Gully Rehabilitation [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Kitir (Amharic)
technologies_1469 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
10/12/2005
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
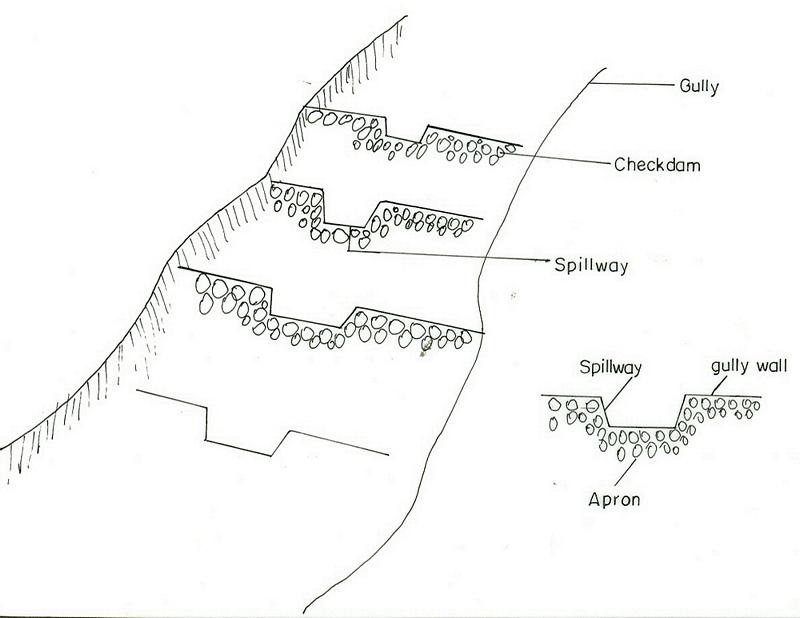
It is a barrier of stone/wood/earth placed across a gully to control runoff and sediment passing through.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
A checkdam constructed from stone, wood or branches of trees. It has an average height of 1m and is spaced at 1m vertical interval. The purpose is to reclaim gully lands to productive lands by controllong the rate of runoff and trapping the soil. By plugging the gully using different checkdams the gully gradient is brought to a gentle slope and flow rates and soil movment is regulated. Constructing of checkdam in a gully starts with smaller checkdams which are regularly maintained and up graded of their heights. Gully plugging by checkdams and vegetative material is suitable to all agro-climatic conditions but the choice of material for establishment depends on the availability of material in the nearby and rate of flow. For a high rate and volume of flows stone checkdams are prefered to wooden or earth chekdams.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
South Gonder
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Meher, Gurara, Melo, Rib, Sebat Wodel, Hamus Wonz
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Introduced to the country about 30 years ago from other countries exprience.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Major food crop: Barley, wheat

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الزراعي الحرجي
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Open grazing, bare land, high erosion risk
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): land slide, erosion
Nomadism: Yes
Grazingland comments: grazing lands are replaced by other land use system or degraded irreversibly and also the number and productivity of livestock is reduced due to shortage of feed and fodder.
Other type of forest: selective felling of natural forests: charcoal
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The communities assigned guards for area closures in order to protect them from illegal cutting and conversion to other land uses. Government or projects used to employ site guards for protecting the enclosures at the initial stage. When the communities started to get benefit from enclosures then decided to take responsibility to protecting them.
Forest products and services: fuelwood, grazing / browsing, protection against natural hazards
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Barley-teff
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Dec
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
- إدارة المياه السطحية (الينابيع، الأنهار، البحيرات، البحار)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.42 km2.
The area is calculated based on gully size.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
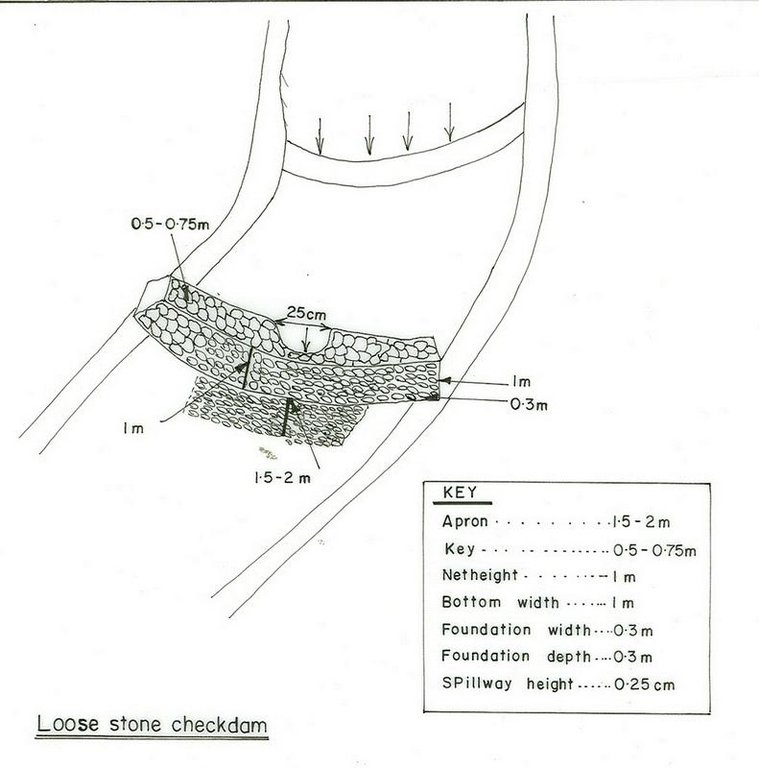
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Amhara
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5m
Vegetative measure: plantation
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 2500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: saligna, dicurense
Grass species: Bana, vetiver, serdo
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 10.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Structural measure: checkdam
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Birr
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
8,6
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
0.80
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | collect planting materials | نباتية | onset of rain |
| 2. | planting | نباتية | during rain |
| 3. | construction | بنيوية أو هيكلية | dry season/after crop harvest |
| 4. | fencing | بنيوية أو هيكلية | dry season/after crop harvest |
| 5. | Stone collection | بنيوية أو هيكلية | January-March |
| 6. | gully reshaping | بنيوية أو هيكلية | January-March |
| 7. | dig foundation | بنيوية أو هيكلية | dry season/after crop harvest |
| 8. | Fencing (live or wood) | إدارية | dry season |
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | replanting | نباتية | rainy season /as required |
| 2. | fencing | نباتية | dry season /once |
| 3. | stone collection | بنيوية أو هيكلية | as required |
| 4. | construction | بنيوية أو هيكلية | as required |
| 5. | maintaining breaks in fence | إدارية | dry season / as required |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Length and width of the structure.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
slope, labour, time of cost recovery payment (period), width (length) of the gully, availability of construction materials.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
It ranges from 1250-1599 mm
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
- شبه رطبة
Subhumid: It is woina dega and dega
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: It ranges between 1500-4033 m a.s.l.
Landforms: Mountain slopes (ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2) and plateau/plains as well as hill slopes (both ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), steep (ranked 2) and rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (More in hilly slopes/steep slopes, ranked 1) and shallow (on rolling areas, ranked 2)
Soil texture: Fine/heavy (At gentle slopes, ranked 1), medium (rolling slopes, ranked 2) and coarse/ light (at the bottom of the gully)
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and high (ranked 3)
Topsoil organic matter is low (continuous cropping and erosion)
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium (steep slopes , ranked 1) and good (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (ranked 1) and high (clay soils, ranked 2)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
60% of the land users are poor and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: No apparent differences could be observed.
Level of mechanization is aniaml traction (ploughing using oxen, horses and cow, ranked 1) and human labour (digging by hoe, ranked 2)
Market orientation of production system: Also mixed (subsistence/ commercial), subsistence in agro-silvopastoralism (farm implements, feul, charcoal)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Mostly from 0.5-0.75 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
no annual crop grown
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
إنتاج الخشب
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
More labour needed for the technology means shortage of labour for farm activities.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
At the boundray of two holdings and questions as to who will have to ues the gully.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to more water retention.
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Biodiversity enhancement
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
35 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Soil erosion control and prevention of gully expansion. |
|
sources of fodder How can they be sustained / enhanced? plant more forage trees |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Fodder production and soil formation rate enhanced How can they be sustained / enhanced? make frequent maintenance |
|
Moisture and water harvesting enhanced How can they be sustained / enhanced? plant useful trees/ nitrogen fixing trees |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| rodents |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Ethiopia Federal RDS, Rural Rural Development policy Strategy and Methods. 2001.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Soil and water management manual, Alemaya. 2003.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية