodiversity and creating habitats for wildlife. |
| This approach improves ecosystem resilience, supports sustainable livelihoods, and promotes climate change adaptation. Restoration ensures long-term sustainability while addressing environmental, economic, and cultural needs. |
| The established FM/RM Associations have become the recognized legal bodies for managing forests, rangelands, and other natural resources. They will be responsible for ensuring sustainability and long-term protection after the project. |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| FM/RM Associations established, but they need to be better organized and recognized. | The Ministry of Agriculture Irrigation and Livestock of Afghanistan may connect and empower these local institutions. |
| Some components of the project were intended for women’s participation; however, due to government restrictions on women's employment, this remains a sensitive issue and can be considered a limitation in project implementation. | Government should consider mainstreaming gender in such projects where gender is a key aspect. |
| This approach has been implemented in faraway forests with little management personnel to enforce law on the ground; unless communities manage these lands well, protection of natural resources could get weak. | Community should take more responsibility for protecting natural resources. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| This approach often requires significant initial investment in terms of funding, materials, labor, and technical expertise. This includes costs for site preparation, planting, irrigation, and ongoing maintenance, which can be limiting for many communities. | Adequate budget and community contribution can overcome or reduce this weakness. |
| This approach can take many years, even decades, to show significant ecological improvements, which can lead to frustration, reduced enthusiasm, or a loss of community and donor support. | Strong mobilization and raising of the ownership sense in the community can overcome this weakness. |
| If local communities are not adequately involved, they may not feel a sense of ownership or responsibility for the project, leading to poor long-term maintenance and protection of the restored areas. | This should be a community-based project, ensuring that, after donor support ends, the community takes responsibility for its ongoing maintenance and sustainability. |
| Insecure land tenure and unclear property rights can lead to conflicts over land use and limit the ability of communities to manage and protect restored areas. | Solving conflict over property rights must be facilitated by the communities themselves; government agencies can empower them on conflict resolution. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
10
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
40
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية