Vallerani system [بوركينا فاسو]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Sabina Galli Vallerani
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Deborah Niggli
technologies_1528 - بوركينا فاسو
- Vallerani System: 16 يوليو، 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani System: 16 يوليو، 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani System: 12 يوليو، 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani System: 15 أغسطس، 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani system: 4 إبريل، 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani system: 4 يناير، 2017 (inactive)
- Vallerani System: 30 سبتمبر، 2020 (public)
- Vallerani System: 8 مارس، 2019 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
03/05/2012
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
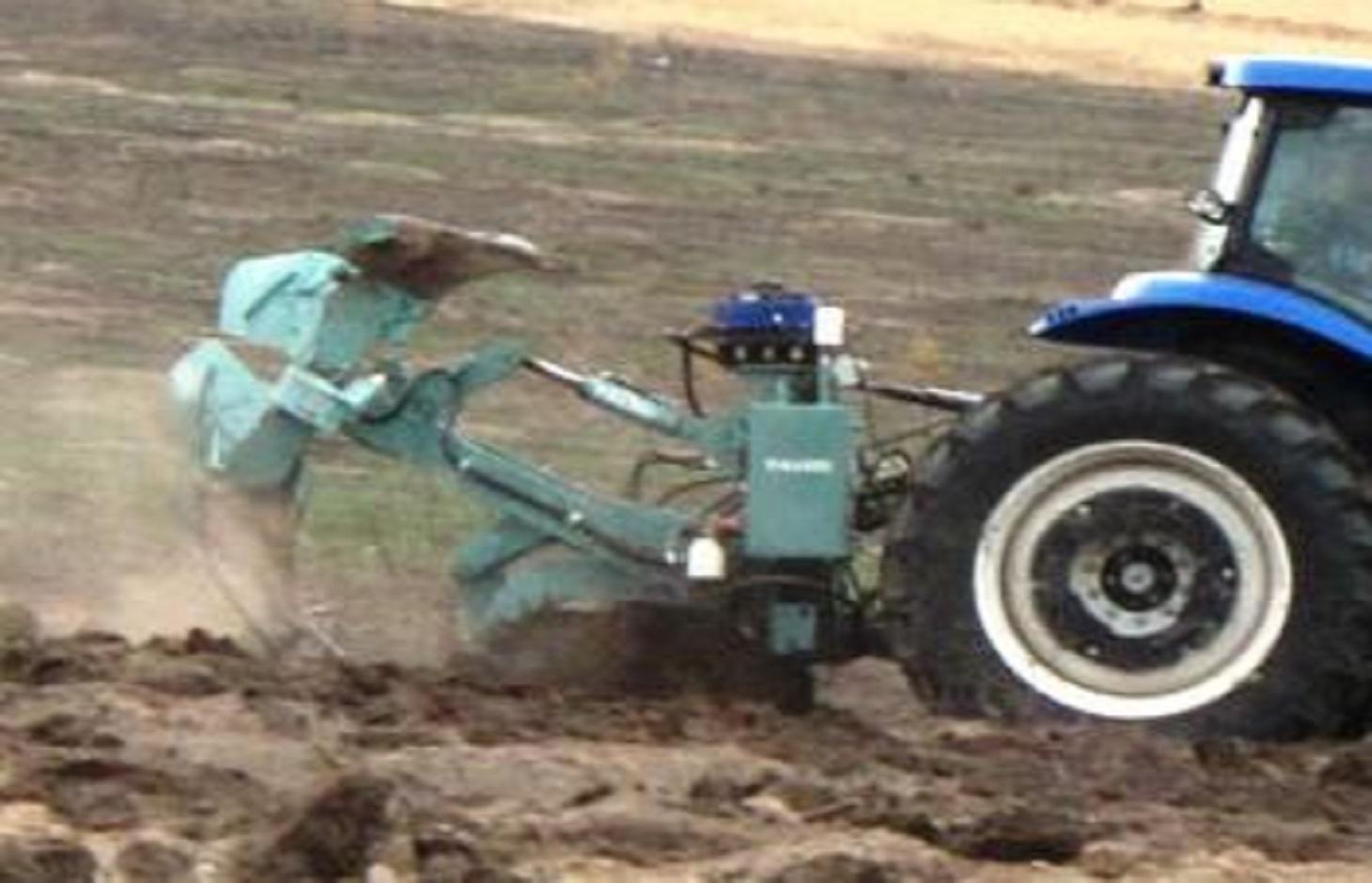
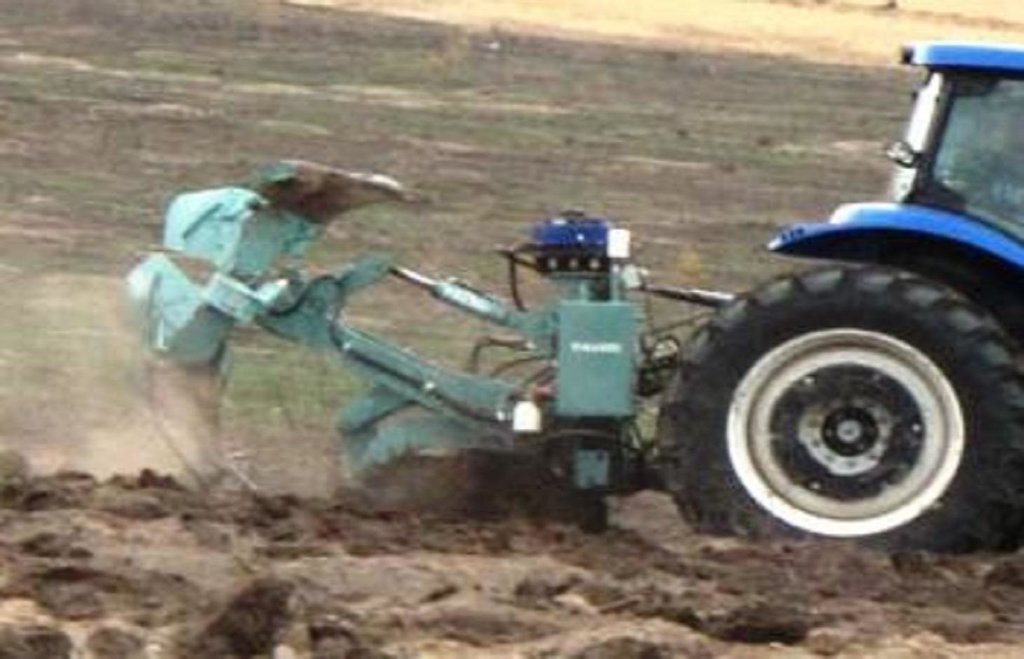
A special tractor-pulled plough that automatically constructs water-harvesting catchments, ideally suited for large-scale reclamation work.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The Vallerani implement is a modified plow named Delfino3, pulled by a heavy-duty tractor. A normal plow on flat land excavates a symmetrical furrow, and earth piles up equally on both sides of the furrow. The Delfino3 plow has a single reversible plowshare that creates an angled furrow and piles up the excavated soil only on the lower (downhill) side. This soil forms a ridge that stops or slows down runoff water as it flows downhill. The plow’s blade moves up and down (i.e. in and out of the soil), creating micro basins about 5 meters long, 50 cm deep and spaced about 2 m, each with a ridge. Two ripper placed before the plow work the soil to a depth of 70 cm, rise at the basin and descend between the basins. Thus to attain, in the stretch of land between the crescent, a collection bag which receives water from the crescents itself. Even with very low rainfall (150-500 mm/year) each micro-basin/storage bag can collect 1500 litres of water, including runoff. This water is protected against evaporation and remains available to plant roots and groundwater.
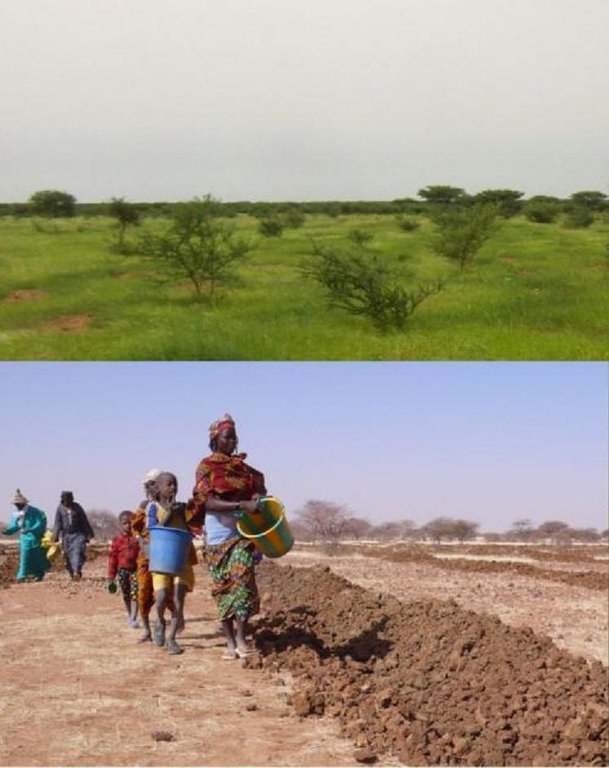
The Vallerani System is based on direct sowing of seeds of shrubs and trees of locally available, indigenous species. They are sown along the ridges of the basins and in the wake of the ripper. In the case study area Acacia tortilis, Ziziphus mauritania, Balanites aegyptiaca, Acacia senegal, Acacia seyal and Faidherbia albida have been sown. While for most species seeds can be collected by the local population, for species rarely present in the region, the seeds have to be purchased from tree nurseries. The use of goat excrements containing seeds has also proven successful (about 95% of all micro basin have at least one tree growing after 3 years) when directly sown. With more moisture available for a long time trees grow rapidly and the herbaceous cover improves in quality and in quantity - providing 20-30 times more livestock fodder (1000-2000kg dry herbaceous biomass ha/year), also helping to conserve the soil. The plowed and sown area is not protected by fences, grazing of animals shall be allowed so that villagers can benefit from the forage and reduce the accumulation of biomass fuel that would further the risk of fires in the dry season.
The Vallerani plow can ‘treat’ up to 20 ha, digging 5.720 micro basins, in a single day. The speed and effectiveness of the Delfino3 plow are its major advantages in the fight against desertification, but can also be its major limitation as to be able to make the best of it, it is necessary to find great availability of land to be reforested or cultivate. This is mainly possible related to a large public or business initiative. The spreading "like wildfire" that has characterized the case study was made possible by the presence on the territory of an NGO already active and rooted in the territory for many years and by perseverance, respect and competence of partner "of the North". Once the project has invested in the tractor and the plow (tractor ~ 70,000 EUR, plough ~ 40,000 EUR), the remaining cost of implementation – labour costs for local workers and drivers, fuel etc. amount to around EUR 125 / ha / year.
The case study area in the north east of Burkina Faso receives about 300-500 mm of annual rainfall. The soils of this agropastoral land are heavily degraded with a low tree density and an almost entirely absent herbaceous cover.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
بوركينا فاسو
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Oudalan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Gorom-Gorom
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land degradation-desertification with reduction of vegetation cover in terms of plant density and species diversity is the main problem: disappearance of grasses and trees, reduction of the size of the plants that are resistant and of the biological activity of the soil. Runoff, water and wind erosion increase. Drought and irregular precipitation have heavy consequences on soil fertility, availability of water for humans and livestock, and recharging groundwater.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 90
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 50 m2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير البنيوية
- S4: تسوية الخنادق والحفر

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, change of seasonal rainfall, droughts
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
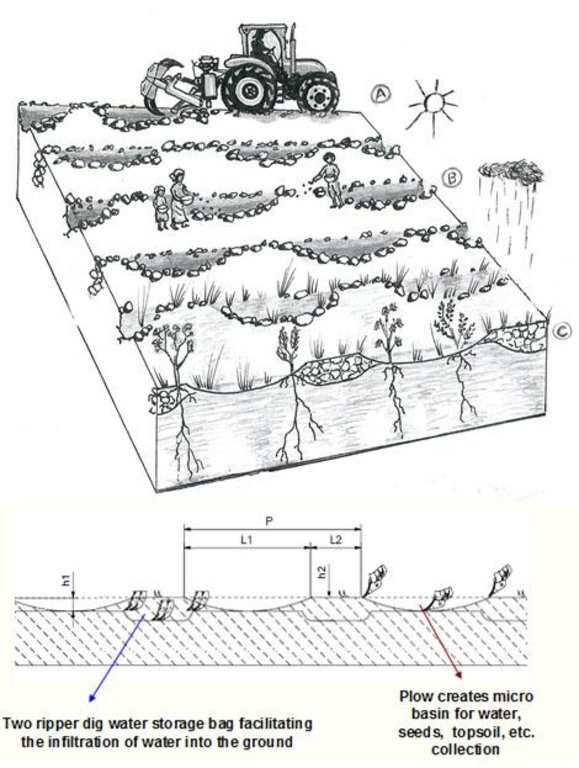
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Above:
A. The land chosen together with the local population is plowed with the special Delfino3 plow. B. Local people sow seeds (collected from local trees or bought if species are rare) or goat dung containing seeds (collected in the night enclosures after feeding the goats shaking trees with ripe seeds). C. The micro basins collect the rain that falls into the crescents and 50% of the runoff water. The water easily penetrates into the soil, fills the storage bags, remains available to plant roots and drains into the groundwater without risk of evaporation. Each micro basin/storage bag can collect up to 1.500 l of water.
Below
h1-Depth of the ploughshares work: =40/50 cm
Width of the micro basin: 40/50 cm
L1-Length of the micro basin, programmable: =3,5/5 m
h2 Depth of the rippers work: =50/80 cm
P-Total length of work: 4/8 m
Tractors horsepower 210/250 (150-198 Kw)
Working speed: 4/7 Km/h
Weight : 2000 Kg
Location: Oudalan, Gorom Gorom province. Burkina Faso
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), water harvesting / increase water supply, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 0.5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 5
Change of land use practices / intensity level
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Project planning, consulting and training by VS and national experts | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 2. | Plowing with the Delfino special plow pulled by a 210hp tractor | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
| 3. | Seed harvesting can be done by local people either collecting them directly from plants or by shaking the plants at the appropriate time, to feed the goats and sheep with the fallen seeds and collect their dung in the night enclosure | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 4. | Missing seeds can be purchased in local markets or, if trees are too rare or if the species is no longer present, seeds must be purchased at a nursery | بنيوية أو هيكلية | When seeds are ripe |
| 5. | Direct sowing | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 72,0 | 72,0 | 50,0 |
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 23,4 | 23,4 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 95,4 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | No maintenance activities are required | بنيوية أو هيكلية |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
All data presented in the table refer to an ideal project which lasts 5 years with 3000 hectares plowed each year. All works are carried for economic retribution. Item number 1 refers to the planning, training and consulting engineers that has a strong impact on the cost per ha ($47). This voice would remain the same if 3 MTU (Mechanized Technical Unit) were used in the same area reducing its impact to $ 15,6 per ha.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Upfront costs for the aquisition of the required materials are around 40,000 EUR for the plough and 70,000 EUR for the tractor.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
400-600 mm
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- قاحلة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The project involves the reforestation and reconstruction of the herbaceous layer for the grazing of livestock that are male dominated activities. Since 2010 women have sown special plants for medical use, domestic use and as raw material for crafts and protected them from grazing.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
Off-farm income specification: The only activity people of the region are engaged in is goat and cattle breading. Crop production is practiced only for subsistence use.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
up to 30% more than before implementation
جودة العلف
إنتاج الخشب
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50 trees/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
350 trees/ha
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The technology can be applied for agriculture producing 2 to 4 times more than with traditional systems
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
No more malnutrition=better health!
الفرص الثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
التعليقات/ حدد:
More wood, fodder and water available= more time available
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Old, young and woman work together for common benefits
المؤسسات الوطنية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Were applied on large scale
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Environment education in theory and practice, is part of the system
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
More fodder and water highly reduces conflict motivations
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
Women have collected, sown and protected medicinal plants and plants for raw materials for handcrafts to sell at the market
Training of skilled labour in disadvantaged regions
التعليقات/ حدد:
Chance to find good jobs
contribution to human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Thanks to the enormous increase of trees, pasture and crop production, the quality of life and health of men and animals have improved considerably.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
فقدان التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
التعليقات/ حدد:
Through the high soil cover with trees and grass fire risk increase, this is avoided through open access to grazing.
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Increased threat from wild animals
التعليقات/ حدد:
Biodiversity highly increases, local people might be afraid of some animals coming back like jackal or snakes
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي للغاية
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The system includes the use of a heavy duty tractor and a special plow whose costs are high though difficult to sustain by the local population. All correlated activities are done (or can be done) without external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The system includes the use of a heavy duty tractor and a special plow whose cost is high though difficult to sustain by the local population. All other activities part of the system are practicable from the population under an initial guidance of someone with specific training. Where the technology is known there is active participation of local people and a strong demand for new interventions
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| This practice allows for the rapid and efficient treatment of large degraded areas within a short time |
| The tree and shrub species planted are mainly indigenous and locally adapted species |
| Through its tillage process the Vallerani system offers the highest degree of efficiency in the first years from processing. Its effects last for a long time so it does not need to be repeated on the same site |
| The VS does not use any water (except rain) in countries where water is rare and precious. It further avoids the risk of soil salinisation. |
| The delfino3 can plow strongly degraded land, this makes that local people often ask to work their worse land |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The investment costs for the machinery are extremely high and cannot be covered by single land users or even communities | projects must be financed externally |
| The speed and effectiveness of the Delfino3 plow are its major advantages in the fight against desertification, but can also be its major limitation as to be able to make the best of it, it is necessary to find great availability of land to be reforested or cultivate | This is mainly possible related to a large public or business initiative. The spreading "like wildfire" that has characterized the case study was made possible by the presence on the territory of an NGO already active and rooted in the territory for many years and by perseverance, respect and competence of the partner "of the North" |
| Since great extentions will be processed, a big organisation is needed for all activities (awareness raising, collecting seeds, personnel training, logistics, etc), | this must be well organized and should operate already before starting plowing |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Conedera, M., N. Bomio-Pacciorini, et al. 2010. Reconstitution des écosystèmes dégradés sahéliens. Bois et Forêts des Tropiques 304(2).
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.vallerani.com/images/Reconstitution.pdf
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Akhtar Ali, Theib Oweis, Atef Abdul Aal, Mohamed Mudabbar, Khaled Zubaidi, and Adriana Bruggeman. 2006. The Vallerani Water Harvesting System. ICARDA Caravan No. 23.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.vallerani.com/images/Caravan-23.pdf
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية