Traditional irrigated rice terraces [النيبال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Ramanand Bhattarai
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Tari khet (Nepali)
technologies_1099 - النيبال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
District Soil Conservation Office (DSCO) - النيبالاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - النيبال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/11/2003
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
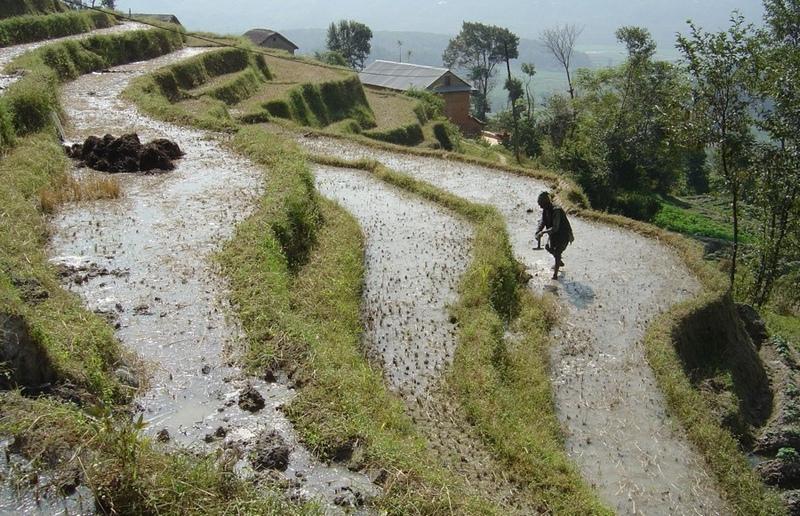
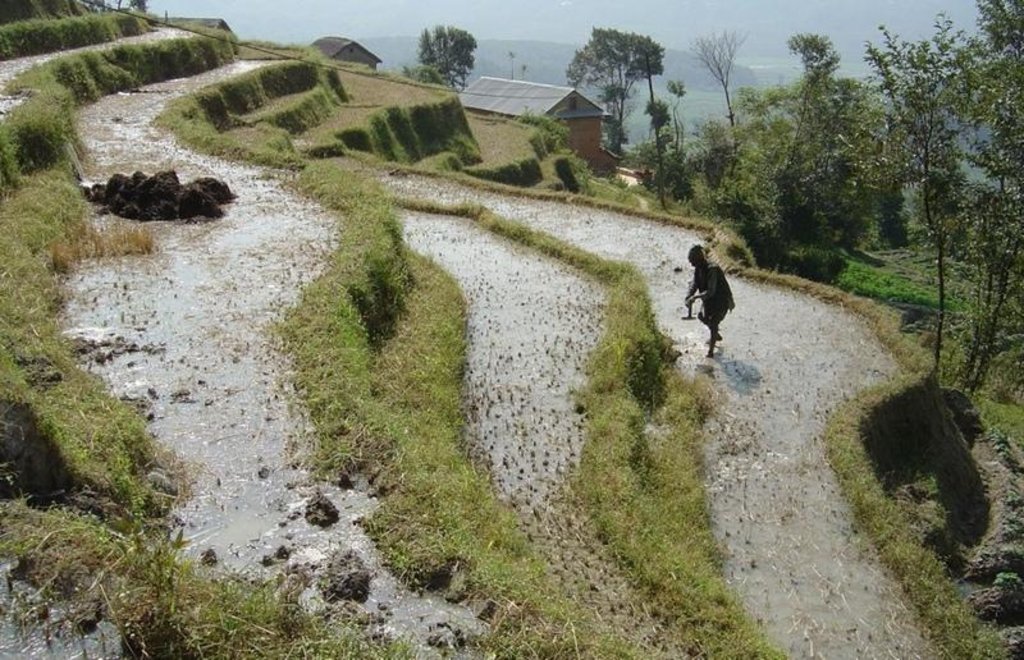
Level bench terraces with risers protected by fodder grasses, used for the irrigated production of rice, potatoes and wheat
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The level bench terrace is a traditional technology that makes irrigated crop production possible on steep, erosion prone slopes. The majority of such terraces in Nepal were constructed by hand many generations ago, but some new land - mostly already under rainfed cultivation on forward sloping terraces - is still being converted into irrigated terraces. The initial costs for the construction of the terraces are extremely high – and annual maintenance costs are considerable also. The climate is humid subtropical, slopes are steep (30%-60%) and soils generally have a sandy loam texture. Terraces are cropped by farmers who mostly have less than 0.5 ha of land each.
Two to three annual crops are grown per year starting with paddy rice during the monsoon, followed by potatoes and/or wheat.
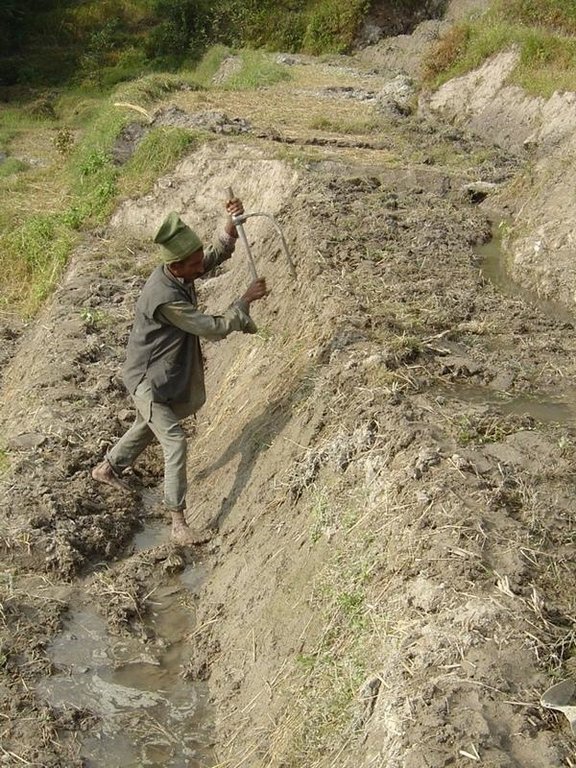
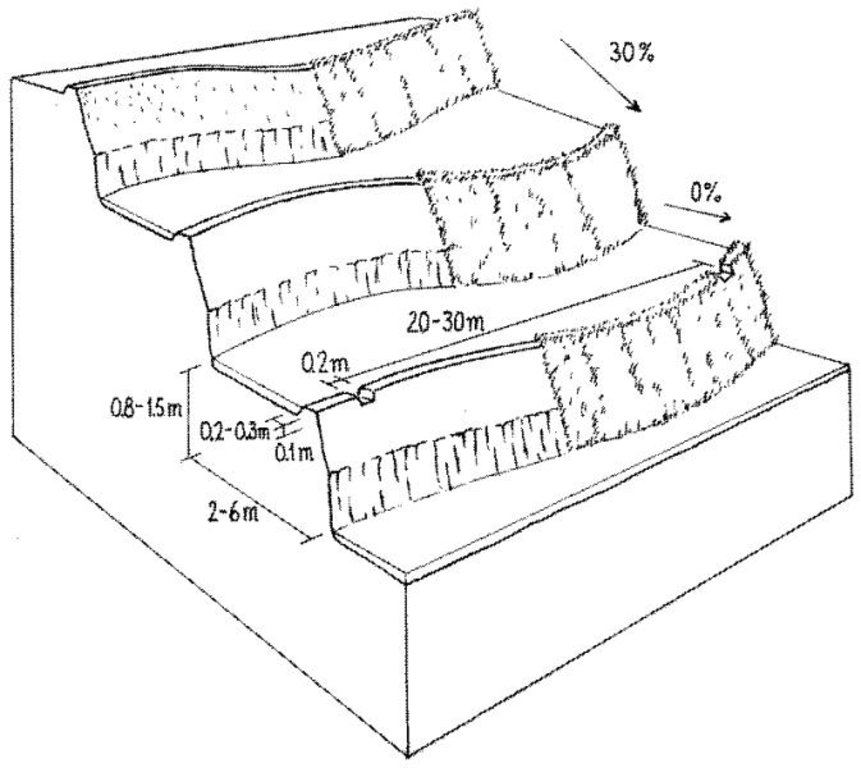
While terrace beds are usually 2–6 m in width, to save labour they are made as wide as they can be without increasing the danger of slips/land slides. Surveying was traditionally done by eye, but now a water-tube level may be used. Risers are 0.8-1.5 m high with a small lip (20-25 cm). The slope of the riser varies from 80 to 160%, depending on the initial gradient of the hill. Stones are incorporated in the risers if available, and grass species such as bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) and napier (Pennisetum purpureum) may be planted for stabilisation and as cattle fodder. The risers are compacted (with hoes) to improve ponding conditions for the paddy rice. Twice per year the risers are scraped with a special tool: (1) at the time of land preparation for paddy rice the lower part of riser is sliced, but the upper part is left protected with grasses against the monsoon rains; (2) at the time of wheat planting the whole riser (including the lip) is scraped and spread as green manure on the terrace.
Terraces are flooded with water for paddy rice cultivation: a smaller amount of water is diverted into the fields for other crops. Excess water is drained to the lower terrace by openings in the lip, which are filled with rice straw in order to filter out sediments. The depth of water for rice - when flooded completely - is normally between 10 and 15 cm. Fertility is maintained by addition of farmyard manure, spreading the scraped soil from the riser, and also through sediment carried in the irrigation water. Nowadays, mineral fertilizers are also applied.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيبال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kathmandu
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Manmata subwatershed
Map
×3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
major cash crop: Potatoes
major food crop: Rice and wheat
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - steep slopes, not suitable for agriculture in their original state (better for forestry, agroforestry, horticulture, and fruit
trees)
- small and scattered plots of land
- land users find chemical fertilizers and water expensive
- there is water scarcity from September to May and too much rain in the monsoon period (June to August) with the danger of erosion and collapse of the terraces
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1 sq km2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wm): مجموعة كبيرة من الحركات الأرضية/انزلاقات أرضية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Layout of irrigated terraces. Openings in the lips drain excess water, grass cover stabilises lips and risers (right). After harvesting of rice, the grass is scraped off the lower part of the risers (left) and spread on the terrace beds
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, control of dispersed and concentrated runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: green/farmyard manure
Vegetative measure: fodder grass at risers
Terrace
Material: earth
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
ha
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting grasses including bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon). | نباتية | during monsoon |
| 2. | Construct bunds (risers) with soil from upper and lower sides | بنيوية أو هيكلية | before monsoon |
| 3. | Level terrace beds (soil moved from upper to lower part of terraces). | بنيوية أو هيكلية | before monsoon |
| 4. | Make lips on edges of terraces | بنيوية أو هيكلية | before monsoon |
| 5. | Compact risers | بنيوية أو هيكلية | before monsoon |
| 6. | Construct irrigation canal | بنيوية أو هيكلية | before monsoon |
| 7. | Make openings in lips for drainage of excess water | بنيوية أو هيكلية | before monsoon |
| 8. | Test-irrigate terrace for accurate levelling | بنيوية أو هيكلية | during monsoon |
| 9. | Plant grasses including Bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) | بنيوية أو هيكلية | during monsoon |
| 10. | After 2–3 years: some narrow terraces may be merged to form single, wider terraces | بنيوية أو هيكلية | during monsoon |
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Flood the paddy fields .. | زراعية | (June/July) / Repeated 3–4 times during |
| 2. | Slice/scrape grass and soil on lower part of risers and spread on terraces | زراعية | (when flooded, June/July) / |
| 3. | Plant rice and apply mineral fertilizer | زراعية | (June/July). / |
| 4. | Harvest rice | زراعية | (October) / |
| 5. | Apply manure (cattle manure), after rice harvest | زراعية | (October). / |
| 6. | Slice/scrape grass and soil from whole of risers and spread on terraces; repairsmall collapses/slumps in risers | زراعية | (October/November) / |
| 7. | Pprepare land | زراعية | (November) / |
| 8. | Apply mineral fertilizer | زراعية | (November/December). / |
| 9. | Irrigate | زراعية | Nov. / repeated several times during cultivation |
| 10. | Harvest of potato/wheat | زراعية | (January-March). / |
| 11. | Planting of rice | نباتية | June,July / |
| 12. | planting of potatoes, wheat | نباتية | November / |
| 13. | Repair of small collapses/slumps in risers. | بنيوية أو هيكلية | (Oct./Nov.)/ |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 185,0 | 185,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 840,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, spade, baskets, (doko), special tool for scraping
Current establishment costs are very difficult to determine since the majority of the traditional terraces were
established a long time ago. Costs depend closely on the present state of the land (forward sloping terraces or uncultivated) and the need for irrigation canals. Farmers say that construction now could cost up to US$ 10,000 per ha if carried out by hand at full labour cost. The cost given for maintening the terraces (approx. US$ 840 per ha) includes all associated annual crop production costs. In this case study, 100% of the construction costs were borne by land users.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good because of the geology and soil texture (loam)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Off-farm income specification: hired labour (on other farmers’ fields) or as porters
Market orientation of production system: Subsistence (rice/wheat) and commercial (potatoes)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
التعليقات:
Land use rights: leased (90% of farmers), individual (10%)
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
منطقة الإنتاج
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
the technology is a part of a complex farming system
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
دخل المزرعة
فروقات اقتصادية
التعليقات/ حدد:
not everyone has access to land for irrigation
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Livestock fodder
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
when the agreed and scheduled water extraction amounts are exceeded
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انزلاقات أرضية / تدفقات الحطام
التعليقات/ حدد:
poor maintenance of topmost terraces may cause landslides
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Soil fertility
Biodiversity
Number of crabs in irrigation water make holes in the terrace risers
التعليقات/ حدد:
which in turn can cause pipe erosion and riser collapse
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
Groundwater recharge
Soil moisture and nutrients downstream
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي للغاية
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Income and production increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper management of the terraces (including all maintenance activities) |
| Easier to cultivate flat terraces/less labour required (after establishment of terraces) |
|
Work sharing: traditional terraces are part of a long tradition of work sharing within the community with no external labourneeded How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prevent loss of well established traditions and norms |
|
Technology is easy to understand/apply. Increased opportunities for irrigation facilities: farmers without level terraces are not allowed (by the irrigation committee at village level) or do not claim irrigation water |
|
The irrigation element of this technology fosters social bonds within the community How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prevent loss of well established norms and traditions. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Decreased grass production (grazing area reduced) | Promote planting of high value grass species on risers (such as bermuda grass). |
| The farmers believe that the terraces are too narrow (for efficient use of tractors); they would like to have wider terraces |
Investigate possibilities of constructing wider paddy rice terraces on steep slopes, which, according to present experience, is not possible. |
| High labour costs for establishment. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
There is considerable literature on the construction and maintenance of irrigated terraces in general, but no references thatspecifically describe the traditional paddy rice terraces in Nepal
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية