Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration [النيجر]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Julie Zähringer
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
technologies_1340 - النيجر
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rinaudo Tony
tonyrinaudo@worldvision.com.au
World Vision
Melbourne
أستراليا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Pasternak Dov
d.pasternak@icrisatne.ne
ICRISAT
Niamey, Niger
هولندا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICRISAT International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) - النيجراسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
World Vision (World Vision) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
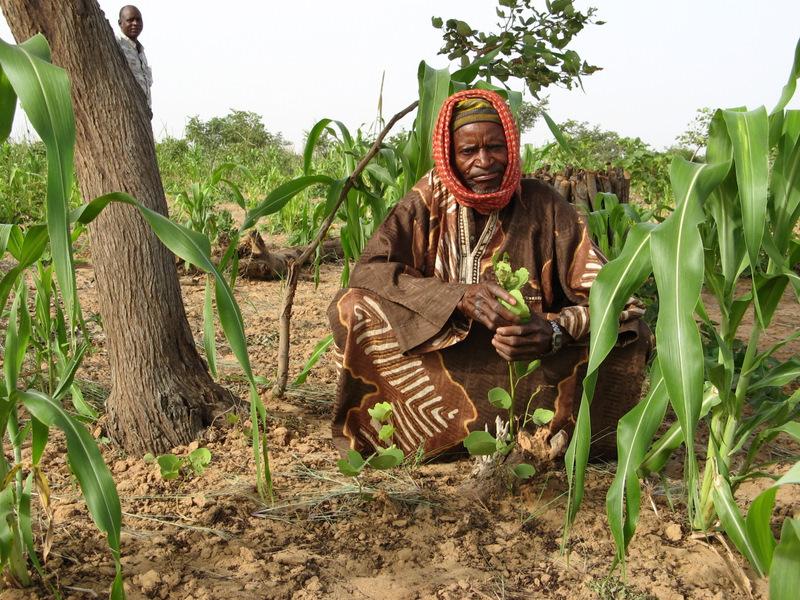
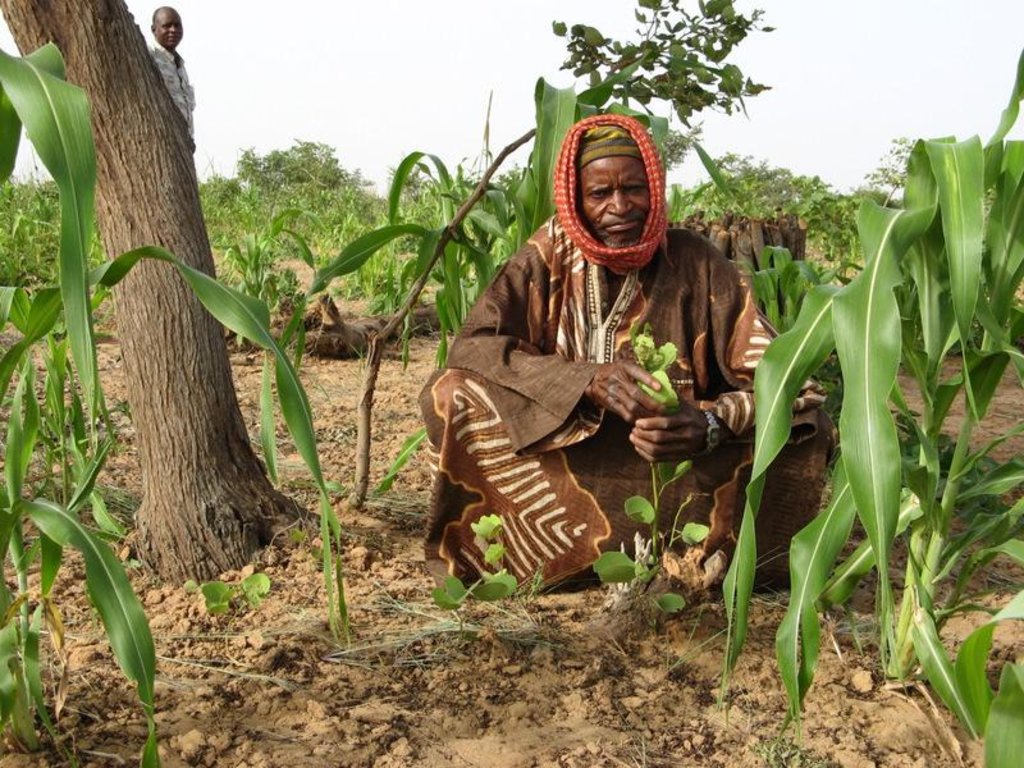
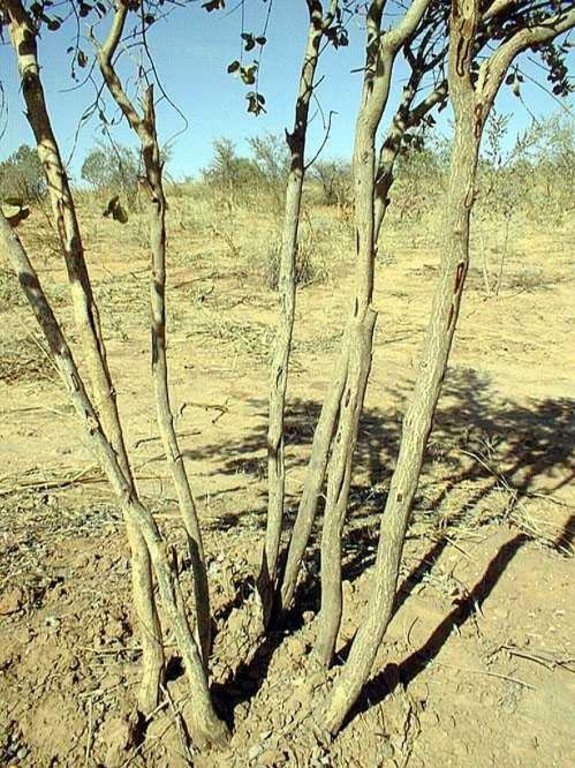
تعريف التقنية:
FMNR is the systematic regeneration of living and sprouting stumps of indigenous vegetation which used to be slashed and burned in traditional field preparation.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
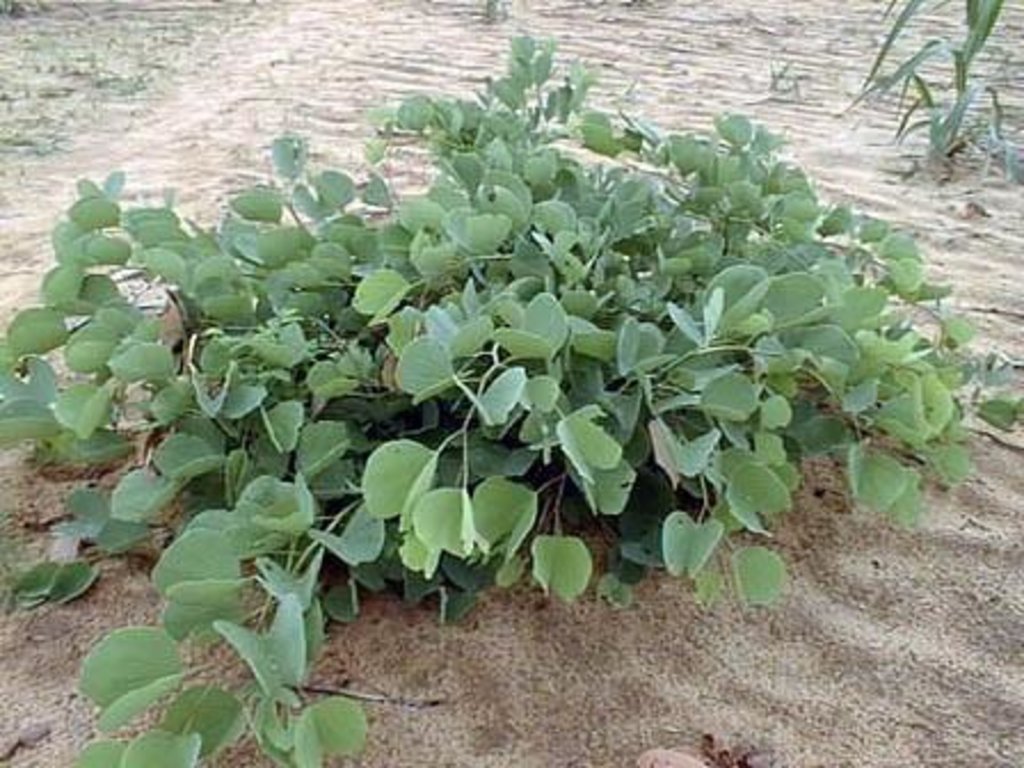
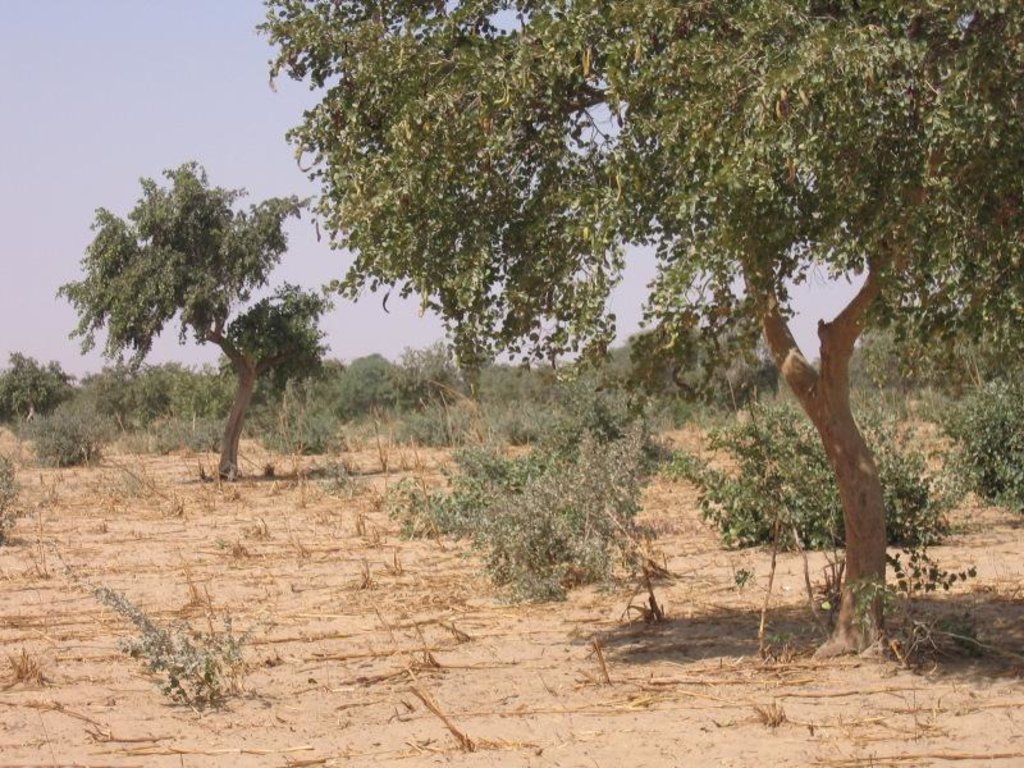
The naturally occurring seedlings and/or sprouts are managed and protected by local farmers. Most suitable are species with deep roots that do not compete with crops and have good growth performance even during poor rainy seasons. In the case study area the three most valuable species – as perceived by land users – are Faidherbia albida; Piliostigma reticulatum and Guiera senegalensis.
Purpose of the Technology: This option allows idle land to become a productive resource during an otherwise unproductive eight-month dry season.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The ideal density, when grown with cereal crops, is between 50 and 100 trees per hectare. For each stump, the tallest and straightest stems are selected and side branches removed to roughly half of the stem height. Excess shoots are then removed. Regular pruning of any unwanted new stems and side branches stimulates growth rates. Farmers are encouraged to leave 5 stems / shoots per tree, cutting one stem each year and letting another grow in its place. On removing a shoot, the cut leaves are left on the surface where they reduce erosion and are then eaten by termites, returning the nutrients to the soil. The remaining shoots continue to grow, providing a continuous supply of wood. From the first year, firewood is collected from trimmings. From the second year on, cut branches are thick enough to sell. A more intensive form of FMNR is to profit from every stump sprouting on the land.
Natural / human environment: FMNR is a simple, low-cost and multi-benefit method of re-vegetation, accessible to all farmers, and adapted to the needs of smallholders. It reduces dependency on external inputs, is easy to practice and provides multiple benefits to people, livestock, crops and the environment. Tree layout will need to be carefully considered if ploughs are used for cultivation.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيجر
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Maradi
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
early 1980's
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Deforestation, Wind erosion, Water deficiency, Movement of sand dunes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الغابات الطبيعية وشبه الطبيعية
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 50000 km2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية
- (Ed): الانكماش والترسب

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Ha: aridification
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase of infiltration
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 50
Trees/ shrubs species: Faidherbia albida, Piliostigma reticulatum, Guiera senegalensis
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select 50 - 100 stumps per hectare for regrowth during the dry season | نباتية | dry season |
| 2. | Select the tallest and straightest stems and prune side branches to roughly half the height of the stem (using sharpened axe or machete and cutting upwards carefully) | نباتية | |
| 3. | Remove excess shoots, leave the cut leaves on the surface | نباتية | |
| 4. | Prune any unwanted new stems and side branches (each 2-6 months) | نباتية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 6,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cut one stem (per tree) each year and let another grow in its place | نباتية | |
| 2. | Once the stems selected for growth are > 2 meters high, they can be pruned up to two thirds | نباتية | |
| 3. | Prune any unwanted new stems and side branches (each 2-6 months) | نباتية |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 4,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: All activities carried out manually
Annual income from selling wood: US$ 140 (from the 6th year after implementation). By some estimates, total benefit per hectare (incl. wood sales, increased crop yield, increased livestock productivity, wild foods and medicines etc) are in the order of US$ 200/ha, compared to an investment in labour US$ 10-15.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Main costs are in the form of labour. One man could prepare one hectare in 1–3 days, depending on tree density (labour is undertaken by the farm owner and rarely through paid labour). No inputs used; no extra tools needed, tools are available on-farm (hoe, axe, machete etc). Maintenance costs depend on tree density also and could require 1–2 days/year/ha.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 200-300 m a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
At least doubled
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Nutritious pods as fodder
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
Production value increased by 57%
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Annual clearing and burning of tree stems (for land preparation) is not necessary any more
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Edible leaves/fruits; bridge food shortages
quality of life
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced wind speeds and dust; shade is available; barren landscape is returning to a natural savannah
disaster risk reduction
التعليقات/ حدد:
FMNR acts as an insurance policy
livelihood and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
30
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
45
التعليقات/ حدد:
trees / ha
Increased tree density on farmland
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
Dung; livestock spends more time in fields with trees
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
From leaf fall and trimmings
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Creation of habitat, food and shelter for predators of crop pests
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Regenerated trees are indigenous and generally have mature root systems
سرعة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Resulting in greater deposition of rich, wind blown silt; improved micro-climate
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
Urban populations benefit from cheaper, sustained wood supply and reduced incidence of dust storms
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Annual income from selling wood: US$ 140 (from the 6th year after implementation).
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Spread has been largely spontaneous, with minimal external assistance. The area covered today by trees from FMNR is estimated to be more than 50,000 km2 in Niger.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| FMNR is a simple, low-cost and multi-benefit method of re-vegetation, accessible to all farmers, and adapted to the needs of smallholders |
| It reduces dependency on external inputs, is easy to practice and provides multiple benefits to people, livestock, crops and the environment |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Scarce presence of live tree stumps | alternatively broadcast seeds of indigenous species (reduced short-term benefits; high mortality rates) |
| Cultural norms and values: ‘a good farmer is a clean farmer’ (= no trees) | work with all stakeholders to change norms |
| Land (including trees) is treated as common property during dry season; damaging and removing trees on other people’s land occurs | create sense of ownership of trees: (1) Encourage communities to develop rules that respect property; (2) Local forestry authorities granting informal approval for farmers to be able to reap the benefits of their work. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Rinaudo T (1999): Utilizing the Underground Forest: Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration of Trees, in Dov Pasternak and Arnold Schlissel (Eds). Combating Desrtification with Plants.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Cunningham PJ and Abasse T (2005): Reforesting the Sahel: Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration; in Kalinganire A, Niang A and Kone A (2005). Domestication des especes agroforestieres au Sahel: situation actuelle et perspectives. ICRAF Working Paper, ICRAF, Nairobi.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Haglund E, Ndjeunga J, Snook L, and Pasternak D (2009): Assessing the Impacts of Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration in the Sahel: A Case Study of Maradi Region, Niger (Draft Version)
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية