Stone wall check dam [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Simon Bach
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Yedengay Keter (Amharic)
technologies_1526 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Bach Simon
bach.si@gmail.com.
Centre for Development and Environment (CDE), University of Bern
Hallerstrasse 10, 3012 Bern, Switzerland
سويسرا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ayele Habtamu
haramaya@haramaya.edu.et
Haramaya University
Haramaya University, P.O. Box 138, Dire Dawa, Ethiopia
أثيوبيا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Haramaya University (HU) - أثيوبيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
02/05/2011
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
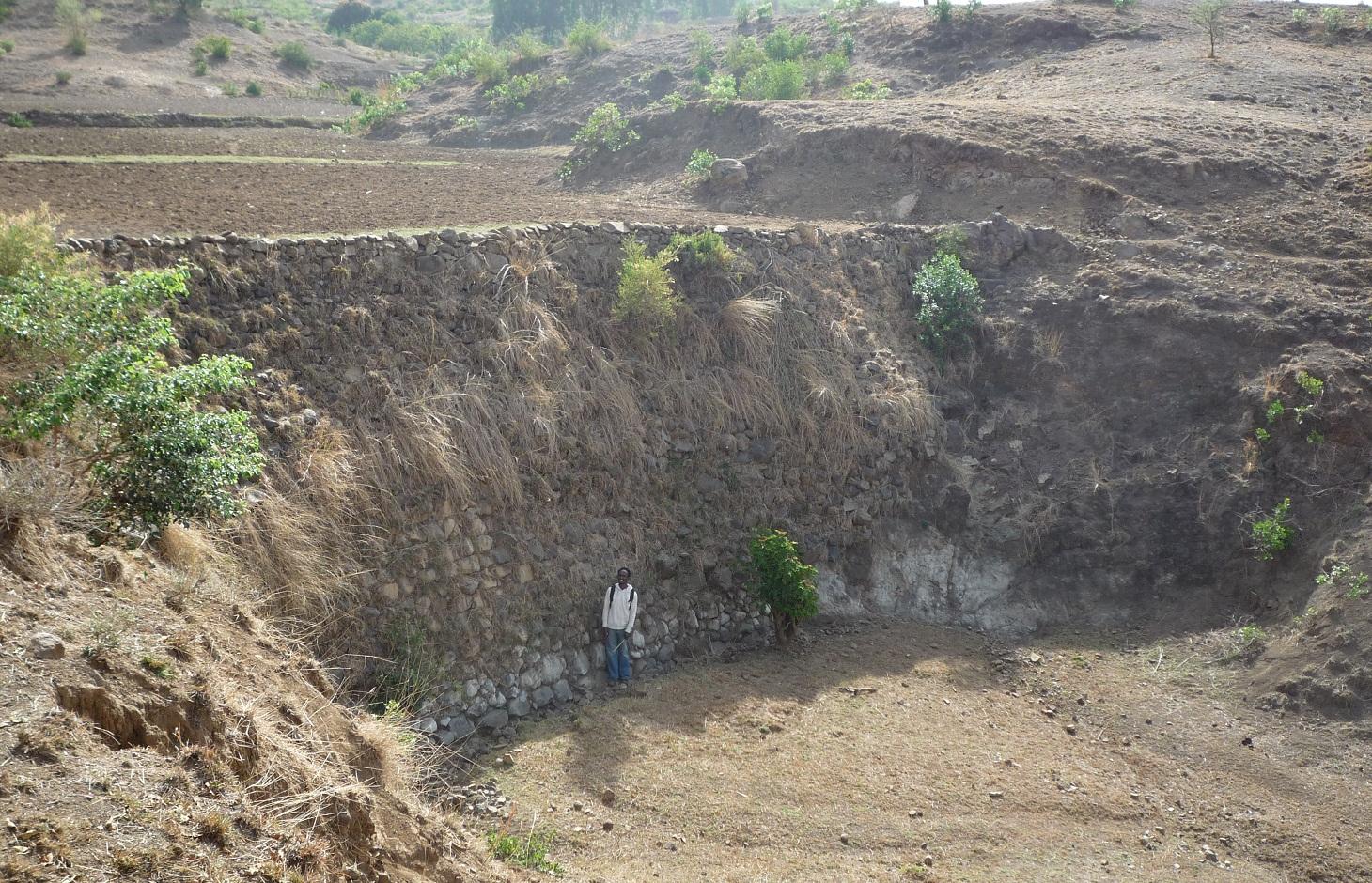
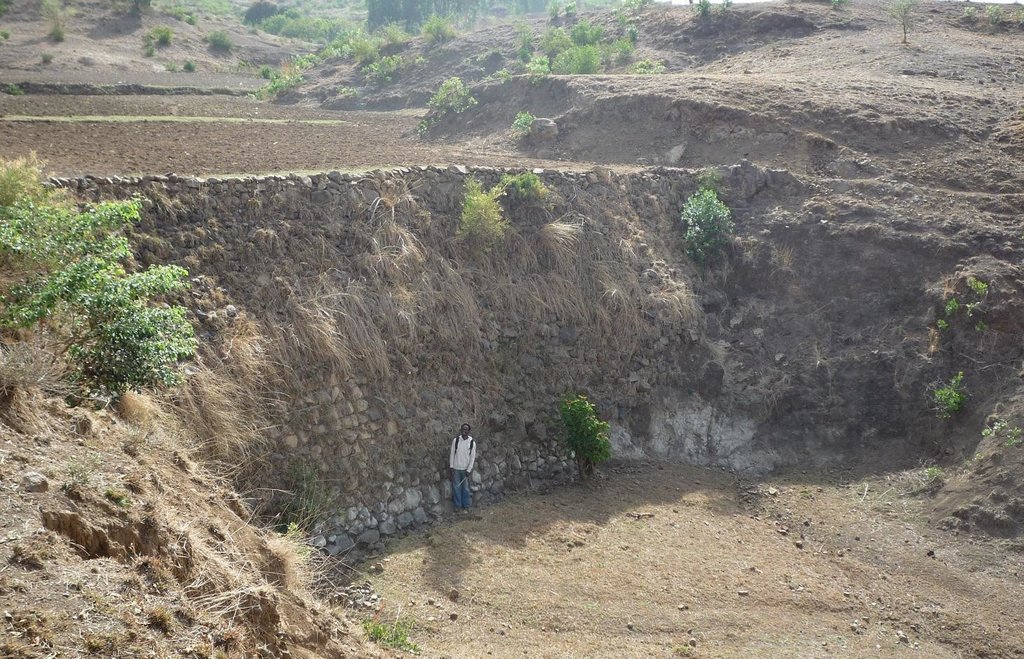
Stone wall check dams are built across a gully to collect alluvial soil and hinder further gully erosion.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
During the 1980s stone walls and terraces were introduced in Ethiopia in order to combat soil erosion. The technology of stone walls or terraces is used to stabilize hills or to refill gullies also in Bati, Ethiopia. Stone walls can form a very strong check dam to rehabilitate gullies even several meters deep.
Purpose of the Technology: Although stone walls can be used for different purposes, this case study is focusing on stone walls used to combat gully erosion. Farmers in the Bati region often use stone walls to rehabilitate gullies if the material is easily accessible, otherwise they may search for alternatives.
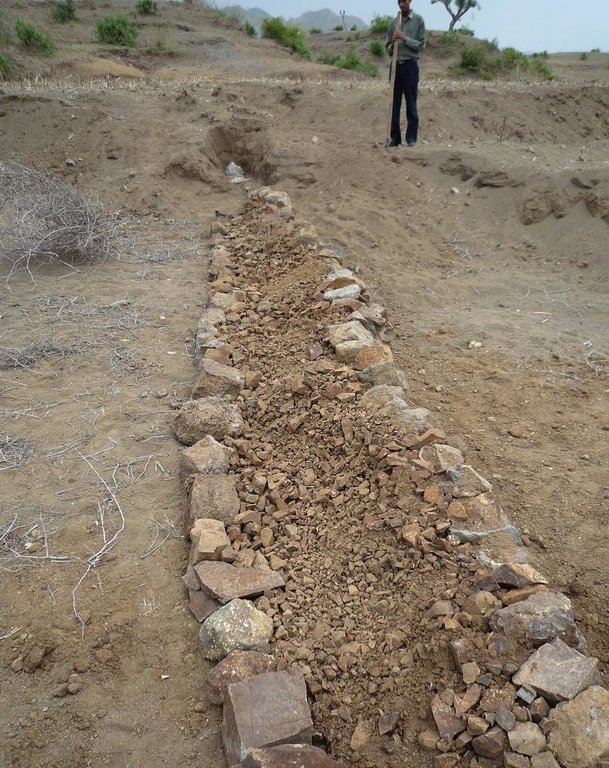
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Following procedure is undertaken to build a stone wall check dam: After breaking the stones in the source-area they are transported to the target-area either by hand, by camels or by donkeys, depending on the distance. After digging a foundation for the wall of approximately 30 cm depth, the gap between two rows of big stones 1 m apart is filled up with smaller stones and gravel. These actions are repeated until the desired height and width of the wall are reached
Natural / human environment: The case study site, Bati, lays in an semiarid climatic zone on 1600 m a.s.l. Rainfalls are erratic and the rain sum per year is between 500-1000 mm. The landscape is very hilly with rather steep slopes. As almost in all Ethiopia, the area has a high population density and growth. The agricultural sector is very dominant and lead by a lot of small scale farming with a lot of livestock and small plots of cropland.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Ethiopia / Amhara Region
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Bati
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Soil and water conservation measures, including stone wall check dams, were mainly introduced to land users during the 1980s by the government. Sometimes the technology is not adequately performed though. In recent years the local Agricultural Office is teaching farmers how to correctly build soil and water conservation measures not only on a technology basis but to take care of an integrated watershed management.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Major food crop: Sorghum
Major other crop: Corn

أراضي الرعي
- Mixed farming
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
Main animal species: Cattle, goat, sheep, camel, chicken (Goat/sheep are main meat source (in household or on market))
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation, overgrazing, cultivation of erosion-sensitive areas or steep slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Too much soil loss and land degradation, no vegetation cover and poor soil moisture.
Grazingland comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Type of grazing system comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
التعليقات:
Water supply: Also rainfed
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: June until September
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.6 m2.
Size of the case study watershed.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
- S6: الجدران والحواجز وسياجات القش، والسياجات
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation for the past 30 years.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Wood collection for cooking and construction.), overgrazing (50% of the watershed area are cultivated - big grazing pressure on remaining land), other human induced causes (specify) (Cultivation of very steep slopes.), change of seasonal rainfall (Erratic rainfall.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (If there is rain, it is intensive.), population pressure (High population pressure.), poverty / wealth (Poor facilities.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Poor soil management practices and lack of awareness.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Annual cropping.), droughts (The research area is considered rather dry.), land tenure (If the land is rented, it is poorly managed.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Poor access to fertilizer. Bad infrastructures.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of awareness for soil degradation.), Low productivity of the land (As a consequence seeking for new/larger areas to increase production.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
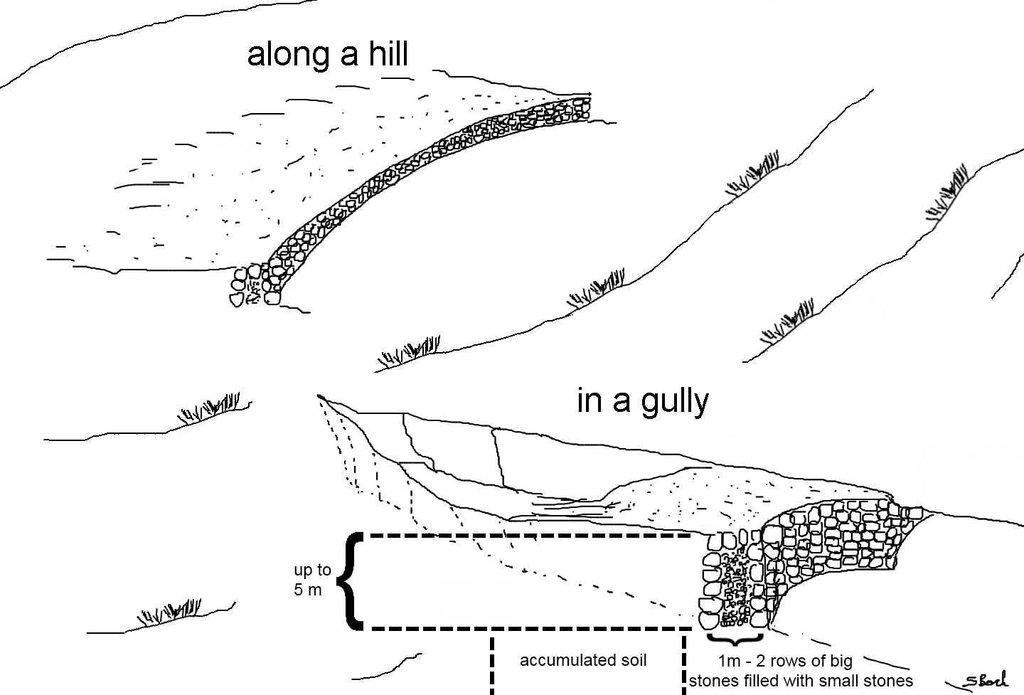
Stone wall check dams as they can be found in the region of Bati. The approximately 1 m wide gap between two rows of larger stones is filled up with small stones or gravel. This is done for every new level of the wall until the wall reaches its final height. The first row of stones is placed in the top 30 cm of the ground and on each side the dam is entering the hill to some extent. After a wall has silted up, the height is increased by other rows of stones until desired dimension is reached. Walls up to 5 m can be found in the case study site.
Location: South-West of Bati. Bati Woreda, Amhara Region, Ethiopia
Date: 26.04.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (To teach the farmers how to perform an integrated watershed management.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (To build a robust check dam there is a lot of knowledge needed.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Ethiopian Birr
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
16,82
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of the stones (500 person days needed). | بنيوية أو هيكلية | During dry season. |
| 2. | Transportation of the stones (depending on the distance). | بنيوية أو هيكلية | During dry season. |
| 3. | Digging a foundation of 30 cm depth (165 person days needed). | بنيوية أو هيكلية | During dry season. |
| 4. | Building of the stone wall (500 person days needed). | بنيوية أو هيكلية | During dry season. |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 1165,0 | 1165,0 | 50,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1170,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare the stones (250 person days needed). | بنيوية أو هيكلية | During dry season if needed. |
| 2. | If dam is silted up, increasing the height by 0.5 m (250 person days needed) | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Every year in dry season. |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 50,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 505,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Shovel, digging hoe, iron rod.
Total costs of a hectare were calculated for a wall of 100 m length and 1 m of height every 20 m (500 m total wall) in the year 2011. Tool prices were estimated and labor costs were calculated with a daily wage of 1$.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Rough topology in the area, questionable availability of construction materials if they are not found nearby.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Erratic rainfall (rainseason from June until September)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics (LGP shorter than 90 days.)
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (The study site is located at 1600m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1) and valley floors (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), rolling (ranked 2) and steep (ranked 3)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (ranked 1) and shallow (ranked 2)
Soil textur: Coarse/light (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: Unknown
Availability of surface water is poor/none (Only during rainy season)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, mostly groundwater)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Relative to other parts of Ethiopia.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 6%
1% of the land users are rich (Adopt the most of SWC technologies).
19% of the land users are average wealthy.
89% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Off-farm income has low importance.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (Plowing by oxen, ranked 1) and manual labour (ranked 2)
Market orientation cropland: Subsistence
Market orientation grazing land: Goat/sheep are main meat source (in household or on market).
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج حيواني
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Conservation of soil water
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Gullies are transformed to fields. Structure needs space but also gains space
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Structure as a new obstacle
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
alluvial soil is relatively fertile
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
new fields lead to higher productivity
تنوع مصادر الدخل
فروقات اقتصادية
التعليقات/ حدد:
additional income due to new fields
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Gully is now flat land and traversable but needs establishment and maintenance work
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Additional space for new fields
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
best practices may spread further on
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
upstream and downstream dialog
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Accumulation of soil leads to new space for fields and additional food security or even income (if crop surplus is sold).
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
increased soil moisture
حصاد / جمع المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
dam blocks water flow
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
increased infiltration, reduced flow velocity
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات/ حدد:
increased infiltration
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Dam blocks water flow but can lead to the fact that additional groundwater may be logged
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
alluvial accumulation behind the structure
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
new habitat for rodents etc.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الفيضانات
التعليقات/ حدد:
flood controll by stone check dams
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
possibility of spring development
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
if a spring can develop
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
increased infiltration/reduced flooding but also less downstream river flow
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
التعليقات/ حدد:
trapping of the sediments by the structure. No off site sediment yields available anymore.
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
التعليقات/ حدد:
increased infiltration
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to gully rehabilitation
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to gully rehabilitation
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي للغاية
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Big labour input for establishment. Also maintenance needs some work every year. But also high benefit by additional farming land gained due to the check dams.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: In the past 6 years the local Agricultural Office has supported farmers to treat their watersheds with SWC technologies based on a food for work programme. Today farmers build the structures on their own but seek support.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Most of the farmers build SWC technologies (includin stone check dams in gullies) because of the food for work programme
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
The stone check dams are conserving soil and moisture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain the dams. |
|
Due to alluvial soil there is additional farming land and therefore increased productivity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Take care of the walls as well of the surrounding area and the whole watershed. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Stone check dams are a quite durable structure. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Stability could be enhanced by additional technologies e.g. similar as gabbions or planting of trees/shrubs in front of the wall to reduce collapsing possibility. |
|
The structure collects alluvial soil which can be plowed and used as new farming fields. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Structure maintenance is important. If the dam fails, the field is washed out as well. |
|
The technology is widely used around the world (perhaps with local adaptations) and is therefore well documented. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep on with documentation and monitoring of limitations and potentials of stone check dams around the world. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The Land users could not tell any disadvantages of the technology. | Could be an indicator that there is enough spare time to build and maintain structures during off-farming season. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Large labour input at establishment and during maintenance period. | Possibly by machinery but it is very expensive. |
| During time of establishment/maintenance there is no time for farming activites. These activities can therefore be seen as hidden costs. | Perhaps a "professional" team that takes care of check dams and is payed for it. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Bach S. (2012) Potentials and limitations of Jatropha curcas as a multipurpose crop for sustainable energy supply and soil and water conservation - a case study in Bati, Ethiopia, using the WOCAT approach. Unpublished master’s thesis, Centre for Development and Environment, University of Bern.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية