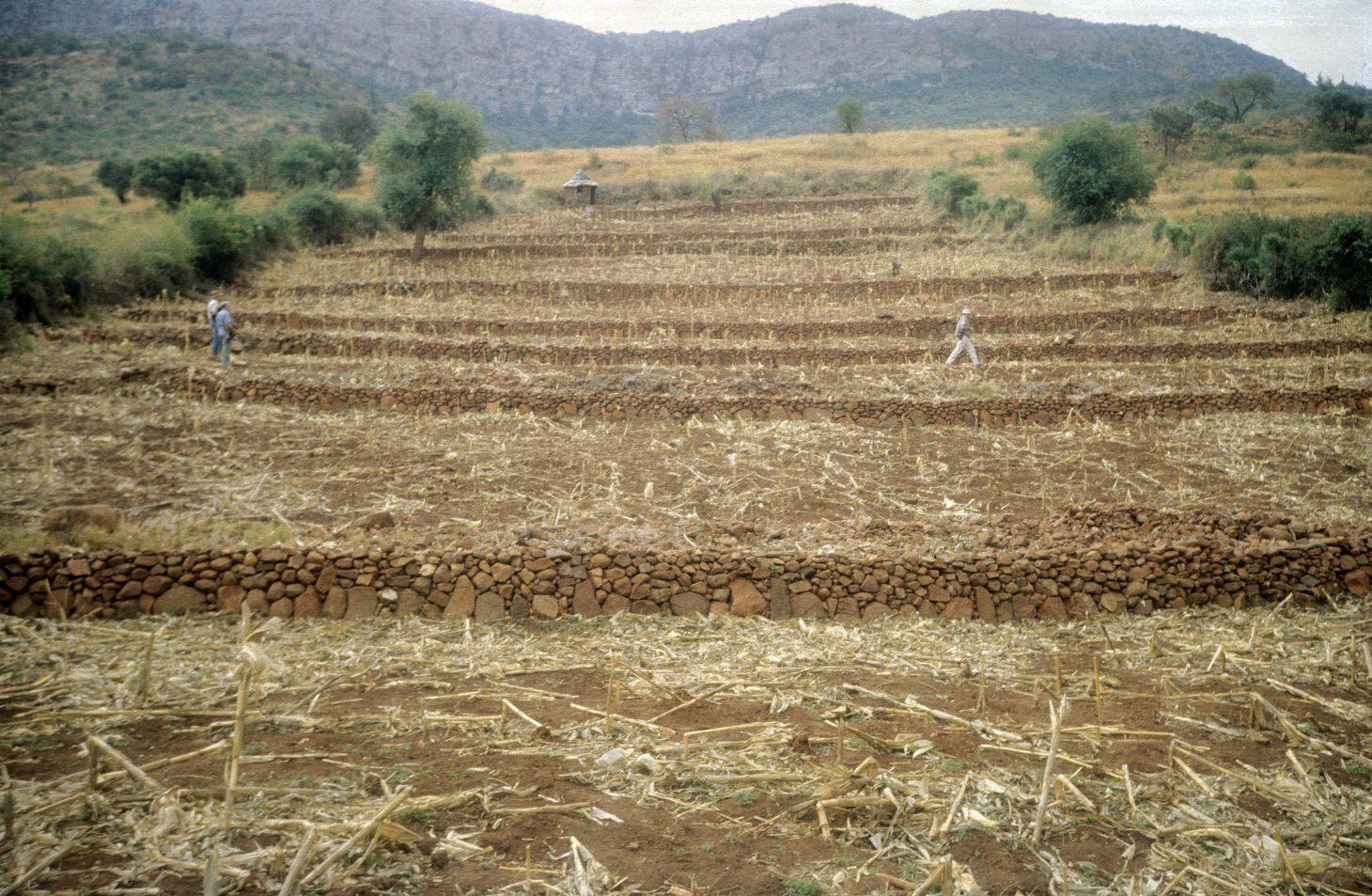
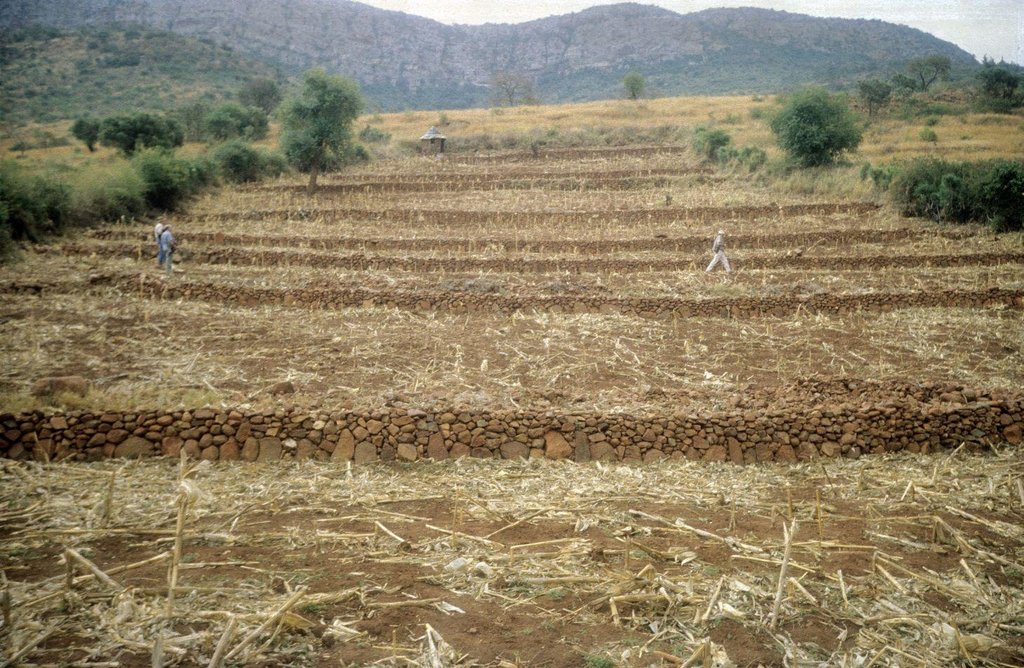
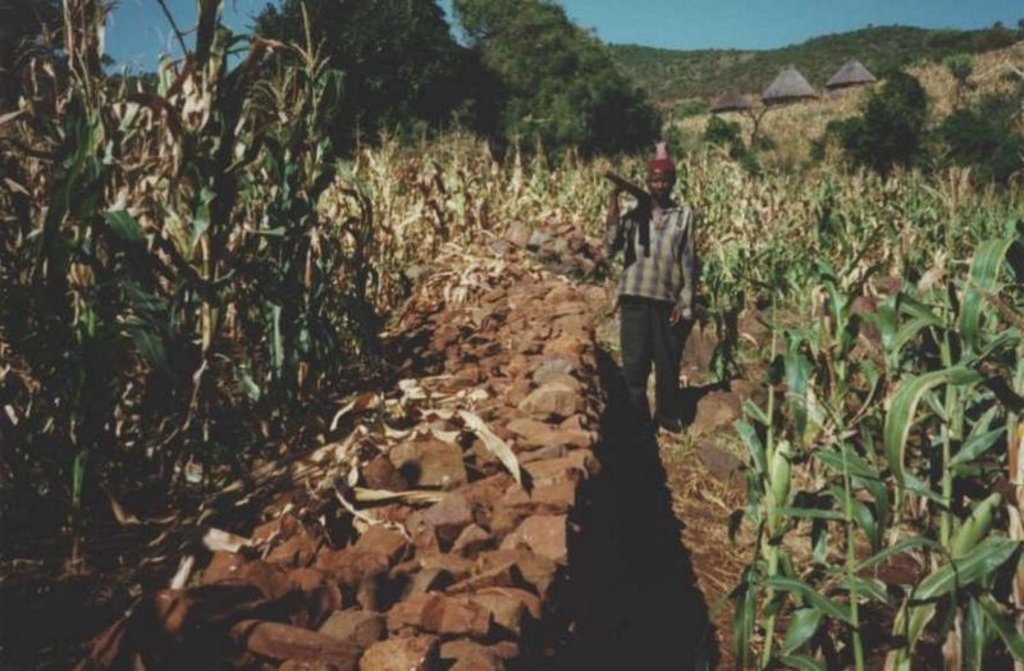
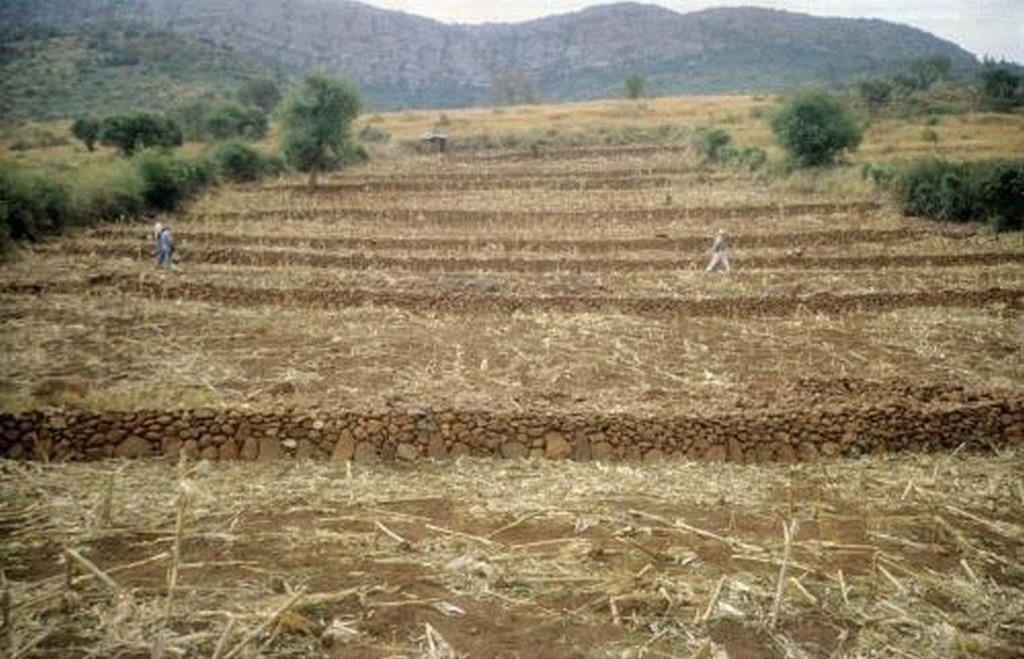
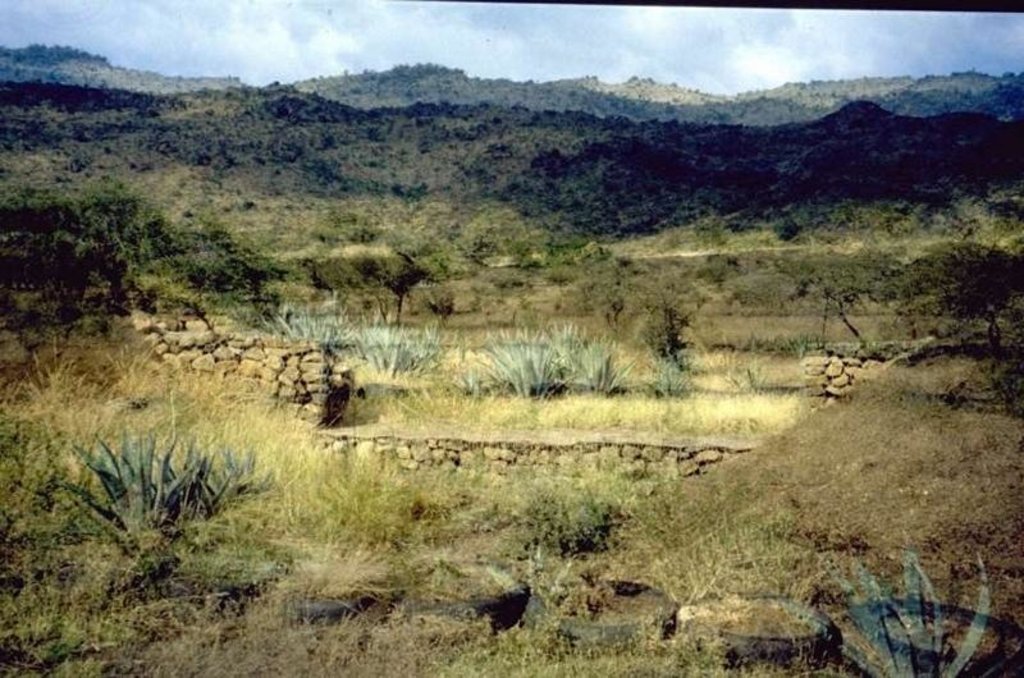
Traditional stone wall terraces [جنوب أفريقيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: William Critchley
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Mitsheto (Venda language)
technologies_1369 - جنوب أفريقيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CIS-Centre for International Cooperation (CIS-Centre for International Cooperation) - هولندا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
16/08/1997
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
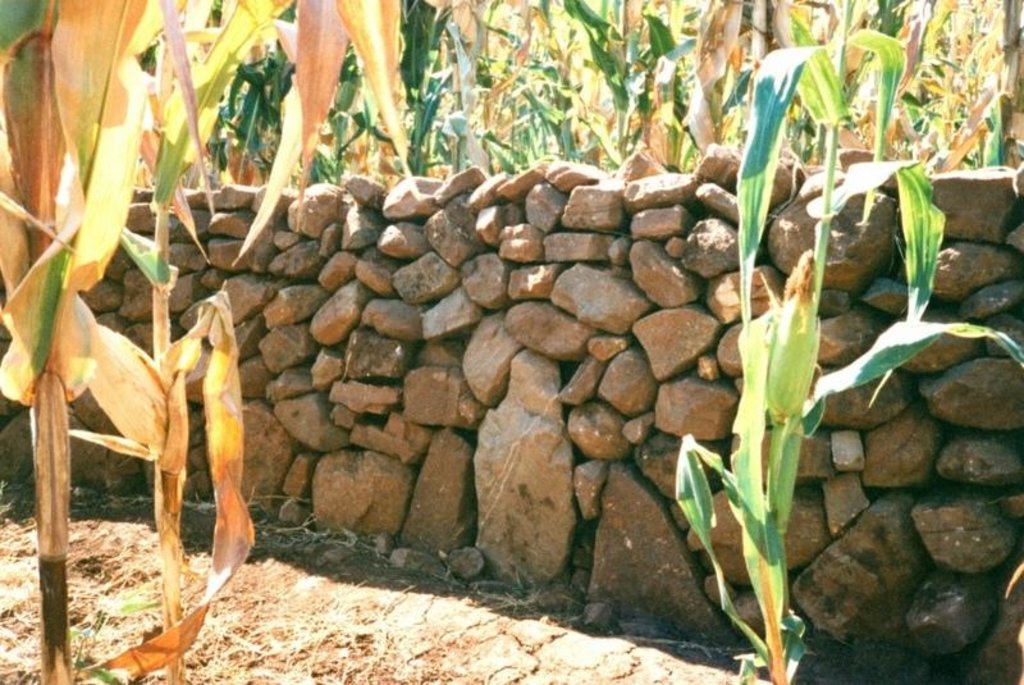
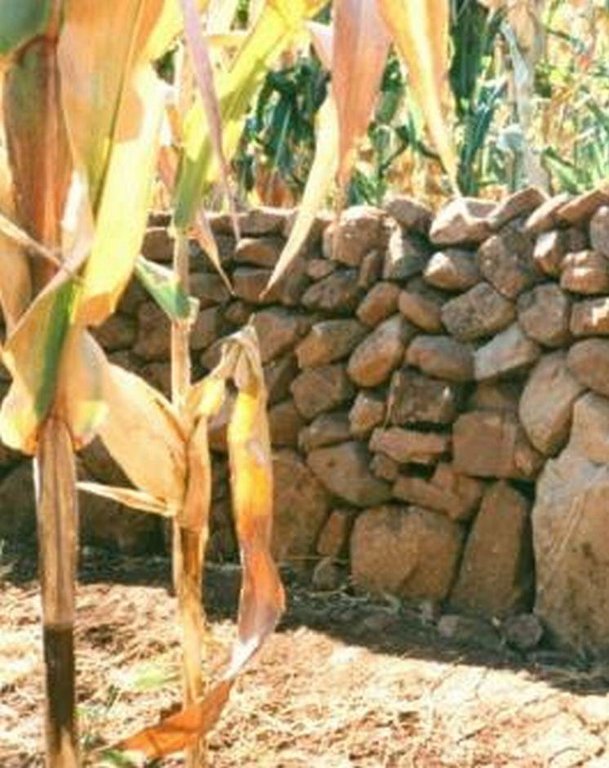
Stone walls built on sloping fields to create terraces for cultivation and conservation: both ancient and contemporary.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
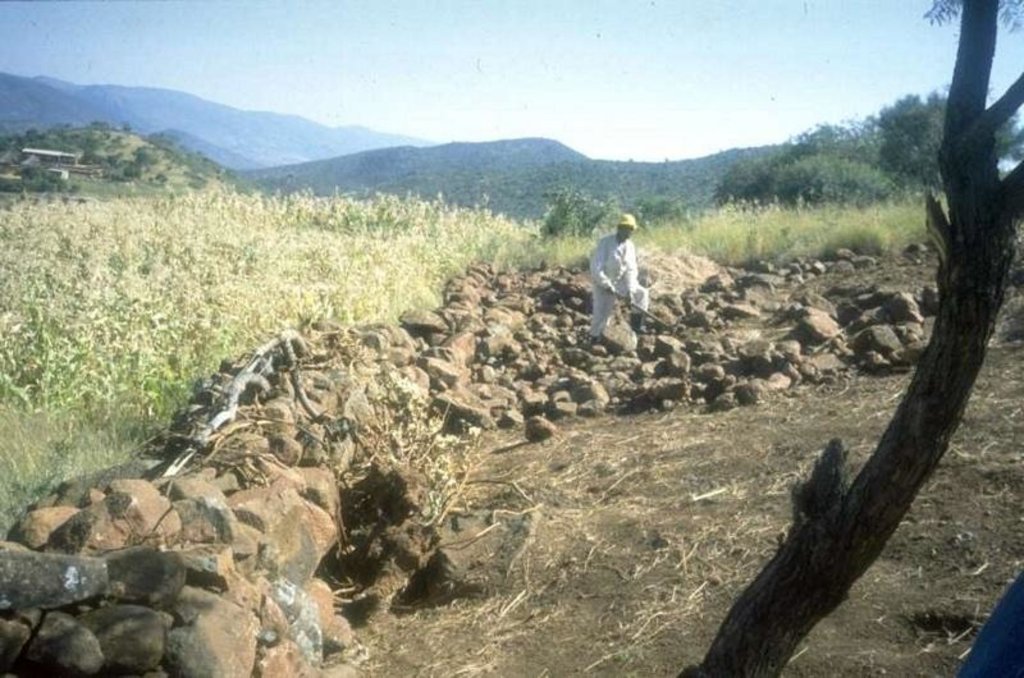
In this hilly, mixed farming area, stone terrace walls are a tradition. They are built across the slope when new land is cleared of loose stone and brought into crop cultivation. The dimensions of the terrace walls and the spacing between them depend on various factors, especially the slope and the amount of stone in the field. The walls may be up to 1.25 m high, from 1.0 to 1.5 m in base width, and between 20 and 50 m long. Spacing is from 3 to 10 m apart. Design of stone terrace walls varies. Some walls are very neatly built, others are merely piles of stone across the slope: this depends on the individual land user. The walls are built up each year with further stones: this may just be as more loose stone comes to the surface when ploughing, or also by digging out larger stones to deliberately build up the height of the walls as it silts up behind. Such terracing is generally confined to slopes between 20% and 50%. From 12% to 20% contour grass strips (thambaladza) are normally used, but below 12% land is rarely protected with structures or strips.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of terracing, apart from simultaneously clearing the land of stone, is to guard against loss of topsoil. Together with contour ploughing this helps to keep soil fertility in place on sloping cropland in a subhumid area. Rainfall is around 1,000 mm per annum and maize is the most common crop, but various other annuals (beans, pumpkins, sorghum etc) and perennials (peaches, avocadoes, oranges etc) are also grown.
Natural / human environment: This example of land conservation is probably unique in a former South African ‘homeland’. In such areas, where the black population were concentrated at high population densities under the former apartheid regime, land degradation rather than soil conservation was the rule. These terraces continue to be built to this day as new land is opened up, despite the high amounts of labour (300-500 person days per hectare) involved in establishment. A study of the conservation systems used in the area and local attitudes to them, showed that the benefits of conservation were well understood by local farmers (see reference). Those questioned identified retention of soil - and of soil fertility in particular - as being of paramount importance. No mention was made of terraces being built simply to remove surface stone. The only downside mentioned (by a few) was the loss of cultivable land area. The key to the persistence of the terraces in this area is, therefore, that the land users understand and appreciate the place of terraces in maintaining soil fertility, and their considerable contribution to crop production.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
جنوب أفريقيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Limpopo Province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Thononda Ward (Thohoyandou district)
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
May have originated with the Shona of Zimbabwe and the tradition brought with them when some moved south to Venda
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
major cash crop: Maize and avocado
major food crop: Maize
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Agreement with the land-user
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Decline in fertility of soil, erosion on roads/from roads, yield burning leading to runoff.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Nov - May
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 8 km2.
Within the Northern region of South Africa's Northern Province (formerly "Venda") a few areas are apparently covered with ancient stone terraces - but Thononda Ward of Thohoyandou district is the best example and the only one
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (slope), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Slope/rainfall)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Burning of veld/grazing land upslope)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
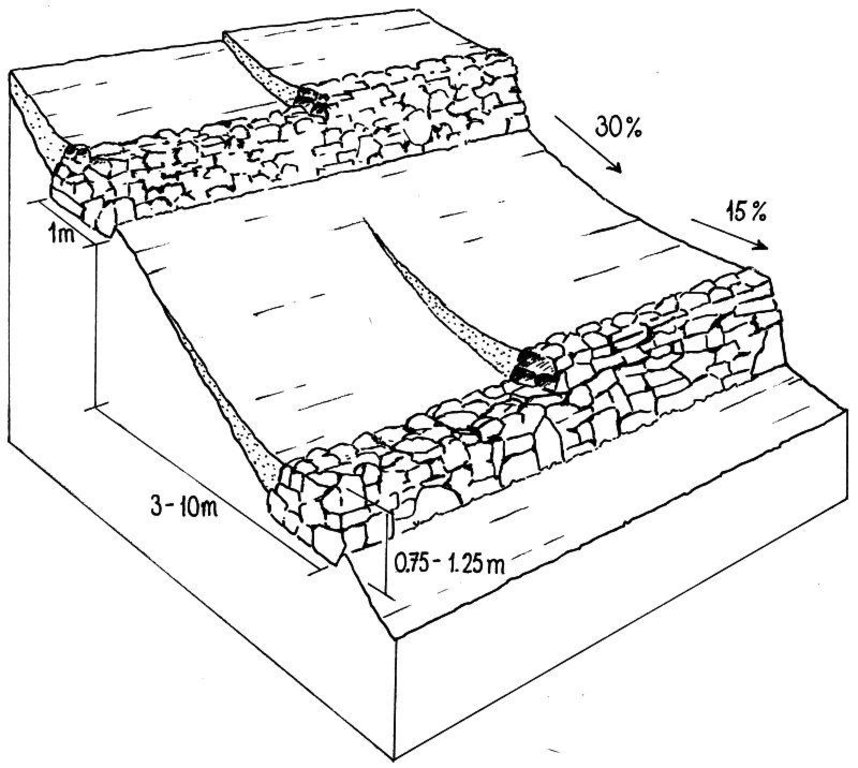
Layout of stone wall terraces: the walls are built up over time (right) as soil accumulates behind the barriers.
Date: Northern Province
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Structural measure: Bunds/banks: contour
Vertical interval between structures (m): varied
Spacing between structures (m): 3 -10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): > 0.75
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): > 1.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 20 -50
Construction material (stone): From within fields only
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 15%
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
ha
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
3.50
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Initial construction of terrace walls (Layout is by eye: no instruments used) | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
| 2. | Construction of new stone walls begins with a shallow trench into which large foundation stones are laid (or rolled downhill with a ‘crowbar’ – a long steel lever - if very big). | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 3. | Terrace walls are then built up with successively smaller stones: design depends on the individual. | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 4. | Stiles (low points) are generally left in the walls to allow human passage, but these are ‘staggered’ (ie not all in a straight line up-and-down slope) to avoid gullies forming. | بنيوية أو هيكلية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Construction of stone walls and terraces | persons/day/ha | 357,0 | 3,5 | 1249,5 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1269,5 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | The walls are increased in height each year as it silts up behind. | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season (winter)/Annual |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Increase hight | persons/day/ha | 46,0 | 3,5 | 161,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 161,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
A 100 m x 100 m field with a slope of about 20 degrees (35%) with bund of 0,75 sqm cross section initially at 10 m horizontal intervals assuming 2 sqm moved per- person-day
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Slope and amount of loose stones available (the more loose stones the more has to been moved to make cultivation possible)
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 800 - 1200
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture: Mainly loans in cultivated areas
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium - high
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Level of mechanization: Also mechnanized.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 2-5 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Estimates
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Estimates
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Estimates
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Estimates
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Estimates
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي للغاية
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
1 household
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: As land becomes more limited for cultivation, people are forced to cultivate steeper and stonier land. This is a "living" tradition!
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Maintains soil and soil fertility |
| Stops crops being washed away |
| Reduces spread of weed species |
| Maintains ploughability |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
This is an important example of a thriving traditional technology in a country where most such ancient practices were ended by apartheid How can they be sustained / enhanced? It has the potential to persist, if the Department of Agriculture acknowledges the importance of the system, encourages and gives training and organises exchange visits between farmers. Exchange of knowledge from farmer to farmer is facilitated by ‘Landcare’ and supported by the government. |
| It makes use of abundant existing materials in the field (stone) and therefore input costs apart from labour are low: this is a win-win situation, clearing and building. |
| Maintenance is simple – merely building up the walls gradually – and is effectively absorbed in everyday farming activities. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Labour cost | |
| Land lost (but equally gained by removal of surface stone) |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High labour investment for establishment | Hand tools, for example pickaxes and crowbars, could be supplied to the poorest families. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Case study of Vhavenda, perception of erosion.... June 97.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Paper submitted to "Development South Africa"
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية