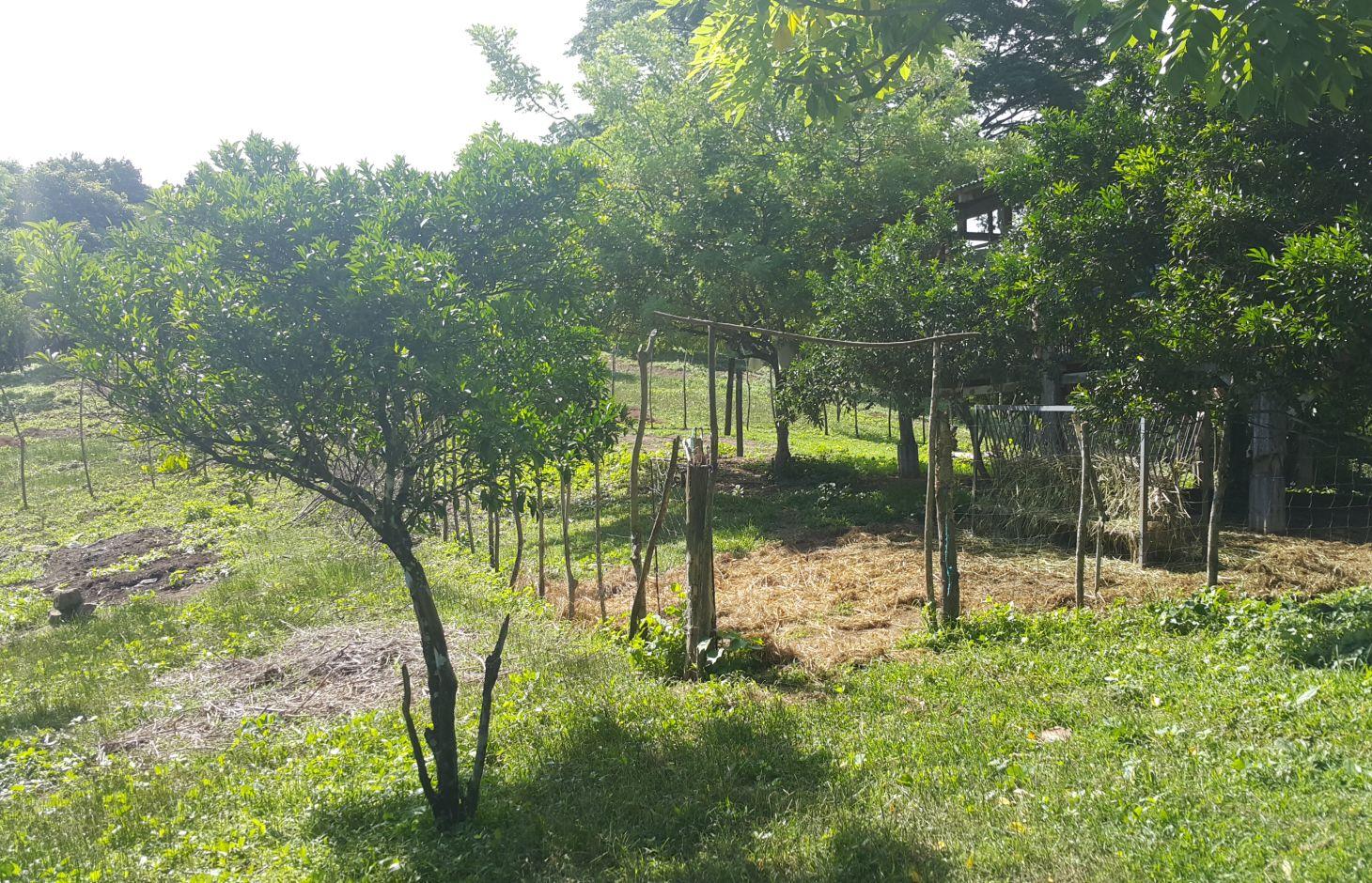
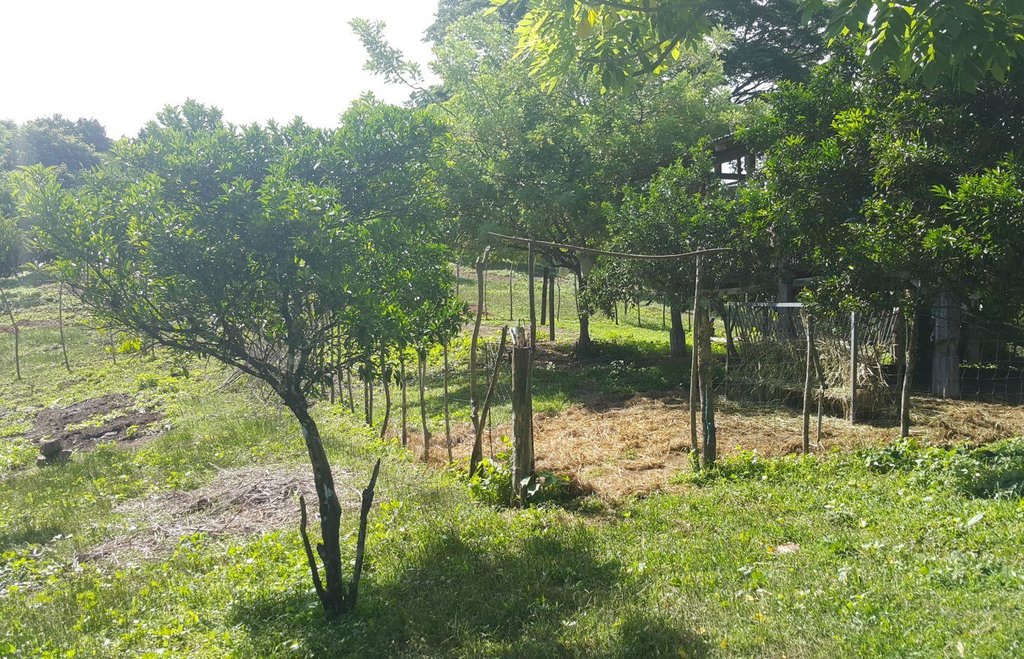
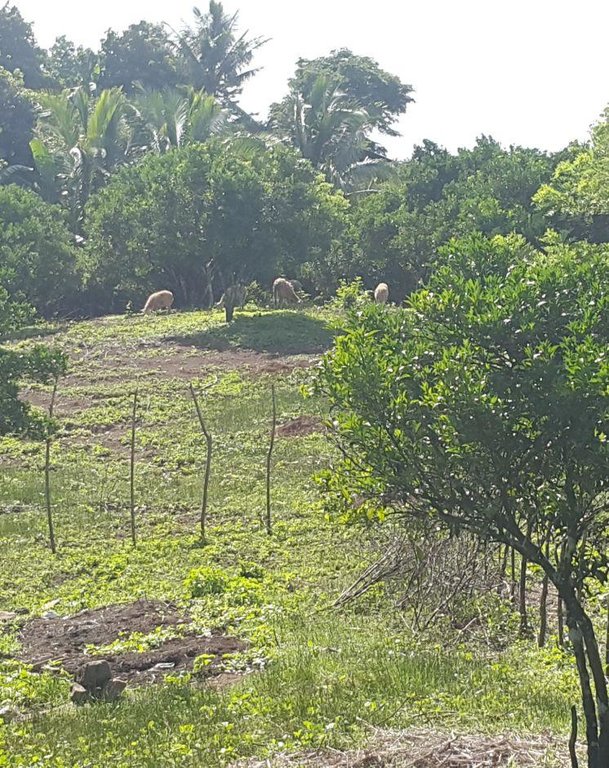
Improved pasture under citrus [الفيليبين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Pastulan sa ilalim ng dalanghitaan (Filipino)
technologies_1321 - الفيليبين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rojales Jose
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Calonge Arsenio
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Millare Kirby
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Quinto Jasmin
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Gultiano Wilfredo
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Cornes Jennelyn Mae
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - الفيليبين1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
29/06/2016
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [الفيليبين]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- جامع المعلومات: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
It is a farming system that integrates the growing of fodder crops under plantation crops.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
It is an integration of livestock and agronomic crop production of incorporating small ruminants in an existing citrus plantation. This technology was based on the private initiative of the farmer where he adapted it from other land users. He further improved it through study of reading materials and ad hoc monitoring of his environment.
Purpose of the Technology: After the adaption of the technology, the land user observed a decrease in the infestation of aphids. The land user observed and concluded that the decline in the aphids infestation was due to the presence of the small ruminants in the area. The small ruminants forage on grasses that were continuously growing, year-round, in the plantation area. The foraging of grasses improved the micro-environment of the plantation crop, which contributed to the decline and almost total eradication of aphids in the area, as observed by the land user. This promoted natural farming and improved the biodiversity.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The area was first established as a citrus plantation inter-cropped with Vigna unguiculata, Cucurbita maxima, and Ipomoea batatas, as cash crop during the vegetative stage of the citrus crop. As the small ruminants increased in number, the land user decided to do “controlled grazing” by dividing the area into 3 paddocks. During lean days of forage grasses, the land user practices “cut-and-carry” system of feeding. In addition, the manure of the small ruminants serves as a source of organic fertilizer for the citrus and other crops grown by the land user.
Natural / human environment: Aside from the eradication of the aphids on the citrus crop, the technology aided in the financial needs of the land user. It increased the land user’s income by an increase in the fruits bore by the crop and the increase in the number of the small ruminants. The land user sells or sometimes suppliers of citrus fruit and goat meat would go to the area to do wholesale buying. As for the community near the area, they to benefit from the area, by wholesale buying the citrus fruit and be the one selling it to the market. The technology does not only contribute to the livelihood improvement of the land user but also to the community.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الفيليبين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Bulacan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
City of San Jose Del Monte
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- experience from other farm land user
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
8 years
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Major cash crop:
Citrus

أراضي الرعي
- Silvo-pastoralism
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
Goat and sheep grazing in combination
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Possibility of pollution in the area. The land user might have applied pesticide to the citrus crops to control the pest, but the land user did not mention of it. Application of herbicide to control the growth of grasses within and outside the area.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Without land conservation, there was an occurrence of pest in the citrus plants.
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): silvo-pastoralism, goat and sheep grazing in combination
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: July to November
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية
- الإدارة المتكاملة للآفات والأمراض (بما في ذلك الزراعة العضوية)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.08 m2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bp): زيادة الآفات/الأمراض، وفقدان الحيوانات المفترسة
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (intercropping planting), droughts (time frame of drought)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (grazing of small ruminants), overgrazing (no. of small ruminants), change in temperature (dry season time frame)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Third goal: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
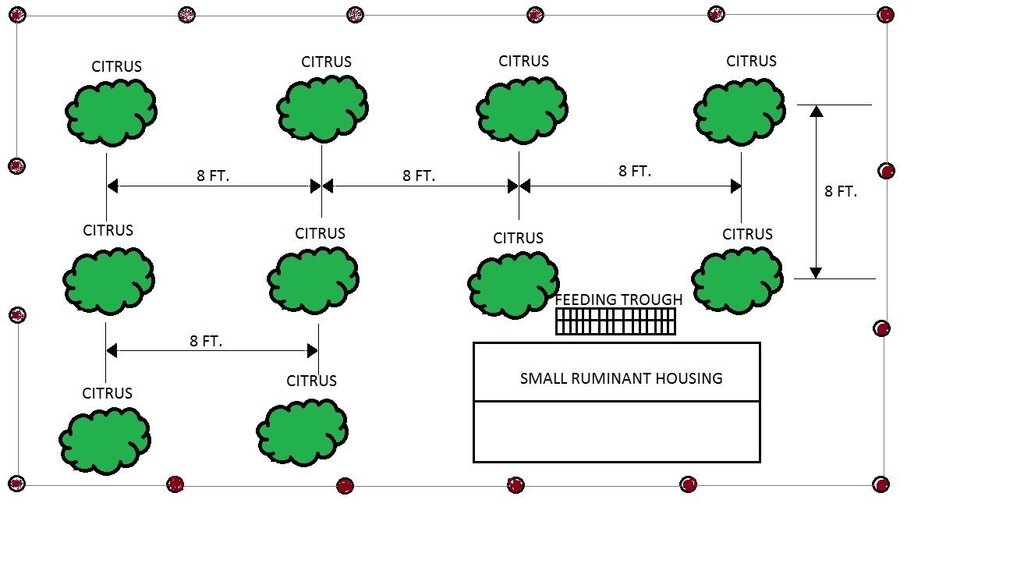
Citrus plants are evenly distributed in the area, with a planting distance of 8 feet by 8 feet. The ground cover are forage grasses for the small ruminants.
Location: Barangay San Roque. San Jose Del Monte, Bulacan
Date: 06/29/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (technical assistance from agricultural advisory from other aspect in land degradation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (land user is open minded with the technology introduced)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase of surface roughness, increase of infiltration, reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: pole sitao-squash-sweet potato/citrus
Agronomic measure: intercropping (1st Year)
Material/ species: pole sitao/citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (2nd year)
Material/ species: squash/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (3rd year)
Material/ species: sweet potato/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 8,800/188
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: goat manure
Quantity/ density: 5,000 kg
Remarks: .5 per square meter
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Philippine Peso
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
47,5
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5.26
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | rotational grazing | نباتية | rainy season |
| 2. | cut-and-carry feeding system | نباتية | dry season |
| 3. | Buying pole sitao | زراعية | |
| 4. | Buying sqaush | زراعية | |
| 5. | Buying citrus | زراعية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,52 | 10,52 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 3160,0 | 3160,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 48,0 | 48,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Hog wire | ha | 1,0 | 397,89 | 397,89 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 3616,41 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
Life span of products:
Pole Sitao - 1 year
Squash - 1 year
Citrus - 50 years
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,52 | 10,52 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 10,52 | |||||
التعليقات:
The above costs usually occurs during the dry season when forage grasses are scarce. Lean months of availability of forages grasses are from the months April to June. This is the time the cut-and-carry method is applied and the start of the maintenance/recurrent cost.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Cut-and-carry method of feeding the small ruminants during lean months of forage grasses.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
2382,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Ridges (concave)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is: Good
Soil water storage is: High
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: It is the countries socio-cultural model, where men is the one working and the women stay at home. According to the land user it is the women who is record keeper.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: off-farm income provides additional income to the land user during the dry season.
Market orientation: Subsistence (small ruminants are bought by the land user)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3,000 kilograms
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
8,000 kilograms
إنتاج حيواني
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5
تنوع المنتج
إدارة الأراضي
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
30,000
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80,000
تنوع مصادر الدخل
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
It gave an opportunity to the neighbors of the land user to work at the field, with pay. Thus, an added income to the neighbor of the land user. According to the land user, he was able to send his children to a decent school for a quality education. It also gave the land user another source of income by purchasing a jeepney used as a public transportation through the increased income from the SLM technogy he adapted.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The increased in the income of the land user contributes to the food security of the family
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Daily chores of herding the small ruminants contributes to the good over health of the land user
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and-carry" style of feeding contributed to the possible overgrazing which is contributor to erosion
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
The land user allows the member of his community to harvest some fruits and sell them to the market without the land user asking for something in return.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
جودة المياه
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and carry" style of feeding contributes to the reduction in surface runoff, grasses are maintained on the soil surface
تصريف المياه الزائدة
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduced soil in any form
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to nutrient recycling
الملوحة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to the increased in soil organic matter content
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further reduced alien species invasion
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further increased biological pest/disease control
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
سرعة الرياح
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface improves soil tilth which further improves infiltration capacity
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Manure of the small ruminants improves the soil tilth, an improved soil tilth improves the buffering/filtering capacity of the soil
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduces erosion due to wind
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | غير معروف |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | غير معروف |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Decreased in occurrence of pest |
| Increased land user's income |
| Helped the land user's neighbor by profit sharing during harvest of the citrus fruits |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Less labor input How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the varietal species of the forage grass |
|
Decreased in occurrence of pest How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain the existing micro environment |
| Rotational grazing |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| There was an inbreeding of the small ruminants | Putting another small ruminants of good genetic quality |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Variety of forage grass is of low quality in terms of crude protein content | Planting of improved variety with a high crude protein content |
| Species of small ruminants are not of good genetic quality in terms of meat quality | Putting of species with a good genetic quality in terms of meat produce |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [الفيليبين]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- جامع المعلومات: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية