Dug-Out Well [الهند]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Alexandra Gavilano
Chahala
technologies_1088 - الهند
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Kar Monoranjan
Project implementing agency, 9437287808
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mohanty Rajib
Watersheds office, DRDA, Balangir, 09437241751
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Watershed Office DRDA - الهند1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
20/09/2006
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
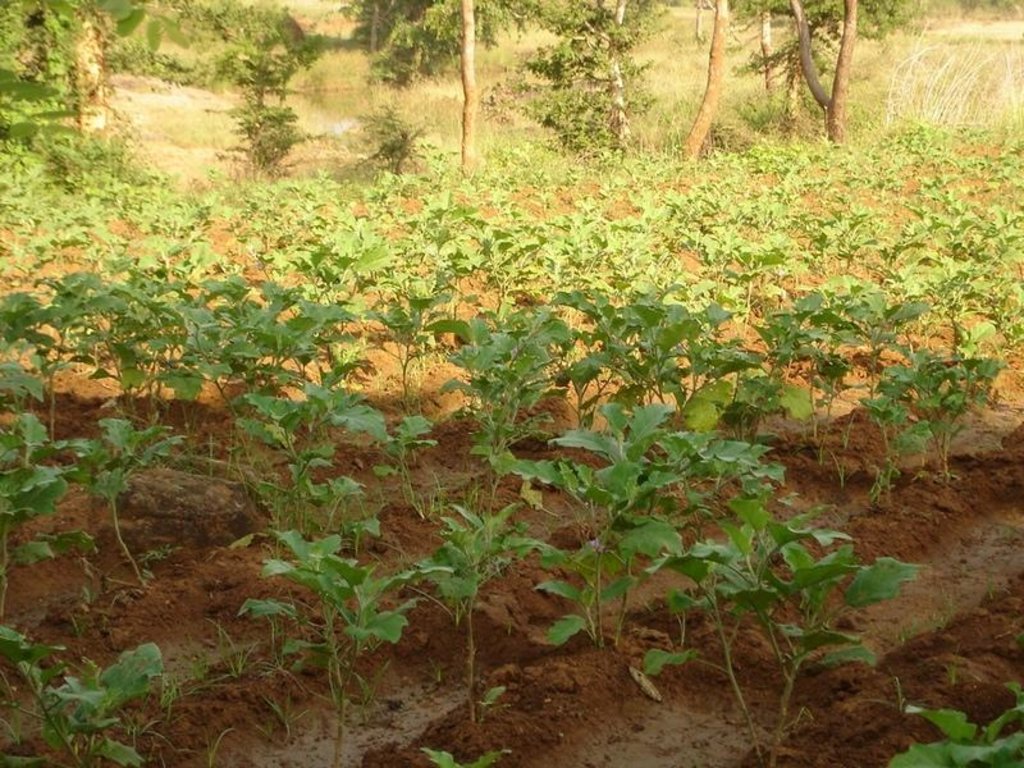
It can be defined as combination of structural & agronomic measures where along with other technology like Water harvesting structures & field bunding on the upper reaches & a dug out well is constructed in the periphery of the drainage line which is a govt land. The 15 acres of land near to its sphere of influence which reamained fallow earlier could yield good production system throughout the year.It is in the semi-arid climatic zone with moderate slope in medium soil depth conditions. The whole idea is to avail water & link with self-subsistance & market oriented production systems from private lands.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
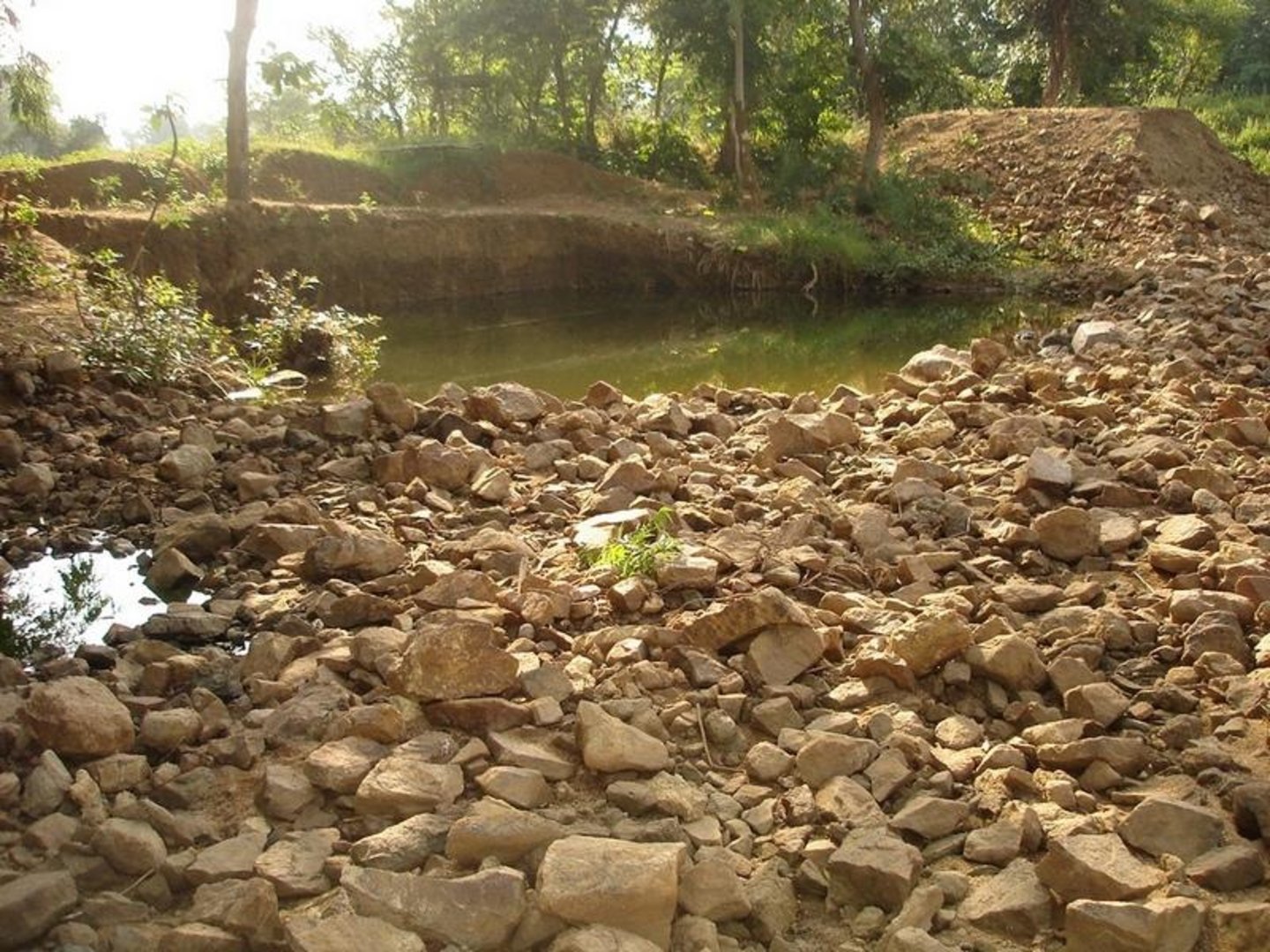
The area is located at the foot-slopes on the major drainage line of the watershed. The technology area is located near the main drainage line, therefore, the sub-surface water availability is more & can be utilised for cultivation of crop even in dry spell of the year. Earlier the farmers near to this place tried to dig a small well & could irrigate for only 2-3 months of the year to get some subsistence crops. Therefore, water availability throughout the year is a first priority of the farmers. At the outset, a livelihood focused micro-plan had been prepared by the villagers stating the details of the base-line data along with problems & alternative solutions. The patch was identified to be the worst affected & the owners of the land are poor people (defined by villagers). Usually the land users used to migrate in search of labour due to loss in the agriculture. It is because the water availability is not there at the time of requirement. The people of this patch are ready to contribute at least 10% of the cost as the structure is to be constructed in government land. In the mean time the project sent the PIA to Water technology centre for eastern region, Bhubneswar to study the linking of water harvesting structure & dug-out well & its relevance in this context of our situation. The technology was done in the village Chareimara which is one out of 3 villages of one watershed, located at the lower reach of the watershed. In the meantime many water harvesting structures & field bunds were constructed due to which the water could be stored in the recharge zone. This area is again a mix of stony patches in the crop land. One water harvesting structure was constructed just at the upper reaches. The surrounding area was totally unbunded with clay loam soil. Therefore, land users are of opinion to go for a deeper dug well which can feed water through out to at least 15 acre of land. The requirement of land users was to get some water in each farmers land to protect the Kharif & rabi crop including summer vegetables. A four-day in field training was conducted by the project to community link workers (SWC), particularly on patch treatment, use of levelling instruments like A-frame, proper planning, design, lay-out of different type of structure in a map & ground. At the same time there was a blind belief that large water harvesting structures are more useful to farmers. So the land users demanded for a large WHS on the drainage bed which requires huge investment & high maintenance cost. But when some farmers of that watershed could get good result by digging well these land users also started thinking about a "community dug-well". After many rounds of discussion with the land users by the SWC specialist followed by a detail transact along with land users, the results of first round transact was mentioned in the micro-plan. But the aim behind subsequent transact was to looking at problems & demarcating on the map. After that estimate was prepared & lay-out of the well was done by SWC specialist with the help of community link workers & land users. The lay-out is also little bit different from traditional well i.e. square shaped in stead of round shape. The work was implemented by the land users & 7 outside labourers with the supervision of the User's group leader & monitoring was done by the SWC specialist. The priority by the land users was agronomic measures like changing the crop in the land. Training was conducted on the probable alternatives of agronomic measures like taking of crop which is of little longer duration, intercrops & cash crops etc. The structural measures are subsidised by the project & the agronomic measures was taken up on loan basis. The development fund was also generated out of contribution from the land users which was deposited in a separate account for future maintenance cost.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الهند
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Orissa, Balangir, Suktel/Mahanadi
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
A group of SWC proffessionals were sent to WTCER, Bhubaneswar to study the replication of ' Linking of water harvesting structure with dug-out wells. . When SWC specialist share their experience to land users, some of the farmers agreed to have a experimentation of the technology. Therefore, modification has been done by the SWC specialists as per the suitability & requirement of the land users.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): This patch of the land used to remian fallow in comparison to other lands of the village, with high concentration of marginal farmer. Due to less water availability at the time of need of crop the farmers were quite hesitant to take up diversified crop. They used to migrated instead of taking up any agriculure due to loss year afte year. The main requirement of water throught out the year.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Run-off was severe at the time of rainy season but difficult to capture water for other period of the year.2. Long duration crops is not possible, ex- paddy,pulses, sugarcane, vegetables etc. 3. Although land is there but it remained fallow in the past due to water availability. They were the migrants because of onstraint in agriculture.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Paddy/Kharif rainfed vegetables, Winter vegetables & spices, summer vegetables.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
أخرى (مثل ما بعد الفيضانات):
- all of them
التعليقات:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - OctSecond longest growing period in days: 80Second longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Feb
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.6 m2.
The concerned watershed is a subsidiary system of the Suktel river drainage sytem. The area of operation is micro watershed , i.e. 500 hac as a unit of the tributary of the Suktel river
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A5: إدارة البذور، الأصناف المحسنة
- A6:أخرى

التدابير البنيوية
التعليقات:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, early planting, mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, deep tillage / double digging
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wr):انجراف ضفة النهر
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Dug Well in Chareimara
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, water spreading
Better crop cover
Material/ species: paddy, vegetables,
Quantity/ density: Average
Remarks: Paddy for subsistence & vegetables in the land with rainfed & market demand.
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Gourd, Brinjal, onion, sugarcane,water melon
Quantity/ density: ealy harve
Remarks: After the Kharif crop
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: 4 -5 cartloads of cow-dung
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Minimum basal doses
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: the cultivation of crop started after the availability of water.
Remarks: Rainfed paddy with vegetables
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: As the land was fallow earlier, breaking of compact soil is necessary.
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: The land where vegetables was grown, deep tillage was required
Structural measure: diversion ditch / cut-off drain
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 26ft
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 35ft
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 33ft
Construction material (stone): Stone excavetd from the well was put as protection embankment
Construction material (concrete): A concrete guard wall will be put on the periphery of well which will be started in the current year
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:150
Change of land use type: After paddy & kharif vegetables,rabi & summer vegetables .Th e bunds of the patch need to be covered with plants
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Inter crops, mixed crops have to be practiced to get optimum benefit.
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Grazing was restricted in these areas & land was optimally used, like bund cultivation.
Major change in timing of activities: Early varieties of vegetables will fetch at least double benefit.
Control / change of species composition: The improved varities seed need to be introduced
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Rupee
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
50,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey | بنيوية أو هيكلية | April-May |
| 2. | Demarkation on map | بنيوية أو هيكلية | April-May |
| 3. | Estimate & lay-Out | بنيوية أو هيكلية | April-May |
| 4. | Implementation of work | بنيوية أو هيكلية | May-July |
| 5. | Survey & demarkation of water line | إدارية | April |
| 6. | Digging of well | إدارية | May-July |
| 7. | Water-way | إدارية | August |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | medium | hectare | 1,0 | 1250,0 | 1250,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1250,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing | زراعية | April-May / |
| 2. | Intercultural operation with manure & compost application | زراعية | June / |
| 3. | Sowing of paddy & rainfed vegetables | زراعية | July & sep for two crops / |
| 4. | weeding & intercultural operation, if required. | زراعية | July / |
| 5. | Harvesting of paddy orvegetables or sugarcane. | زراعية | Nov / |
| 6. | Winter early variety vegetables like onion, brinjal, leafy vegetables, gourds etc. | زراعية | Dec / |
| 7. | Harvesting of winter spices & vegetables | زراعية | Feb-March / |
| 8. | Sowing of summer vegetables like water melon etc | زراعية | March / |
| 9. | Intercultural operation | زراعية | April / |
| 10. | Harvesting of vegetables | زراعية | May / |
| 11. | Management of surplus water | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Rainy Season/annual |
| 12. | Collapsing of bund | بنيوية أو هيكلية | annual |
| 13. | Well must be desilted | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season/each cropping season |
| 14. | Control of surplus water-flow | إدارية | August-Sep / annual |
| 15. | Stabilisation of bund at weak points | إدارية | Nov-Dec / annual |
| 16. | Desiltation of well. | إدارية | April-may / annual |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | medium | hectare | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 10,0 | |||||
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Stones are to be excavated from such a height of 26 ft.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
1% of the land users are poor (2-3 acres of land).
Off-farm income specification: Others have also activities like NTFP collection, keeping small ruminants like goats, chicks etc.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 0.5-1 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Water availilbilty |
| A vibrant community institution could be strngthed. |
| A well is much better than a large water harvesting structure, it became a eye opener in the surrounding villages. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Water availability in the dry spell How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integrated & threes season land use practice |
| The water availability will be there through out the year.Therefore, 15 acres of land can be irrigated & three seasonal crop can be taken up. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية