Cropping perennial grasses (Miscanthus sinensis gigantheus) on soils contaminated with heavy metals [رومانيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Andrei Vrinceanu
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Deborah Niggli
Cultivarea cu Miscanthus a solurilor poluate cu metale grele (Romanian)
technologies_1706 - رومانيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Horia Barbu
Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu
رومانيا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
National Research and Development Institute for So (National Research and Development Institute for So) - رومانيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
18/05/2015
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
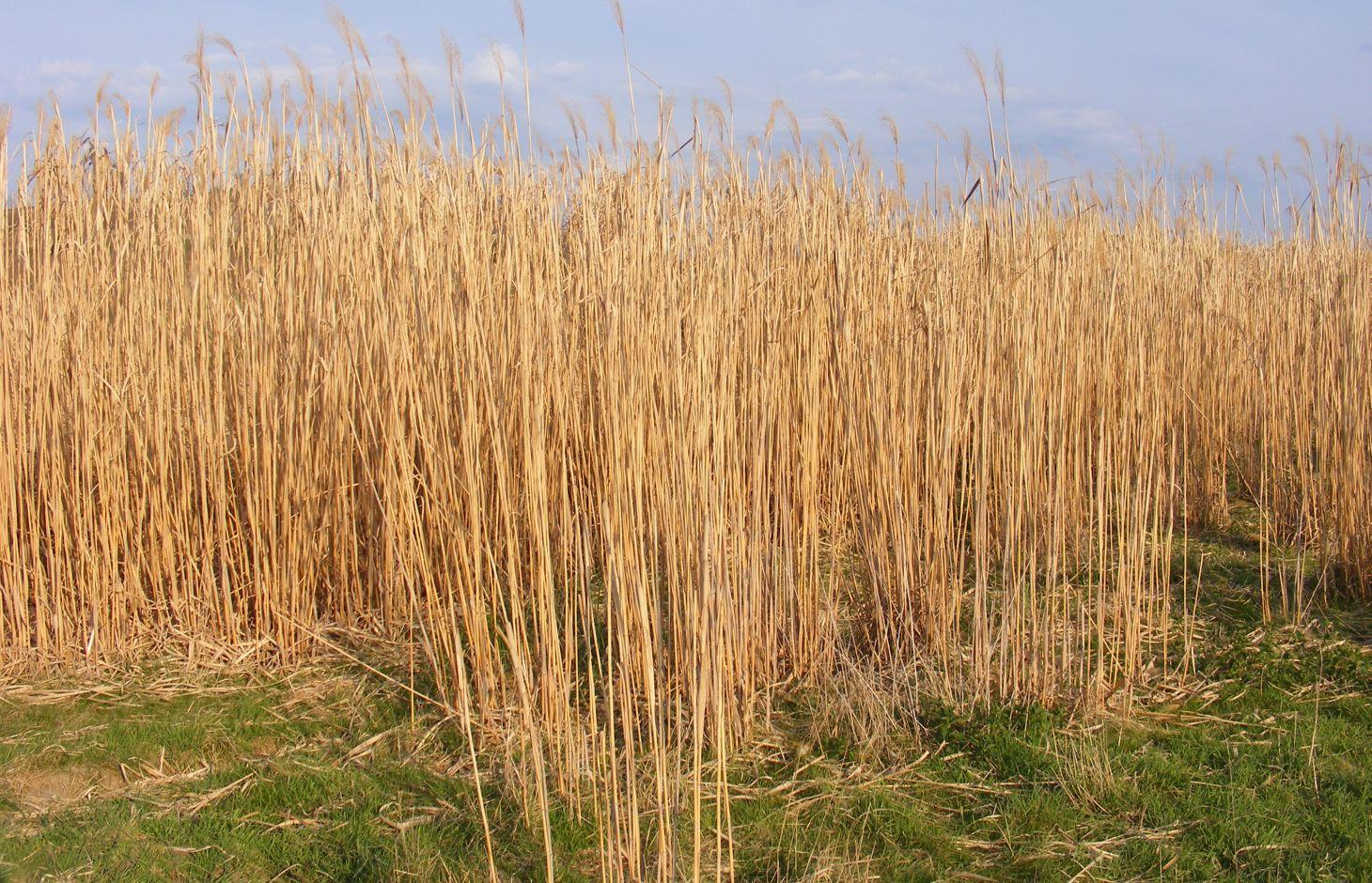
Miscanthus sinensis gigantheus is a perennial warm-season grass used as a commercial energy crop on soils contaminated with heavy metals.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Cropping Miscanthus sinensis gigantheus mainly addresses the problem of land contamination with toxic materials namely soil pollution with heavy metals due to industrial activities. Miscanthus is a perennial warm-season grass used as a commercial energy crop. The plant is a sterile hybrid, unable to produce viable seed, vegetative propagation being by rhizomes, therefore reducing the risk to become invasive. Its special type of photosynthesis (C4) implies the return of the nutrients in the rhizomes during the cold season. As temperatures cool in the fall, the dark green foliage fades to buff and drops, leaving the stems which are the most important commercial part of Miscanthus. Regarding cropping on contaminated soils, research has shown that the amount of heavy metals uptaken by Miscanthus is extremely low, making the plant unsuitable for phytoextraction but allowing it to be used for green energy or in various other fields like pulp and paper industry, without any risk. Miscanthus sinensis gigantheus stands for an alternative crop, from which an annual income can be obtained, instead of food crops and fodder that can represent a risk for human and animal consumption in areas with soils contaminated with heavy metals.
The aim of this technology is to assure a sustainable use of polluted soils with heavy metals through cultivation of energy crops with economic value and very few risks for humans, animals and environment. Studies of Miscanthus sinensis gigantheus behaviour on contaminated soils with heavy metals showed that very small amount of Pb (Lead) and Cd (Cadmium) were detected in the upper parts of the plants. In comparison, higher amounts of heavy metals is being retained at root level in rhizomes, which in time will decrease when root system will develop deeper, in less affected soil horizons as roots can reach 2-3 m in depth. The applied technology increases overall soil quality in terms of organic matter, nutrients and structure. Miscanthus cropping enhances the nutrients cycle in the plant–soil system. As a result of the high input of leaves, rhizomes and roots, the alluvial sandy loam soils, on which Miscanthus is currently croped, can benefit of increased organic carbon amount.
The establishment phase takes place on arable land (annual cropland) which after implementation will become a permanent cropland with perennial (non-woody) cropping, as the crop has the potential to be in the ground for at least 15 years. Miscanthus cropping technique consists of the following: weeding the site in July-August by spraying herbicides for controlling perennial weeds, deep ploughing in October-November to improve subsoil structure and soil aeration possible affected by compaction or hardpan, harrowing in February-April to ensure an adequate seedbed for rhizomes and planting in March-May. Early planting is being recommended as it takes advantage of spring time soil moisture and allows an extended first season of growth. The operation can be made using a modular potato planter or specialized planter like Miscanthus ETPM4. The planting rate is 10 000 rhizomes per hectare in order to provide a good crop density required to achieve optimal yields from year three onwards and effective weed suppression through competition. Rhizomes need to be planted at a depth of 8-15 cm and at 1m x 1m wide spacing. The crop is harvested annually during February-March, typically with conventional farm machineries or specialized ones like Miscanthus CRM Harvesting Cropper. The crop needs 3 to 4 years to reach a mature yield between 15-18 t/ha. The technology requires mechanized agricultural operations and investments in specialized equipment, if necessary.
The technology is applied mainly on alluvial sandy loam soils (Fluvisols), with deep depths, on low lands with flat-gentle slops (0-5%), placed in valley floors/floodplains. The climate is temperate, semi-arid, with an average annual rainfall between 550-600 mm. The plots cropped with Miscanthus are privately owned but leased. Size of crop land where the technology is applied is usually small up to 2 ha. The farmers receive agricultural subsidies and the production system is mechanized and market oriented.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
رومانيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Romania/Transylvania
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Sibiu/Axente Sever
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
from 2008
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
التعليقات:
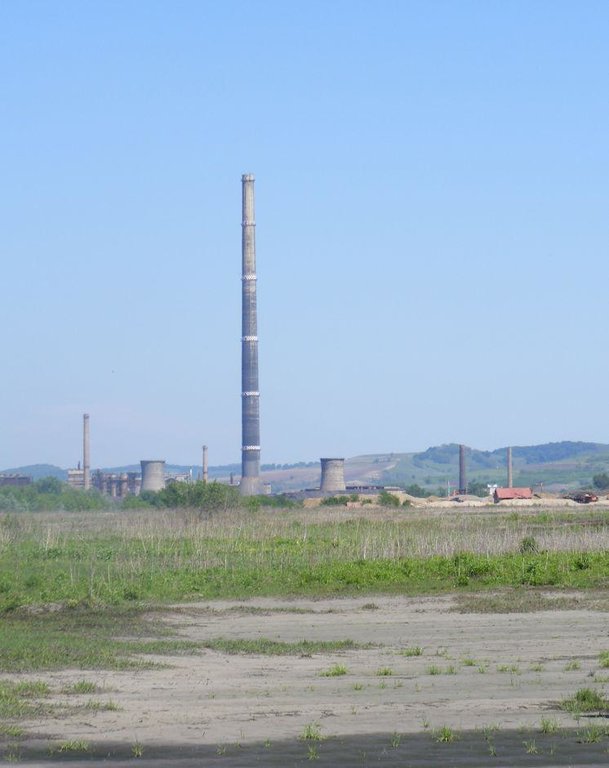
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil contamination with heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Zn).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil contamination with heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Zn).
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: April until October
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.14 m2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
- M4: تغيير كبير في توقيت الأنشطة
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Ed): الانكماش والترسب

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cp): تلوث التربة
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: release of airborne pollutants (urban/industry…) (Heavy metals contamination (Pb, Cd, Zn))
Secondary causes of degradation: governance / institutional (Non-ferrous industry was a strategic activity in communist period with high mass production on the expense of environmental investments (e.g. filters).)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
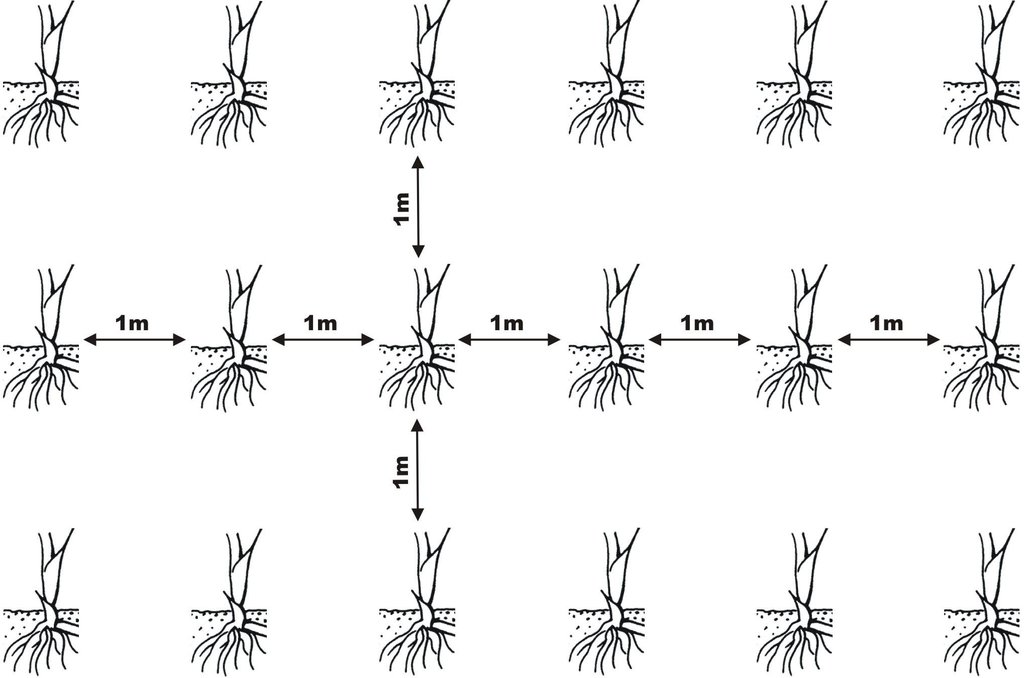
Schematic diagram indicating the spatial distribution of Mischantus rhizomes (1 m between plants) - part of the planting technology
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), retain heavy metals at roots level
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 10000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Perennial crops species: Miscanthus sinensis gigantheus
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from rotational cropping to mono-cropping
Major change in timing of activities: from land preparation and planting in the first year to only harvesting from year 3 to 15
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Lei
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
12.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Treatment with herbicides | نباتية | month VII -VIII |
| 2. | Deep ploughing | نباتية | month X-XI |
| 3. | Soil preparation by harrowing | نباتية | month II-IV |
| 4. | Planting | نباتية | month III-V |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | ha | 1,0 | 102,0 | 102,0 | 93,0 | |
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 237,0 | 237,0 | 93,0 |
| المواد النباتية | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 2180,0 | 2180,0 | 93,0 |
| المواد النباتية | biocides | ha | 1,0 | 62,0 | 62,0 | 93,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 2581,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 9 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvest | نباتية | month II-III |
| 2. | Harvest | إدارية | month II-III |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | ||
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 124,0 | 124,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 149,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: MISCANTHUS ETPM4 Planter; MISCANTHUS CRM HARVESTING Cropper; Deep Reversible Plough; Disc Harrows; Sprayers machime; Tractor, MISCANTHUS ETPM4 Planter; MISCANTHUS CRM HARVESTING Cropper; Deep Reversible Plough; Disc Harrows; Sprayers machime; Tractor
The costs are indicated per ha of land where the technology is implemented. The establishment costs are high but after this in the next 15 years the crop requires only harvesting. As part of the National Rural Development Programme, energy crops receive a subsidy of 173 US $ per ha. Prices are for spring 2015.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The price of rhizomes (seeds) per hectare and harvesting activity involving special machines that cut and chop stems are the most determinate factors affecting the costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
573 mm/year; May and June register the highest amount of rainfall during the year: 85-100 mm
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land.
and own 25% of the land.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إدارة الأراضي
توليد الطاقة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Miscanthus is an energy crop cultivated for generation of heat and biofuels
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Usually from year two no agricultural inputs (fertilizers and pesticides) are required. In case of establishment losses, additional planting is needed to achieve the plant density for optimal yields.
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
farm energy independence
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع الحيواني
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
خطر الحريق
سرعة الرياح
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
1 land user family
التعليقات:
The farmers receive subsidies provided for energy crops.
There is no trend towards (growing) spontaneous adoption of the technology. The establishment costs are considered high.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
High economic value of the crop |
|
Simple agricultural technique |
|
Low-cost of maintenance / recurrent activities |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
This technology allows a sustainable land use of contaminated soils with heavy metals with minimum risk for humans, animals and environment |
|
It is very effective for biomass production with multiple uses: biofuel, animal bedding or cellulose production |
|
Miscanthus sinensis gigantheus is a phytoexcluder with low heavy metal uptake from contaminated soils |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High costs for initial establishment. The cost of rhizomes (seeds) represents 85% of total initial investment costs | Initial costs could be reduced if a proportion of the crop is used as a “mother crop” for the production of rhizome cuttings |
| High costs for purchasing special machines for harvesting activity | Subsidizing |
| Undeveloped energy crop market | Support for creating local or regional markets for energy crops |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Low suitability on lands without phreatic input | Selecting sites with good groundwater availability |
| Relatively long period (three to four years) for achieving a mature yield | Maintaining the energy crop subsidies |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Barbu, C.H., Pavel, P.B., Sand, C.; Pop, M.R., 2013. Reduced uptake of Cd and Pb by Miscanthus sinensis x giganteus cultivated on polluted soil and its use as biofuel, Environmental Engineering & Management Journal (EEMJ), Vol. 12 Issue 2, pp: 233-236
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Barbu, C.H., Pavel, P.B., Sand, C.; Pop, M.R., 2009. Miscanthus sinensis gigantheus’ behavior on soils polluted with heavy metals, Metal Elements in Environment, Medicine and Biology, Tome IX, Cluj University Press, pp: 21-24
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية