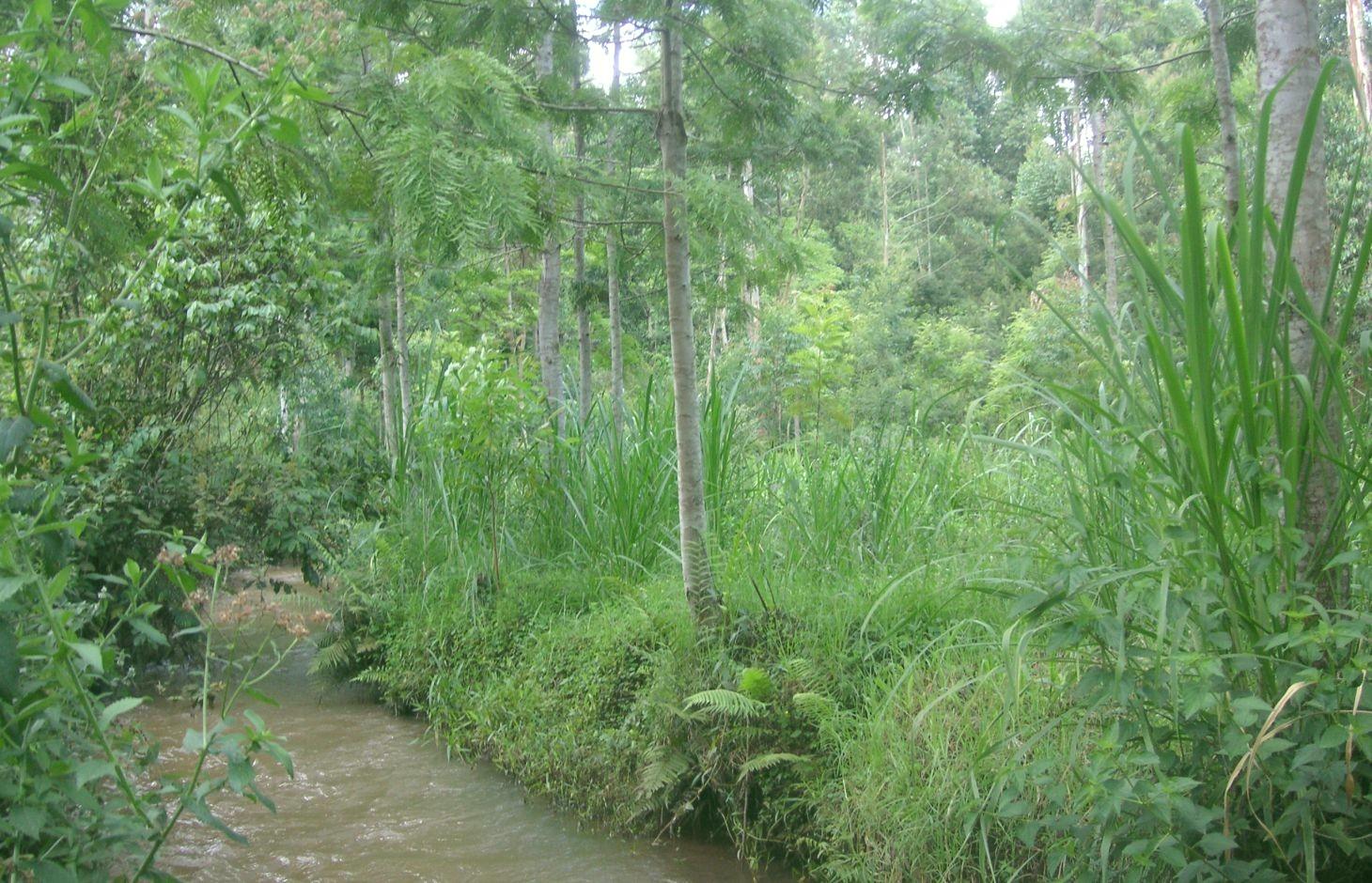
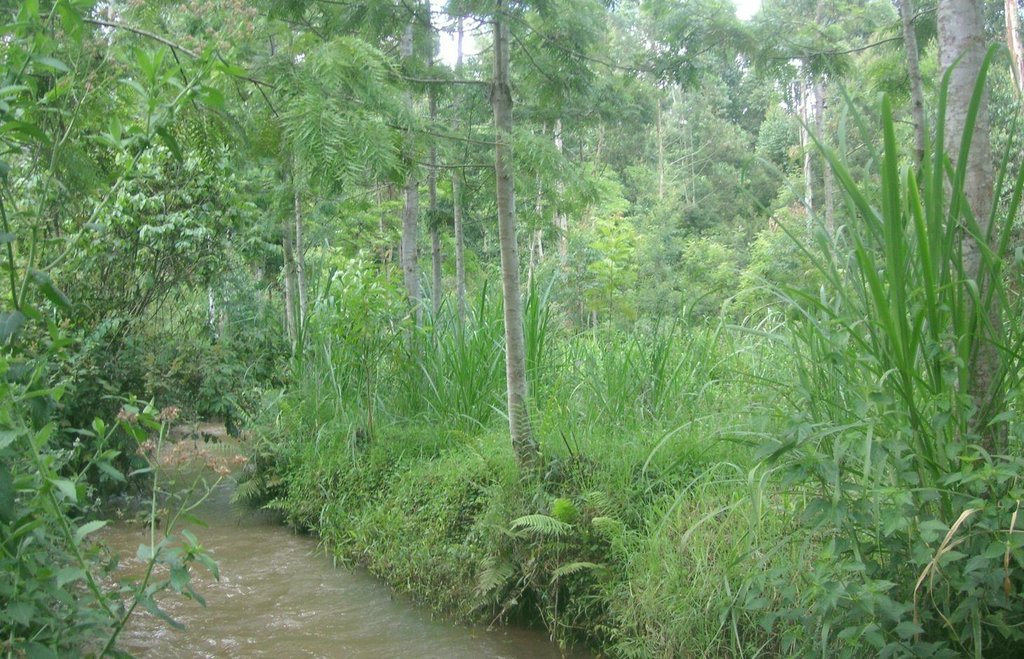
Productive use of the riparian area using Napier grass and protection of the riverbank with indigenous trees at Kapingazi River [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Manuel Fischer
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
technologies_1558 - كينيا
- Productive use of the riparian area using Napier grass and protection of the riverbank with indigenous trees at Kapingazi River: 28 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
- Productive use of the riparian area using Napier grass and protection of the riverbank with indigenous trees at Kapingazi River: 4 سبتمبر، 2019 (public)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
مستخدم الأرض:
Nyaga Robinson
0726 408 839
كينيا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
16/11/2012
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
A riparian area that is frequently flooded requires a special treatment because conventional agriculture is not possible. Trees along the riverbank and Napier grass on the remaining space still allow a productive use despite the difficult circumstances.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
On the southeastern slopes of Mt. Kenya, the circumstances are ideal for agricultural activities, the rains are plenty and normally reliable. The plot owner started realizing a problem of riverbank degradation 17 years ago. But still he continued the traditional way of agriculture, planting beans and maize. Since his plot is on the slip-off slope only few metres above the river level, it experienced regular floods in case of heavy rainfalls, destroying the plants and leading to crop failures. Conventional plants like maize and beans do not resist such an excess of water. To fight the land loss and the bad harvest, the farmer introduced indigenous trees along the river and Napier fighting the riverbank degradation. Behind that, several rows of the flood resistant Napier grass were planted to still use the area in a productive way.
Purpose of the Technology: Above all, the goal of this technology is to get a high grass production. As a side effect results a quite good protection of the riparian area. The vegetation prevents rainwater from running directly from the fields into the water. Therefore, the chemicals from the field get stuck in the riparian soils and don't pollute the river. In the same way the infiltration in the riparian enlarges the total infiltration since the water would go to the river directly. Especially the raw surface of the riparian allows more infiltration and interception storage of water. This surplus of stored water is able to provide river water for a longer period, when rains are humble for a longer period. In case of floods, the increased infiltration potential can cut the peak flow and thus prevent damages. The grass yield is used as a fodder for the cows.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Before planting the indigenous trees, water guzzlers like eucalyptus trees were cut down. Indigenous seedlings were planted right along the river at a distance of 1 m. Behind the tree row, Napier grass is planted and harvested twice a year. The cutting and harvesting of the grass is done regularly such that animals can be provided with fodder every day. As soon as the trees are big enough, they function as a source of fire wood, they can be pruned every 5 months.
Natural / human environment: The studied plot is situated between the tea and the coffee zone at an elevation of 1663 m.a.s.l. This small-scale farm does not produce tea nor coffee, there is mainly subsistence agricultural production and some few products are sold on the market. Rainfall is reliable and ensures a regular production.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kenya/Eastern Province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Embu
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Farmer asked neighbours for advice.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
Cows are living on the farm. The farmer carries the fodder to the stall.
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The excessive water on the plot hinders conventional agriculture and the floods lead to riverbank degradation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land plot is situated right beside the river and is less than a metre above the river. Flood destroyed regularly the harvest of maize or french beans. Parts of the riparian have been removed.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Water supply: Also post-flooding
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: march to may Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: october to december
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين أصناف النباتات/سلالات الحيوانات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
The area along the river is very small, namely 750m2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wr):انجراف ضفة النهر

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع

تدهور المياه
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wr: riverbank erosion, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, floods (The floods are mostly responsible for the riverbank degradation and destroy conventionally cultivated crops.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), population pressure, land tenure (By law the riparian should be protected. The land owner uses it in a productive way.), poverty / wealth
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
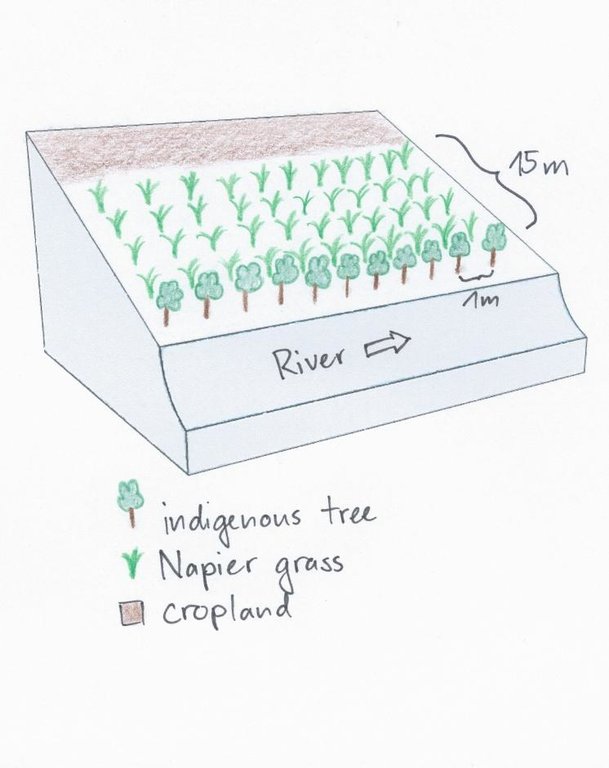
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
A tree row is aligned directly beside the riverbed with a spacing of 1m. Directly behind the trees, Napier grass is planted up to a width of 15m. Adjacent to the Napier grass, there is cropland.
Location: Manyatta. Embu West / Eastern Province
Date: 28.12.2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.8
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.8
Trees/ shrubs species: Grevillea, Mutundu, Miburu, Mulinga, Mugumo
Grass species: Napier Grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0%
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
3.33
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chopping bad trees | نباتية | anytime |
| 2. | Tree planting | نباتية | rainy season |
| 3. | Planting of Napier grass | نباتية | Beginning of rainy season |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Chopping bad trees | Persons/day | 2,5 | 3,2 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Tree planting | Persons/day | 5,0 | 3,6 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Planting of Napier grass | Persons/day | 2,0 | 2,75 | 5,5 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedling | Pieces | 70,0 | 0,114285 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 39,5 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.3 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Adding manure | نباتية | 2 times a month |
| 2. | Harvest of Napier | نباتية | 2 times per year after rainy season |
| 3. | Pruning | نباتية |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Adding manure | Persons/day | 0,2 | 2,25 | 0,45 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Harvest of Napier | Persons/day | 2,0 | 3,3333 | 6,67 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Prunning | Persons/day | 2,0 | 3,25 | 6,5 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 13,62 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Jembe (Hacke), Panga (Machete)
The plot is situated right at the riverside and gets flooded regularly. 70 trees were planted along the river in one row. The area of the Napier grass is approximately 750m2 big, harvest is two times a year. Costs were calculated in 2012.
The costs per hectare were calculated for a riparian area with a length of 100m and a width of 10m, since hectares are difficult to apply on a riparian context. The determinant factor for the costs is labour and the area of the plot. The required equipment like a spade is available on nearly every farm or can be borrowed from neighbours and is thus not added to the costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1703,00
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
source: http://www.wri.org/publication/content/9291
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics. http://www.levoyageur.net/weather-city-EMBU.html
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 1668 m a.s.l., source: aster gdem
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture (topsoil): It is called Murram
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Species diversity: Also low
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Market orientation of production system: Family of 10 children
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- فردي
التعليقات:
Abstractions are controlled by the local Water Resource Users association (WRUA), but everybody can take water by hand.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
إنتاج حيواني
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الدخل والتكاليف
تنوع مصادر الدخل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Fuelwood production through pruning
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
التربة
غطاء التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
تنوع الموائل
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Stabilization of riverbank
Infiltration
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Establishment and maintenance costs are quite low.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The knowledge is spreading and people acknowledge the benefits.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Protection of the riverbank and reduced riverbank erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular management of riparian trees by replacing dead trees with new ones. |
|
Productive function of the Napier grass in terms of fodder and of the trees in terms of pruning for fire wood. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Careful use of the trees and the grass enables a sustainable use of the plants. |
|
No more crop failures. How can they be sustained / enhanced? One should only cultivate plants that can cope with the local excess or scarcity of water. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Riverbank stabilisation due to the plantation of trees. How can they be sustained / enhanced? A good idea would be to establish a second row of trees along the river and thus enlarging the number of trees and their positive effects on riverbank stabilisation and filtering of the runoff. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| After the harvest of the Napier, the land is bare and vulnerable to erosion. | Instead of cutting the whole plot at once, only a quarter of the Napier grass should be cut at once. So that the land is not completely vulnerable to rain. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية