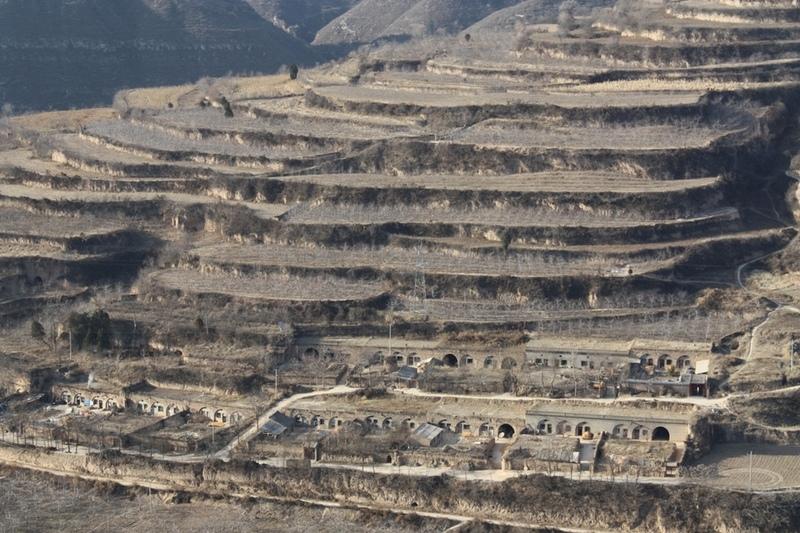
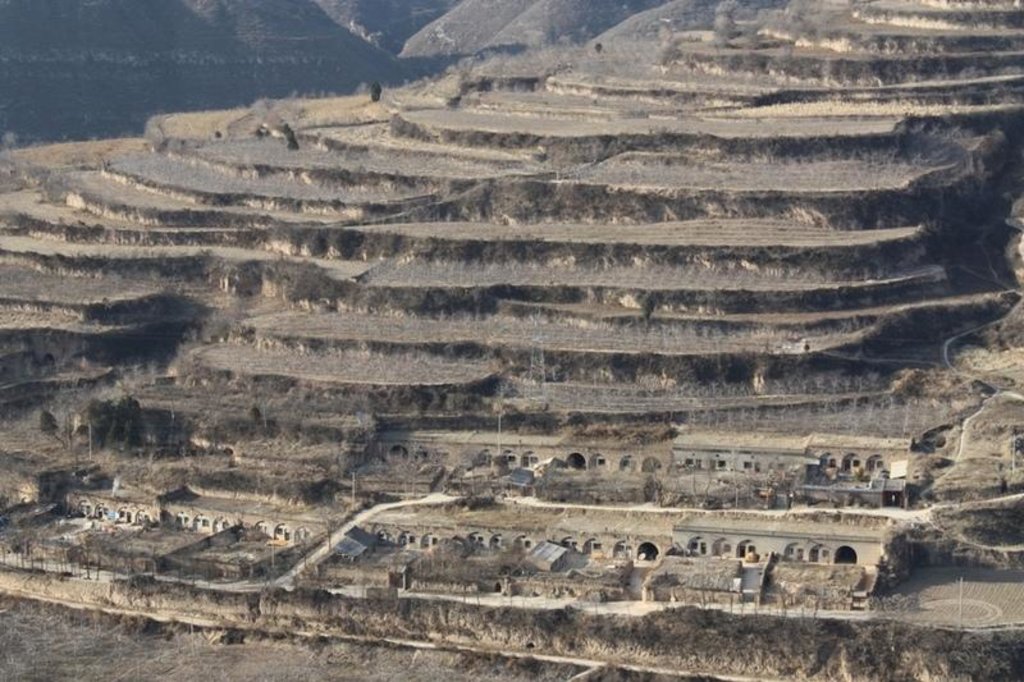
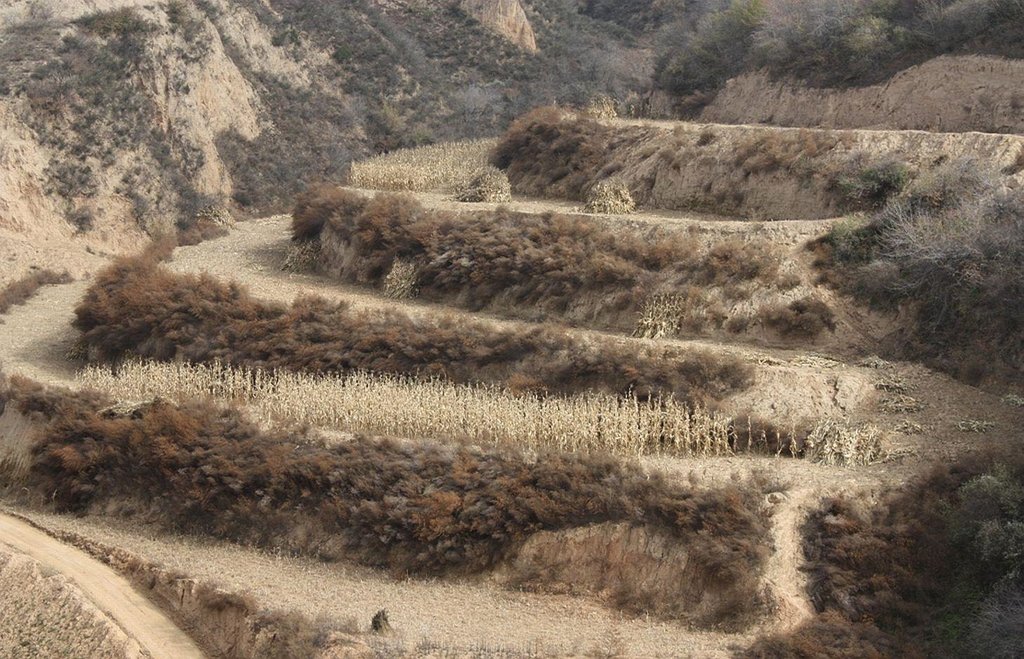
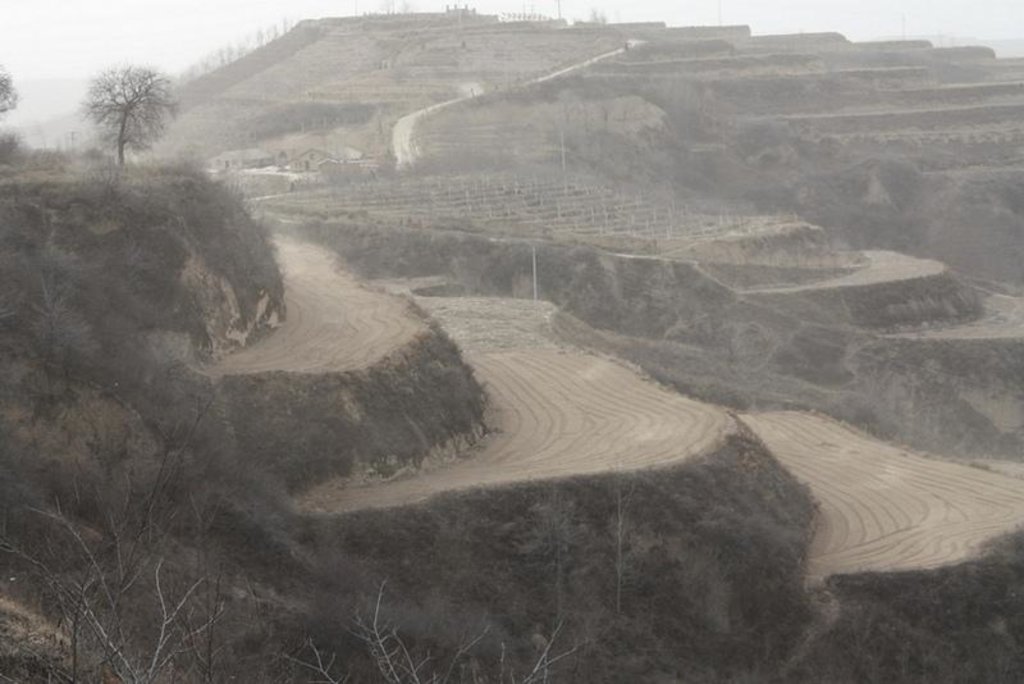
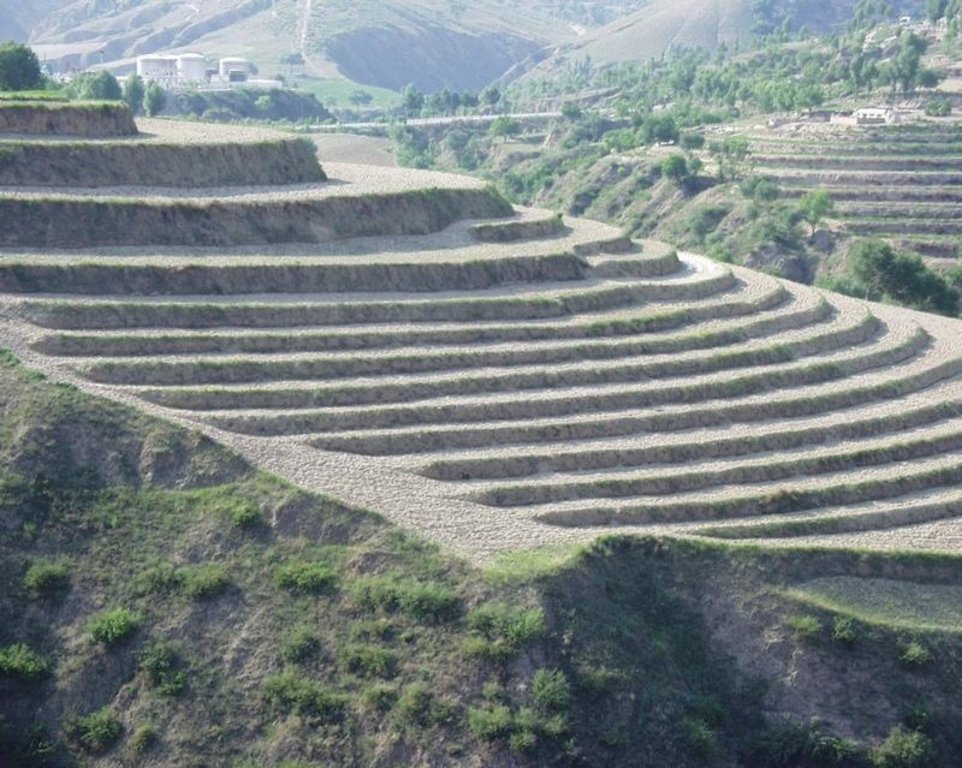
Bench terraces on loess soil [الصين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Fei WANG
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
土坎梯田,梯地
technologies_1445 - الصين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
20/01/2009
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
A Terrace is a structural SLM practice with a raised flat platform built on the slope to reduce soil loss and runoff on the slope, increase the rainfall infiltration and yield.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
A terrace is a leveled section of a hilly cultivated area, designed as a method of soil conservation to slow or prevent the rapid surface runoff and erosion of topsoil. Often such land is formed into multiple terraces, giving a stepped appearance.
Purpose of the Technology: To change the landform for better agricultural condition of operation of tillage and harvasting, reduction of soil erosion and water loss and finally for higher production.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The building of a terrace in the loess plateau takes long because loess is very soft and deep and the severe soil erosion and shortage of water in agriculture hinders the process, as well. Previously, terraces were constructed by hand. These terraces weres narrow and damaged by the great storms. Now, the machinery is used to build wide terrace with high bank size in the loess plateau. The establishment of terrace needs a lot of money but it is a long-term investment. The maintenance of terrace is considerable economic because the major efforts are the annually improvment of terrace bunds .
Natural / human environment: The soil erosion is very severe because of the cohesionless loess soil and very intensive rainfall storms in the summer and autumn that would destroy the land surface into broken hilly area. Terrace is a kind of measure to resolve it combining with crops. The human activities here is very intensive because they must plant on the slopes that would make the soil erosion greater.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الصين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Shaanxi Province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Yanhe River Basin
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The terrace in this site has been formed since 1994 with machinery. The land is quite wide and large enough for agriculture in the hilly loess region,
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Main cash crops: Beans, sunflower, apple, Chinese date, alfalfa
Main food crops: Potato, millets, maize, buckwheat
other crops: vegetable
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water losses are alarming in this region. The loose loess, steep slopes, and intensive storms in the summer and autumn, accelerates this process. Aditionally, the lack of rainfall negatively impacts agriculture and vegatation. Sediment deposition could increase the river bed and diminish capacity of reservoirs. On one hand side floods occur frequently because of fast and large runoff and on other hand side sedimentation in rivers reduce their water carring capacity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The low yield of crops and the low income from land is more important for the local people. It is necessary to improve the agricultural conditions. The land, especially the tableland and gentle slope land could be convert into terrace.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The composation of agriculture is very simple here.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 300Longest growing period from month to month: March to NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 200Second longest growing period from month to month: April to October
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 253.3 m2.
The total area with different measures is till to 2000. Yanhe River is a first class branch of Yellow River, China. The average channel slope is 3.26‰, and the area of whole basin is 7,687 km2. It is in the semi-arid North Temperate Zone with an average annual precipitation varying from 500 to 550 mm, and an average annual air temperature ranging from 8.5 to 11.4℃. It is in hilly gully area of the Loess Plateau covered by loess. The landform is seriously broken by cutting gullies induced by water erosion. The gully density (the length of channel in one km2) is amount to 2.1 to 4.6 km•km-2. The soil loss is severe all along.
The Ganguyi Hydrology Station (109°48′E, 36°42′N) located in the Ganguyi Town, Baota Country, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province. The area up Ganguyi Hydrology Station is 5,891 km2, including of Jingbian County(256km2), Zhidan County(708km2), Ansai County(2,699km2) and Baota County(2,228km2). The average annual runoff is 0.22 billion m3, and the runoff modulus accounting for 4,776.36 m3•km-2•yr-1. The average annual sediment flow is 4.776
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hw): تناقص القدرة التخفيفية للمناطق الرطبة
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (The natural vegetation in this region is grass on theslope and trees on the gully and alluvial land. After the destroy of natural, the soil loss increases greatly.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (About 70% of annual rainfall is in the summer and autumn. The storm is very intensive.), population pressure (The population density account for 71 capita per square km.)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (The rainfall varies greatly in different year and different seasons. The drought happened frenquently.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
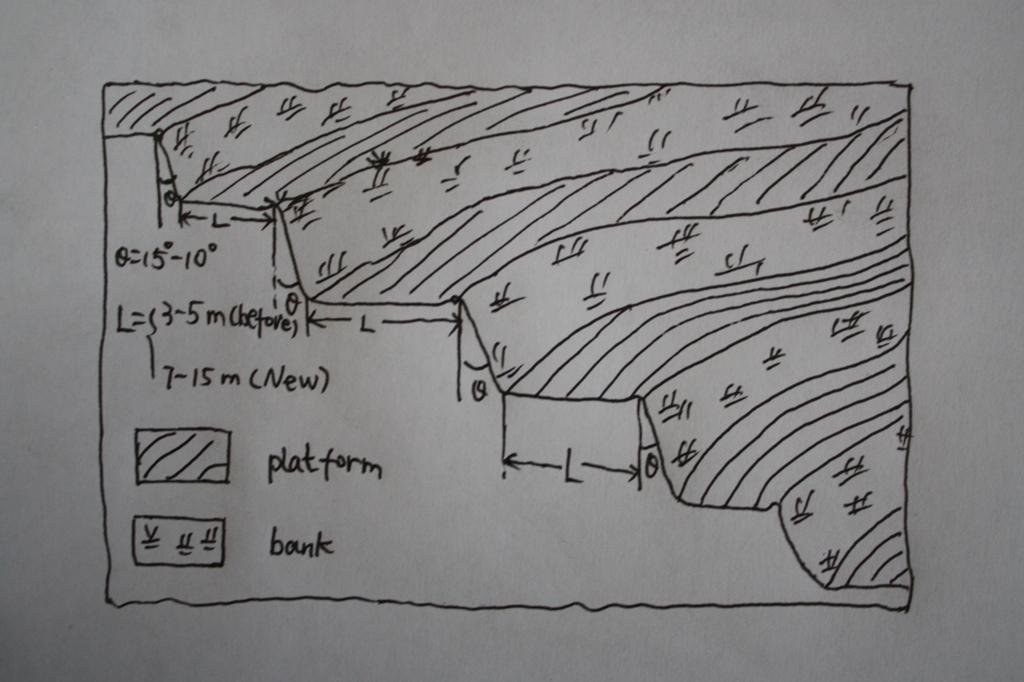
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
The brief structure of terrace in the Yanhe River Basin.
Location: Zhifanggou Watershed. Ansai County, Shaanxi, China
Date: 2008-12-15
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (The location selection and how to build a good terrace need special knowledge on soil engineering.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It is easy to know the benefit for all the local farmers.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 50000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Grass species: Natural grass to protect the bank of terrace.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.5
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 8
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-100
Construction material (earth): The terrace in the Loess Plateau are used local soil/earth directly.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 30-60%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Wild grassland or range land before mostly. Some time the cropland on the slope.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The labor is less intensive on the plain platform.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,83
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
8.8
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey and design | إدارية | Before construction |
| 2. | Move the topsoil to other place | إدارية | 1st step of construction |
| 3. | Built the platform and bank with soil digged | إدارية | 2nd step of construction |
| 4. | Backcover the topsoil on the surface of platform | إدارية | 3rd step of construction |
| 5. | Check and accept the terrace | إدارية | After the terrace finished |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Survey and design | Person/day | 45,0 | 8,8 | 396,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Building terraces (machine price included) | Person/day | 75,0 | 19,0 | 1425,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1821,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.5 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reinforce the bank | بنيوية أو هيكلية | annually |
| 2. | Fill the erosion hole of the landform | بنيوية أو هيكلية | annually |
| 3. | Build the edge in some terraces | بنيوية أو هيكلية | annually |
| 4. | Reinforce the bank | إدارية | annually |
| 5. | Fill the erosion hole of the landform | إدارية | annually |
| 6. | Build the edge in some terraces | إدارية | annually |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Keep Terraces in shape | Person/day | 30,0 | 8,8 | 264,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 264,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Crawl dozer and small traditional hand tool., crawler tractor, spade
In general condition, slope and soil, in the middle reaches of Yan River Basin. The prices of labour-day and Machine-hour are around 2005.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The terrace on the steep slope need more input for more soil and earth should be moved. It is the most important factor.The soil depth is not so important for the deep soil layer here.The cost of labour increases greatly in the last several years and the cost of construction of terrace increased.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
The mean annual rainfall in the basin is 515.2 mm in the duration from 1952 to 2000. The rainfall from May to Oct accounts for 446.8 mm, up to 86.7%; and that from Jun to Sep accounts for 367.6 mm, up
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate. The accumulating time that temperature above 0 ℃ about 3800 hours, and that above 10 ℃ is more than 3200 hours.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات محدبة أو نتؤات
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms also: mountain slopes and hill slopes
Slopes on average also very steep
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture: There are more than 50% soil particle are fine sand with size between 0.05 and 0.1 mm.
Soil fertility very low: Lack of N, P and SOM.
Topsoil organic matter: The average Top-SOM of cropland is about 0.05%
Soil drainage / infiltration good: The inflitration of Loess is very fast, but it is prone to sealing when flashing.
Soil water storage capacity low: It is easy to evaporation and drainage.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water medium: It is very stable in this region.
Availability of surface water also poor/none: Nearly all the branches of Yanhe are seasonal river.
Ground water table: It depends on the landform. In valley and alluvial land, it is shallow.
Water quality: Good quality for there are few pollution sources.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
It is very stable in this region.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No clear difference.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
80% of the land users are average wealthy (The terrace are build together in some villages for all the people funded by national subsidy.).
Off-farm income specification: The yield of terrace is much high and stable.
Level of mechanization manual work: The harvesting and other management are by hand, even the tillage on the nerrow terrace
Level of mechanization animal traction: Tillage with animal power mostly in the wider terrace.
Market orientation mixed subsistence/ commercial: Some production for themselves, but most of production is exchanged on the market.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
According to 0.054 ha per capita.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
Like other rural area in China.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
600
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2200
إنتاج حيواني
إنتاج الخشب
خطر فشل الإنتاج
تنوع المنتج
منطقة الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
نوعية مياه الشرب
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
43.9
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
120
تنوع مصادر الدخل
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
Livelihoods and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Evaporation form the wall of terrace, Especially for the narrow terrace
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
More inflitration of rainfall, but the evaporation near to the wall increases
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10000t/km^
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2000t/km^2
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Hazards towards adverse events
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | غير معروف |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
التعليقات:
Loess is very prone to erosion and extreme storms would destory the bank of terrace. In the study site sesonal rainfall increased and the loess terrace could retain more soil water and reduce the runoff.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The yield of terrace is stable and relative higher. The income from terrace is high and the maintain cost is low.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
100 households
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
95 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Most land farmers have some terrace. I do not know the exact number of land user families who adopted the technology.
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: the old narrow terraces, now a very small area left, are build voluntarily.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nearly all the people know the benefit of terrace. the benefits of terraces are very good for crops and orchards are high enough in this region.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Increase yield and income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the terrace is maintained well, the water condition would be better than that on the slope land even in dry year with low precipitation. |
|
Convenient to till and harvest How can they be sustained / enhanced? Tillage and harvesting is much easier on the plain flat land than on the slope. The maintainance of terrace is important. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Reduce soil erosion on the slope. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The loess soil is prone to erosion because of its loose character induced by fine sand content and low soil organic matter. The plain flat makes the dispersion and transportation of soil particls difficult. |
|
Reduce runoff and increase the soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? The runoff generation is smaller on the plain than on the slope. Slow movement of surface water lead to more soil infiltration. |
|
Increase yield. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Water is the limit factor in the loess plateau. The yield would increase if there is enough water available. |
|
Decrease flood risk. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is a kind of off-site benefits because less runoff generation and gentle process of runoff decrease flooding. Reduction of sediment also diminish flood risk because the drainage capacity of channel and adjusting capacity of reservior increase when sedimentation decrease. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The output is also low in contrast with other industries. | No way to overcome it. The total and net income is too low because the area of terrace per capita is very small. |
| The income is relative compared with other industries. | No way to overcome it. The net income is low because the labour costs are increasing, and the total income because labour cost and very small area of terrace per capita. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| There is possible damage of terraces because the loess is very loosen and prone to collapse. | Keep upmaintaining the bank and land well. |
| Decrease runoff of lower stream. | No way to overcome it, but it also could decrease the risk of floods. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Soil and water conservation records of Shaanxi Province. 2000. Shaanxi People's Press, Xi'an City, China
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Library of ISWC, CAS
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
The soil and agriculture of the Loess Plateau. 1989. Zhu Xianmo, Agriculture Press, Beijing City, China
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Library of ISWC, CAS
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Statistical tearbook of Yan'an. 2003. Compiled by Editorial Board of Statistical tearbook of Yan'an
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Library of ISWC, CAS
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Impact of human activities on runoff and sediment change of Yanhe River based on the periods divided by sediment concentration. 2008. WANG Fei , MU Xing-min ,JIAO Ju-ying, LI Rui. Journal of Sediment Research
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://159.226.100.28/asp/Detail.asp
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Changes of soil erosion intensity due to conversion of farmland to forest and grassland in Yanhe River. 2007. BasinWang Bangwen, yang Qinke, Liu Zhihong, Meng Qingxiang, Science of Soil and Water Conservation
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://159.226.100.28/asp/Detail.asp
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية