Hillside Terracing [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Hans Hurni
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Yegara irken (Amharic), Kenetawi metrebawi zala (Tigrigna)
technologies_1388 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
27/06/1995
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
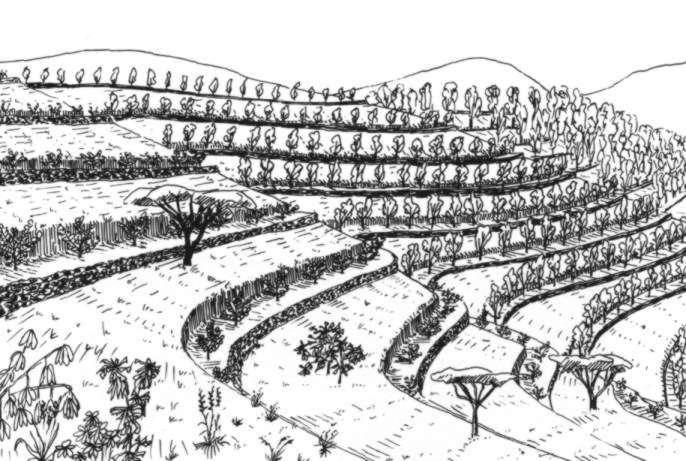
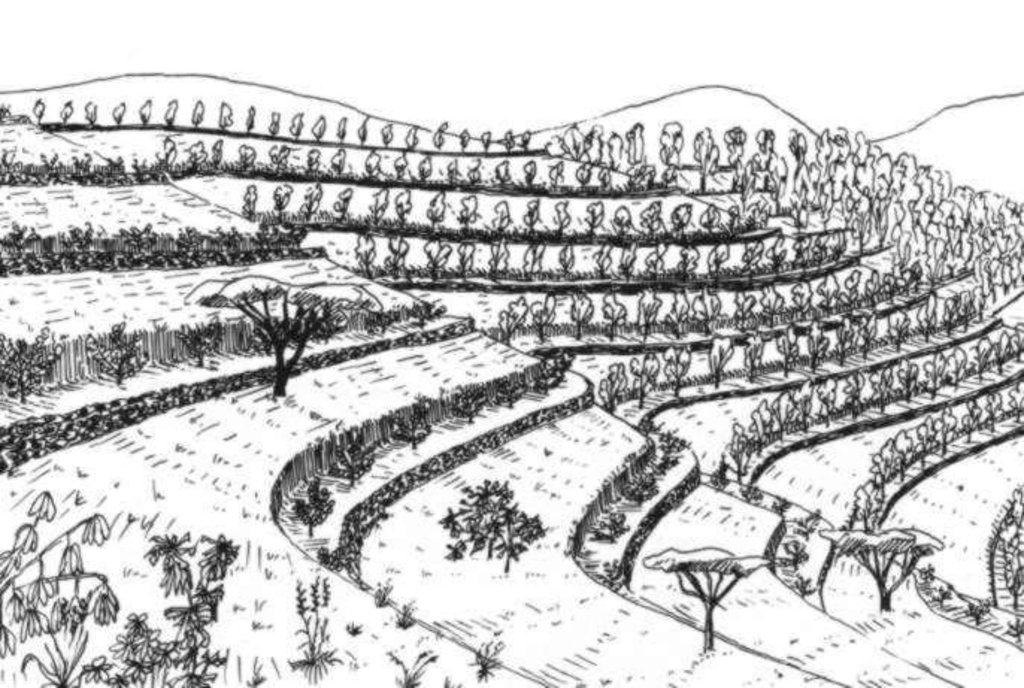
A hillside terrace is a structure along the contour, where a strip of land is levelled for tree planting.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
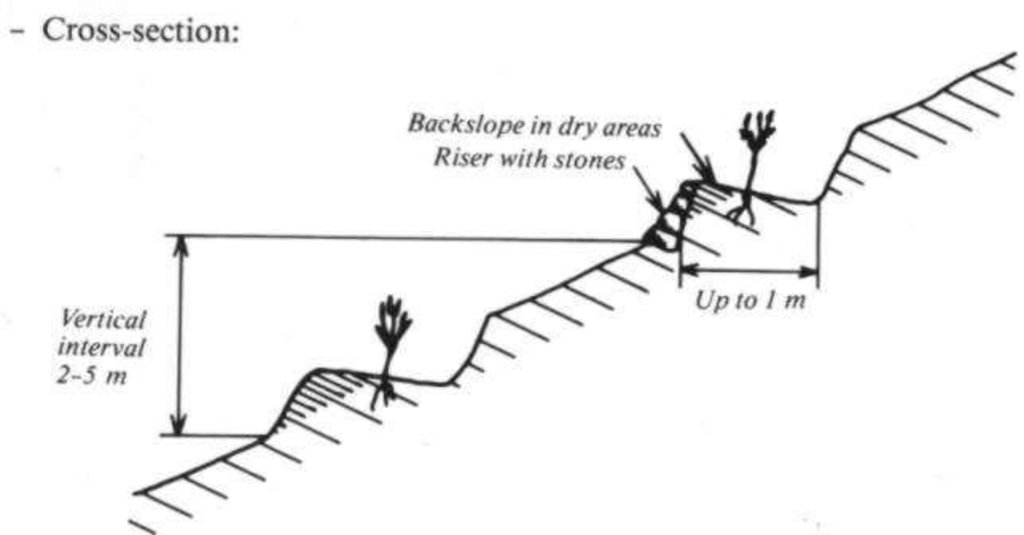
Hillside terraces are up to 1 metre wide and constructed at about 2-5 m vertical inteals. Hillside terraces should only be applied if there is a strong necessity of erosion control and/or water conservation justifying their construction. In Ethiopia and Eritrea, they have been mainly applied in the highlands, although the area of their applicability would be rather in the drier and lower lying agroclimatic zones. Slope range is 50-100%, soil range particularly on eavily degraded land. Hillside terraces are mainly used to prevent damage of flooding the area below steep slopes.
Hillside terraces help retain runoff and sediment on steep sloping land and to accommodate tree seedlings to be planted on them. They are also effective on badlands and in areas with low rainfall to conserve water. Hillside terraces are usually combined with area closure (against grazing). Little materials are needed for their construction: Line levels, digging instruments, stones, and other materials as needed for combined measures. Little management is needed for their maintenance, except for taking care of the tees planted, and for correcting damage that may be caused by livestock grazing.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Harerge, Shewa, Wello, Tigray, Gonder, Sidamo, and Hamasien (Eritrea)
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Originated from engineering handbooks and Indian experience. Has been applied in Eritrea & Ethiopia since ~1978
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
منتجات وخدمات:
- حطب الوقود
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
- الرعي/ رعي أطراف الأشجار الفتية (الجلح)
- حفظ/حماية الطبيعة
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): High run-on from steep slopes onto cultivated land. Sheet and rill erosion from slopes, and subsequent gullying on cultivated land along footslopes. Lack of grass and woody biomass.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of grazing for livestock. Lack of cultivation land. General food deficiency.
Grazingland comments: Insuffient land at curent population density and low productive farming systems.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Almost the natural forest is not exist. Low growing condition.
Type of grazing system comments: Insuffient land at curent population density and low productive farming systems.
Constraints of wilderness: these are mainly badlands which are totally degraded
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Water supply: Also full irrigation
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: May - OctSecond longest growing period in days: 30Second longest growing period from month to month: Feb - Apr
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10,000-1,000 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1800 m2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
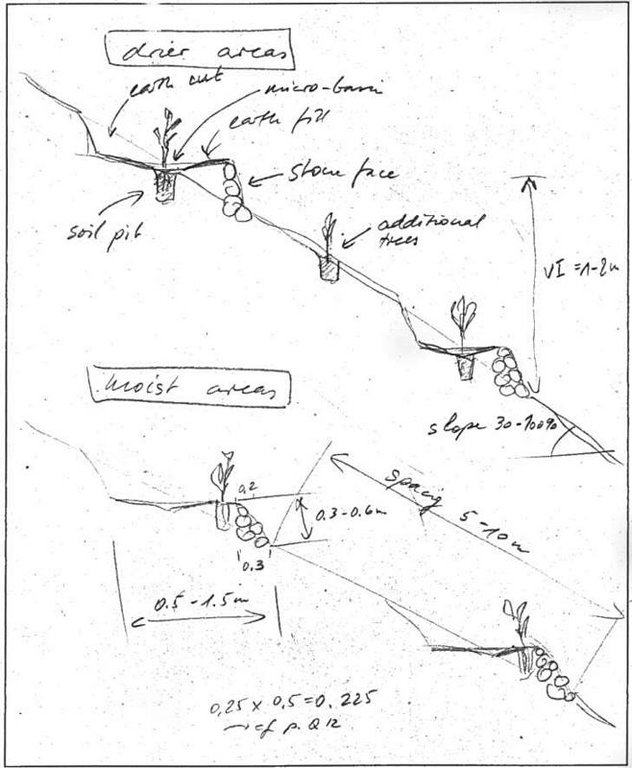
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Hillside terrace cross-section. Linied out along the contour, vertical interval between two terraces 2-5 m. (In: Soil Conservation in Ethiopia. CFSCDD, 1986)
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Trees/ shrubs species: Eucalyptus, Cupressus, Juniperus
Construction material (stone): Cut and fill with stone wall in front
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10
Change of land use type: closed area
Other type of management: livestock management - prevention of grazing, cut and ary system
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Ethiopan Birr
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
7,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transplanting | نباتية | beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Seeding | نباتية | nurseries |
| 3. | Construction | بنيوية أو هيكلية | dry season |
| 4. | Planting | بنيوية أو هيكلية | beginning of rainy season |
| 5. | Community guarding of closed areas | إدارية | annual |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | نباتية | rainy season /each cropping season |
| 2. | Control of grazing | بنيوية أو هيكلية | always/annual |
| 3. | Care taking of seedlings | بنيوية أو هيكلية | rainy season/each cropping season |
| 4. | communty guarding of closed areas | إدارية | continuos / annual |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Length of structure on an average slope
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Slope, soil condition, length of terrace per hectare.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Annual rainfall: Also 1000-1500 mm
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
- شبه رطبة
- شبه قاحلة
- قاحلة
Semi arid: Too little rainfall
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average: Everything below 16 % is to genly sloping to be useful
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
5% of the land users are rich and own 40% of the land.
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Labour offered to projects.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40
التربة
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
55
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
30
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
30600
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
30000 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
2% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
600 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Very recently, some villages have begun to see the value of hillside terracing, afforestations and area closure if they are given full responsibility to manage the area by a group of land users.
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Hurni H. : Soil Conservation in Ethiopia. Guidelines for Development Agents.. 1986.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
SCRP Addis Abeba
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية