Primary strip network system for fuel management [البرتغال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Celeste Coelho
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Primary strip network system for fuel management
technologies_1361 - البرتغال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Louro António
Aflomação - Forest Association of Mação
البرتغال
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ventinhas Marta
Aflomação - Forest Association of Mação
البرتغال
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Bragança Nuno
Aflomação - Forest Association of Mação
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mariano Inês
Aflomação - Forest Association of Mação
البرتغال
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - البرتغالاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Forest Association of Mação (Aflomação) (Aflomação) - البرتغال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
16/10/2011
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
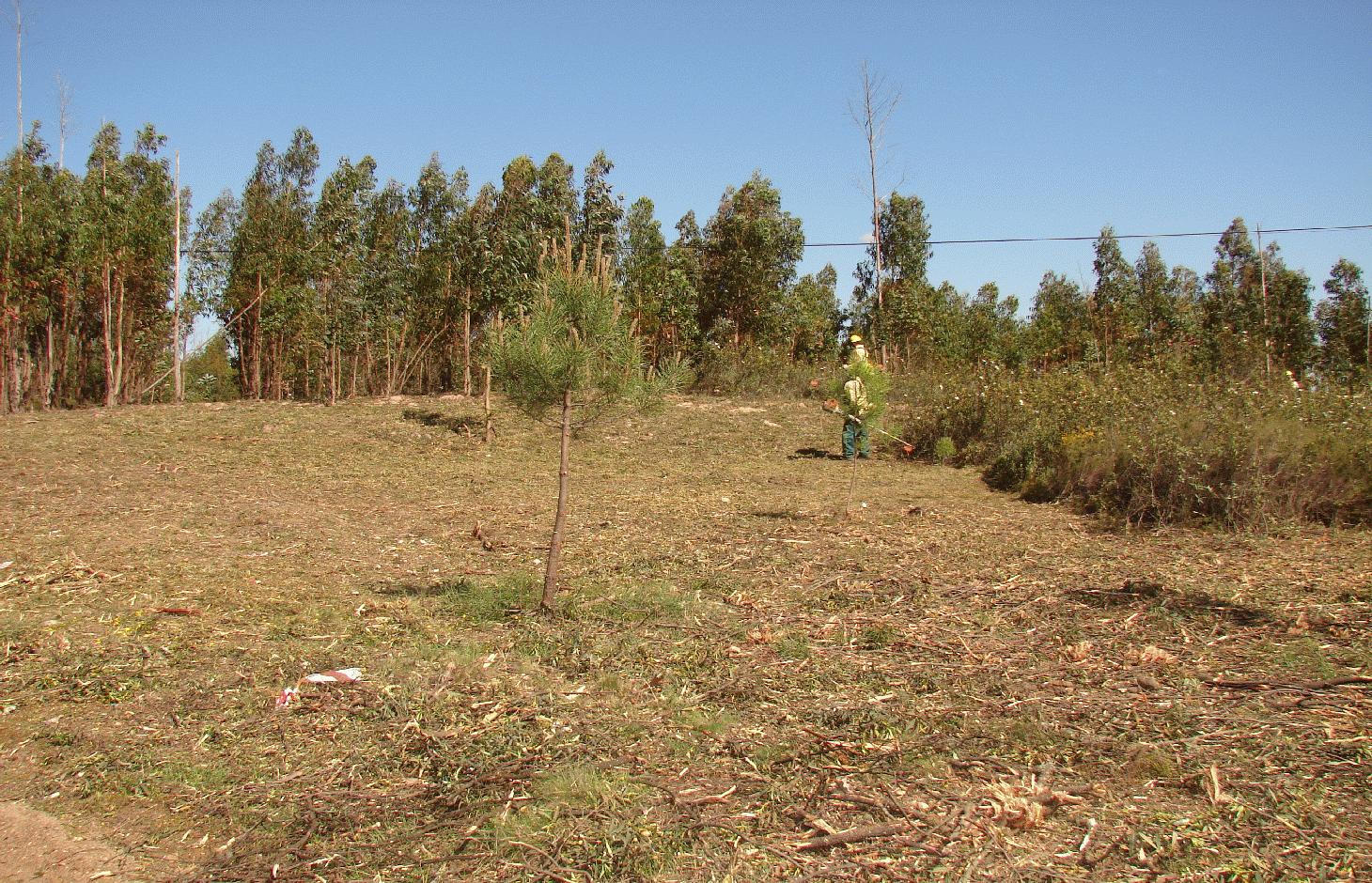
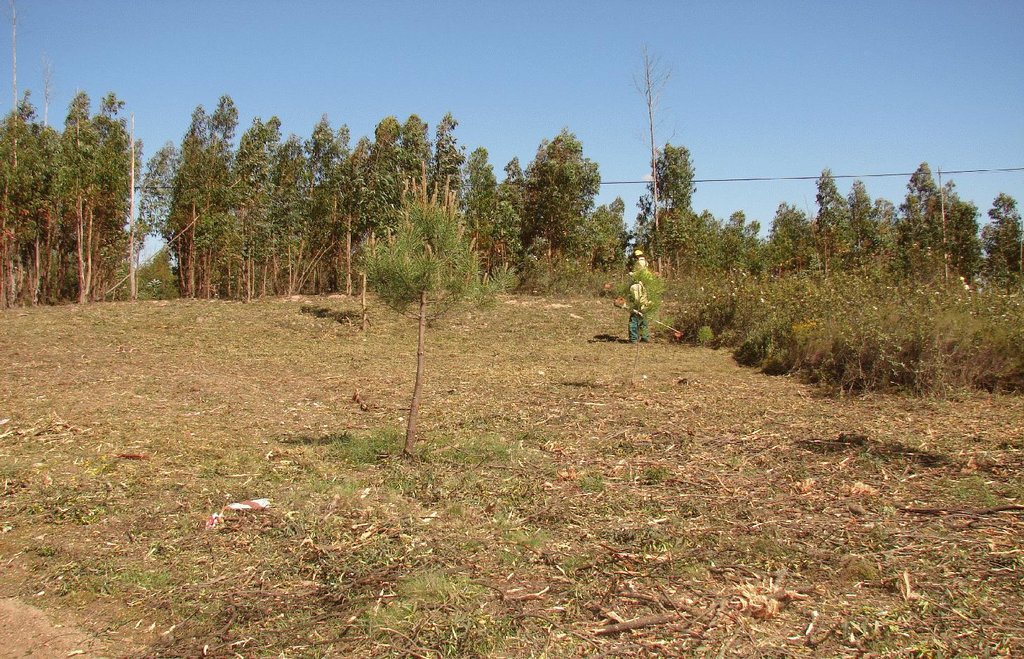
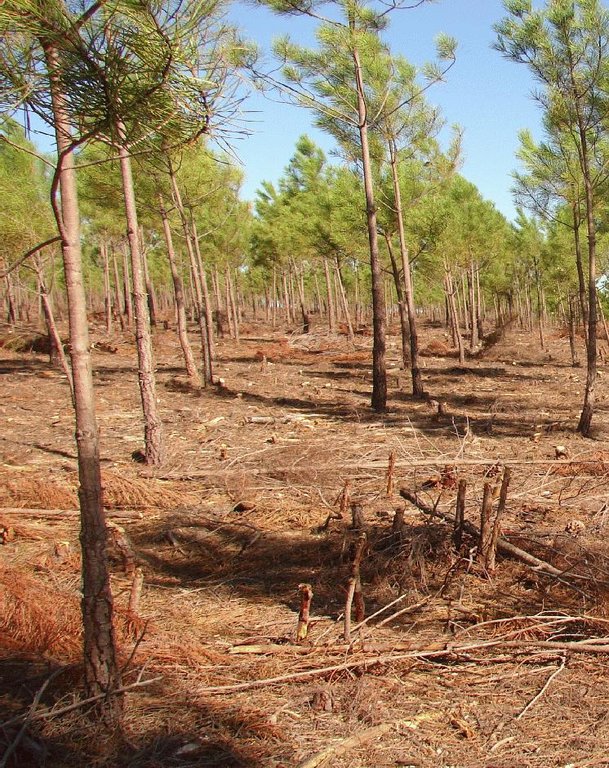
Linear strips are strategically located in areas where total or partial removal of the forest biomass is possible. This technology contributes towards preventing the occurrence and spread of large forest fires and reducing their consequences for the environment, people, infrastructures, etc.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
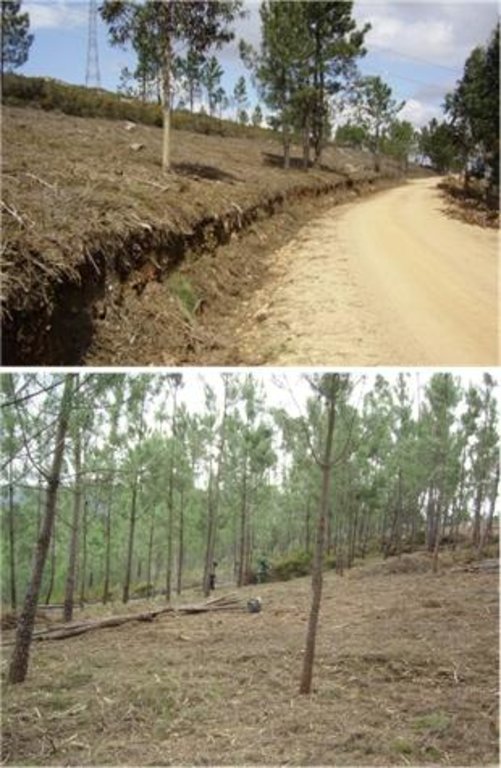
There are three types of strip for fuel management in forest areas: primary, secondary and tertiary, defined by the Law 17/2009. The most important differences between them are in terms of size (primary being the widest and the tertiary the narrowest) and scale (primary referring to the district level, secondary to the municipal level and tertiary to the parish level). The primary strip network system for fuel management (RPFGC) is integrated in the National System to Prevent and Protect Forest against Fires and it is defined by the National Forest Authority (AFN).
Purpose of the Technology: The RPFGC aims to re-arrange landscape elements, through the establishment of discontinuities in the vegetation cover, in forest areas and in the rural landscape (for example using water bodies, agricultural land, pasture, rocky outcrops, shrubland and valuable forest stands). Land tenure is private in most of the areas covered by the RPFGC. The main objectives of this technology are: to decrease the area affected by large fires; to enable direct access by fire fighters; to reduce fire effects and protect roads, infrastructures and social equipment, urban areas and forest areas of special value; and to isolate potential fire ignition sources.
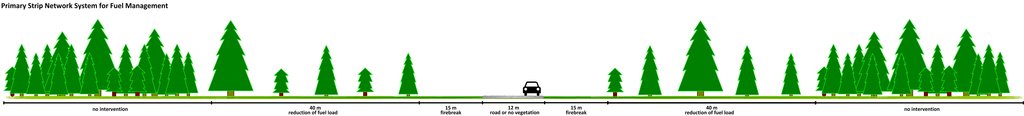
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: These primary strips are ≥ 125 metres wide and preferably between 500 and 10,000 ha in area. The tree cover should be less than 50% of the area and the base of the tree canopy should not be lower than 3 metres. The RPFGC concept should include the adoption of a maintenance programme. The implementation and maintenance operations can be performed through different agro-forest technologies, such as clearance of bushes and trees, pruning, prescribed fire, harrowing and cultivation of the ground beneath the trees. Timber products can be sold and the removed litter can be used in a biomass power plant or applied to the fields to improve soil fertility, using mulching technology.
Natural / human environment: This SWC Technology needs considerable financial resources in terms of labour and equipment at the implementation phase. Costs, however, undergo considerable reduction thereafter. The implementation of this infrastructure to prevent and protect the land from forest fire is entirely funded by the government and implemented by the forest municipal services.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
البرتغال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Portugal
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Santarém / Mação
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
- قطع الأشجار الكلي
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الحرجي
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
Main species: Goats and sheep.
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Forest fires increase due to rural depopulation and to land management abandonment.
Other grazingland: silvo-pastoralism: Goats and sheep.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Pine.
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: Eucalyptus.
Other type of forest: clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: Eucalyptus.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood
Constraints of settlement / urban: Proximity of forest to urban areas.
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): Ignition sources.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 1Longest growing period from month to month: 1 per year
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الغابات الطبيعية وشبه الطبيعية
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث بالاستناد على النظام البيئي
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 400 m2.
There has been some work carried out to develop the secondary system of linear strips for fuel management. These will provide the basis for the implementation of the primary system. The PROF | PIS - Plano Regional de Ordenamento Florestal do Pinhal Interior Sul (Regional Plan for Forestry Management and Planning of the Pinhal Interior Sul) has designated an area of 1752 ha with a total length of 141 km as the contribution to the primary system of fire prevention by the Mação municipality.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S11: غير ذلك
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bf): الآثار الضارة للحرائق
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bf: detrimental effects of fires
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Forest fire frequency and intensity.), Property size (Small pieces of land (< 0.5 ha).)
Secondary causes of degradation: Population density (Ageing population structure and depopulation.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المؤلف:
João Soares, University of Aveiro, Campus Universitário de Santiago, 3810 - 193 Aveiro, Portugal
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
This technical drawing indicates the technical specifications, dimensions and spacing for the Primary Strip Network System for Fuel Management. The figure shows a road as the axis of the RPFGC, but it can also be a river or a ridge, amongst other breaks in the forest cover.
Location: Portugal. Santarém / Mação
Date: 16/01/2009
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of fires
Secondary technical functions: reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Euro
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,76
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
18.75
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Primary System design | بنيوية أو هيكلية | n. a. |
| 2. | Shrubs cleaning + Thinning (reduction of fuel load) + Pruning | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
| 3. | Removing the cut waste material | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 4. | Litter Shredding | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 5. | Transport to the Biomass Plant | بنيوية أو هيكلية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 1076,0 | 1076,0 | |
| معدات | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 568,0 | 568,0 | |
| معدات | Transport | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1744,0 | |||||
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
The costs calculation was made for the implementation of the first section of the RPFGC. The implementation phase lasted for 2 or 3 months during the dry season. This section included 28 ha and 4 teams of forest sappers were involved.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The costs include the activities to ensure the vertical and horizontal discontinuity of the fuel load and also the activities needed to manage the waste produced from the shrubs cleaning and thinning.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
The rainfall ranges from 1000 mm in the North to less than 600 mm per year in the South of the municipality.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average is very shallow: Thin and stony terrains
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative; 2%
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
50% of the land users are poor and own 50% of the land.
Level of mechanization is manual labour or animal traction (Small machines are used)
market orientation is mixed (more subsistence than commercial).
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, < 0.5 ha, 2-5 ha
Size of forest/ woodland area per hosuehold: 25 plots.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
Individual, not titled: Usually, legal documents for the property are missing.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
telecommunications:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, produces fresh growth for grazing.
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
The new growth provides more diverse and nutritious fodder.
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
The low fuel load can be maintained through grazing.
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
Most of the primary system will be implemented in zones of low productivity. However, in some areas tree thinning can cause a decrease in wood production.
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase of by-products from grazing.
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
The use of wood as a fuel for a power station and the use of vegetation to feed the cattle can promote the development of new crops and land uses.
In some areas, the implementation of the primary system can occupy productive land. The main aim of this technology is always to provide protection from forest fires instead of creating productive land.
توليد الطاقة
التعليقات/ حدد:
After cutting the shrubs, biomass is taken to a plant to energy production.
The cleared ground, on mountain summits, of the primary system is used for wind farms. Cleared vegetation could be used as fuel for a power station.
الدخل والتكاليف
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The strips will mainly occupy areas of low productivity. The vegetation removed can be used as fuel for a power station. The maintenance of the primary system through grazing will create opportunities in terms of cattle grazing and all the resulting by-pr
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Costs of implementation
التعليقات/ حدد:
The implementation of the primary system is very costly.
Maintenance costs
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved air quality by reducing forest fires risk.
الفرص الثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Some forest owners can have some difficulties in accepting the loss of their land to this technology. This can be even more difficult if they have some wood production on such land, so that it represents an income reduction.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
reduced risk of wildfire
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Associated with the vegetation removal.
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Associated with the vegetation removal.
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, enhances the diversity of the new vegetation cover. In some cases thinning the trees will have a positive effect by reducing the competition for water, sunlight and nutrients and (...)
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Sometimes a loss which is associated with the immediate effects of vegetation removal.
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, enhances the appearance of new plants.
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
The fuel load management in the primary system, involving the implementation of good forest practices, including the removal and control of invasive species.
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, enhances the appearance of new plants and consequently of new associated animals. The installation of fodder on the strips will promote grazing activities, increasing the number of goats, (...)
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
But also increased habitat fragmention
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
خطر الحريق
سرعة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
In some cases, where there is a total removal or a huge reduction in vegetation cover.
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Risk towards adverse events
التعليقات/ حدد:
This technology is an impediment to forest fire propagation and therefore reduces fire risk.
Soil erosion
التعليقات/ حدد:
Usually, the soil in the areas designated for the implementation of the primary system is thin and poor. The use of machinery and vegetation removal can accelerate the soil erosion processes.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
التعليقات/ حدد:
Forest area.
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The technology aims to reduce forest fire frequency and intensity, and the associated damage.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The maintenance will only start 2 or 3 years after the technology implementation, so no returns are expected at short-term.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: 100% of the technology was implement by local administration, with support from the government.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: After the implementation period there was a high local acceptance of the technology. It is also expected that grazing activities contribute to the technology maintenance
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Fuel load reduction How can they be sustained / enhanced? This will be achieved using prescribed fire and specialised machinery. The efficacy of prescribed fire depends on the collaboration of technicians and forest sapper teams. To guarantee the effectiveness of RPFGC implementation, long-term maintenance has to be ensured. |
|
Reinforcement of the forest path system How can they be sustained / enhanced? Clearing the strips of the RPFGC can enhance the forest track network. |
|
Forest fire prevention and fighting How can they be sustained / enhanced? The know-how of the local stakeholders and communities will contribute to the design of the RPFGC . This information should be integrated into the Municipal Plans to Prevent and Protect Forest Against Fires (PMDFCI). Any further information should be provided to the Civil Protection Agencies and to the Forest Technical Office and also to the local fire-brigade team. |
|
Increase in landscape resilience How can they be sustained / enhanced? This will only be effective if the RPFGC is continuous and without gaps. The acceptance of the RPFGC by the landowners is fundamental to widespread the use of this technology. Information and awareness about the need to change vegetation cover is also very important, in order to avoid extensive areas of monoculture. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Soil erosion increase | Forestry good practices should be used in the RPFGC implementation, especially concerning the use of machinery and avoiding disturbance of soil at depth. Soil cover after the removal of the existing vegetation should be promoted (by seeding, mulching or creating a low intensity pasture). |
| Soil cover reduction | Soil cover after the removal of the existing vegetation should be promoted (by seeding, mulching or creating a low intensity pasture). |
| Runoff increase | Soil cover after the removal of the existing vegetation should be promoted (by seeding, mulching or creating a low intensity pasture). Excessive vegetation removal should be avoid, especially near water courses where the removal should be nil or minimum. |
| Budget for implementation and maintenance | European and national funds. Collaboration of the local government providing equipment and labour force. Information and awareness to the landowners about the importance of this technology. Campaigns of national awareness and definition of this technology as ‘public use’ to overcome some potential social conflicts concerning the land rights. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Decree-Law n. 124/2006, 28 June. Official Gazette n. 123 – I series: 4586-4599; Decree-Law n. 17/2009, 14 January. Official Gazette n. 9 – I series: 273-295.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية