Capacity Building Process for Participatory Watershed Development [الهند]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Arun Bhagat
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Udo Höggel
Community Participation in Participatory Watershed Development
approaches_7656 - الهند
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rajapure Ganesh
+91 9422226412
ganesh.rajapure@wotr.org.in
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR)
Paryavaran Sarasnagar Road, Behind, Market Yard Road, Ahilyanagar, Maharashtra 414001
الهند
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
D’Souza Marcella
+91 9422226415
marcella.dsouza@gmail.com
W-CReS (the WOTR Centre for Resilience Studies), Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), Pune
The Forum, 2nd Floor, Pune - Satara Rd, above Ranka Jewellers, Padmavati Nagar, Corner, Maharashtra 411009
الهند
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Dadas Dada
+91 9892763960
dada.dadas@wotr.org.in
W-CReS (the WOTR Centre for Resilience Studies), Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), Pune
The Forum, 2nd Floor, Pune - Satara Rd, above Ranka Jewellers, Padmavati Nagar, Corner, Maharashtra 411009
الهند
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Khedkar Vishnu
+91 7798818283
vishnu.khedkar@wotr.org.in
W-CReS (the WOTR Centre for Resilience Studies), Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), Pune
The Forum, 2nd Floor, Pune - Satara Rd, above Ranka Jewellers, Padmavati Nagar, Corner, Maharashtra 411009
الهند
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR) - الهند1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
24/09/2025
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
The Capacity Building Process for Participatory Watershed Development is a structured approach to strengthen the technical, managerial, and social skills of Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs), Partner Implementation Agencies (PIAs), and Village-level Institutions (VIs). It includes orientation, training, participatory tools, mentoring, exposure visits, monitoring, and institutionalization. The process enhances competencies, fosters creativity and confidence, promotes community ownership, and ensures effective, sustainable planning, implementation, and management of watershed-based natural resource management and climate-resilient interventions.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
Capacity Building Process for Participatory Watershed Development:
Many Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs), Partner Implementation Agencies (PIAs), and Village-level Institutions (VIs) aspire to implement participatory natural resource management (NRM) using a watershed approach. However, they often lack the technical expertise, practical skills, and experience needed for effective implementation. To address this gap, a structured capacity-building and induction strategy is essential. Such a strategy strengthen the technical and managerial competencies, nurtures creativity, and enhances their confidence to plan, implement, and sustain watershed interventions. In turn, it transforms their approach to resource mobilization, management, and sustainability. A common environmental challenge—such as water scarcity, land degradation, and climate change—creates opportunities to unite communities around shared needs. The Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR) has effectively used watershed development as a unifying framework to bring people together, encouraging collective action for improving livelihoods and building resilience—especially among the poor and vulnerable.
Purpose of Capacity Building:
The overarching goal of the capacity-building process is to develop the knowledge, skills, attitudes, and confidence of NGOs, PIAs, and VIs in designing, implementing, and sustaining participatory, watershed-based NRM and climate-resilient development interventions.
Expected Outcomes:
•Improved competence in managing watershed-based NRM and climate change adaptation.
•Strengthened community ownership and participation.
•Effective and sustainable implementation of interventions.
•Positive transformation in approaches to resource mobilization and local governance.
Methodology and Key Steps:
The capacity-building approach comprises a series of interlinked steps, each reinforcing the others. Together, they form a comprehensive and adaptive learning process.
Step 1: Orientation and Sensitization
Objective: Build a common understanding and motivation among all project stakeholders.
Approach:
•Conduct orientation sessions explaining linkages between natural resources, livelihoods, and resilience.
•Share success stories and best practices to inspire commitment.
•Define roles and responsibilities of community-based organizations and NGOs.
Step 2: Capacity-Building Training Modules
Objective: Strengthen technical and managerial skills, especially among field-level stakeholders.
Core Modules:
•Technical Skills: Soil and water conservation, water budgeting, sustainable agriculture, climate resilience, and ecosystem-based adaptation.
•Social & Institutional Development: Social mobilization, gender inclusion, facilitation, group dynamics, and strengthening local institutions.
•Project Management: Planning, budgeting, reporting, and monitoring for effective implementation.
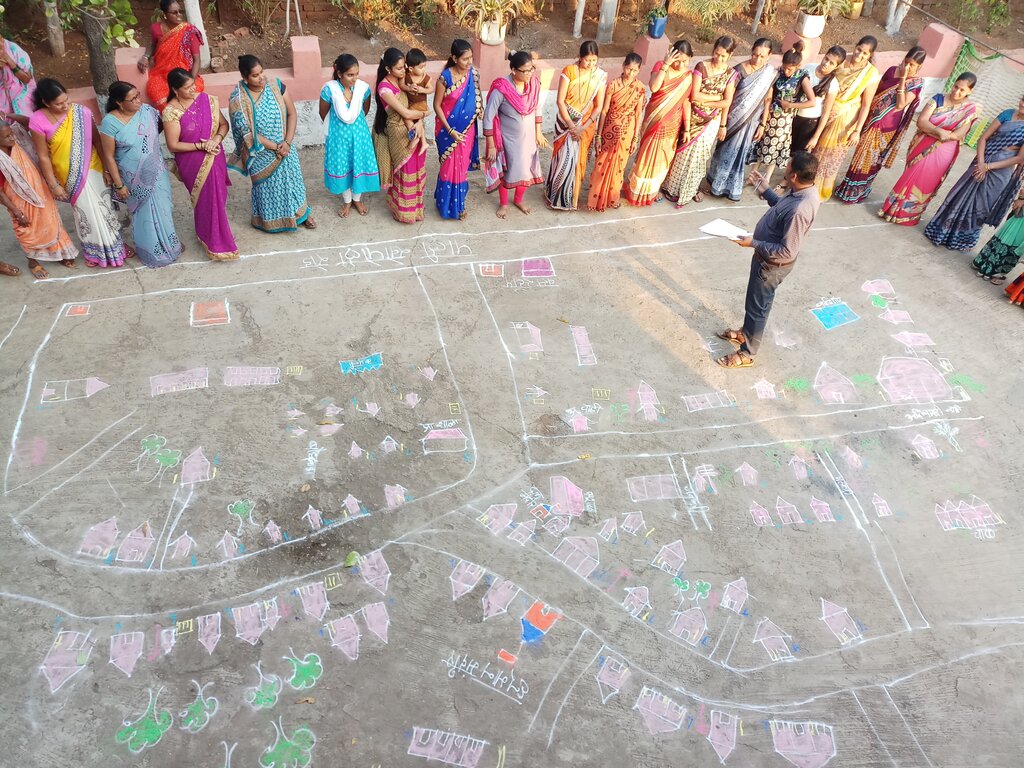
Step 3: Participatory Tools and Methodologies
Objective: Equip local groups with practical tools for participatory planning and action.
Tools and Methods:
•Participatory Rural Appraisal (PRA) tools such as resource mapping, seasonal calendars, and wealth ranking.
•Participatory Net Planning (PNP) for micro-level watershed planning.
•Use of digital tools and simple MIS platforms for data management and progress tracking.
Step 4: Mentoring and Handholding Support
Objective: Ensure continued learning, quality implementation, and motivation.
Approach:
•On-site technical and managerial guidance by experienced facilitators or resource NGOs.
•Regular review and feedback meetings to troubleshoot challenges.
•Peer learning and cross-visits among different project sites for shared learning.
Step 5: Exposure Visits and Learning Exchanges
Objective: Promote experiential and peer-to-peer learning.
Approach:
•Organize visits to successful watershed and NRM sites.
•Facilitate interactions with experienced community institutions and farmer groups.
•Encourage farmer-to-farmer extension to build local confidence and innovation.
Step 6: Monitoring, Evaluation, and Learning (MEL)
Objective: Foster accountability, reflection, and adaptive learning.
Approach:
•Train partners in participatory monitoring, data collection, documentation, and reporting.
•Develop and use simple, participatory monitoring tools to track outcomes and learning.
•WOTR’s existing participatory MEL tools are adapted for partners to ensure consistent data and insights.
Step 7: Institutionalizing Knowledge and Ensuring Sustainability
Objective: Build long-term local ownership and reduce dependence on external support.
Approach:
•Develop local resource persons, for example para-professionals.
•Establish local training and resource centers for continuous on-the-ground support.
•Document best practices, lessons learned, and local innovations for knowledge sharing.
•Gradually transfer leadership and responsibility to community institutions.
2.3 صور عن النهج
ملاحظات عامة بخصوص الصور:
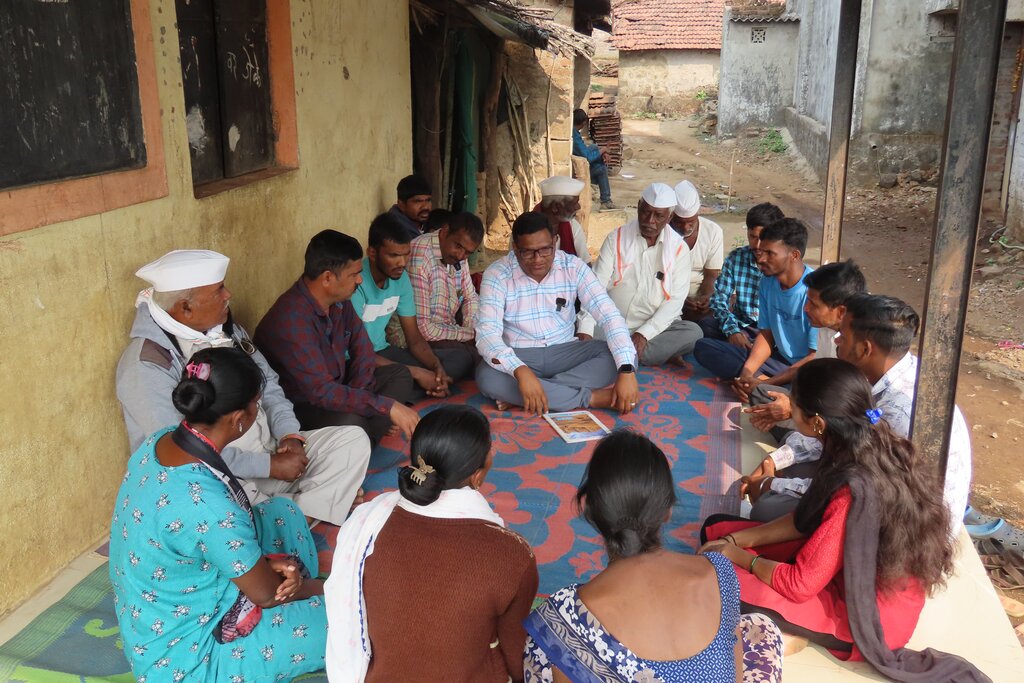
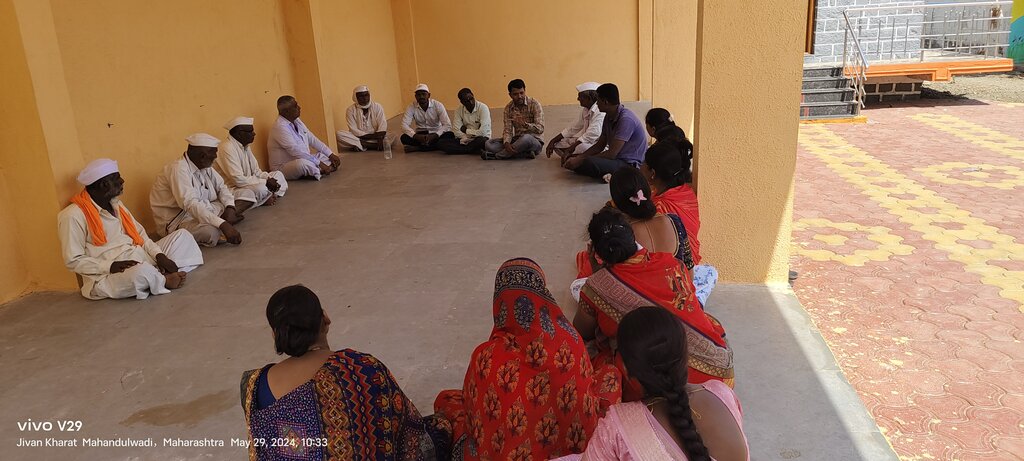
Photos of activities like resource mapping are important as they visually document community participation, local knowledge, and the planning process. They help capture the involvement of villagers, the use of PRA tools, and the mapping outcomes. Such photos serve as powerful evidence of participatory planning, support monitoring and reporting, and effectively communicate project processes and impacts to stakeholders and partners.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
الهند
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Maharashtra, MadhyaPradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh states
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Ahilyanagar, Jalna, Hyderabad, Sanga Reddy, Mandala, Gajapati, Rayagada, and more, etc.
التعليقات:
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), established in 1993, has been actively engaged in capacity building since its inception (Stared from this location). This participatory approach continues to be implemented in WOTR-supported villages across nine states in India.
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي لبدء النهج:
منذ 10-50 سنة
التعليقات:
Year of termination is not applicable because capacity building is essential in participatory watershed management.
2.7 نوع النهج
- The capacity-building process (approach) combines traditional and indigenous knowledge, recent local innovations, and project or program-based approaches for effective and sustainable watershed management.
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The main aims/objectives of the Capacity Building Process for Participatory Watershed Development are
• Strengthen technical, social, and managerial skills of NGOs, PIAs, and Village-level Institutions for effective watershed management.
• Promote participatory planning, community ownership, and active engagement in watershed interventions.
• Build project management capacity, including planning, budgeting, monitoring, and reporting.
• Support continuous learning through mentoring, exposure visits, and peer exchanges.
• Ensure sustainability by institutionalizing knowledge, developing local resource persons, and transferring leadership to communities.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
المعايير والقيم الاجتماعية /الثقافية/ الدينية
- تمكين/تمكيني
Living together for a common purpose forms the foundation of society. A strong sense of ownership and active participation is essential for achieving sustainable development.
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- تمكين/تمكيني
Transparency acts as a social audit, it serves as an effective tool for accountability and openness.
الإطار المؤسساتي
- تمكين/تمكيني
It provides a platform for community members to develop and exercise leadership.
التعاون/التنسيق بين الجهات الفاعلة
- تمكين/تمكيني
It forms the foundation for building strong and sustainable institutions.
- معيق
Conflicts may arise among community members due to differing opinions, taboos, or perceptions.
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
Village-level Institutions (VIs) are linked with the local governing body, i.e., the Village Panchayat.
السياسات
- تمكين/تمكيني
It facilitates the process of social auditing.
حوكمة الأراضي (صنع القرار والتنفيذ والإنفاذ)
- تمكين/تمكيني
It enhances community participation in planning and implementation.
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- تمكين/تمكيني
Through training that provides technical knowledge on the project’s key components.
الأسواق (لشراء المدخلات وبيع المنتجات) والأسعار
- تمكين/تمكيني
Training materials can be procured.
عبء العمل، توفر القوى العاملة
- تمكين/تمكيني
Provides local animators to assist in project implementation.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
Farmers, Women, and Youth
Consent to work, willingness to participate in mobilization activities, and attendance at capacity-building events.
- المنظمات المجتمعية
Men, Women, and Local Representatives
Making informed decisions and managing conflicts effectively. Encouraging active community participation, carefully selecting beneficiaries, and monitoring the impacts of interventions.
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون
NGO staff and team members
Planning, implementing, and monitoring activities
- الباحثون
Researchers and community members (men and women) involved in planning, implementation, and impact monitoring
Researchers design and guide training activities, facilitate knowledge sharing, provide technical expertise, monitor progress, and assess the impact of interventions to strengthen the skills and capacities of communities and stakeholders.
- المعلمون / أطفال المدارس / الطلاب
School and nursery teachers.
Facilitating learning, guiding children, and supporting community education initiatives
- منظمة غير حكومية
Board members
Board resolution
- القطاع الخاص
Technical Expert - Individual or Group
Support to the SLM specialist
- الحكومة المحلية
Gram Panchayat (PRI)
Local governance body
Necessary resolutions
- الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار)
Concern Departments
Content and Guidelines for Capacity-Building Efforts
- منظمة دولية
Donor Agencies
Content and Guidelines for Capacity-Building Efforts
Funding, technical support, and guidance for community development and capacity-building initiatives
إذا كان هناك العديد من الأطراف المعنية، قم بالإشارة إلى الوكالة الرائدة:
The main implementing agency will take the lead role in planning, coordinating, and executing the activities (Capacity-building processes are closely linked to project implementation, so the project’s nodal agency takes the lead role).
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | التعبئة الذاتية | Community members need to demonstrate their willingness to actively participate in project planning and implementation. |
| التخطيط | تفاعلي | Farmers, CBO (Community-Based Organisation) members, women, and village-level animators actively participate in planning and review meetings, and contribute by passing resolutions in CBO meetings. |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | Farmers, CBO members, women, and the project team actively participate in executing activities and in collecting relevant contributions. |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | CBO members participate in joint monitoring visits and share information for impact documentation and research studies. |
| تفاعلي |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
الوصف:
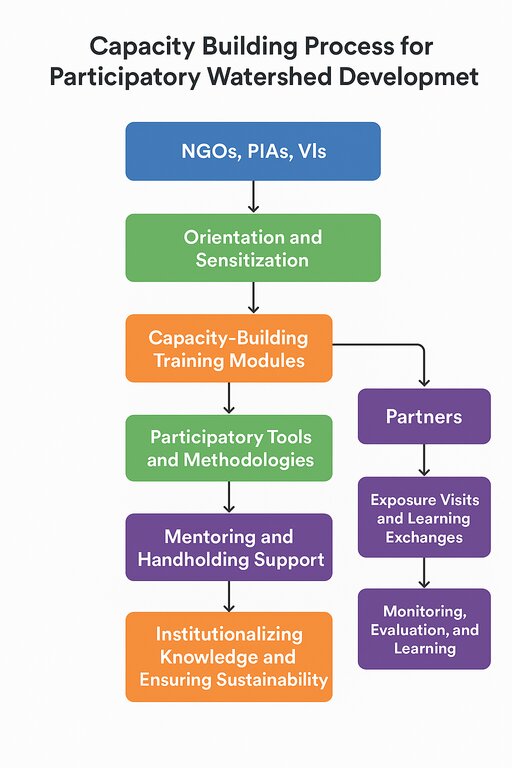
This visual is illustrating a Capacity Building Process for Participatory Watershed Development using a step-by-step flowchart.
It starts with key implementing institutions such as NGOs, PIAs, and Village Institutions (VIs). The process begins with Orientation and Sensitization, followed by Capacity-Building Training Modules that strengthen skills and technical knowledge. From here, the approach branches into two parallel components:
1. Participatory Tools and Methodologies → enabling communities to actively take part in planning and decision-making.
2. Partners → supporting collaboration through exposure visits and knowledge sharing.
The next stage provides Mentoring and Handholding Support to guide field-level implementation.
Finally, the process moves to Institutionalizing Knowledge and Ensuring Sustainability, ensuring that skills, systems, and learnings remain within the community for long-term development impact. Overall, the diagram shows a structured learning pathway that builds capacity, supports practical application, and ensures sustainable watershed management.
المؤلف:
Dr. Arun Bhagat
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- جميع الجهات الفاعلة ذات الصلة، كجزء من نهج تشاركي
اشرح:
The NGO plays a leading role in initiating the process, while community members become actively involved as the process progresses.
حدد على أي أساس تم اتخاذ القرارات:
- تقييم المعرفة الموثقة جيدًا بشأن الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي(اتخاذ القرارات القائمة على الأدلة)
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
- موظفون ميدانيون/ مستشارون
إذا كان ذلك على صلة، حدد الجنس والعمر والوضع والعرق وما إلى ذلك.
Community members of all age groups.
شكل التدريب:
- في العمل
- من مزارع إلى مزارع
- مناطق العرض
- اجتماعات عامة
المواضيع المغطاة:
Key concepts and topics include: Environmental degradation, Natural Resource Management, Watershed Development, Participatory planning and monitoring tools, Community participation and contributions, Role of stakeholders, Portfolio management, Women empowerment, Gender inclusion, Sustainable agriculture, and Post-project management.
التعليقات:
Training modules are designed to meet the specific needs of the project and location.
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
وصف/تعليقات:
In today’s era of climate change and volatile markets, Indian farmers face growing challenges that affect productivity and food security. Unlike urban areas that benefit from the digital revolution, rural farmers need timely, localized, and actionable information on sustainable farming practices. WOTR’s FarmPrecise app addresses this need, providing a comprehensive, data-driven tool to support informed agricultural decisions. Previously, WOTR developed an Agromet Advisory System delivering crop- and location-specific advisories via SMS using data from the India Meteorological Department (IMD). While valuable for weather forecasts, this system lacked personalization and direct farmer engagement.
WOTR launched the FarmPrecise app in 2019 to provide dynamic, farm-specific advisories. Since then, it has grown substantially, with over 1 lakh downloads, covering 30 crops across the Indian States of Maharashtra, Telangana, Odisha, and Madhya Pradesh, and is available in five languages: English, Hindi, Marathi, Telugu, and Odia.
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
حدد المستوى (المستويات) التي تم فيها تعزيز أو إنشاء المؤسسات:
- محلي
صف المؤسسة والأدوار والمسؤوليات والأعضاء وما إلى ذلك.
Village Development Committee (VDC): Responsible for planning and executing project activities, selecting beneficiaries and work sites, managing conflicts, overseeing community contributions, ensuring quality supervision and monitoring, maintaining records, and conducting social audits.
Self-Help Groups (SHGs): Organize women into savings and credit groups and manage SHG operations.
Village Water Management Team: Promote water budgeting, coordinate water governance, and support sustainable water management practices.
حدد نوع الدعم:
- بناء القدرات/التدريب
اعط مزيدا من التفاصيل:
Capacity-building inputs are delivered in a sequence of trainings aligned with the project cycle tenure.
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
In regular Community-Based Organization (CBO) trainings, the monitoring component is a key focus area.
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، فهل من المقصود استخدام هذه الوثائق للمراقبة والتقييم؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
It is used for follow-up purposes as well as for knowledge dissemination.
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- علم الاجتماع
- الاقتصاد / التسويق
- علم الايكولوجيا
- تكنولوجيا
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
The baseline survey tool is used for impact documentation. It helps reach beneficiaries to record their quality of life and assess the effects of project activities.
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- < 2000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Main sources of funding / major donors: National and international donors, and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) contributions.
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد نوع (أنواع) الدعم والشروط والمزودين:
Although not through direct financial or material support, land users (community) benefit from improved skills and knowledge, and gain advantages through active participation and involvement.
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- غير موجود
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- تطوعي
التعليقات:
While labor is not required, participation of land users in the capacity-building process is essential. Landowners contribute their knowledge and time to share ideas and insights.
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
5.5 حوافز أو وسائل أخرى
هل تم استخدام حوافز أو أدوات أخرى لتشجيع تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين وتحسين مشاركة الأطراف المعنية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Greater awareness and better understanding of project management and its impact on project components led to higher participation
هل مكّن النهج من اتخاذ القرارات المبنية على الأدلة؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The progress of project components is presented in common meetings, such as Gram Sabhas, enabling CBO members to make informed decisions.
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Active and well-informed participation in planning, execution, and ensuring quality work.
هل نجح النهج في تحسين التنسيق والتنفيذ الفعال من حيث التكلفة لأنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Capacity building produces synergistic outcomes.
هل نجح النهج في تعبئة/تحسين الوصول إلى الموارد المالية لتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The participatory Net Planning (PNP) tool in support of capacity building approach facilitates proper land-use planning with budget allocation for specific plots.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين معرفة وقدرات مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Capacity building activities and net planning exercises provide inputs on the technical know-how of watershed structures.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين معرفة وقدرات الأطراف المعنية الأخرى؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The capacity-building approach improved stakeholders’ knowledge and skills through training, hands-on exercises, participatory planning, and active involvement in decision-making.
هل ساهم النهج في بناء/تعزيز المؤسسات والتعاون بين الأطراف المعنية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The capacity-building process brings all stakeholders onto a common platform, fostering a shared vision, sustainable impact, and resilience.
هل ساهم النهج في التخفيف من حدة الصراعات؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
It helps unite the community and reduces conflicts related to resource management.
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The principle of equity was upheld during the capacity-building process, with community members from all sectors actively involved and given equal representation in CBO and VI structures.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين المساواة بين الجنسين وتمكين النساء والفتيات؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Special emphasis was placed on women, with a separate Plan of Participation (POP) developed to ensure their inclusion and promote gender equity.
هل شجع النهج الشباب/الجيل القادم من مستخدمي الأراضي على الانخراط في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Special focus was placed on engaging youth in the net planning process to ensure their active participation in local support and supervision.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسن في مسائل حيازة الأراضي / حقوق المستخدمين التي أعاقت تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Informal land user issues are resolved during the implementation process.
هل أدى هذا النهج إلى تحسين الأمن الغذائي / تحسين التغذية؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
A well-designed capacity-building process ensures quality implementation, leading to better outcomes.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين الوصول إلى الأسواق؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Market-related inputs are included in the training modules.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين الوصول إلى المياه والصرف الصحي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
A well-designed capacity-building process leads to quality implementation, resulting in positive outcomes.
هل أدى النهج إلى استخدام طاقة/ مصادر طاقة أكثر استدامة؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The capacity-building approach promoted sustainable energy use by training stakeholders on efficient practices, demonstrating renewable technologies, and encouraging participatory planning for optimal resource use.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسين قدرة مستخدمي الأراضي على التكيف مع التغيرات المناخية/الظواهر المناخية المتطرفة والتخفيف من الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
A well-designed capacity-building process, combined with effective training, ensures quality implementation, leading to positive outcomes and impacts, while enhancing individuals’ resilience through adaptation.
هل أدى النهج إلى توفير فرص عمل ودخل؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Improved agriculture creates both on-farm and off-farm livelihood opportunities.
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
Enhanced soil moisture and soil quality, along with increased awareness and adoption of improved agricultural practices.
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
Reduced soil erosion and land degradation, along with improved knowledge of water and land management practices.
- القواعد واللوائح (الغرامات) / الإنفاذ
Land users practice and uphold equality at all levels.
- الوعي البيئي
Integration of climate change–related topics into capacity-building strategies.
- تعزيز المعرفة والمهارات في مجال الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
A structured and systematic process for implementing Sustainable Land Management (SLM) practices.
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، صف كيف:
The principle of ‘learning by doing’ is central to the capacity-building process. Communities gain hands-on experience in various project components, developing strong technical and managerial skills at the local level. This enhances sustainability, as trained village institutions such as VDC members and community workers possess the necessary knowledge and skills for continued implementation and impact documentation.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Inclusion of Indigenous Knowledge: The approach allows local and traditional knowledge to be integrated into planning and implementation, making interventions more relevant and practical to the local context. |
| Enhanced Knowledge on NRM: Land users gain valuable knowledge and information about Natural Resource Management (NRM), helping them make informed decisions on soil, water, and land use practices. |
| Leadership Development: Community members get opportunities to take leadership roles in planning and decision-making processes, strengthening local governance and ownership. |
| Social Inclusion: The process ensures participation from all sections of society, including marginalized groups, women, and youth, promoting equity and collective action. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Systematic Approach: The capacity-building process follows a structured and step-by-step framework, ensuring consistency, clarity, and efficiency in planning, implementation, and monitoring. |
| Tested and Proven Strategy: The approach is based on field-tested methodologies and past experiences, which have demonstrated successful outcomes in participatory watershed and NRM projects. |
| Operational Guidelines: Well-defined operational guidelines provide a clear roadmap for facilitators and implementing agencies, helping to standardize procedures and maintain quality across different project sites. |
| Set of Tools: The process includes a comprehensive toolkit—such as participatory planning tools, training modules, and monitoring formats—which helps streamline learning, participation, and evaluation. |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Time Constraints: The capacity-building process requires continuous engagement, which can be time-consuming and may interfere with regular livelihood activities of land users. |
Flexible Organization of Capacity-Building (CB) Events: Conduct training and awareness sessions at times and locations convenient for community members to ensure higher participation, especially for women and farmers with field responsibilities. Use of Social Media and Digital Platforms: Share project updates, training materials, and success stories through WhatsApp groups, community radio, and other social media tools to reach a wider audience effectively. |
| Lack of Confidence to Participate: Some community members, especially those with limited education or exposure, may initially hesitate to engage actively in discussions or decision-making. |
Rapport Building: Establishing trust and positive relationships with community members helps facilitators engage participants more effectively and encourages open communication. Interactive Methods – Games, Exercises, Personal Talks, and Corner Meetings: Use participatory and informal methods to make learning enjoyable, build confidence, and promote active involvement among community members. Use of Participatory Rural Appraisal (PRA) Tools: PRA methods like mapping, ranking, and seasonal calendars help participants express local knowledge and experiences, increasing confidence and ownership in the planning process. |
| Social Constraints and Gender Barriers: Cultural taboos and social norms may restrict women’s participation in meetings or leadership roles, limiting their ability to contribute fully to capacity-building and project implementation. |
Encouraging attendance and use of Information: Motivate community members to regularly attend meetings, apply shared knowledge in their practices, and contribute ideas for better project outcomes. Confidence Building Among Men and Women: Conduct targeted sessions to enhance the confidence of both men and women, ensuring balanced participation and reducing gender-based hesitation in community discussions. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Language and Cultural Barriers: Differences in language and cultural practices can make it difficult to communicate technical concepts effectively, especially in diverse and multi-lingual communities. | Rapport Building and Understanding of the Community: Spend adequate time in the field to understand local culture, traditions, and social dynamics. Building mutual trust enhances participation and improves the quality of capacity-building interventions. |
| Limited Literature in Local Language: The scarcity of training materials and technical documents in local languages restricts understanding and limits wider participation at the grassroots level. | Translation of Reading and Training Materials: Translate manuals, handouts, and key reference materials into local languages to make technical content accessible to all community members and ensure uniform understanding. |
| Communication and Facilitation Skills: Successful capacity building depends on skilled facilitators. In some cases, inadequate communication or facilitation skills among trainers can reduce the effectiveness of training sessions and field interactions. | Upgrading Skills of Trainers and Facilitators: Provide regular refresher training and exposure opportunities for facilitators to enhance their communication, facilitation, and technical skills—ensuring more effective delivery of capacity-building programs. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Two field visits are conducted to engage the village community in discussions on the capacity-building process, its impact, importance, and role in fostering ownership.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Interviews were conducted with six land users.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Interviews were conducted with five land users.
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
The information is sourced from a capacity-building methodology that has been developed and is currently under publication.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
WATERSHED DEVELOPMENT GUIDELINES (Revised 2001), Community and Rural Development Department,
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://megcnrd.gov.in/forms/WSD.pdf
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
The Wasundhara Approach. 2013. Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR).
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/read/19427351/the-wasundhara-approach-wotr
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Wasundhara Approach, Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR)
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r3YHpkm9qFY&t=364s
العنوان/الوصف:
Water Gives Life, Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR)
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=thdevpZ-vio&t=149s
العنوان/الوصف:
How to do Wealth Ranking in Watershed
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ygiAy7f7Gpc
العنوان/الوصف:
Wasundhara
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r3YHpkm9qFY&t=364s
العنوان/الوصف:
A New Beginning
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LBzF7DXbedM&t=2s
العنوان/الوصف:
Rising Together: Building Resilient Communities for a Sustainable Tomorrow
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0gCFkwkfwdg&t=2s
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية