Riverbed reclamation & silt trapping for sugarcane [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Kithinji Mutunga
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Kyanda (Kikamab)
technologies_1096 - كينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ngati Mbuvi
MOARD
كينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mwendwa Linus
MOARD
كينيا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
17/04/2000
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Silt harvesting on riverbeds to maximise sugarcane growing in semi arid area
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
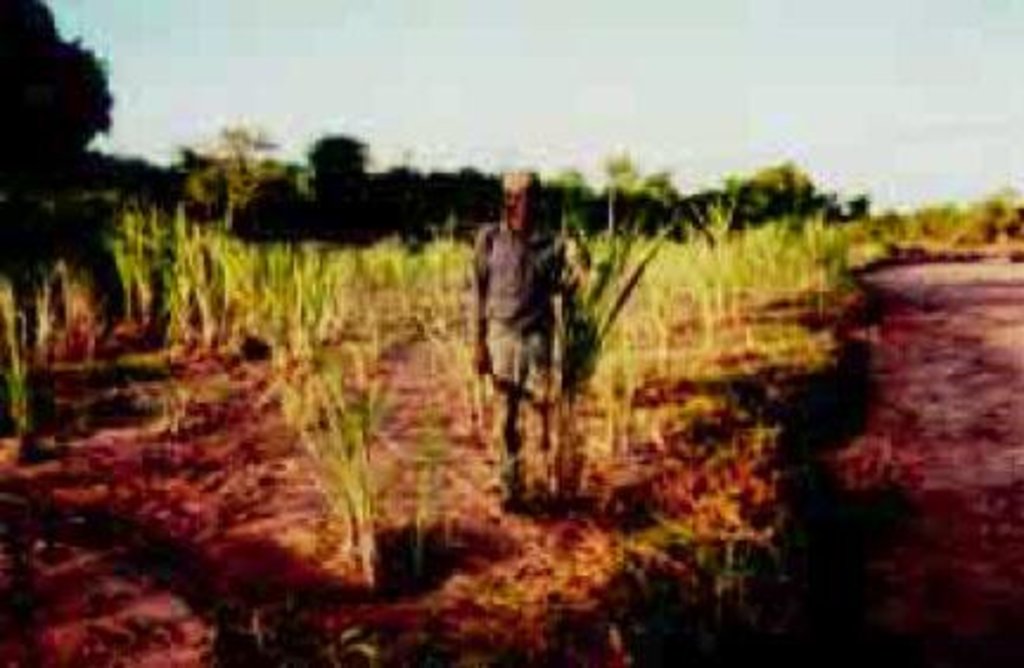
The technology first involves fencing off part of a riverbed with cut thorn scrub in order to keep livestock away. The enclosed area is then mulched with brushwood and herbaceous materials in places. Sugar cane is planted and harvested piecemeal when mature. Kamuti plants a perennial grass (Cynodon dactylon) between the canes to help bind the sand. This exercise has been done, incrementally, over a series of seasons, enclosing an increasingly large area. When the rains return and the river flows, floodwater passes through and over the sugar cane and silt is deposited as the flow is slowed.
Purpose of the Technology: This initiative is categorized as an agronomic/vegetative measure, for reclamation of land. Its purpose is to increase water stored in the soil and to increase fertility by sediment harvesting, as a way of making land productive, while simultaneously addressing riverbed erosion. Farm income increase from the sale of sugar cane is the main production/ socio-economic benefit, while the ecological benefits include sediment accumulation, soil (ie riverbed and bank) loss reduction, soil cover improvement, increase in soil moisture and increase in soil fertility.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The action involves cutting tree branches, trimming pegs about 1m long, and hammering these pegs into the bed of the sand river, parallel to the bank, enclosing a long narrow strip. This initial strip may be 10 metres wide in a riverbed of 100 meters wide. The tree branches and trimmings are used to form a brushwood-netting barrier, which protects the area from livestock, and simultaneously slows the river flow and traps sediments. To further strengthen the barrier, star grass (Cynodon dactylon) is planted along the line of the fence. Inside the fenced-off area, sugar cane cuttings are buried at a depth of 0.4 m, and the same grass planted between the canes. The area is mulched with brushwood, which rots down to increase organic matter in the soil. These cuttings sprout and an intercrop of grass and sugar cane is the result. Maintenance comprises repairing the fence and cutting grass for mulching. No special tools are required. To be effective, the technology requires mulching every season, as the old mulch is covered by the silt load during the rainy period. The perimeter fence is maintained seasonally and requires considerable material. Occasionally when the rainfall is heavy, the sugar cane is swept away by floods and needs replacing.
Natural / human environment: The farm on which this technology is applied is in the arid far-north of Mwingi District. During the rainy season the farm can be inaccessible. The farmer, who is over 60 years of age, lives with his wives and children in what effectively forms a mini-village. The annual average rainfall in this area is barely 500 mm, and famine years are common. Temperatures are consistently high. The farm borders a dry sand riverbed.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Eastern Province
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Farmer own intiative
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Extensive grazing of animals/unit area, uncontrolled felling and burning of tree in land preparation, low soil fertility due to continous cultivation without conservation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low yields hence opening of large areas for cultivation. Difficult soils, hence ploughing during the rains. Infertile soils.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 75 Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - May Second longest growing period in days: 60 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Dec
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
- حصاد المياه
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 m2.
This technology is along a riverbed and it is not adapted by other farmers
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A6:أخرى

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير البنيوية
- S6: الجدران والحواجز وسياجات القش، والسياجات

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
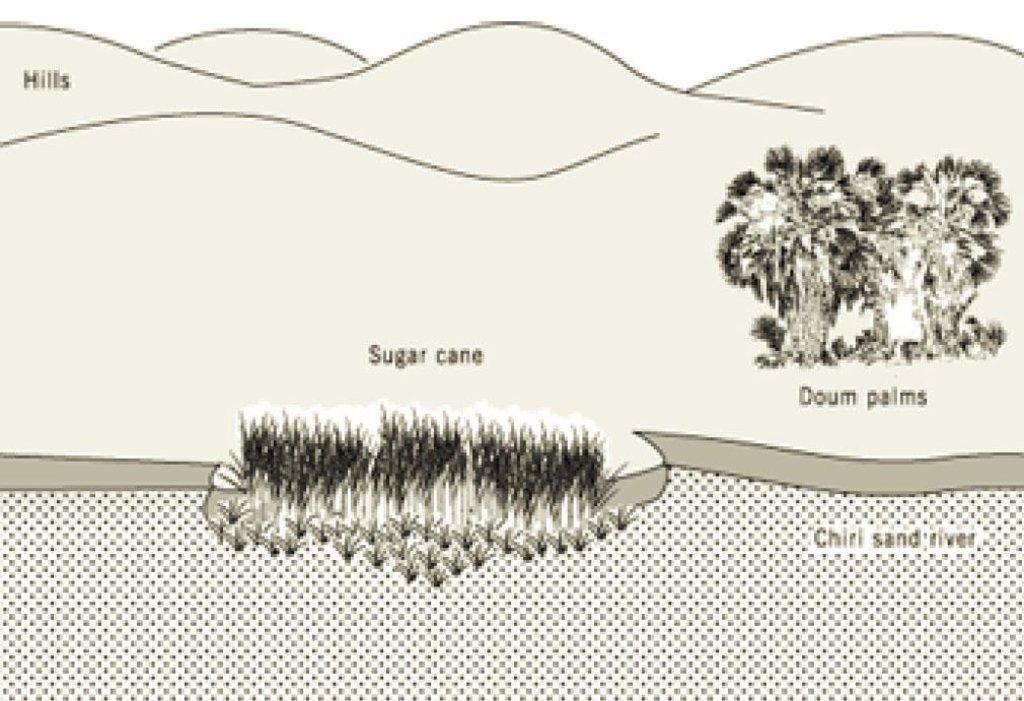
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Reclaiming part of sand river bed with Sugar cane
Kenya
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: grasses
Quantity/ density: 2
Remarks: grass scattered
Grass species: stargrass
Change of land use type: fencing off portion of river bed
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Kenya shilling
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
70,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1.50
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | fencing | نباتية | after rains |
| 2. | mulching with bushes | نباتية | before rains |
| 3. | planting of sugarcane | نباتية | dry season |
| 4. | cuting grass for mulch | نباتية | rainy season |
| 5. | fencing riverbed to keep off animals | إدارية | after rain |
| 6. | planting grass | إدارية | after rain |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | fencing | زراعية | dry season / when height goes down |
| 2. | mulching with trash | زراعية | dry '' / after clearing |
| 3. | grass planting | زراعية | dry / before rains |
| 4. | sugarcane planting | زراعية | wet / end of rain |
| 5. | collection of mulch | زراعية | dry / biannual |
| 6. | fencing | نباتية | after rain /biannual |
| 7. | cutting grass for mulch | نباتية | rainy /biannual |
| 8. | scatterin thorn bushes | نباتية | during rain /biannual |
| 9. | fencing | إدارية | after rain / each cropping season |
| 10. | spreading brushwood | إدارية | after / annual |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: oxen plough, 2 pangas , 2 hoes
the above cost were calculated in terms of purchase of tools,material and manday used.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
labour affects cost as it is required in large quantities
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
- قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Topsoil organic matter: Becomes medium after the technology
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is very low - medium
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 33% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 25% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 12% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 8% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 21% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: most of harvest are low and hence dependent on off farm income.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction is used for assembling the thorny bushes and for marking farrows
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- مجتمعي (منظم)
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Sugar cane
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Sugar cane
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
12
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
30 households (1% of the area stated)
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: after farmer tour organised by the PFI most are attempting. At least five farmers had adopted the innovation by the beginning of 1999 (exact figures not available). This is a particularly site-specific system, and thus wide replication is simply not possible. It is only relevant to those who have farms bordering sand rivers with wide beds.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| This innovation demonstrates how productive use can be made of sub-surface moisture in sand rivers in arid areas while simultaneously protecting the riverbed and bank from erosion |
| Farm income increase through land reclamation |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
|
Planting within a riverbed is, strictly speaking, against regulations. |
Such technologies should not be attempted without consulting the local agricultural office. |
| The fence is constructed with thorn bush cuttings which have to be constantly replenished |
A live fence is recommended as an alternative to constantly having to replenish the fence with cut thorn bush. The fence is required to avoid grazing of the cane by domestic livestock. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Farm management Guidelines. 1989.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
MOA, Nairobi
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kithinji M., Critchley W. 2001. Farmers' initiatives in land husbandry: Promising technologies for the drier areas of East Africa. RELMA Technical Report series no. 27
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية