The “Green Liver System”: eco-friendly water purification [البرازيل]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Marianna Siegmund-Schultze
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Fitorremediação (Portuguese)
technologies_1710 - البرازيل
- The “Green Liver System”: eco-friendly water purification : 7 مارس، 2019 (public)
- The “Green Liver System”: eco-friendly water purification : 29 إبريل، 2017 (inactive)
- The “Green Liver System”: eco-friendly water purification : 20 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
- The “Green Liver System”: eco-friendly water purification: 8 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
- The “Green Liver System”: eco-friendly water purification: 7 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Leibniz-Institut für Gewässerökologie und Binnenfischerei (IGB) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Potsdam-Institut für Klimaforschung (PIK) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Universität Hohenheim - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Technische Universität Berlin (Technische Universität Berlin) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft Dresden (HTW Dresden) - ألمانيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Water purification using macrophytes to treat effluent from fish farming.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
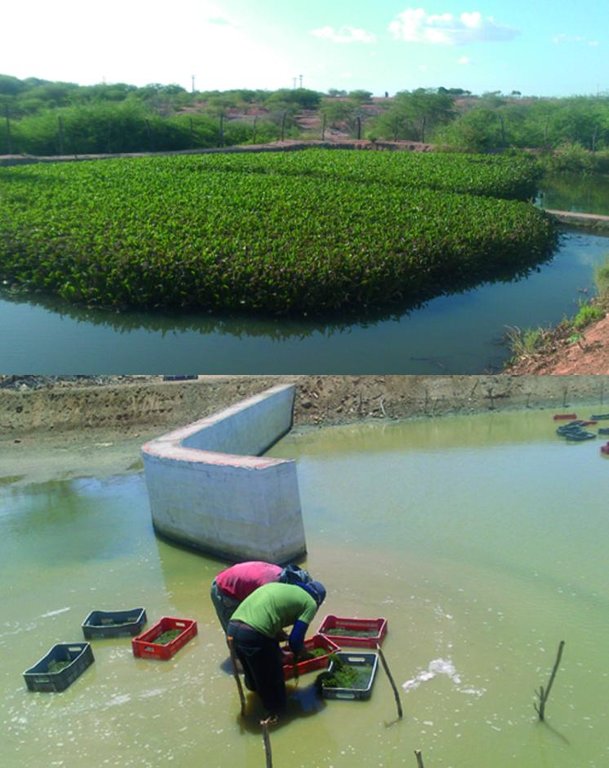
The “Green Liver System” uses aquatic plants, established in artificial wetlands, to remove, transfer, stabilize or eliminate pollutants in wastewater from fish farms. The use of large quantities of feed in aquaculture, along with the application of antibiotics, hormones and probiotics, has negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems due to the introduction of nitrogen, phosphorous and drug residues into the system. The Green Liver System is a form of phytoremediation (phyto = plant and remediate = correct) that uses a range of plants to decompose, extract, or hold contaminants present in soils and waters. This technology has been considered as an innovative alternative and a low cost option compared to others used in contaminated sites - like membrane bioreactors, upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB), and others.
Purpose of the Technology: The plants selected for use in Green Liver System artificial wetlands depend on the pollutant to be removed. Research shows physiological differences between species, which need to be taken into account when planning wastewater treatments. Ideal plants for phytoremediation need: a) a fast growth rate; b) high biomass production; c) long rooting systems; d) easy maintenance/pruning; e) to be able to persists, and f) to have the ability to store trace metals within specific parts which can be later removed.
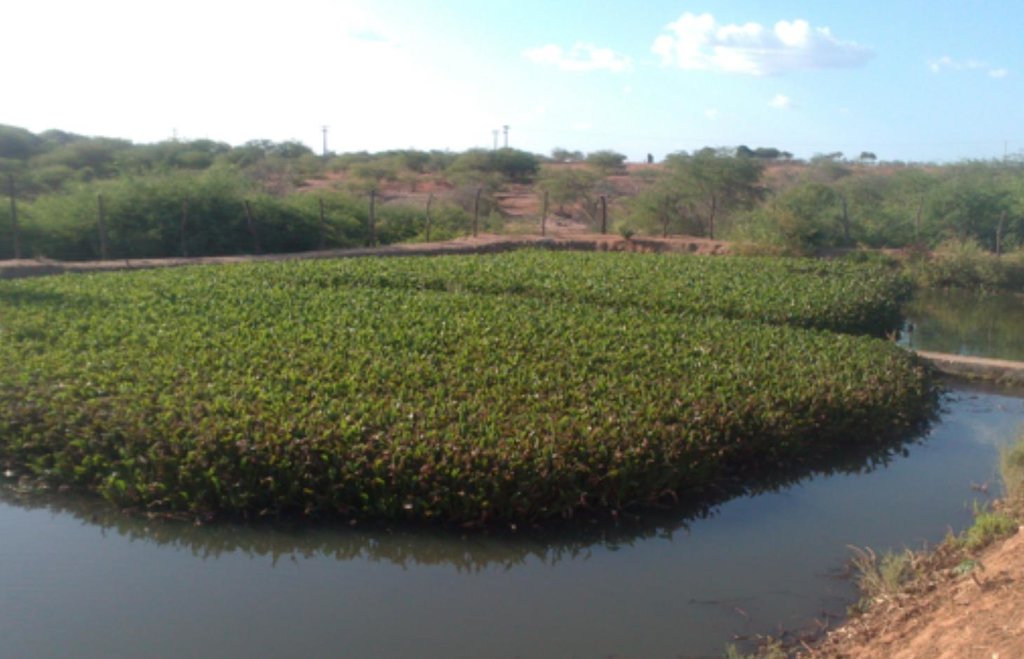
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The Green Liver System uses aquatic macrophytes, which extract contaminants from the water, store them, or even metabolize them - transforming them into less toxic or harmless products. In the case of Eichhornia crassipes, most of the solids in suspension are removed by sedimentation or by adsorption in the root system. The dense coverage of these plants reduces the mixing effect of the wind, as well as minimizing thermal mixture. Shading by the plants restricts algal growth and the root system prevents horizontal movement of particulate material. In this way, particles are removed from the wastewater and microorganisms associated with the plants’ rhizosphere slowly decompose. Many organisms can be used in biodegradation: these include bacteria and fungi as well as plants, and the efficiency of one or the other depend, in many cases, on the molecule structure and of the presence of enzymes that are effective in degrading the pollutant.
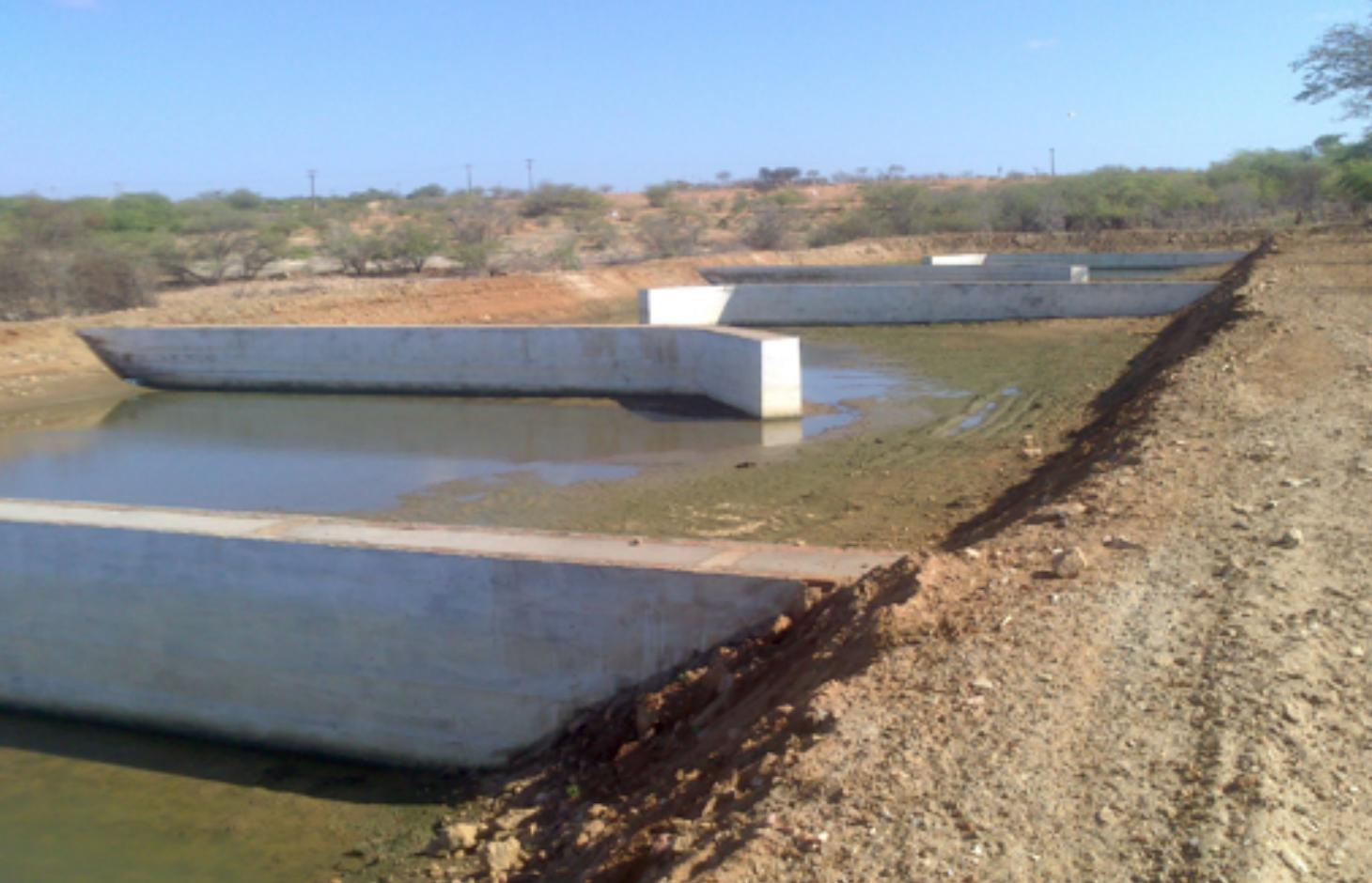
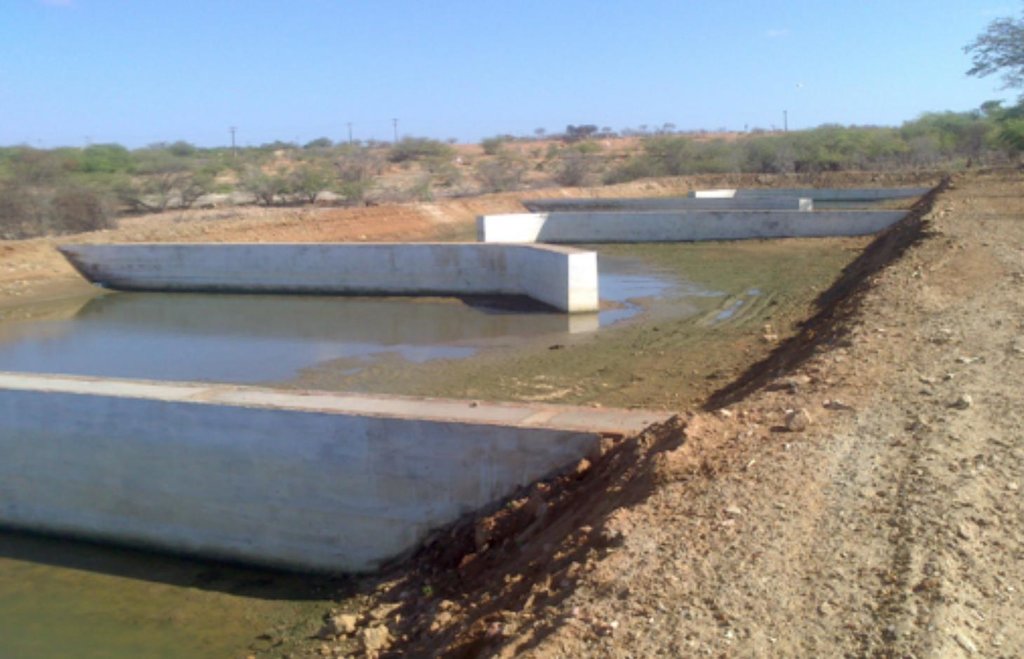
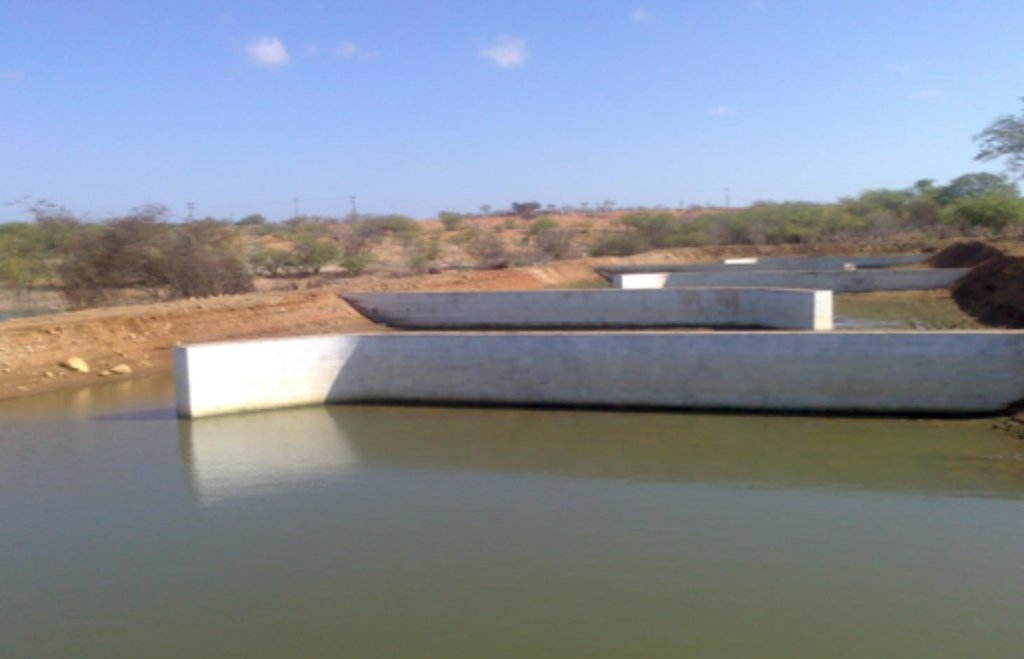
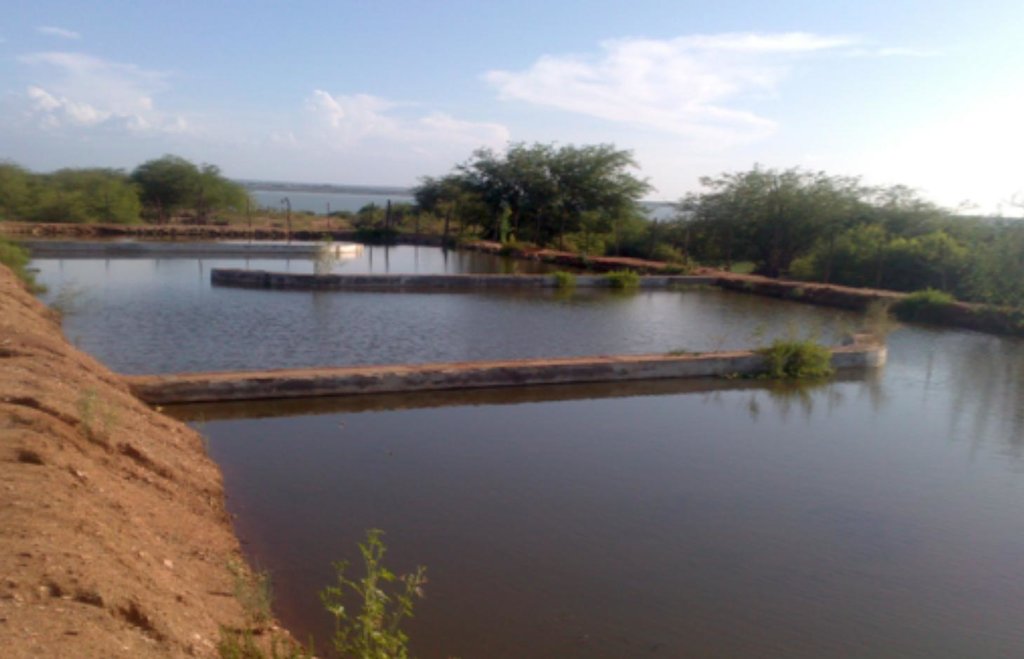
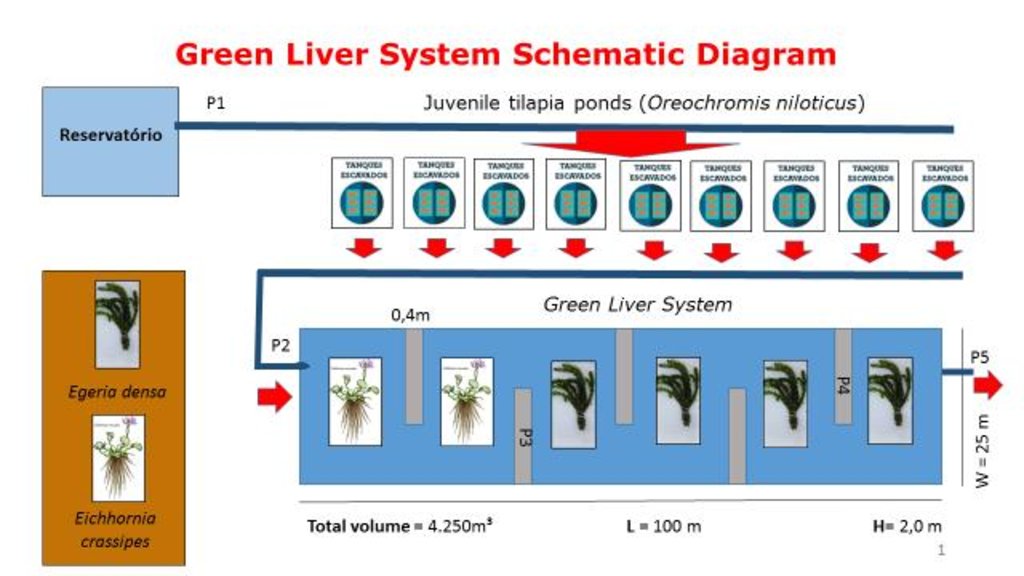
Natural / human environment: The fish farm used as an example here is located on the margins of the Itaparica reservoir in Brazil. There are dozens of excavated tanks used to produce tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and “tambaqui” (Colossoma macropomum) fingerlings and juvenile fish. As well as these tanks, there are many net enclosures installed in the reservoir where the fishes are reared to maturity. Part of the wastewater from the excavated tanks is released into a stabilization lagoon, and the remainder goes to the Green Liver System. The effluent is enriched with spare feed, and excreta from the fish, which includes drug residues. If not treated, this may cause eutrophication because of its mineral richness. The Green Liver System consists of an excavated tank of 100m x 20m x 2m in size. The tank is subdivided into six parts: two planted to Eichhornia crassipes and four to Egeria densa. A mesh barrier stops fish from being flushed into the tank. Regular monitoring of the physical, chemical and biological parameters is required to control environmental fluctuations.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
البرازيل
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Pernambuco
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Vila do Coité, Itacuruba
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Construction took place in 2013, building on earlier experiences of the principal scientist, for instance in South Korea.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

المجاري المائية، المسطحات المائية، الأراضي الرطبة
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The Itaparica reservoir was completed in 1988 to generate hydropower. About 40,000 people were compulsorily relocated. The construction of the reservoir had interrupted fish movement, leading to a shortage of fish, making aquaculture a viable and profitable alternative, and current law allows this. However excess feed and excreta of fish, partly containing drug residues, add nutrients and pollute water. ECONOMIC ASPECTS: The agricultural economy of this semi-arid region is characterized by pastoral activities, as well as the cultivation of crop species resistant to drought, such as cotton, corn (maize), beans, and cassava in humid areas. Irrigation from the reservoir was potentially possible but investments in aquaculture proved more profitable. In general, the commercial companies involved do not treat effluent, leading to pollution. Even though monitoring is mandatory, almost nobody does it, nor do they make substantial efforts to purify the effluent.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There are several conflicts over water and related land use in the region. Some people say the water quality in the reservoir is good (and use it directly for drinking), others report ill-health especially during times of low water levels. Commercial aquaculture primarily produces tilapia. Invariably, some tilapia escape from their net cages and take over from other local species. The hydroelectric company manages the reservoir according to national needs in electricity – thus sudden water level fluctuations are frequent. Commercial aquaculture and associated land use dominate the shoreline, preventing access for artisanal fishermen to their traditional fishing grounds.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Ow: Waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams
Constraints of transition land, fallow or sporadicall used by roaming livestock (mainly goats) (area in between the land-based aquaculture and the lake)
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period from month to month: all year due to tropical climate
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة المياه السطحية (الينابيع، الأنهار، البحيرات، البحار)
- حماية/ إدارة الأراضي الرطبة
- Water purification
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2 m2.
The reservoir is 100m long and 20 m wide, with a depth of 1.7 m, but the area may be larger depending on the volume of effluent to be treated. The whole area comprises the fish ponds.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V5: أخرى

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Specification of other vegetative measures: macrophytes, different species
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تدهور المياه
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hp: decline of surface water quality
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (slash-and-burn practices), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood and charcoal making), overgrazing (free roaming run-wild donkeys, and small ruminants), urbanisation and infrastructure development (construction works near to body bodies (not respecting conservation areas)), discharges (point contamination of water) (indiscriminate disposal of effluents; excrements, drugs and surplus feed from fishes in net-cages), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (abstraction of water from the reservoir without prior registration, not holding water use permits), change in temperature (supposed to be climate change induced), change of seasonal rainfall (high variability in semi-arid regions rather normal; though rainfall appears to fall in shorter periods), droughts (recurrent droughts are "normal", they appear to last for longer periods), poverty / wealth (limited livelihood sources in the rather remote municipality), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (spoilage and low quality), education, access to knowledge and support services (often little value attached to natural resources), war and conflicts (conflicts among two families; conflicts among indigenous and commercial users), governance / institutional (restricted enforcement of existing rules; clientelism)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), industrial activities and mining, release of airborne pollutants (urban/industry…), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, population pressure, land tenure, labour availability
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المؤلف:
Stephan Pflugmacher-Lima, TUB, Faculty VI Planning Building Environment; Sekr. A1; Str des 17. Juni 152; 10623 Berlin; Germany
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
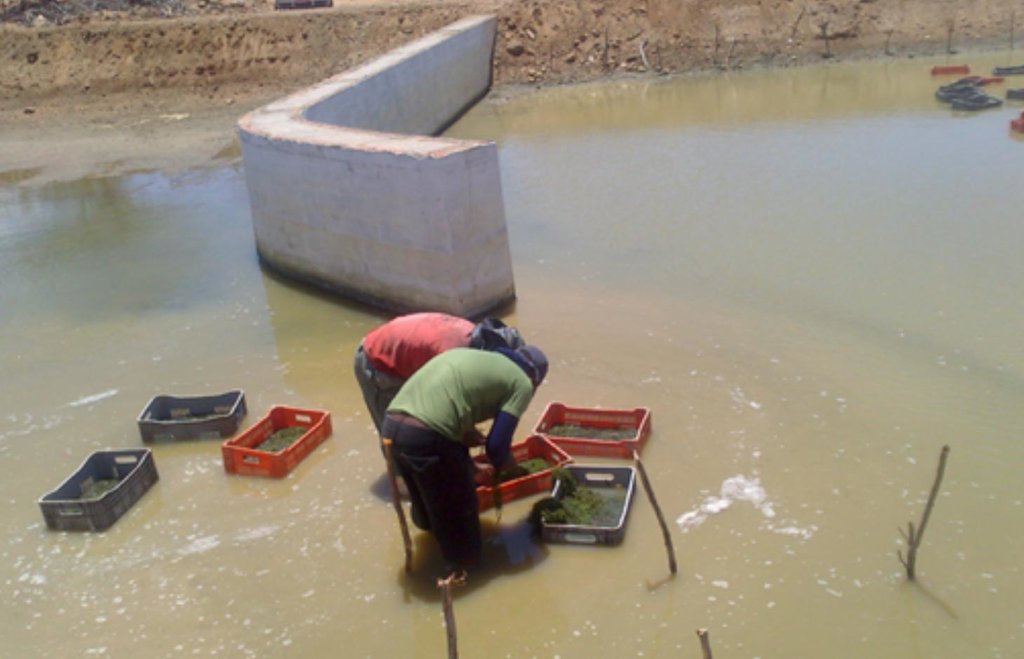
The constructed wetland termed a “Green Liver System” is 100m x 25m x 2.0m in size. It is divided into six parts (one third of the tank planted with Eichhornia crassipes the remainder with Egeria densa). The average outflow during the period was 1,800 m³/h. Point P1 is the catchment from the reservoir. Point P2 is the inlet that receives the discharge of effluent from 10 ponds with juvenile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Point P3 is the stage after the treatment with Eichhornia crassipes. Point P4 is the stage of the treatment with Egeria densa. Point P5 is the outlet into a containment basin.
Location: Itacuruba. Pernambuco
Date: 2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (It is a sophisticated system which requires close observation and monitoring. Site-specific adaptation might be necessary (for instance fencing to avoid goats entering the area).)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (It is a sophisticated system which requires close observation and monitoring. It will be easier with some experience.)
Main technical functions: improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
In blocks
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 250000
Other species: Egeria densa; Eichhornia crassipes
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.7
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 20
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Wall/ barrier
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.7
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): ca 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): ca 15
Construction material (other): tubes, valves
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 3400m3
Dimensions of spillways: ca 100m
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
3,17
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
25.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging the pit, stabilizing the walls | نباتية | |
| 2. | Fencing | نباتية | |
| 3. | Building separation walls | نباتية | |
| 4. | Planting macrophytes in place | نباتية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Construction | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | ||
| العمالة | Macrophyte installation | 1,0 | 1900,0 | 1900,0 | ||
| معدات | Truck for removal of soil | 1,0 | 125,0 | 125,0 | ||
| المواد النباتية | Macrophytes | 100,0 | ||||
| المواد النباتية | Wooden fence posts | 100,0 | ||||
| مواد البناء | Walls/baffles (cement) | 1,0 | 475,0 | 475,0 | ||
| مواد البناء | Barbed wire | 1,0 | 315,0 | 315,0 | ||
| مواد البناء | Earthwork | 1,0 | 250,0 | 250,0 | ||
| مواد البناء | Tubular elements | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | ||
| غير ذلك | Labour: Cutting fence posts | 1,0 | 160,0 | 160,0 | ||
| غير ذلك | Labour: SUpervision | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | ||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 7255,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Exchange macrophytes | نباتية |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | ||
| معدات | Nylon fabric | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | ||
| المواد النباتية | Macrophytes | 1,0 | 100,0 | |||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 3015,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Because of the tropical climate of Brazilian northeast there is a need to remove Eichhornia crassipes periodically because it grows very quickly as there is plenty nutrients and warm temperatures during all year. The cost of removal of the macrophytes is permanent and must be made monthly as the plant reaches adulthood it loses its capability in removing nutrients and gives it back to the water.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
It happened to be less than 100mm in 2013. Very unreliable rainfall pattern. Rainfall from Dezember to May, most rain often in March
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics. Bsh according to Köppen classification
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
- needs official registration and permission; heavy water use has a price
- needs official registration and permission; heavy water use has a price
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
extension service:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
توافر المياه للماشية
توافر مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Biomass of macrophytes for potential ethanol production.
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Labour cost
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase of maintenance costs as manual labor is required for management of macrophytes.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Better water management in a setting of decreasing seasonal rainfall.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The technology contributed to improved water quality, which is directly related to people's health.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Any open water body is subjected to the very high potential evaporation in the region. Though, the surface of the system is very small as compared to the adjacent reservoir.
التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The vegetation had to be removed in order to construct the artificial wetland.
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Vulnerability
التعليقات/ حدد:
A nylon grid prevents the macrophytes from occasionally breaking loose into the reservoir.
The ecology of the system is sort of fragile. If the macrophytes float too much, the system can break down.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: A broad adoption is not yet expectable at this stage of experimental analysis and testing. Few people did already express their interest.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
If the environmental authority increases controls of how effluent from aquaculture ponds is handled (checking pollution and nutrient loads in the effluent which is usually returned to the reservoir without any treatment), the technology would help compliance with existing rules. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Enhancing control and penalties would favour the adoption of such a green technology. Currently controls are rare or non-existent. |
|
The technology can be constructed using locally available material. How can they be sustained / enhanced? As long as cheap labour is available and rural shops exist, the availability of inputs is adequate. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Water purification is realized by using natural processes. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the related tilapia production unit could gain a green or ecological stamp, this would be beneficial and maybe trigger the adoption of the technology. |
|
Among the advantages of adopting the Green Liver technology are the low costs, the speed of construction and it's relatively easy operation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Easily accessible and comprehensive information is needed, as well as the possibility to exchange experience among users or future users. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Additional manual labour increases costs (and hinders adoption) | The more people use such techniques, for instance due to improved environmental monitoring and fines imposed, the more such extra expenditure will be accepted as regular running costs. |
| The management of the system is not simple. Many different and unexpected disturbances can occur. Experience and close, constant watch out is needed. | Exchange of experience among users would facilitate its management. An updated list of threats could be helpful. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| From time to time the macrophytes have to be removed, tubes may need cleaning and the system needs to be set up again. Sometimes, the removal of almost all water may be indicated. Major maintenance can cause peak labour needs. Manual labour required to monitor the system on a regular basis, and perform maintenance according to needs. Depending on the number and size of Green Liver Systems in action, caring for them can be a full-time job. | The maintenance costs have to be well budgeted in the overall planning of costs and benefits of the related productive units. |
| The disposal of the removed macrophytes is still a problem to be solved. If the macrophytes have accumulated high levels of toxins, the biomass cannot be used for compost making or livestock feeding. | The removed macrophytes should be analysed for their pollutant content. A biodigester could be the solution to the disposal of contaminated biomass, generating energy for the productive unit and possibly for the local population too. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Pflugmacher, S., Kühn, S., Lee, S.-H., Choi, J.-W., Baik, S., Kwon, K.-S., Contardo-Jara, V., 2015. Green Liver Systems® for water purification: Using the phytoremediation potential of aquatic macrophytes for the removal of different cyanobacterial toxins from water.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
AJPS 06 (09), 1607–1618. doi:10.4236/ajps.2015.69161.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Nimptsch, J., Wiegand, C., Pflugmacher, S., 2008. Cyanobacterial toxin elimination via bioaccumulation of MC-LR in aquatic macrophytes: An application of the “Green Liver Concept”
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Environ. Sci. Technol. 42 (22), 8552–8557. doi:10.1021/es8010404.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية