Post-fire salvage logging; post-fire traditional logging [البرتغال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Maruxa Malvar Cortizo
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Extração material lenhoso pos-incêndio
technologies_1713 - البرتغال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Keizer Jan Jacob
+ 351 234 370200
jjkeizer@ua.pt.
Centre for Environmental and Marine Studies (CESAM) - Department of Environment and Planning-University of Aveiro
Campus de Santiago, 3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal
البرتغال
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - البرتغال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
21/09/2016
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Post-fire salvage logging is the practice of harvest the trees after fire, the employed methodology is clearcutting which involves the cut of essentially all the trees and the removal of logging residues.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
In the 2015 summer a wildfire affected the Semide mountain range nearby the Lousã massif, central Portugal. The area was afforested with eucalypt and pine plantations during last XX century and nowadays landscape is composed mainly by eucalypts at different stages of development and, the understory shrub vegetation.
The research team of the University of Aveiro set up an experiment to test the effect of post-fire logging in soil erosion and other selected soil properties.
Purpose of the Technology: Post-fire logging is a common management practice usually undertaken to recover burnt timber resources, to plant new seedlings and to reduce possible insect infestation hazard. In Portugal, about 10x106 m3 of timber could be harvested every year and a considerable percentage of this figure comes from recently burned eucalypt and pine stands.
Post-fire logging could have a multiple detrimental effect on ecosystem as fire-affected ecosystems are sensitive to further disturbance. This multiplier effect concerns soil compaction, soil (fertility) losses, with serious implications for in-situ plant growth, soil biota and for downstream aquatic systems. Furthermore, post-fire logging undermines the effectiveness of costly rehabilitation efforts aimed at reducing soil erosion. Hence, the post-fire logging practice is still controversial in terms of economic benefit and environmental consequences, in many parts of the world.
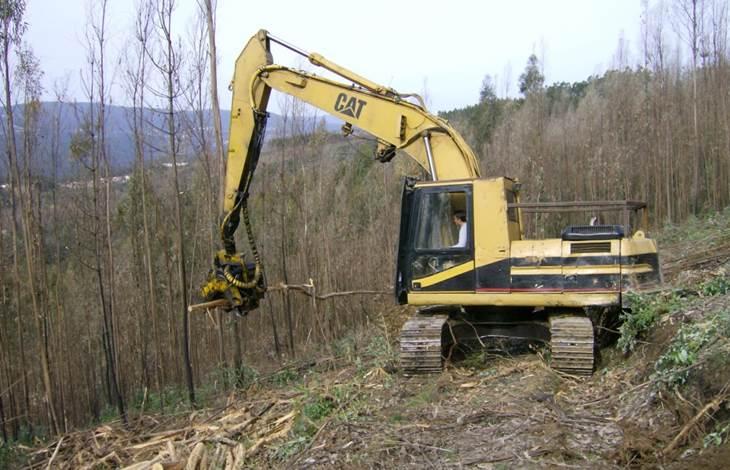
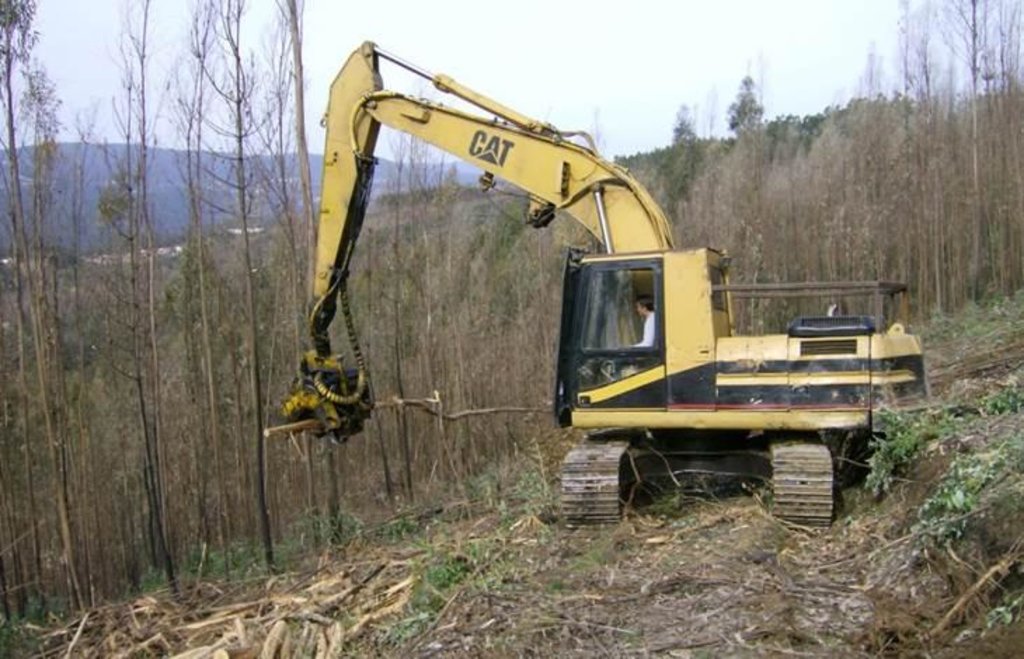
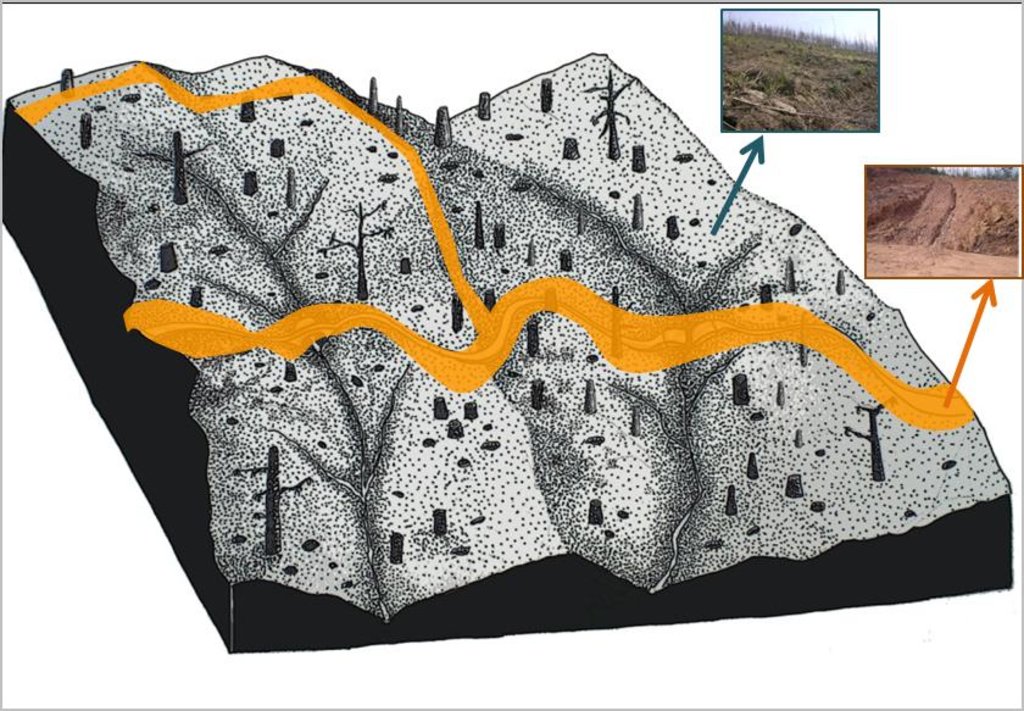
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The standard logging technique consists of felling burned trees either with a harvester or manually with a chainsaw depending on slope conditions and machinery available. The logs will be gathered with the harvester, using a cable-skidder or pulling logs down-slope with a cable attached to a tractor. A forwarder will transport them to the main pile prior to load and removal by trucks.
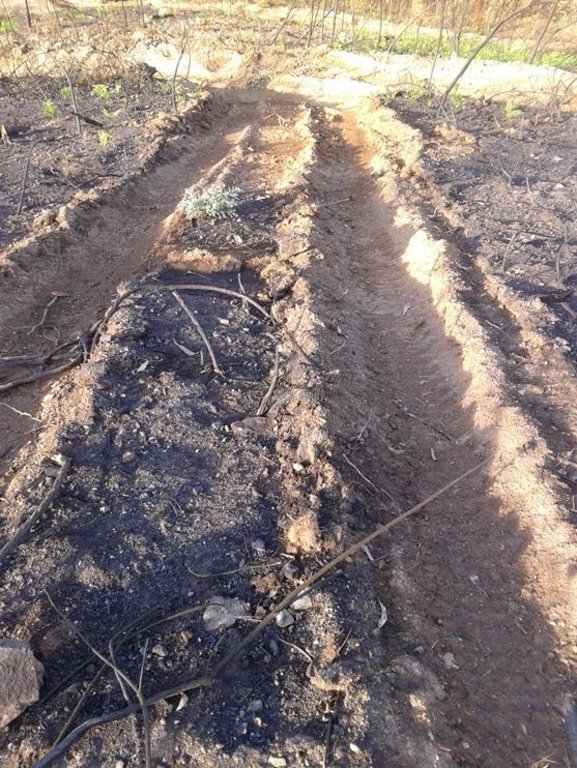
The slope will present two well differenced units according to soil surface disturbance, the skid trail or the logged area.
Natural / human environment: The eucalypt trees in the region are typically planted as monocultures for paper pulp production, and harvested every 7-14 years. The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-)natural and man-made agricultural and afforested lands. Since the 1980´s, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, aided by a general warming and drying trend but driven primarily by socio-economic changes.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
البرتغال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Coimbra
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Coimbra
2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Strong increases in runoff and erosion should be a main land management concern following wildfires, as they constitute a serious threat to land-use sustainability and downstream aquatic habitats and human infrastructures. In addition to fire itself, post-fire logging activities can greatly increase erosion response of recently burnt areas. Furthermore, logging is typically the most common practice after fire, and recently burnt soils are more erodible than long-unburnt soils.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of wood resources and productivity.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 3
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: September to May
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الغابات الطبيعية وشبه الطبيعية
- إدارة مزارع الغابات
- Post-fire logging
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
The studied area is a hillslope scale but total logged area is larger
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V3: إزالة الغطاء النباتي

التدابير الإدارية
- M7: أخرى
التعليقات:
Main measures: management measures
Specification of other management measures: Recover burnt timber resources and improve the re-sprout of new eucalypts
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bf): الآثار الضارة للحرائق
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pc: compaction, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bf: detrimental effects of fires
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Eucalypt plantations are prone to forest fires), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Logging increases soil erosin risk and soil compactation), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Logging increases the lost of vegetation cover), population pressure (Since the 1980´s, eucalypt plantations increased greatly, driven primarily by socio-economic changes.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
The slope will present two well differentiated units according to soil surface disturbance, the machinery trail and the logged area. The soil erosion risk will be associated with the loss of ground cover due to mechanical disturbance. Furthermore, the machinery trail presents the risk of concentrated overland-flow with the subsequent rill formation.
Location: Semide. Coimbra
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (The use of machinery is preferable but not essential)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan)
Other type of management: Recover burnt timber resources and improve the re-sprout of eucalypt stumps
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
euros
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,92
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
60.87
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1 person with chainsaw | إدارية | 24 |
| 2. | Harvester transport ( in a radio of 50 km)Harvester working (with person)Forwarder (with person)Final transport (in a radio of 50 km) | إدارية | 60 |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 1461,0 | 1461,0 | |
| معدات | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 5870,0 | 5870,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 7331,0 | |||||
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
The prices were determined for a clearcutting of a slope with acceptable slope degree and accessibility. Prices were calculated by hectare in winter 2015 for central Portugal.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Accessibility and steepness will raise the costs. The use of machinery is not a mandatory. Small land owners decrease the total cost by doing manual work with a family framework.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is medium-high
Topsoil organic matter is high (afforested soils)
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor-medium ( Soil water repellency)
Soil water storage capacity is low (very shallow soils)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water is good - medium (very dry summer)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Burnt soil
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Harvesting forest areas is typically a men work, probably due to the machinery use and/or the physical strength needed.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), mixed (subsistence/ commercial, commercial/ market
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الخشب
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Promoves eucalypt monocultures
توليد الطاقة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Biomass
الدخل والتكاليف
تنوع مصادر الدخل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
التعليقات/ حدد:
The logging of the burnt trunks arguably improves the esthetic value of the area, including by removing evidence of the fire
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Yes, because timber production is a complementary income for many families in the region
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
سرعة الرياح
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Soil erosion locally
Crop diversity
Habitat fragmentation
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
There is no maintenance
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Small land owners need to request the clearcutting to harvester companies; but they do it spontaneus
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Short-term economic benefits How can they be sustained / enhanced? Decrease wildfires will increase the economic value of the timber |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
The chance to obtain an economic benefit from forest plantations diminished depopulation of rural areas in the region. How can they be sustained / enhanced? A diversification toward native forest species cultivation (i.e. cork oak, olive trees, and chestnut tree) would be a very good alternative for the improvement of the ecosystem services, the reduction of wildfires risk and the increase of the socio-economic conditions in the region |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| When timber quality is no good (due to fire) there is no economic benefit | Take the advantage to modify eucalypt plantations toward more sustainable land use |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Increased runoff and soil erosion and possibly modify soil properties | There are several mitigation treatments that can be used to decrease the risk of soil erosion/degradation after logging activities. The use of water dams in the machinery trails and/or the spread of logging residues on the uncover/disturbed soil are techniques that can give good results |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
DellaSala, D.A., 2006. Post-fire Logging, Summary of Key Studies and Findings. World Wildlife Fund, Washington,USA.
http://www.nccsp.org/files/Postfire%20Summary%20of%20Key%20Findings.pdf
Fernández. C, J.A. Vega, Fonturbel.T Pérez-Gorostiaga P., Jiménez E., Madrigal.J., 2007. Effects of wildfire salvage logging and slash treatments on soil degradation. Land Degrad. Develop. 18: 591–607. DOI: 10.1002/ldr.797.
Inbar, M., Wittenberg, L., Tamir, M., 1997. Soil erosion and forestry management after wildfire in a Mediterranean woodland, Mt. Carmel, Israel. International Journal of Wildland Fire 7: 285–294.
Malvar, M.C., Martins, M.A.S., Nunes, J.P., Robichaud, P.R., Keizer, J.J., 2013. Assessing the role of pre-fire ground preparation operations and soil water repellency in post-fire runoff and inter-rill erosion by repeated rainfall simulation experiments in Portuguese eucalypt plantations. Catena, 108, 69-83.
Prats S.A., Malvar M.C., Vieira D.C.S., Keizer J.J., 2013, in press. Effectiveness of hydromulching to reduce runoff and erosion in a recently burnt and logged Maritime Pine stand in central Portugal. Land Degradation and Development. (accepted in June 2013).DOI: 10.1002/ldr.2236.
RECARE project: Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe trhough Land Care.
http://www.recare-project.eu/
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
internet
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية