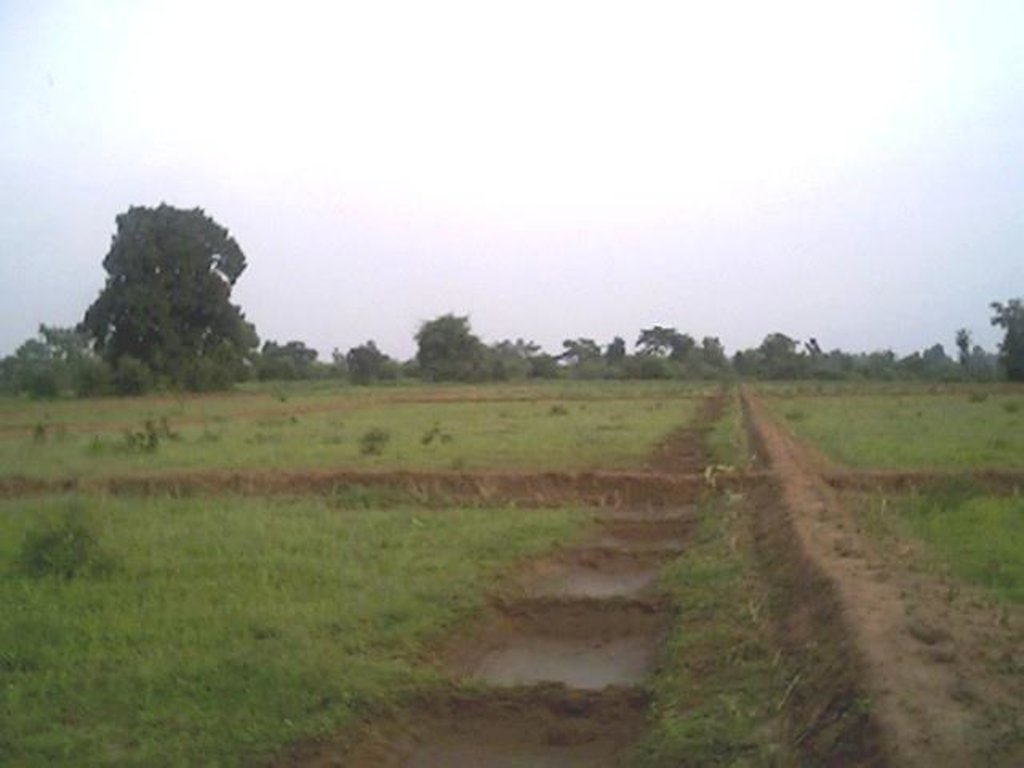
Dug-out sunken pond cum countour bund [الهند]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Buda Gata with Adibandha
technologies_1086 - الهند
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mohanty Rajib Kumar
الهند
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
17/12/2004
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Community based sustainable livelihoods [الهند]
Sustainable livelihoods enhanced through people's organisations by linking with other resource organisations prticularly for resource poor.
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
It can be defined as combination of structural & vegetative measures where contour bunds are constructed from the excavated sandy loam soil of cultivated wastelands in semi-arid climatic(?) zone with moderate slope in medium soil depth conditions in order to link with self-subsistance & market oriented production systems from private lands.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The area is located at the foot-slopes & hill slopes area where run-off is at peaks very often at the time of rainy season. Therefore, sand casting came as a first order priorities by the farmers of this patch. At the outset, a livelihood focused micro-plan had been prepared by the villagers stating the details of the base-line data along with problems & alternative solutions. The patch was identified to be the worst affected, concentraton of poor people (defined by villagers), people of this patch ready to contibute at least 20% of the cost. In the mean time project sent the PIA to BAIF, Bangalore to study the linking of farm ponds & its relevance in this context of our situation. As a demonstration, PIA & other technical team facilitated the villagers. One water harvesting structure was constructed by line deptt of soil conservation just at the down hills to harvest rain water & protect the lands below from sand casting. But there were no alternatives for the land users of that patch about the optimum utilisation recharged water. The surrounding area was totally unbunded with sandy loam soil. Therefore, land users are of opinion to go fo field bunding. Earlier the practice was to dig a trench at upper gadient & put a bund below it out of the excavated soil from trench. But the requirement of land users was to get some water in each farmers land to protect the Kharif & some early rabi crop.(june-dec). By which the lands where, farmers take up only minor millets for their subsistance, that too less production & land So the main purpose of this technology was to convert the land into bunded lands along with to fetch some water at the time of dry spell in between the monsoon period. A four days in field training was conducted by the project to community link workers(SWC), particularly on patch treatment, use of levelling instruments like A-frame, proper planning, design, lay-out of different type of structure in a map & ground. After many rounds of discussion with the land users, one of them ( rich farmers with more land) was ready to do it in his own land. But, the SWC specialist did a detail transact along with land users, although results of first round tansact was mentioned in the micro-plan. The main pupose was to looking at problems & demarkating on the map. After that estimate was prepared & lay-out of key contour was done by SWC specialist with the help of community link workers & land users. The work was implemented by by the labourers with the supervision of the respective User's group leade & monitoring was done by the SWC specialist. The prioty ranking by the land users vegetaive measures like vertiver & Sabai (grass plantation on the bund along the side of the bund. For that, the necessary requirement like nursery, seedling collection was done by agriculture specialist. Training was conducted on the probable alternatives of agronomic measures like taking of crop which is of little longer duration, intercrops & cash crops etc. The vegetaive & structructural measures are subsidised by the project & the agronomic measures was taken up on loan basis. The development fund was also generated out of contribution from the land users which was deposited in a separate account for future maintainance cost.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الهند
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Orissa
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Khaparakhol
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
A group of SWC proffessionals were sent to BAIF Karnatka to study the replication of ' Linking of farm ponds models. After a detail study we concluded that the climate in particular & rainfall in general of our area is not fit for that technolgy. When SWC specialist share their experience to land users, some of the farmers agreed to have a experimentation of the technology. Therefore, modification has been done by the SWC specialists as per the suitability & requirement of the land users.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Major cash crop: Ground nut
Major food crop: Paddy/minormillets
Major other crop: Cotton

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الزراعي
- الرعي الزراعي الحرجي
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
Major cash crop: Fruit like mango/Custard apple
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): This patch of the land is poor in the nutrient status in comparison to other lands of the village, with high concentration of marginal farmer. Heavy top soil erosion over the years yields to decreasing of productivity of land. The main requirement of water is in the dry spell in between the monsoon period.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Run-off was severe at the time of rainy season which causes heavy soil erosion. 2. Sand casting on down below lands . 3. Long duration crops is not possible, ex- Ground nut, paddy, cotton etc. 3. Lands was not levelled for smoothening of ploughing operation. 4. The uncultivated wasteland(according the record of rights) was distributed to some landless persons who are unable to take up any productive cultivation in these lands.
Ranching: Although technolgy is not directly applied, but indirect effect is there on grazing.
Grazingland comments: The major cause of loss in livestock is that there is no option for the villagers for stall feeding. Example- in summer no availability of green fodder or less availabity.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Minor Millets/ Paddy(june-Sept)- Black gram or pulses(Sep-Dec) or cotton as the sole crop for nine months.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 90Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - SepSecond longest growing period in days: 75Second longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Dec
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
- حصاد المياه
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 km2.
The concerned watershed is a subsidiary system of the Suktel river drainage sytem. The area of operation is micro watershed , i.e. 500 hac as a unit of the tributary of the Suktel river.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wm): مجموعة كبيرة من الحركات الأرضية/انزلاقات أرضية
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Suitable alternatives which will yield more benefit with less investments.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Knowledge sustainable livelihoods framework)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Maintainance & responsibility sharing for protection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Particularly vegetation which yields non-timber forest produce.), overgrazing (Uncontrolled & free grazing at the period Dec-June restricts the land users to go for second crop.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Frequent drought occurs in every alternative 3rd year.), poverty / wealth (Initiation of any activities for sustainance of livelihoods need some capital)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Better crop cover
Material/ species: paddy, minor millets, groundnut, vegetables
Quantity/ density: Average
Relay cropping
Material/ species: pulses after minor millets or short duration paddy
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Ground nut, green gram & fibre crop(Jute)
Remarks: Line sowing- 5 lines of green gram with one line of green gram & jute on the fence of the land.
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Cotton as a demonstation practice.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: The silt deposits in the sunken pond is used in the nearby land.
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: After paddy the land is used for pulse
Minimum tillage
Remarks: Previously unbunded, now bunded upland rquires minimum tillage.
Pits
Remarks: Thecontour bunds & field bunds constructed out the excavated soil from the pits.
Agronomic measure: Soil moisture condition
Remarks: It is enhanced due to the technology
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 15-20 ft
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 1250
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 inches
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 inches
Trees/ shrubs species: Teak
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, Custard Apple
Grass species: Vertiver & Sabai
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5.00%
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Spacing between structures (m): 50 ft
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6 ft
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25 ft
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25 ft
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 ft
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 ft
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50ft
Construction material (earth): The earth from the dug-out sunken pond is used for the construction of contour bunding
Construction material (stone): Stone is used at the weak point for stabilisation
Change of land use type: Minor millets, long duration upland paddy, Grount nut, pulses after paddy/millets or cotton etc.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: After harvest of first crop like minor millets/ paddy, next crop is taken up by land users along with some vegetables(Horticulture crop).
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Grazing was restricted in these areas & land was optimally used, like bund cultivation.
Major change in timing of activities: Tthese lands were last option for the land users.But now the activities like summer plough has changed the time.
Control / change of species composition: Earlier sole crop, like only minor millets/Upland paddy. But now land users have started intercropping systems.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Rupee
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
50,0
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey & alignment of key Contour & lay-out of tanks | نباتية | Beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Digging of pits for grass, fruit plants & timber | نباتية | June |
| 3. | Collection of Vertiver & Sabai grass from external source | نباتية | july |
| 4. | Collection of seedling of Trees/Plants | نباتية | July |
| 5. | Survey & contour demarkation | بنيوية أو هيكلية | April-May |
| 6. | Demarkation on map | بنيوية أو هيكلية | April-May |
| 7. | Estimate & lay-Out | بنيوية أو هيكلية | April-May |
| 8. | Implementation of work | بنيوية أو هيكلية | June |
| 9. | Survey & Key Contour line demarkation at 75 ft interval | إدارية | June |
| 10. | Digging of Sunken ponds | إدارية | July |
| 11. | Top level dressing of bund | إدارية | July |
| 12. | Water-way with connection Dug-out sunken ponds | إدارية | August |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 | 20,0 |
| معدات | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 120,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing | زراعية | April-May / annual |
| 2. | Intercultural operation with manure application | زراعية | June / annual |
| 3. | Sowing | زراعية | July & sep for two crops / each cropping season |
| 4. | weeding & intercultural operation, if required. | زراعية | July / annual |
| 5. | Harvesting of paddy or minor millets or ground nut | زراعية | Aug-sep / annual |
| 6. | Sowing of pulses as relay crop | زراعية | Aug-sep / each cropping season |
| 7. | Harvesting of pulses | زراعية | Nov-Dec / each cropping season |
| 8. | Collapsing of bunds may damage th evegetation | نباتية | Rainy Season /annual |
| 9. | Checking against free grazing | نباتية | Jan-June / |
| 10. | Watering to plants | نباتية | Dec-May /annual |
| 11. | Management of surplus water | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Rainy Season/Once in Year |
| 12. | Collapsing of bund | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 13. | Tanks must be desilted | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season/Once in Year |
| 14. | Control of surplus water-flow | إدارية | Rainy season / once a year |
| 15. | Stabilisation of bund at weak points | إدارية | August / once a year |
| 16. | Desiltation of ponds | إدارية |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 7,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: in a typical area of 5 hac, around 30,000 has been spent in which 20% of the establishment cost is borned by the land users.
There are two types of dug-out sunken pits of specifications. The sunken pit was dug & the earth from the sunken pit was put on a contour bund. So the earth-work was calculated as per cubic ft. The seedlings were bought from nursery & planted with 20% contribution of labour.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Soil depth is very less, hard soil with slope variation because of undulating lands. The labour was also not sufficiently available at the time of establishment, because the work was implemented at time of main growing season. At that time land users are busy in their own field because of cultivation work.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
1000-1500 mm: Ranked 1, Avg rainfall from liz kiff report. The study of 20 years of rainfall data shows that, drought comes in every alternative 3 years. The rainfall varies from a minimum of 715.6 mm to maximum of 1863 mm
500-750 mm: Ranked 2
1500-2000 mm: Ranked 3
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (as per the record in the topo-sheet No-64 P/1 with scale1:50,000)
Slopes on average: Gentle (As the stretch of land is at the hill slopes. The slope firstly from 5-8% where as the land where dug-out sunken ponds were dug is of slope 2-5%, ranked 1) and moderate (ranked 2)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, due to continuos soil erosion the topsoil eroded completely which resulted into varied soil depth where only deep rooted crops & plants are possible) and moderately deep
Soil texture: Coarse/light (Ranked 1, the soil is basically reddish in colour with sandy loam texture) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1, the soil fertility of uplands is very low where the said technology is established. But the lands near to it some what medium land with medium soil fertility) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (the watershed map from the topo-sheet shows that there only one drainage line where two contributaries are there. That is the perinneal stream where water from the lands drain out to main drainage lei, ranked 1) and poor (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (the soil texture being the sandy loam category, the storage capacity is very low. Therefore, after monsoon rainfall the soil is unable to maintain the water requirement at the dry spell to high percol, ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- متوسط
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
20% of the land users are very rich (1-2 farmers having more than 10-15 acre of land).
30% of the land users are average wealthy (land users having upto 5 acres(Little less in comparison to first categ).
50% of the land users are poor (land users having only0-2 acres(more in No. in this patch)).
Off-farm income specification: Others have also activities like NTFP collection, keeping small ruminants like goats, chicks etc.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, wooden plough) and manual labour (ranked 2)
Market orientation cropland: subsistence (self-supply, minor millets/paddy/pulses, ranked 1) and mixed (ground nut & vegetables, ranked 2)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Cropland: 1-2 ha (micro-plan)
Grazing land: 0.5-1 ha (130 Households with 25 hac of grazing lands)
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Per hac production/economic cost.
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vertiver as fodder on bund.
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vertiver as fodder on bund.
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
Teak plants has been planted this year. The yeild is yet to come.
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Land users believe that some land is wastage due the structure.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Ploughing operation.
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Resource rich & resource poor land users accrued double benefit by changing the crop.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farm employment at lean period. Income through labour
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Field Demonstration- living institution
التعليقات/ حدد:
Alternatives to mitigate drought.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Contribution labour from land users because of convincing benefit from the technology. The women also contributed in plantation activities.
المؤسسات الوطنية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Members from other areas of district also learnt the technology through exposure visit.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Some of the land users of other patch of the village decided to take up similar activity.
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Transparency: The details of activity is shared amongst all the villagers.
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
Land users having land below 1 hac are getting more benefit out this technology.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Earthen hume pipes.
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
This condition help the land users to take up second crop.
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Particularly top-soil.
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
30
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
تنوع الموائل
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Soil fertility
التعليقات/ حدد:
Production/ Economic benefit becomes double.
Water availability in dry spell
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
19
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
19 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Many farmers & SWC specialists visited the spot for the learning purpose. All we cannot say that it is a spontaneous adoption, but they have started taking up this technology in their own area.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Maintainance is very less How can they be sustained / enhanced? Only timely care is needed. |
|
Land users can have water in their field other than rain water to be used for different purpose. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Some demos agriculture was done in this patch which has to be repeated for the second year for confidence building of the land users. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Water availability in the dry spell How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the land users will desilt the pond timely & care to plants grass on the bund. |
|
The land where only one crop is possible, vegetable & pulse crop can be taken up as second crop How can they be sustained / enhanced? Some methodology is to be applied to keep water in the pond for longer duration. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Ploughing operation will be difficult. | This is although difficult but th benefit is more, therefore land users will compromise with this type of difficulty. |
| Water availability in dry period & desiltaion process. | This can be overcomed by planting vertiver on the sides of the pond & low cost polythene can be used for prolonging percolation rate of water in sandy loam soil. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The farmers started taking up cotton & paddy in stead of minor millets | Improved variety of minor millets is supplied to farmers for better yield in comparison to country variety. |
| Diversion of surplus water | The land users have to dig atleast one more feet & earthen pipes will be used for the diversion of surplus water. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Community based sustainable livelihoods [الهند]
Sustainable livelihoods enhanced through people's organisations by linking with other resource organisations prticularly for resource poor.
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية