Improved grazing land management [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Daniel Danano
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Gitosh masheshal
technologies_1049 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Ethiopia (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) - أثيوبيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/07/2003
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
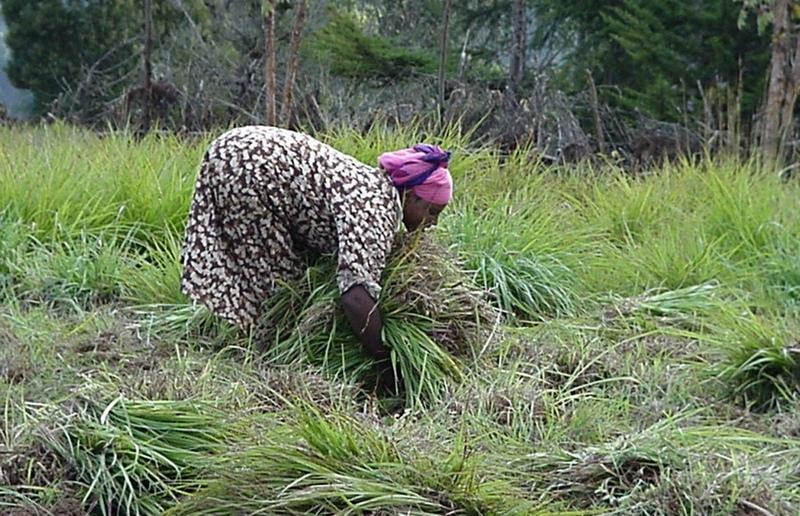
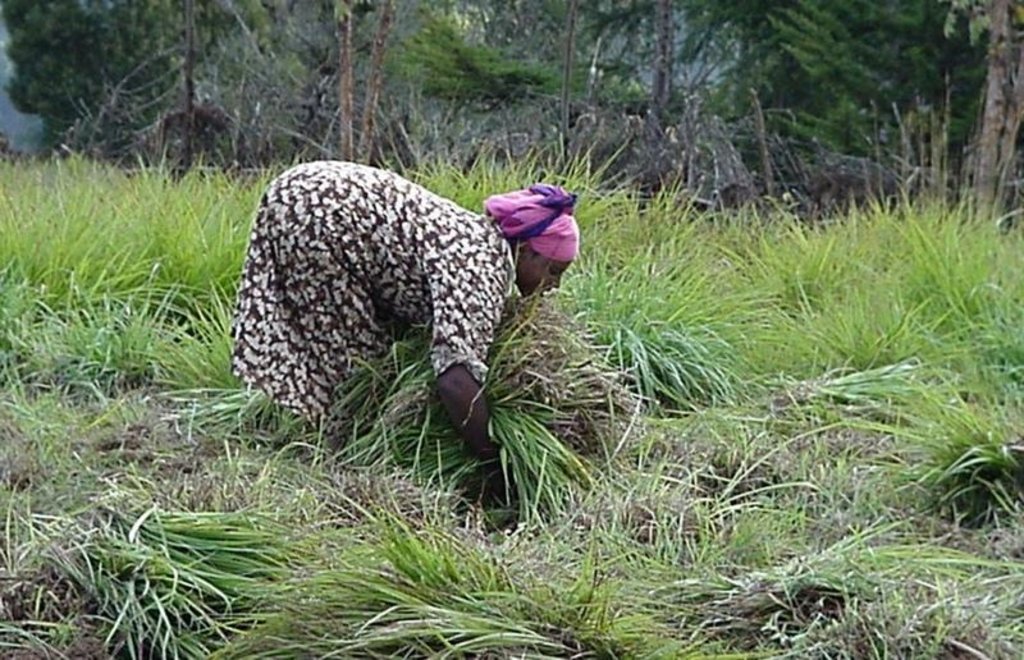
Rehabilitation of communal grazing lands, through planting of improved grass and fodder trees and land subdivision, to improve fodder and consequently livestock production.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
This case study focuses on the highly populated, humid highland regions of Ethiopia that experience serious shortages of pasture. Due to rapid population growth, communal grazing areas are increasingly being converted into cropland. This has led to enormous pressure on the little remaining grazing land, through overstocking of dairy cows and oxen, and thus overgrazing, resulting in considerably decreased productivity.
Improved grazing land management is vital to increase food security and alleviate poverty, as well as to bring environmental rewards. To address these problems, the national SWC programme in Ethiopia initiated a grazing land management project over a decade ago. Implementation of the technology includes the initial delineating of the grazing land, and then fencing to exclude open access. This is followed by land preparation, application of compost (and, if necessary, inorganic fertilizers) to improve soil fertility, then planting of improved local and exotic fodder species, including multipurpose shrubs/trees such as Leucaena sp. and Sesbania sp. and the local desho grass (Pennisetum sp.). Desho has a high nutritive value and regular cuts are ensured. It is planted by splits, which have high survival rates and establish better than grasses which are seeded. Other grass seeds, as well as legumes, including alfalfa (lucerne: Medicago sativa) and clovers in some cases, are mixed with fodder tree seeds and then broadcast.
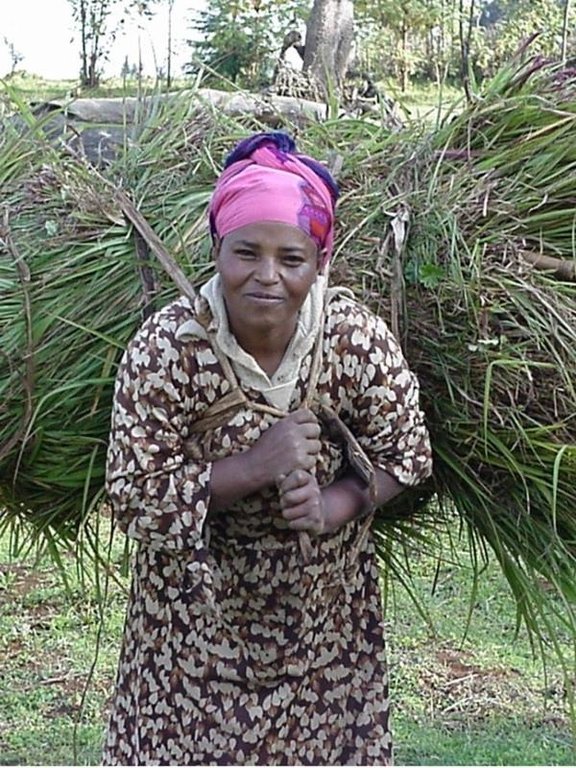
Maintenance activities such as weeding, manuring and replanting ensure proper establishment and persistence. Fodder is cut and carried to stall-fed livestock. Once a year, grass is cut for hay, which is stored to feed animals during the dry season. Experience shows that such grazing land is best managed when individually owned and used. In the study area, the community has distributed small plots (<0.5 ha) of communal grazing land to individual users to develop, manage and use.
The overall purpose of the intervention is to improve the productivity of grazing land and control land degradation through the introduction of productive techniques and improved fodder species, which consequently improve livestock production. Commercialisation of animals and marketing of their products increases the income of farmers. The government provides technical assistance, close follow-up, and some inputs for initial establishment. Land users are trained in compost/ manure application, planting of seeds, splits and seedlings, and general maintenance.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Chencha
Map
×2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- مربى ماشية محدد
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
before SWC

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الحرجي
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
After SWC - cut-and-carry (desho gras (Pennisetum sp.)), legumes (alfalfa, lucerne: Medicago sativa), trees (Leucaena sp, Sesbania sp.)
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Population growth has resulted in a substantial reduction in land holdings (<0.5 ha per family) and this in turn has led inevitably to encroachment onto communal grazing lands for cultivation. Livestock numbers on the other hand have remained unchanged, and this has led to overstocking of the few areas left. Livestock production, which accounts for 40% of the average household income, is thus reduced and farmers’ income declines correspondingly.
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: March - September
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إغلاق المنطقة (إيقاف الاستخدام، دعم الاصلاح)
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- تحسين أصناف النباتات/سلالات الحيوانات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20 km2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Splits of desho grass (Pennisetum pedecillatum) are plantet in lines, using a hand hoe, after good seedbed preparation. Spacing between grass splits is 10 x 10 cm. The white line is a boundary between two households' plots (width of plot: 15-20 m). Trees are planted at rirregular spacing (around 5 m apart), layout is not specified.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, control of dispersed runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure, control of concentrated runoff
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: animal manure, leaf litter, wood ash, soil
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucaena sp., Sesbania sp.
Grass species: Desho grass (Pennisetumsp.), alfalfa (lucerne: Medicago sativa)
Other type of management: change of intensity level
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Delineation of the area to be conserved and establishment of a fence | نباتية | before the onset of rain |
| 2. | Subdivision of communal land into individual plots of 0.3–0.5 ha. | نباتية | |
| 3. | Planting material preparation in nurseries: grass splits (desho) | نباتية | |
| 4. | Good seedbed preparation | نباتية | (at the onset of the rains). |
| 5. | Planting of grass splits and tree/shrub species in lines; sowing of grass | نباتية | (early in the rainy season). |
| 6. | Weeding. | نباتية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 320,0 | 320,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 17,0 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 50,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | Grass splits (tillers) | ha | 1,0 | 450,0 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 140,0 | 140,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Deadwood for fencing | ha | 1,0 | 55,0 | 55,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1052,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Compost/manure preparation. Material used includes animal manure, | زراعية | / initial establishment |
| 2. | Compost application | زراعية | / one month after planting, initial establishment |
| 3. | Cut-and-carry, to stall-fed animals, begins when fodder is ready. | نباتية | (after 2–3 months growth) /2 -4 times |
| 4. | A final cut for hay is taken early in the dry season when the grass has matured well. | نباتية | (end of October) / |
| 5. | Weeding | نباتية | /each year. |
| 6. | Compost/manure application, mixed with soil, during seedbed preparation (only where plants have died and need replacement and fertilisation). | نباتية | |
| 7. | Enrichment planting and gap filling | نباتية | after a year / repeated each year. |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 35,0 | 35,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 35,0 | 35,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Deadwood for fencing | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 126,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Seedlings are given by the government for initial establishment. For further extension of area and replanting, the
land users set up their own nurseries. After 2-3 years maintenance costs decrease substantially as the grass cover closes up and maintenance activities such as replanting/enrichment planting and compost application are reduced or cease. The local daily wage is about US$ 0.70 a day, but varies depending on the intensity of the work. In this calculation the standard rate has been applied.
Farmers usually cannot afford fertilizers. Milk production compensates for some of the high investment costs (previously, production was low).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Local term: wett dega
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and foot slopes (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 2) and low (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Off-farm income specification: source of off-farm income includes petty trade and weaving
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
1-2 ha: Ranked 1
< 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha: Both ranked 2
2-5 ha: Ranked 3
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase in livestock production
إنتاج الخشب
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase in the availability of livestock products on the market
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Decrease in size of grazing plots due to land fragmentation
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Selling animals and their products
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Dependence on incentives
التعليقات/ حدد:
Initially high. Incentives such as free seeds, seedlings, tools
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improvement in household diets (milk)
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased willingness
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Biodiversity
Soil fertility
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
Sediment transport
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: 50 households who accepted the technology in the initial phase, did so with incentives. They were provided with planting materials (seeds, seedlings, grass splits) and hand tools.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The rate of spontaneous adoption is very high. At present over 500 households have taken up the technology and the total area covered is about 20 km2.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Increased national income due to export of animals and their products. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Availability of fodder (grass, hay, shrubs) in sufficient quantities, and all year round How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase the area under such development. |
|
Reduction in soil loss and land degradation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain adequate cover by planting more grass. |
|
Introduction of high yielding species as well as increase in land productivity and livestock production How can they be sustained / enhanced? ntroduce bigger variability of quality species and improve maintenance activities such as weeding and cultivation. |
|
Improved diet: livestock by-products such as milk, butter and cheese are essential food items required by the households How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep on increasing/improving quantity/quality of livestock feed. |
|
Increased income through commercialisation and marketing of animals and their by-products. Meets financial needs for paying taxes, school fees, clothes etc. |
| Rehabilitation of communal grazing lands is both a technical and social challenge. Here is a promising example from Ethiopia that is spreading quickly. The key is subdivision of land into individual plots where cut-and-carry of grass and stall-feeding of livestock is practiced. This is only a possible option, however, where rainfall is favourable. land use rights: individual for cropland, open access (unorganised/communally used) for grazing land, except for the case study area where the rights to rehabilitated grazing land are given to individuals |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| At the initial stage of establishment it is very labour intensive | Use of improved land preparation methods such as oxen ploughing. |
| Substantial cash for inputs, particularly seedlings, is required | Produce seedlings of improved species and making compost in backyards. |
| Needs high fertilizer application | Focus more on organic fertilizers. |
| High pressure on remaining grazing areas | Keep animals in stall (stable) or park, at least part of the day and during the night, and introduce cut-and-carry more widely. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Adane Dinku, Chencha Wereda, Natural Resources Management Annual Report,. 2001 and 2002.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية