System of rice intensification (SRI) [مالي]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Dieter Nill
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Deborah Niggli
Système de riziculture intensification (French)
technologies_1654 - مالي
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Kouyate Djiguiba
IICEM
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Traore Minamba
tbaminan@gmail.com
IICEM
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Intgrated Initiative for Economic Growth in Mali (IICEM) - مالي1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/07/2012
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
The objective of a system of rice intensification (SRI) is increased yields.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
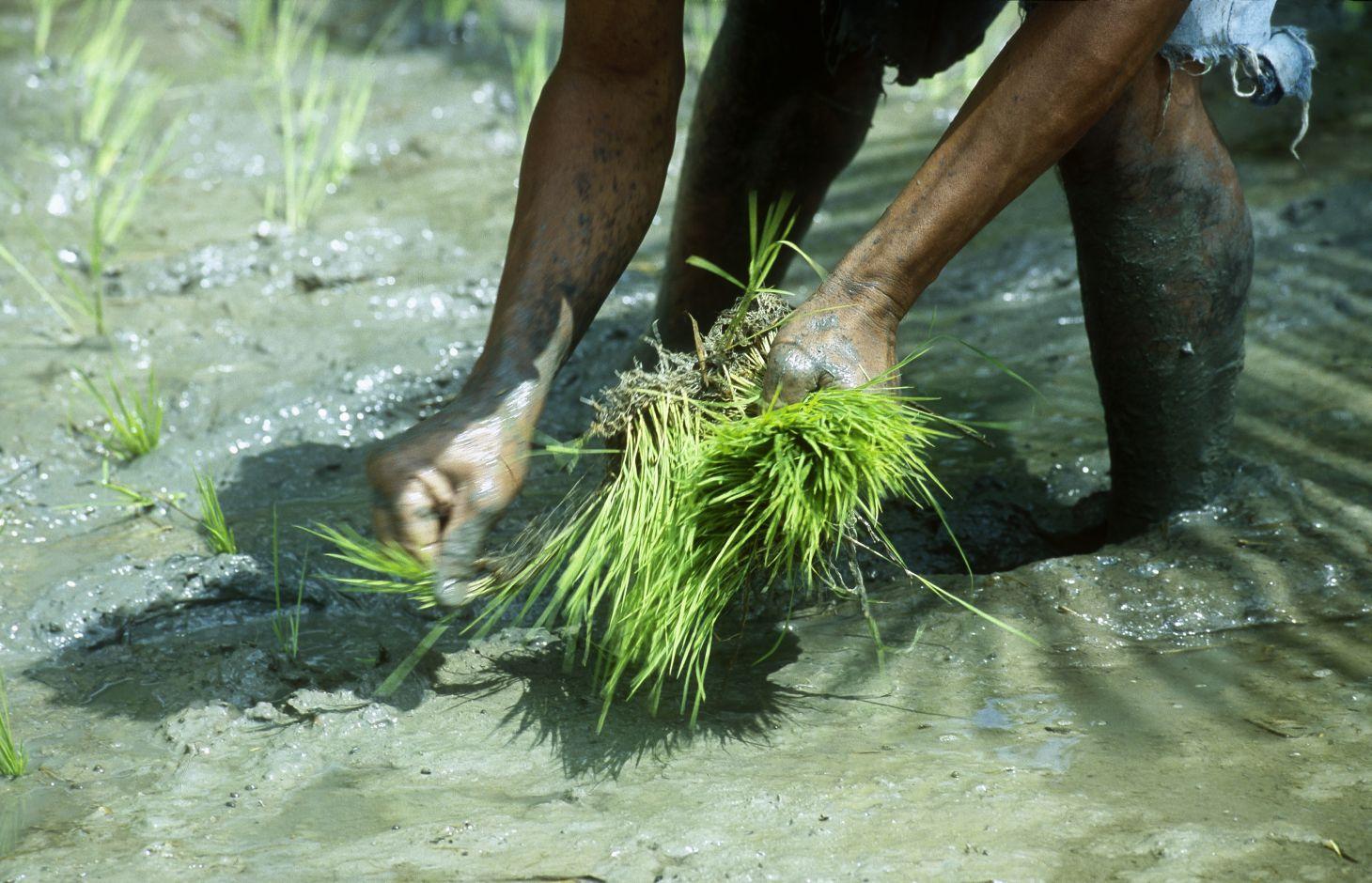
الوصف:
This can be achieved when rice plants are provided with sufficient air and space for their ripening process. Irrigation water supply requirements are lower, which means the approach can be deployed in low-rainfall areas or the rice growing areas can be extended using the same quantity of water (climate change adaptation). The technique requires less seed and fertiliser.
SRI optimises the soil-water-plant relationship. It increases the plants’ potential for production by correcting disadvantageous practices. In practical terms, this involves growing rice on lowlands and plains using fewer seeds (with the rice variety selected according to the water regime) and less fertiliser.
The system of rice intensification proves that rice is not strictly speaking an aquatic crop. Rice growing simply requires a very humid environment. The water level is maintained considerably lower down the rice stalk than it is in traditional rice paddies, where water levels range from 10 to 25 centimetres.
SRI makes it possible to increase yields by around 35% compared to average yields. It has been possible to cut costs given the shorter growing season (90 days). Growers reduce seed use by 8 to 10 kilograms per hectare. Water use drops by around 35%, given that the rice is not constantly submerged and water levels in the paddy are low.
Implementation: Firstly, the growers are sensitised and informed about the principles and benefits of SRI in terms of yields and production costs, and are given the opportunity to sign up for technical training in SRI. IICEM takes charge of monitoring the proper application of the SRI methods over the
growing season. Seedlings are planted out individually to ensure each plant has sufficient space to grow. The rice plants are grown individually in rows, which reduces the number of seeds required and makes weeding easier.
Operation: 1) Selecting the most appropriate rice varieties according to the water regime of the area in question (rainfed rice and lowland rice). SRI rice crops adapt well to flood and recession waters, meaning rising and falling water source levels can be managed. 2) Respecting the irrigation cycles developed with the planner: An irrigation cycle is drawn up with a planner. Training is then provided to the growers managing the irrigation system to ensure they adhere strictly to the cycle. It is important for growers in the same hydraulic area to plant out at the same time so their irrigation supply needs correspond. This ensures that the water requirements of the rice crops are met and reduces pumping costs.
Roles of the actors involved: IICEM delivers training to raise awareness about SRI and provide the relevant skills. Conscious of the need to increase yields, IICEM ensures that this learning is applied in the field. Sometimes local NGOs are tasked with providing training and monitoring. Growers apply the SRI approach and monitor inputs and yields so that operations can be effectively evaluated.
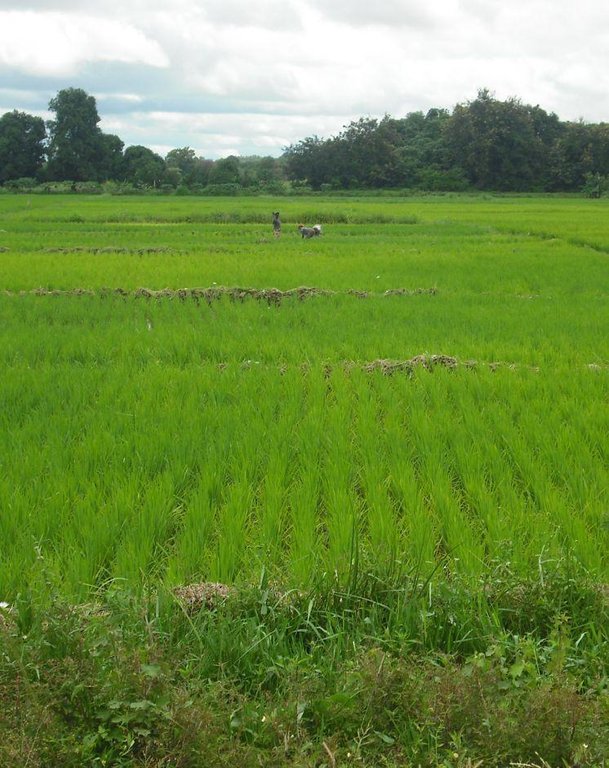
The practice was rolled out in the Mopti, Timbuktu and Gao regions of northern Mali and in Sikasso in the south. Two very small-scale rice fields were installed: one in Deibata in Youwarou Circle and one in Mopti. Farmer organisations supported by IICEM are benefiting from the technique. The practice has been carried out since 2009 by IICEM. It was deployed in Madagascar prior to its introduction in Mali.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
مالي
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Mali
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Mopti, Timbuktu, Gao, Sikasso
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): low rice production, high amount of seeds, fertilizer and water required, high production costs
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: August to November
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
The practice was rolled out in the Mopti, Timbuktu and Gao regions of northern Mali and in Sikasso in the south.
Two very small-scale rice fields were installed: one in Deibata in Youwarou Circle and one in Mopti. Farmer organisations supported by IICEM are benefiting from the technique.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

تدهور المياه
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, improved plant management, improved water management, increases the plants’ potential for production
Change of land use practices / intensity level: system of rice intensification (SRI)
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
CFA Franc
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Growers are sensitised and informed about the principles and benefits of SRI | إدارية | |
| 2. | Opportunity to sign up for technical training in SRI | إدارية | |
| 3. | Selecting rice varieties according to the water regime | إدارية | |
| 4. | Seedlings are planted out individually to ensure each plant has sufficient space to grow. rice plants are grown individually in rows, which reduces the number of seeds required and makes weeding easier. | إدارية | |
| 5. | irrigation cycle is drawn up with a planner | إدارية |
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Species diversity: medium, low
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
The irrigated land is allocated by the chief
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
خطر فشل الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
reduced demand for seeds and fertilizer, shorter growing season
دخل المزرعة
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
الفرص الثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
Contribution to human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
SRI makes it possible to increase yields by around 35% compared to average yields. It has been possible to cut costs given the shorter growing season (90 days).
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The practice has been carried out since 2009 by IICEM. It was deployed in Madagascar prior to its introduction in Mali. Growers who have been trained in SRI continue using the technique as they value its effects;
namely, achieving higher productivity without incurring excessive costs related to inputs, pump unit consumables, etc.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The rice plants are grown individually in rows, which reduces the number of seeds required and makes weeding easier. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| SRI makes it possible to increase yields by around 35% compared to average yields. |
| It has been possible to cut costs given the shorter growing season (90 days). |
| Growers reduce seed use by 8 to 10 kilograms per hectare. |
| Water use drops by around 35%, given that the rice is not constantly submerged and water levels in the paddy are low. |
| Growers who have been trained in SRI continue using the technique as they value its effects; namely, achieving higher productivity without incurring excessive costs related to inputs, pump unit consumables, etc. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
|
SRI growers are strongly advised to use organic fertilisers to supplement soil nutrient levels. Organic fertiliser is not, however, available. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Farmer Returns to Rice, IICEM
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
IICEM leaflet on SRI
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية