Terrace [الصين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Meili WEN
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Terrace
technologies_1367 - الصين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - الصين1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
18/05/2002
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
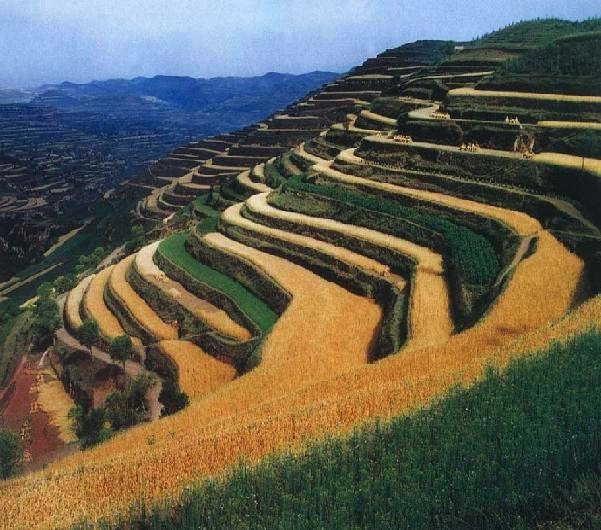
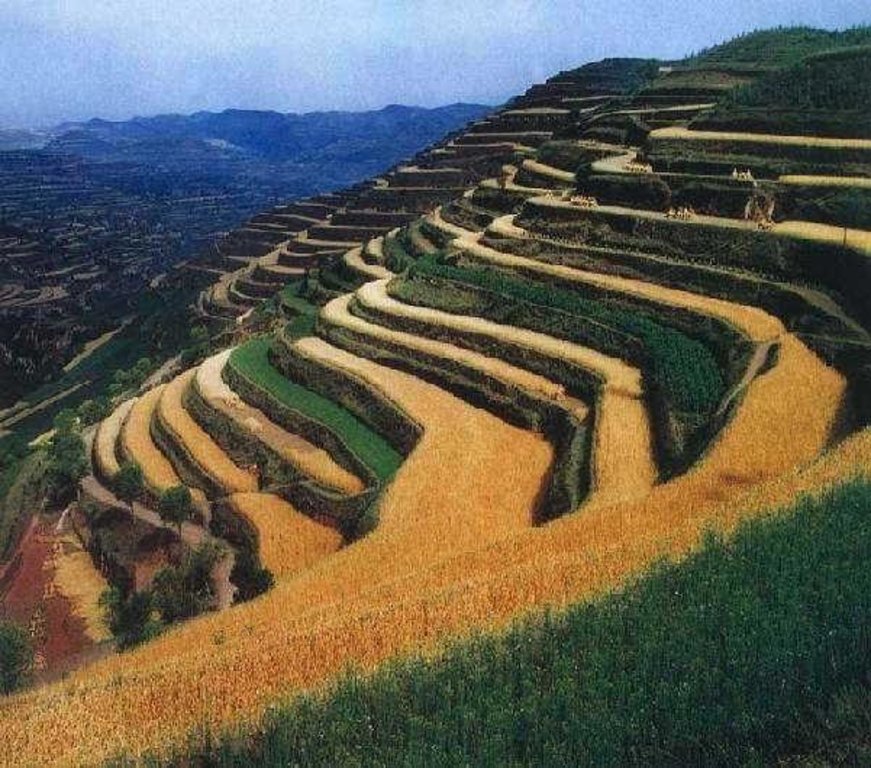
A terrace is a kind of measure to change the slope, which has a raised bank of earth or stone with vertical or sloping sides and a approximately flat top.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
A terrace has a raised bank of earth or stone with vertical or sloping sides and a approximately flat top. It can reduce slope angle and length, retain runoff, increase infiltration and reduce the soil loss. Crops can grow well because water increases in soils. Meanwhile, ground cover is improved. Terrace can be constructed by manual labor or machine. Firstly, determining the width of the field according to the slope angle and soil texture. Secondly, putting the topsoil aside. Thirdly, leveling up the slope and constructing banks. At last, putting the topsoil to the top of the flat surface.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الصين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Shaanxi, Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Henan, Gansu
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Summary from farmers' long term experience in SWC, later being innovated.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
maize, Pease
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water lose seriously, soil degrades, soil fertility decreases and crop yield declines.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): crop yield declines, weak ability of resisting drought
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Water supply also mixed rainfed - irrigated
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: May-Sep
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- > 10,000 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 26666.7 m2.
Terrace is one of the most outstanding achievements in SWC in China. It can prevent soil and water loss so that slope land can be sustainable development. There are about 26.7 million ha of terrace in China, of which more than 13.3
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
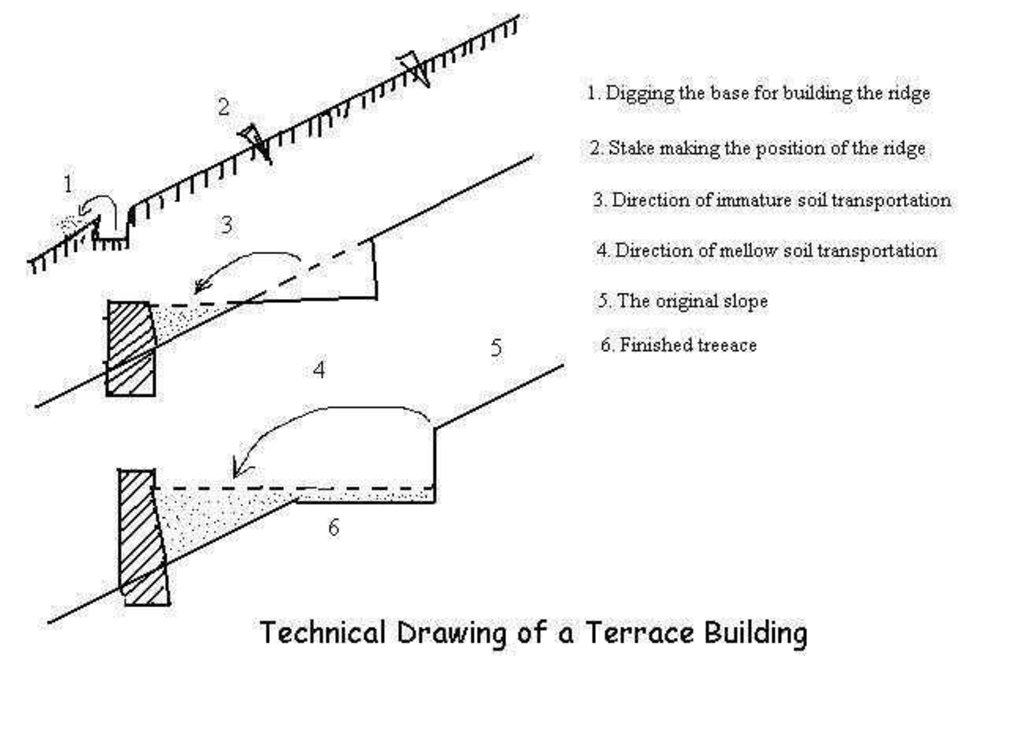
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Drawings of a terrace building in the Loess Plateau
Location: the Loess Plateau. Shaanxi, Shanxi, Henan, Gansu, Inner Mongolia
Date: 2002
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Construction material (earth): Construct ridge of terrace
Construction material (stone): Construct ridge of terrace
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 10%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 80%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:6
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
3.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | survey | بنيوية أو هيكلية | After harvesting crop |
| 2. | constructing terrace: determine the excavation line which should make the excavation and the filling equal and the least workload | بنيوية أو هيكلية | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 3. | constructing terrace: pilling mellow soil up to the middle of a bench | بنيوية أو هيكلية | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 4. | constructing terrace: moving the immature soil of lower part to fill the upper part or moving the soil from inside to fill up outside | بنيوية أو هيكلية | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 5. | constructing terrace: building the ridge | بنيوية أو هيكلية | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 6. | constructing terrace: spreading the mellow soil on the surface | بنيوية أو هيكلية | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | periodically inspecting | بنيوية أو هيكلية | After a storm/About 1 year |
| 2. | repairing where terrace is collapsed | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Whenever finding it is destroyed/timely |
| 3. | level up the field | بنيوية أو هيكلية | after harvesting crops/timely |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Terrace section, building by bulldozer.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The factors are topography, soil texture, means of construction. The section of terrace is the most important factor.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
449,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average also rolling
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
مستوى المكننة:
- الجر الحيواني
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Relative level of wealth: all selected
Relative level of wealth: very rich, rich, average, poor, very poor
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: estimate
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- مجتمعي/قروي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
4
التربة
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
180
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
58
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي للغاية
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: If they have enough money, they would like to do, because they have known the benefits from terraces.
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
(inner resources) Suide Water and Soil Conservation examination station of Yellow River Water Resources Committee.. 1981.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
orpus of Test Research of Water and Soil Conservation (the second volume), p130~185.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
(inner resources) Water and Soil Conservation Department of Yellow River Water Resources Committee of Ministry of Water Resources and Electric Power.. 1987.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Corpus of economic benefits of water and soil measures, p77~102 ,510~514
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Dongyinglin,Changpiguang ,Wangzhihua. Discussion on the several questions on increasing production of the terrace with two banks.. 1990.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.1, p36~37
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Jiangdingsheng. Discussion on section design of the terrace on the Loess Plateau.. 1987.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ACTA CONSERVATIONIS SOLI ET AQUAE SINICA, Vol.1, No.2,p28~35.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Liangqichun, Changfushuang , Liming. A study on drawing up budgetary estimate quota of terraced field.. 2001.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, Vol.21,No.5, p41~44.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Liumingquan, Zhangaiqin, Liyouhua. Pattern engineering of reconstruction the slope cropland.. 1992.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.3, p18~21.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Lixuelian,Qiaojiping. Synthetic technology of fertilizing and improving production on the new terrace.. 1998.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.3, p13~14.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Ministry of Water Resources of China. Terraces in China.. 1989.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
The press of Jilin science & technology.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Wangxilong,Caiqiangguo,Wangzhongke. The consolidating function and economic benefit analysis of the terrace hedgerows in the hilly loess region of northwest Hebei Province.. 2000.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Journal of Natural Resources,Vol.15, No.1, p74~79.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Xuyuanxu.The surveying report of the terrace benefits in yanbian autonomous prefecture. 1995.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Water and Soil Conservation,No.4, p50~52.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Zhujianqiang,Lijing. Experimental study on soil compact characteristics and its shearing strength in changing slope field into terrace on south shaanxi province.. 2000.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ransaction of the CSAE,Vol.16, No.2, p36~40.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية