Contour Farming using hedgerows [الفيليبين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Eduardo Alberto, Alexandra Gavilano
Contour Farming
technologies_1287 - الفيليبين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Luistro Aida
DA_STIARC, RFO IV-A
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Gregorio Elizabeth
DA_STIARC, RFO IV-A
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Dinamling Djolly Ma.
DA-BSWM
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Gutierrez Albert F.
alfergu@yahoo.com
LGU of La Libertad, Negros Oriental
الفيليبين
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
LGU of La Libertad - الفيليبيناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Southern Tagalog Integrated Agricultural Research Center (STIARC) - الفيليبيناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - الفيليبيناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Regional Field Office N0. 4A (RFO IV-A ) - الفيليبين1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
27/05/2015
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Conservation Farming Village [الفيليبين]
A modality in mobilizing resources for sustainable upland development which utilizes a basket of strategies, technologies, and interventions to catalyze the widespread transformation of traditional upland farming systems into resilient and sustainable upland production systems.
- جامع المعلومات: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
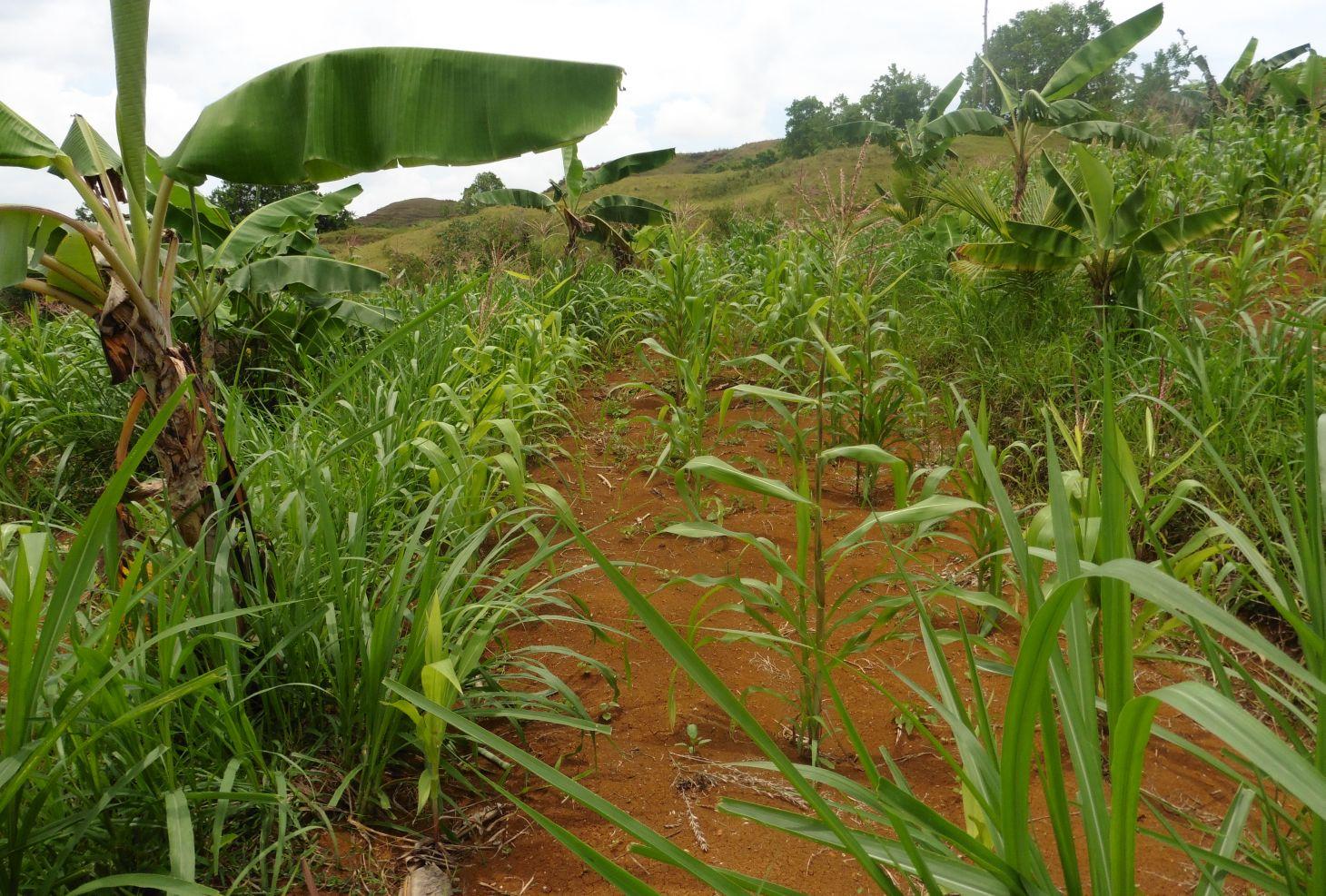
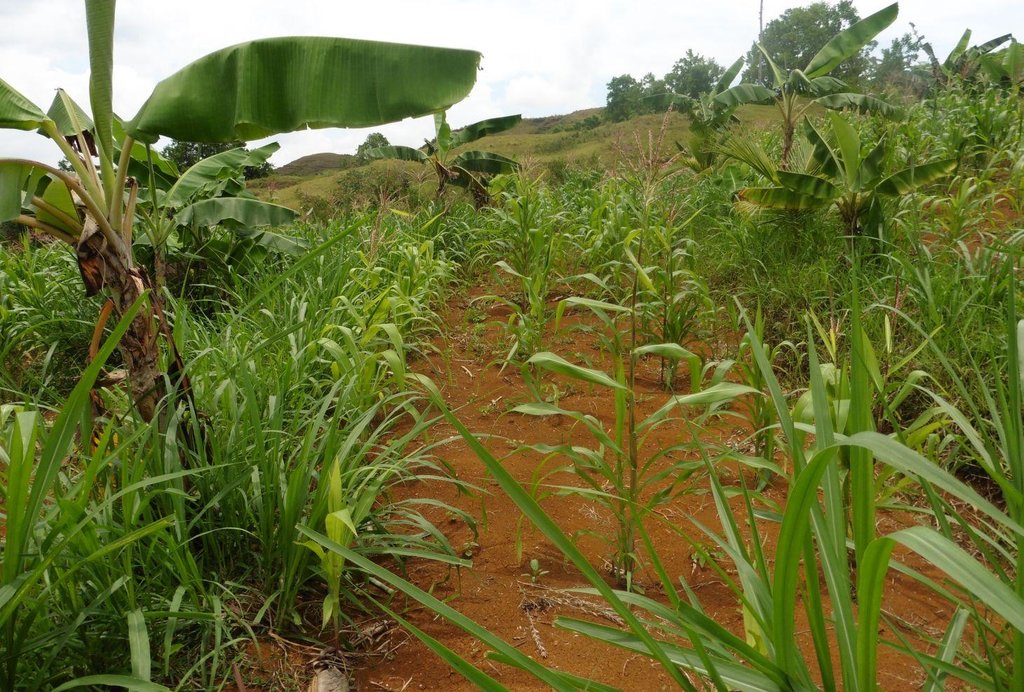
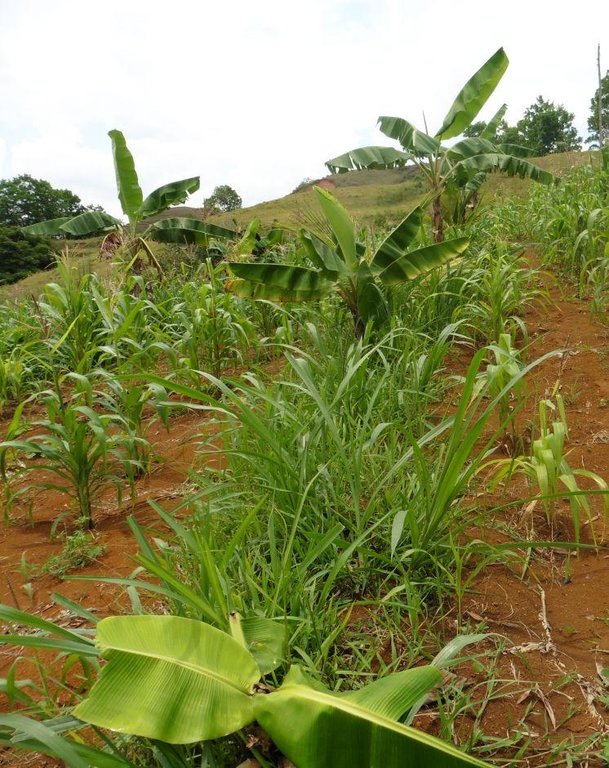
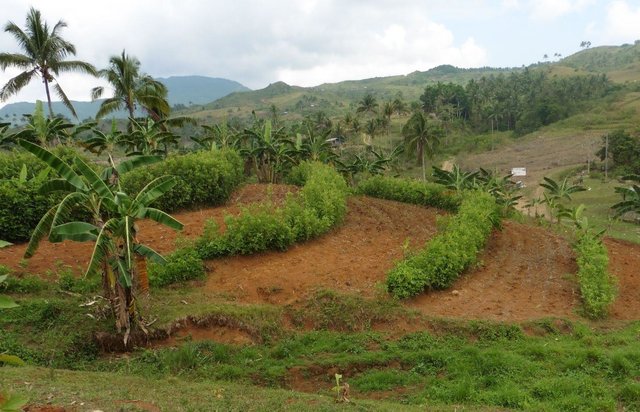
Contour farming is a technology practiced in sloping areas in which hedgerows are established along the contours and other annual/cash crops are grown in the alleys between the hedges.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Contour farming is being practiced by the farmers in sloping areas to prevent or control soil erosion. Hedgerows are established along contour lines using napier grass and permanent crops like banana and coconut. In between contour lines, corn is inter-cropped with peanut. It is a traditional practice of farmers and one of the conservation techniques for the Conservation Farming Village Approach (CFV).
Purpose of the Technology: This is practiced by farmers to control surface run-off, erosion and to conserve natural soil fertility. Napier grass is also planted as source of feeds for the livestocks. The technology controls dispersed runoff, reduce slope angle and length.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Contour lines were established using an A-frame to determine the location of the hedgerows to be planted. Napier grasses are planted along the contour at 8x8m and 4X4m distance. Grafted cacao trees are also inserted in between banana at 4X4 distance. The alleys between hedges measuring 4m wide and 30m long are planted with corn and peanut. Napier grass is regularly trimmed to maintain a height of not more than a meter, using the cuttings as livestock fodder.
Natural / human environment: The area is under a humid climate condition with an average annual rainfall of 1000-1500 mm. Its elevation is 500-1000 m above mean sea level.The average cropland size of land users is less than or equal to 0. 5 hectare with a slope ranging from 18-25%. Income of land users are derived from the crops sold. The Local Government Unit (LGU) provides truck to transport the harvested crops of the farmers from the village to the town market twice a week.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الفيليبين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
La Libertad
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Negros Oriental
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The technology is a traditional practice in the Philippines and was integrated as part of the conservation techniques under the Conservation Farming Village approach.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
major cash crop: peanut
major food crop: corn, banana, cacao, coconut
Other: Napier grasses
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion and soil fertility decline.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of animal grazing areas and limited plain or level areas for crop production.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0025 m2.
Farmers practice contour farming only in small areas or parcels of land
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
- A4: المعالجة تحت السطحية

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, contour planting / strip cropping, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, breaking crust / sealed surface
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Lack of knowledge on fertilizer usage), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (intensive tillage due to crop production), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (illegal logging, slash and burn), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (charcoal making for livelihood)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
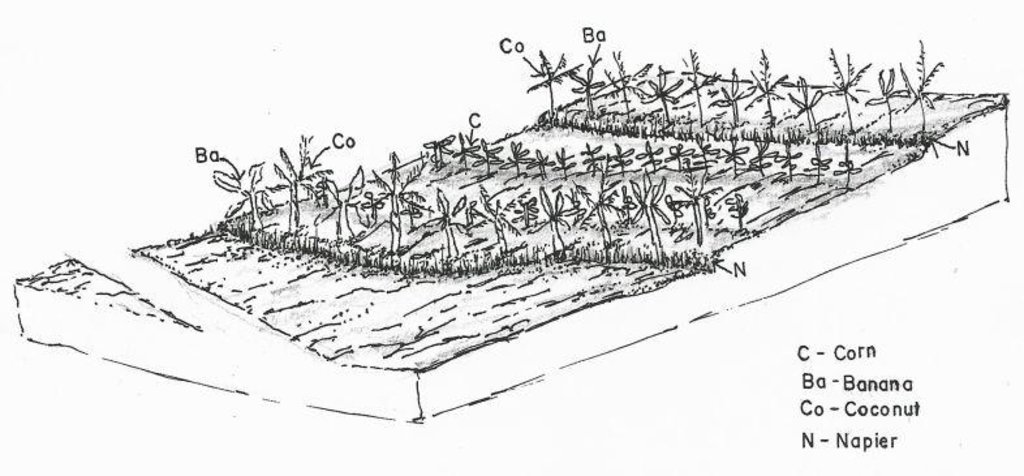
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Crops planted in the contour.
Location: Brgy. Talaon. La Libertad, Negros Oriental
Date: May28, 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, Minimize soil erosion due to runoff, Serve as soil nutrient traps
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: corn and peanut
Quantity/ density: 10kg/.25ha
Remarks: in between contour hedges
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: napier, banana, coconut and cacao
Quantity/ density: 20kg/.25ha
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 20kg/.25ha
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: vermi-compost
Quantity/ density: 500kg
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Material/ species: rotavator
Remarks: plowing two times
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): drill
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vegetative measure: contour (banana)
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 64
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vegetative measure: contour (cacao)
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 64
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vegetative measure: contour (cococnut)
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 32
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Fruit trees / shrubs species: banana, cacao, coconut
Grass species: napier grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 3-5%
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 hectare
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
49,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
2.22
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Laying out and establishment of contour lines/hedgerows | نباتية | before onset of rainy season |
| 2. | Planting of hedgerows (Napier grass) | نباتية | Rainy season. one week after laying out |
| 3. | Planting of perennial crops along contour | نباتية | Rainy season. 1 week after laying out |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
إذا كان ذلك ممكنًا، قم بتفصيل تكاليف التأسيس وفقًا للجدول التالي، مع تحديد المدخلات والتكاليف لكل مدخل. إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف، فقدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
122,77
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Laying out and establishment of contour | Person/day | 3,0 | 2,22 | 6,66 | 40,0 |
| العمالة | Planting of crops and hedgerows | Person/day | 10,0 | 2,22 | 22,2 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | napier seeds | kg | 300,0 | 0,0133 | 3,99 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | banana seeds | plants | 64,0 | 0,11093 | 7,1 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | cacao seeds | plants | 64,0 | 0,55565 | 35,56 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | coconut seeds | plants | 32,0 | 0,88875 | 28,44 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | herbicide | liter | 1,0 | 17,78 | 17,78 | 40,0 |
| مواد البناء | bamboosticks | picks | 50,0 | 0,012 | 0,6 | 40,0 |
| مواد البناء | A-frame | unit | 1,0 | 0,44 | 0,44 | 40,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 122,77 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land clearing/ preparation (plowing, rotavating, harrowing) of alleys between contours | زراعية | Before onset of rainy season |
| 2. | Furrowing | زراعية | |
| 3. | Planting of corn (first cropping) | زراعية | Raining season |
| 4. | Weeding, insect control | زراعية | |
| 5. | Harvesting of first crop | زراعية | |
| 6. | Land Preparation for the second cropping (plowing, harrowing/rotavating, furrowing) | زراعية | |
| 7. | Planting of corn + Planting of peanut (second cropping- corn + peanut) | زراعية | |
| 8. | Weeding / Insect control | زراعية | |
| 9. | Harvesting of corn and peanut | زراعية |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
إذا كان ذلك ممكنًا، قم بتفصيل تكاليف الصيانة وفقًا للجدول التالي، مع تحديد المدخلات والتكاليف لكل مدخل. إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
146,63
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Land Preparation with machine / furrowing | Person/day | 3,0 | 7,11 | 21,33 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Animal Labour | Person/day | 2,0 | 2,67 | 5,34 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Other Labour: Weeding, harvesting | Person/day | 14,0 | 2,22 | 31,08 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Corn seeds | kg | 10,0 | 0,444 | 4,44 | |
| المواد النباتية | Peanut seeds | kg | 20,0 | 2,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds undefined | kg | 10,0 | 0,444 | 4,44 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | kg | 500,0 | 0,08 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 146,63 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: rotavator
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The slope of the area contributes to the additional labor cost in the establishment of contours.The steeper the slope, the higher labor cost will be incurred.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zones: 720 m
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
70% of the land users are poor and own 70% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Hired laborers for the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) Project on National Greening Program
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10 bags
إنتاج الأعلاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1350 bundles
جودة العلف
تنوع المنتج
إدارة الأراضي
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
Improved livelihood and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
سرعة الرياح
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | ليس جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
More income added from Napier grass
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
18 land user families have adopted the Technology
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
التعليقات:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Single farmer focused on napier production and used as hedgerows
28% of land user families (4) who have adopted the Technology did it spontaneously.
4 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Practiced contouring but some are partial adoption (rock wall)
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Additional barangays will be adopting the technology.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Availability of labor force in the community. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage more farmers to adopt the technology and utilize available labor force. |
|
The technology generated jobs and increase the income of the landusers practicing the technology. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To conduct continuous capacity building to land users and their children to ensure sustainability. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Soil erosion was reduced because of the presence of the hedge rows that traps eroded soil. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Include other structural measures such as silt traps and brush dams to trap silts. |
|
The kind of hedgerows planted depends on the need of the landusers. Farmers with livestock used napier and forage grasses as hedges while others planted perennial and cash crop to supplement their food requirement. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conduct crop suitability evaluation and market study. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Poor road network from the center of the town to the barangay. | Construction of farm-to-market road to improve the accessibility of the barangay. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Lack of irrigation system in the cropping area | Provision of irrigation system such as solar pump and small farm reservoir. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Conservation Farming Village [الفيليبين]
A modality in mobilizing resources for sustainable upland development which utilizes a basket of strategies, technologies, and interventions to catalyze the widespread transformation of traditional upland farming systems into resilient and sustainable upland production systems.
- جامع المعلومات: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية