Zero Tillage [الصين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Zhanguo Bai
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
No Tillage
technologies_969 - الصين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ISRIC World Soil Information (ISRIC World Soil Information) - هولندا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
17/05/2002
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Zero Tillage [الصين]
Zero tillage approach was developed to protect the soils from sealing rainfall, to achieve and maintain a open internal soil structure, to enhance biological processes in the soil, and to develop a means for safe disposal of any surface runoff that nevertheless will occur.
- جامع المعلومات: Zhanguo Bai
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Zero tillage technology was developed to protect the soils from sealing rainfall, to achieve and maintain a open internal soil structure, to enhance biological processes in the soil, and to develop a means for safe disposal of any surface runoff that nevertheless will occur.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
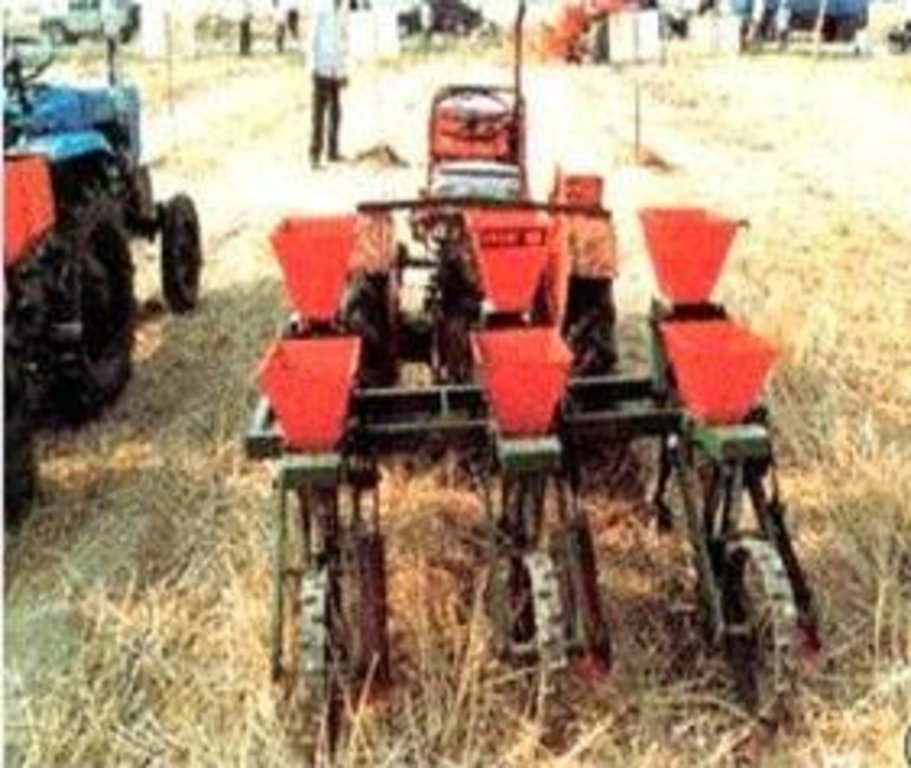
No tillage with residual mulching is developed to minimally disturb soil structure, directly to sow in the residual mulching covered soils. The crop system is rotated. It is used to maintain the soil moisture and particles that would be moved by runoff and improve soil fertility.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الصين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Henan province
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
USA, Canada
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Traditional till farming (multi-till system) has made soil loose and easily being moved on the dry and semi-dry slope farmland. No coverage exist after harvest and till leading to serious erosion. Meanwhile less and less organic fertilizer is applied and replaced by increase in chemical fertilizer use so that soil fertility and crop quality decline.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): More and more input are needed to maintain stable yield, quality of the crops and fruits are declining.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: After harvest of wheat in June, corn or peanut or bean are saw and harvest in later autumn
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - SepSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Sep
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 800 m2.
This technique has been successfully applied in the slope farmland, especially in the Loess Plateau and in the dry-semidry regions in the NW China. It is an ideal approach to infiltrate all precipitation in soils and reduce soil erosion and water loss in slope farmland.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - irrational tillage on the slopeland), land tenure (Land subdivision)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (insufficient rainfall and not well distribution), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, improvement of soil structure, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: film
Quantity/ density: 60% of sur
Remarks: alignment
Agronomic measure: residual cover
Material/ species: residual, straw
Quantity/ density: 80% of sur
Remarks: mean
Zero tillage / no-till
Remarks: Leaving residual after havest
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5.00
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 96 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | applying fertilizer | زراعية | after harvest / each cropping season |
| 2. | Sowing using no-till machine | زراعية | after harvest / each cropping season |
| 3. | weeding | زراعية | crop growing / each cropping season |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: No-till machine, tractor
Subsidy is needed at the beginning of the SWC implementation.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Zero tillage machine and tractor
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
646mm for Luoyang/Henan
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
- قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Hill slopes: SE part of the Loess Plateau, mainly hilly area
Plateau / plains: low proportion in the whole SWC applied area
Valley floors: small area in the whole SWC applied area but output high with better irrigation systems
Slopes moderate: There is not much terraces built in this area and slope degree remains natural status
Slopes hilly: This part of the slope land have been developed for cultivation due to increasing population
Slopes steep: It is used by mixed treatment of forest and crop land.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth deep: In the area the soil parant material is loess with thickness.
Soil depth shallow: Mainly distributes in the mountain slope
Soil texture medium: The soil parent material is loess which is loose with porous structure of particle "point-prism contact".
Soil texture fine heavy: The loess mainly originates from aeolian deposition.
Topsoil organic matter medium: organic matter is applied.
Topsoil organic matter low: mainly loess (earth) with little organic matter applied in the area
Soil fertility is low or very low and little or very little organic matter is applied in the area
Soil texture medium: The soil parent material is loess which is loose with porous structure of particle "point-prism contact".
Soil texture fine: The loess mainly originates from aeolian deposition.
Soil drainage is medium because the soil (earth) is loose.
Soil water storage is low or medium: No mulching on the soil surface and high evaporation and low under gound level.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
مستوى المكننة:
- الجر الحيواني
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
20% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (generally young person with skills).
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: SWC users can get much more subsidies from governments or projects than those who take no SWC technology.
Animal traction is individual
Machines are shared or leased.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
30
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5
التربة
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
25
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 50-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
800 families (35 percent)
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
التعليقات:
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
600 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technique can bring ecological, social and economic benefits
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Report of ninth-Five plan project on Dryland Farming. Jan. 2002.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
internal reference
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Introduction of Luoayng physicography. 2000.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
unpublished materials
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
No-till farming for sustainable rural development. 2002.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
World Bank
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
A road map from conventional to no-till farming. 2002.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
World Bank
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Conservation agriculture. 2001.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
FAO
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Zero Tillage [الصين]
Zero tillage approach was developed to protect the soils from sealing rainfall, to achieve and maintain a open internal soil structure, to enhance biological processes in the soil, and to develop a means for safe disposal of any surface runoff that nevertheless will occur.
- جامع المعلومات: Zhanguo Bai
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية