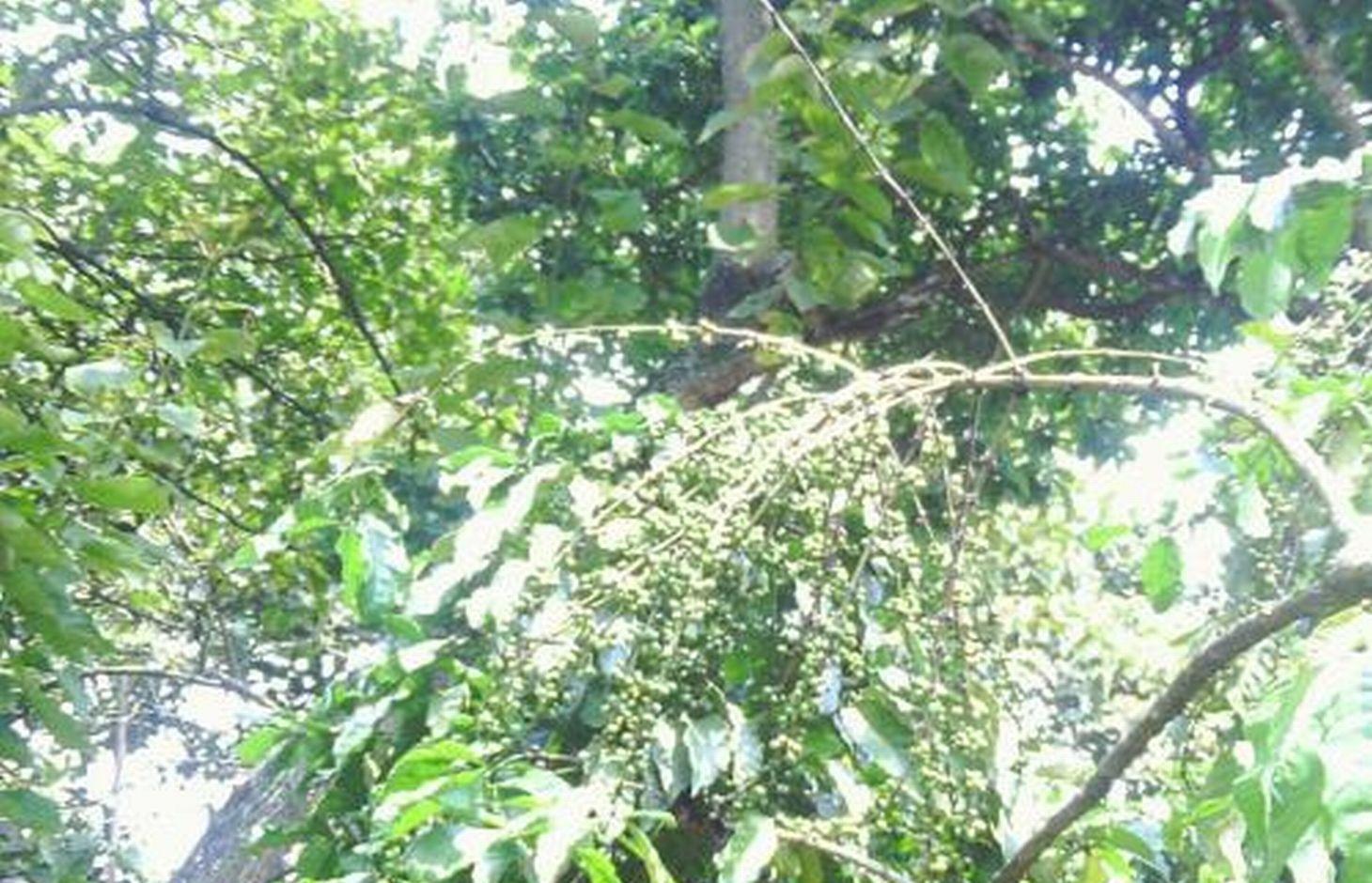
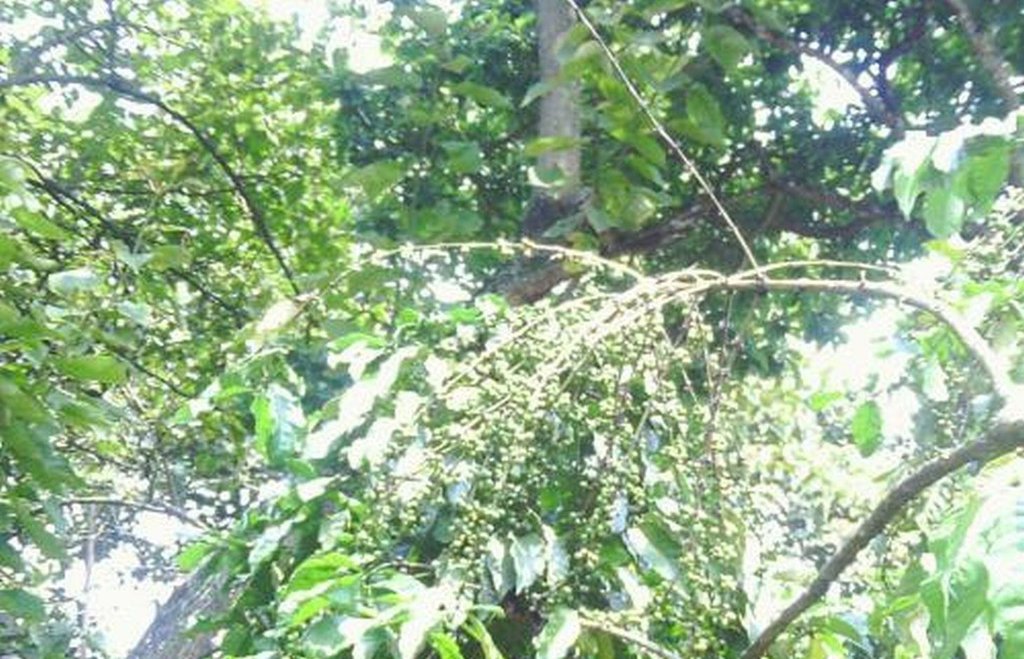
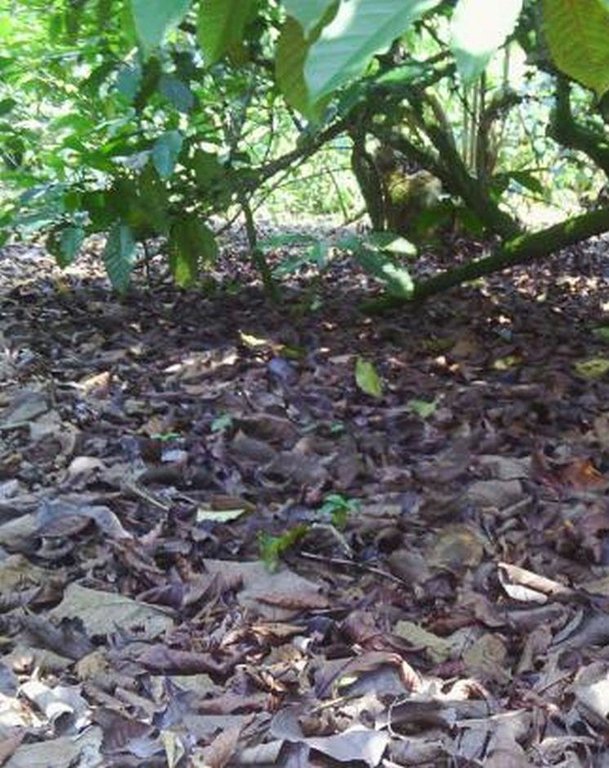
In situ mulching of coffee using Cordia Abbysinica [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Bertha Munyaga
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Alexandra Gavilano
Kgutela igitutu ckimwani
technologies_1191 - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
11/02/2014
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Use of indigenous trees to provide shade and leaves droppings as mulch for coffee production
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Establishment of Robusta coffee farms by an individual,on a cropland by mixing indigenous tree spp which provide a shade and dropping leaves save as natural mulch.The technology has been developed through land user initiatives over 40 years ago. Establishment activities include land clearing and preparation,preparation of holes,seed collection and planting which involve family labor Seeds are collected from neighboring village from mature trees. Holes are prepared randomly about 4 meters apart. No inputs are applied at the establishment stage only hand tools are used (hand hoe, matchet)
Shade trees are planted after establishment of coffee which are randomly planted, tree spp dominating is Cordia abbysinica which has broader leaves and easy to decompose.Other tree spp included are Erythrina,Meosopsis eminii,Ficus thornngii,Makhamia lutea and Tephrosia vogelii.
Maintenance include weeding which is done by pulling weeds by hand or using hand hoe at early stage after establishment because few leaves have dropped. The farm is mainly meant for coffee production however,few crops which are cassava bananas, fruit trees Jack fruit, Mangoes, Citrus spp which are planted in the peripherals,and Dracaena sppplanted to demarcate the farm along road side.
Pruning of tree branches is done before the shade is heavy as to allow ventilation.Coffee pruning is done to an individual tree depending on number of branches it has at time of harvesting, normally 4 branches are left. Bending of coffee branches is practiced to avoid branch breaking during harvesting.
Settlement is within the farm with few livestock which are sheep, cattle and chicken.
Purpose of the Technology: To increase coffee production by mixing coffee with indigenous tree spp which drop / shed its leaves.Selected trees are those broad leaved which its leaves decompose easily hence improve soil fertility and due to high accumulation of dropped leaves there is an increase in soil moisture content.
Trees act as wind break hence no flower drop.Dracaena spp are planted very close along the road side to demarcate his plot from neighbors and public infrastructure and this helps to reduce land conflicts among neighbors and community as well.
Hand weeding is done as the technology suppress weeds to the big shade.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A farmer bought a piece of land from the village government.Establishment activities include land clearance by removal of shrubs using a matchet.This is followed by land preparations and planting holes which are 30cm depth and 30cm width. These activities are done from May to July by family labor.Planting is normally done between September and October by collecting seedlings from mature trees in neighbors fields.Planting of indigenous tree spp is done randomly after coffee planting to allow ventilation 80 different spps are planted in 1.5 acres. Seeds and seedlings are obtained from neighbors farms.Maintenance includes weeding which is done using family labor who use hand hoe. This is done twice a year in May and December to January. Pruning and bending of coffee tree branches is done once per year after harvesting of coffee as well as trees in June and July using a matchet. Each coffee tree is treated individually only 4 branches are allowed per tree. Bending is done to avoid breaking of branches during coffee harvesting.
Gap filling is done few months after transplanting between February and March at the beginning of long rains. and this was followed pruning and bending of coffee branches.
Demarcation of coffee farm using Dracaena (shrub) done on one side of his farm along the road.
Natural / human environment: Land use type: Establishment of coffee has been done on crop land.
Agronomic: Natural mulch from leaves falling on ground.
Vegetative: Demarcation of boundary using Dracaena spp.
Climatic zone: Sub humid more than 269 growing days.
slope: 2-5% gentle slope
Soil type: Clay loam
Soil depth: Deep
Tools and inputs: Hand hoes,bush knife,axe, seeds and cuttings.
Land ownership: Individually owned.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tanzania
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Ngara District
التعليقات:
Boundary points of the Technology area: 236229742E 236229740E 236229639E 236229639E
9726279N 9726387N 9726293N 9726392N
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The technology was adopted from Muleba district and adapted in Kirusya village
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات

أراضي الرعي
- Tethering: rapid decline of land due to expansion of settlements and crop production
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, water loss/moisture stress, loss of nutrients through leaching and flower drop which lead to reduced yield.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Poor soil fertility and water stress
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: September-DecemberSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: March-May
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
10-25 LU /km2
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير الإدارية
- M3: التخطيط وفقا للبيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
التعليقات:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues, minimum tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (indigenous tree,fruits and coffee. (shrubs)), change in temperature (Loss of water due to evapo transpiration), labour availability (Vegetation degradation)
Secondary causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Change of seasonal rainfall), wind storms / dust storms (De flowering leading to production loss)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
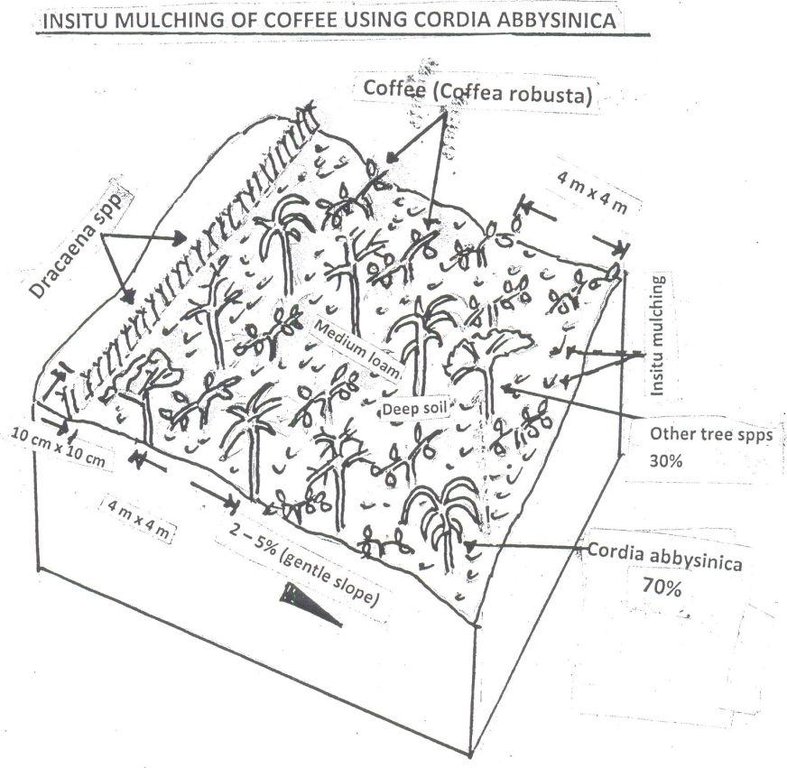
Indigenous tree are randomly planted and Cordia Abbysinica accounts for 70% of the indegenous tree spps. Demarcation of a coffee farm is done using Dracaena (shrub) done on one side of the farm along the road. Natural mulching is done by tree leaves/debris falling on ground. Slope category range from 2-5% gentle slope. Average spacing of Robusta coffee is 4m x 4m.
Location: Karushya Nyamigango. Ngara/Kagera/Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Mulching
Material/ species: leavesof indigenous trees drop
Quantity/ density: 6 cm depth
Remarks: natural falling and irregular aligment
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: indigenous trees
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Hand pulling sometimes use simple tools.
Aligned: -along boundary
Number of plants per (ha): 1,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Scattered / dispersed
Number of plants per (ha): 375
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 60
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 60
Trees/ shrubs species: Cordia abbysinica, Ficus spp,Erythrina spp,Makhamia spp,Tephrosia spp Maesopsis spp (planted)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: avocado, mandarine,
Perennial crops species: Coffee
Other type of management: (Land protection and demarcation)
Planting Dracaena along the road side
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Tanzanian shillings
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
1600,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
3000.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hole preparation | نباتية | Nov. |
| 2. | Seed collection and preparation | نباتية | Nov to Dec |
| 3. | Seedling planting | نباتية | Dec |
| 4. | Demarcation and excavation of small trench | إدارية | September-before long rains |
| 5. | Preparation of cuttings | إدارية | September-December |
| 6. | Actual planting | إدارية | September-December |
| 7. | labour | إدارية | |
| 8. | pangas (matchet) | إدارية | |
| 9. | handhole | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 10. | tree & coffee seedlings | نباتية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | 1,0 | 2510,4 | 2510,4 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | tools | 1,0 | 21,88 | 21,88 | 100,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | seeds | 1,0 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 100,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | 1,0 | 61,73 | 61,73 | 100,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 2625,26 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning-Trees-Coffee | زراعية | After harvesting, June-July |
| 2. | Weeding | زراعية | after long rain season |
| 3. | Gap filling | زراعية | March,during short rains |
| 4. | Bending and layering | زراعية | Once after harvesting |
| 5. | Gap filling | نباتية | before short rains |
| 6. | Prunning | نباتية | Dry season |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | 1,0 | 63,63 | 63,63 | 100,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | 1,0 | 33,05 | 33,05 | 100,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 96,68 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, panga (matchet) and axe, Panga (Matchet), hand hoe and axe
The cost assesment was completed on 18 February 2014. The cost of labour can be reduced during the onset of rain when the soil is a bit workable.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months above 18°C
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Tree and coffee pruning is done by men because it needs climbing
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land (He is getting income from coffee).
20% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Most of the residents are permanent farmers
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
Water is accessed friendly, land is inherited.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
16bags/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
58 bags/ha
إنتاج الأعلاف
إنتاج الخشب
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3cub.m/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
12cub.m/ha
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
62 kg/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0 kgs/ha
عبء العمل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
15 md/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2 md/ha
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
improved
الوضع الصحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
little
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
inreased
الفرص الثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
none
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
available
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
none
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
available
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
جودة المياه
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التربة
رطوبة التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
medium
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
medium
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
التعليقات:
Introduction of contour ridge
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
In 10 years he has obtained more money from sales of coffee and tree products
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Increased production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology among other farmers |
|
Easy maintenance acctivities e.g. easy to keep weeds under control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Fuel wood availability How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Availability of fruits How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Improved kowlledge regarding SLM and soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
This is cheap and affordable technology which can be used by smallholder farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology among other farmers |
|
Large potential for increased income (higher coffee yields) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Improve soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote crop and livestock intergration (manure production) |
|
Increased soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate maintenance acttivities |
|
Erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain sufficient soil cover |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Land competition with food crops | Promote technology among other farmers |
| High cost of tools, especially pruning scissors | Provide required tools |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Risk to fire during dry season | Introduce fire breaks |
| In areas where frost persist can lead to fungal diseases if not well pruned | Improve pruning |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية