Rehabilitation of poor soils through agroforestry [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Natalia Mityakova
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Tajikistan - Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM/ИСЦАУЗР)
technologies_1052 - طاجيكستان
- Rehabilitation of poor soils through agroforestry: 15 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
- Rehabilitation of poor soils through agroforestry: 20 يوليو، 2017 (inactive)
- Rehabilitation of poor soils through agroforestry: 21 أغسطس، 2019 (inactive)
- Rehabilitation of poor soils through agroforestry: 2 نوفمبر، 2021 (public)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Urakov Buran
buran.urakov@undp.org
UNDP
طاجيكستان
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
United Nations Development Program (United Nations Development Program) - طاجيكستاناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Sustainable Land Management - Multicountry Capacity Building (CACILM - MCB) - قرغيزستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
13/04/2011
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
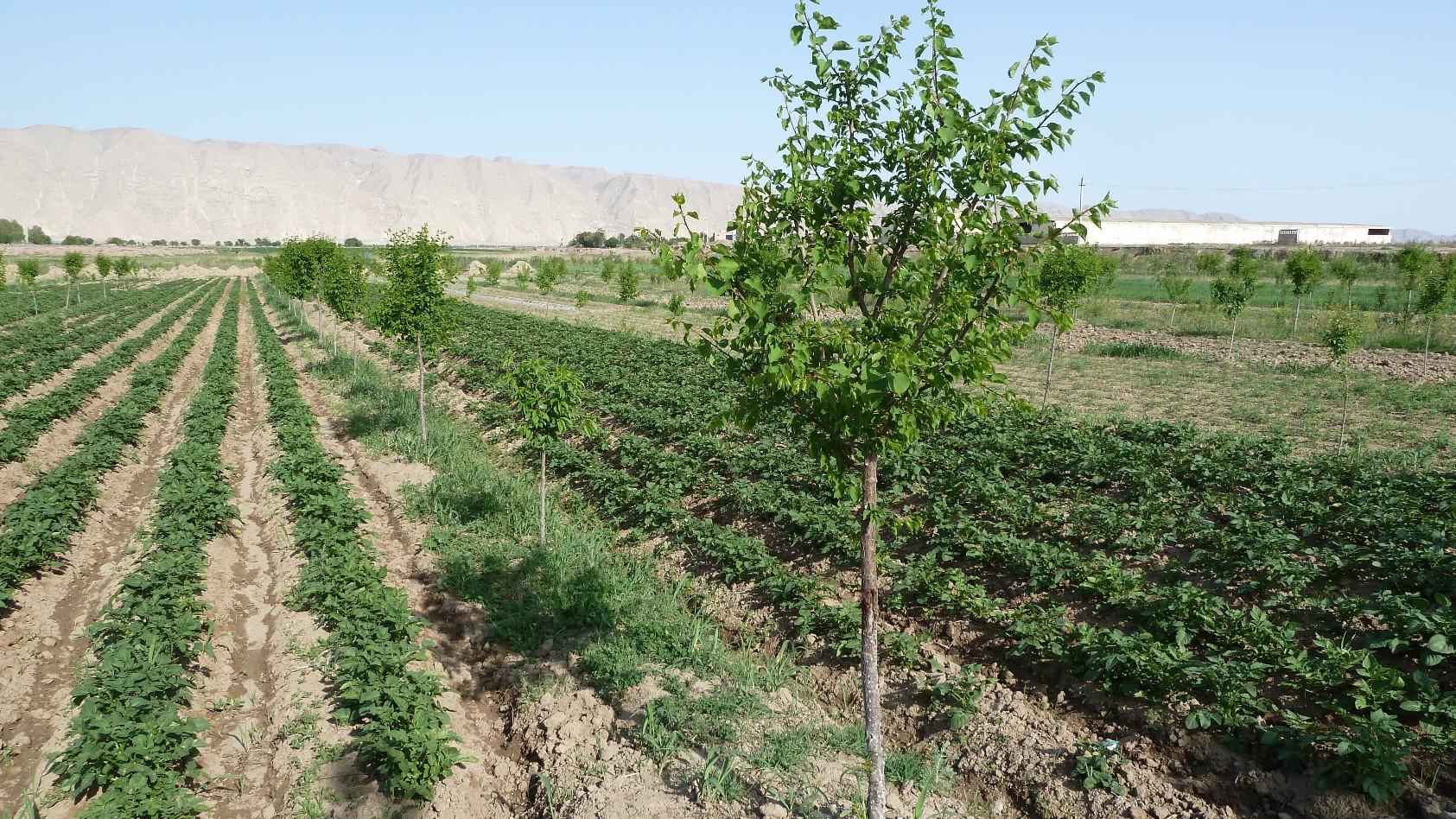
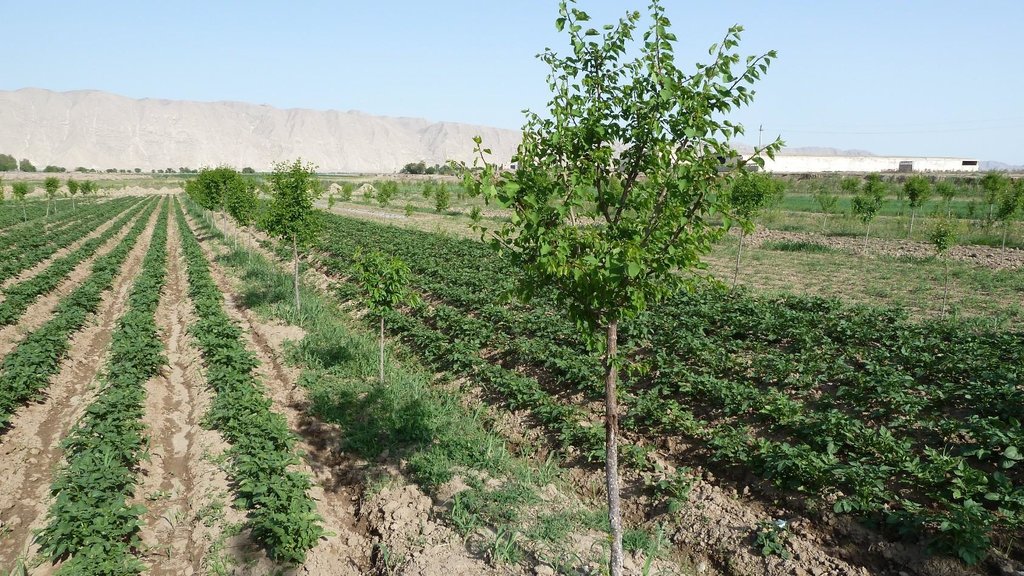
An agroforestry system with peach, plum, sweet cherry and persimmon trees was established on a plot of land, with poor soil quality.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
In the arid environment of Kabodion, large areas that had been irrigated during the Soviet times were abandoned after independence, and the irrigation facilities were neglected. Soils were highly degraded due to the long periods they had been without proper irrigation. On an area of poor quality soil, and previously abandoned plot of land covering about 6 ha, UNDP supported one family (Dehkan)to establish an agroforestry system by covering the costs of tree seedlings.
Purpose of the Technology: The aim of the technology was to improve agricultural production through a combination of measures such as improving soil fertility, increasing soil humidity through covering the soil with plastic sheets and preventing excess water drainage, and protection through a shelterbelt. Resilience to adverse climatic events is enhanced by increasing product diversification with a number of different tree, vegetable and crop species being planted.
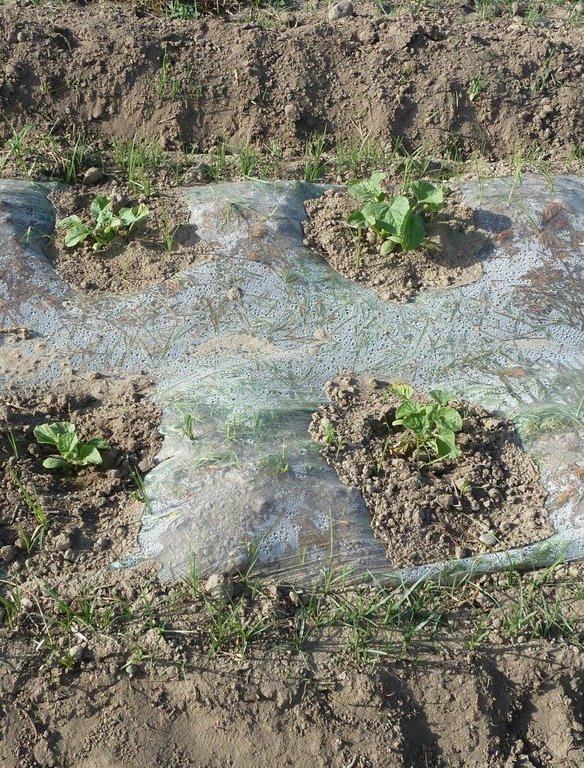
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: First, the soil had to be washed to reduce the high salt content. Plum, peach, sweet cherry and persimmon tree seedlings were planted in lines with intercropping of potatoes, watermelon, beans and wheat inbetween. The seedlings were purchased from the Kabodion nursery. Labour was provided in the form of "hashar" or voluntary neighbourhood help. On the windward side of the field, a shelterbelt consisting of White Poplar (Populus alba) trees was established to protect the field from wind erosion, and to reduce evapotranspiration. In order to improve soil structure annual crop rotations were practiced. Every 4 years 40 tones of cow dung are spread out per ha of land. The application of organic manure constitutes an important cost factor for the farmer, as 40 tons of manure costs about 180 to 220 USD. To improve soil humidity and to enable early planting for watermelons, cultivation seeds are planted under a tight plastic film with irrigation water filled underneath the sheet. As soon as the seedlings emerge a hole is made in the plastic to create space for the plants. Irrigation is applied only sparingly to prevent the soil from a new rise in salinity. The plot is situated on a gentle slope which facilitated the establishment of a drainage system by digging a trench at the foot of the field to absorb excess water. The farmer was able to cover the costs of this initial investment himself using the revenues from the first harvest. At the foot of this field, salt tolerant Russian Silverberry (Elaeagnus angustifolia) trees were planted to promote biodrainage to help prepare the adjacent land for conversion to agroforestry at a later stage. The farmer gained the knowledge that was necessary for the establishment of the system through attending the farmer field schools (see approach TAJ018).
Natural / human environment: This technology is suitable for other arid environments, and the economic benefits are high compared to the establishment and maintenance costs. When this was realised by the neighbouring farmers they adopted the technology on an area of land that was actually three times larger.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khatlon, Kabodion
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Khudokulov Jamoat
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
major food crop: potatoes, wheat, beans, watermelons

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الحراجة الزراعية
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
major food crop: plum, peach, sweet cherries, persimmons
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): degradation of vegetation cover, loss of topsoil through wind erosion, poor access to irrigation water,
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): salinity, waterlogging, low soil fertility, low agricultural production
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- ري كامل
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: October - May (winter wheat)Second longest growing period in days: 120Second longest growing period from month to month: June-September
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- تحسين أصناف النباتات/سلالات الحيوانات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.06 m2.
The technology was initially applied on 5.8 ha of denuded land, however, it has been spontaneously adopted by a neighbour who has about 18 ha.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- S3: الخنادق المتدرجة ،والقنوات، والممرات المائية
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues, rotations / fallows, furrows (drainage, irrigation)
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, aligned: -linear
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pw): تشبع التربة بالمياه

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Pw: waterlogging, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: soil management (soils were under irrigation for a long time and had salinity problems), droughts, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (breakdown of irrigation facilities), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge about agroforestry), governance / institutional (no freedom to farm)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: organic manure
Quantity/ density: 40 tones
Remarks: ha
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: annual crop rotation
Furrows (drainage, irrigation)
Material/ species: drainage
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 845
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Trees/ shrubs species: Elaeagnus angustifolia (for shelterbelt and fence around plot)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Diospyros kaki, Prunus avium, Prunus persica, Prunus domestica
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 200
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
SOM
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4,5
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
20.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of tree seedlings in field and along boundary | نباتية | early spring |
| 2. | Digging up irrigation ditch at the foot of the field | بنيوية أو هيكلية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Planting of tree seedlings | Persons/day | 50,0 | 20,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Digging up irrigation ditch | Persons/day | 40,0 | 20,0 | 800,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 274,0 | 274,0 | |
| معدات | 1,0 | |||||
| المواد النباتية | Tree seedlings | pieces | 844,0 | 3,14573 | 2655,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 4729,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Annual crop rotation | زراعية | |
| 2. | Application of organic manure | زراعية | every 4 years |
| 3. | Cover soil around crops with plastic cover | زراعية | early planting season |
| 4. | Tillage | زراعية | |
| 5. | Continuous daily irrigation for tree seedlings | نباتية | daily during hot months |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Daily irrigation for tree seedlings | Persons/day | 186,0 | 20,0 | 3720,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Organic/manure | tons | 40,0 | 25,0 | 1000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Plastic cover | m | 1,0 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Tillage | ha | 1,0 | 430,0 | 430,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 5151,8 | |||||
التعليقات:
Costs were calculated per ha. Labour costs for irrigation of tree seedlings were calculated assuming that one person has to irrigate daily during 6 months of the year and were included under annual recurring costs.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The cost of the tree seedlings is the most determinate factor. Labour costs are high if labour has to be paid, however, in this case labour is provided free by the farmer.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
100,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor: water logging occurs
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: Too high, danger of waterlogging
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Level of mechanization: Land cultivation is a mixture of mechanisation and manual labour
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
6 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
التعليقات:
family Dehkan farm
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
lucerne (alfalfa) production
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
diversification
تنوع المنتج
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
before the land was denuded
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
vitamin-rich fruits are more readily available
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
through participation in farmer field schools
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
jealousy by other land users who would like to cultivate this land now they can see how productive it is
Livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmer does not need to migrate to Russia anymore to find work, and could afford to buy a house.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
الملوحة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
In the beginning the farmer was not sure about the short-term benefits, but he confirmed that even after just two years he received eight times more than what he invested initially.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
1 household
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Already 10 other farmers who noticed the success of this plot, have adopted this technology themselves.
Neighbour applied technologie spontaenously.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Improved livelihood as revenues are greater than those gained as a seasonal worker in Russia and enough capital produced to buy own house |
| Feeling confident about the future |
|
Improved yields How can they be sustained / enhanced? continue with application of organic manure, soil cover with plastic sheets, crop rotation, integrated pest management etc. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Greatly increased income opportunity in an arid environment How can they be sustained / enhanced? disseminate knowledge to other farmers in the region |
| Diversified system and therefore reduced risk of production failure |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| increased conflicts as land users who used to cultivate this land before and gave up would now like to have the land back. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية