Ecological engineering for biological pest control in lowland rice agroecosystems [الفيليبين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Martin Wiemers
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
technologies_1720 - الفيليبين
- Ecological engineering for biological pest control in lowland rice agroecosystems: 3 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
- Ecological engineering for biological pest control in lowland rice agroecosystems: 4 إبريل، 2018 (inactive)
- Ecological engineering for biological pest control in lowland rice agroecosystems: 13 يونيو، 2019 (public)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Vetterlein Doris
+49 345 558 5415
doris.vetterlein@ufz.de / doris.vetterlein@landw.uni-halle.de
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research - UFZ
ألمانيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Settele Josef
e-mail: josef.settele@ufz.de
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research - UFZ
ألمانيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Rice ecosystem services (LEGATO) - الفيليبيناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice) - الفيليبين1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
05/05/2016
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
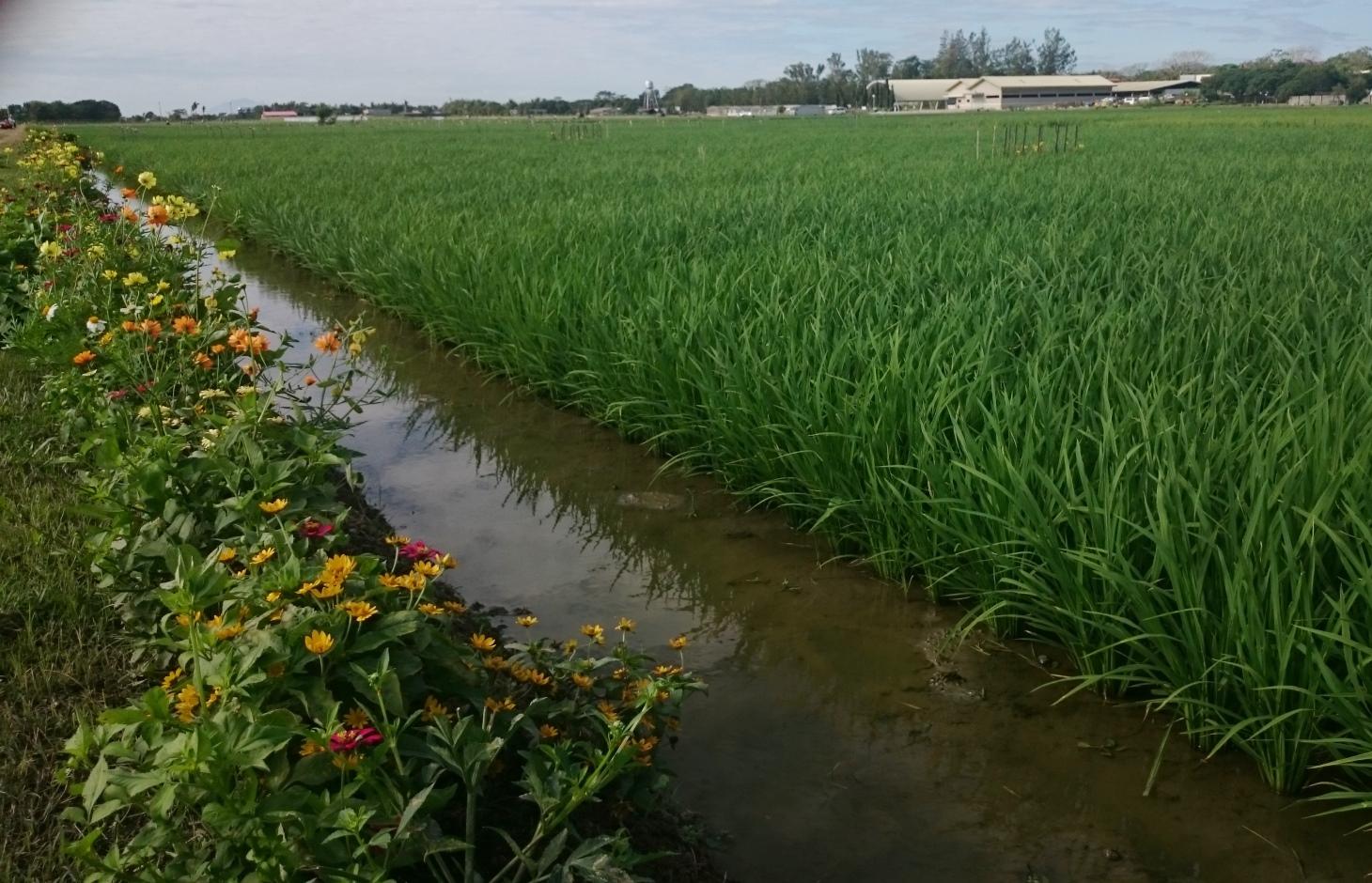
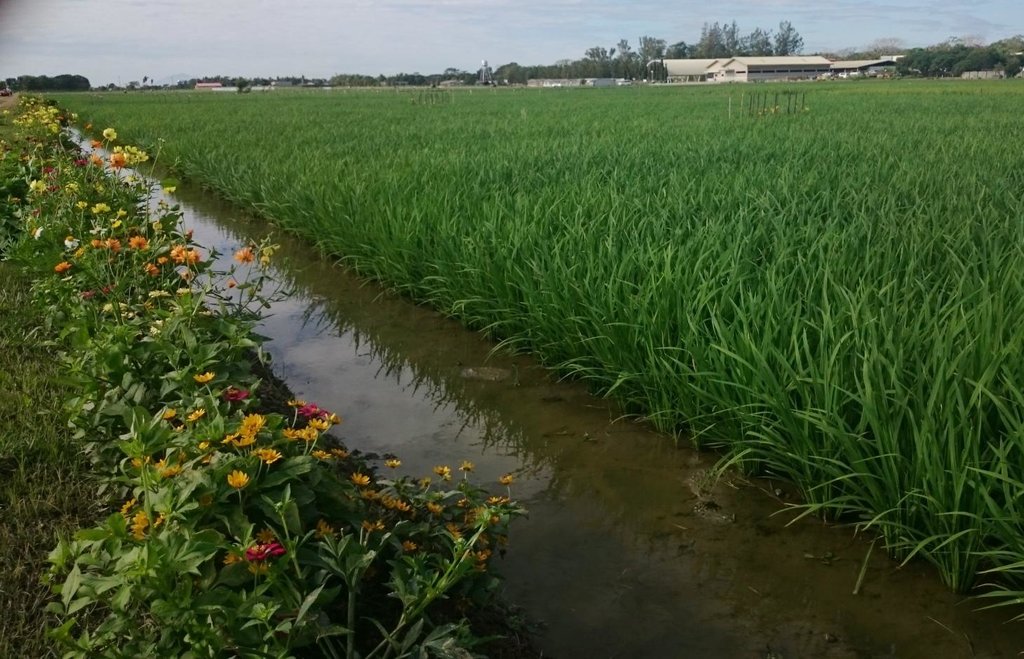
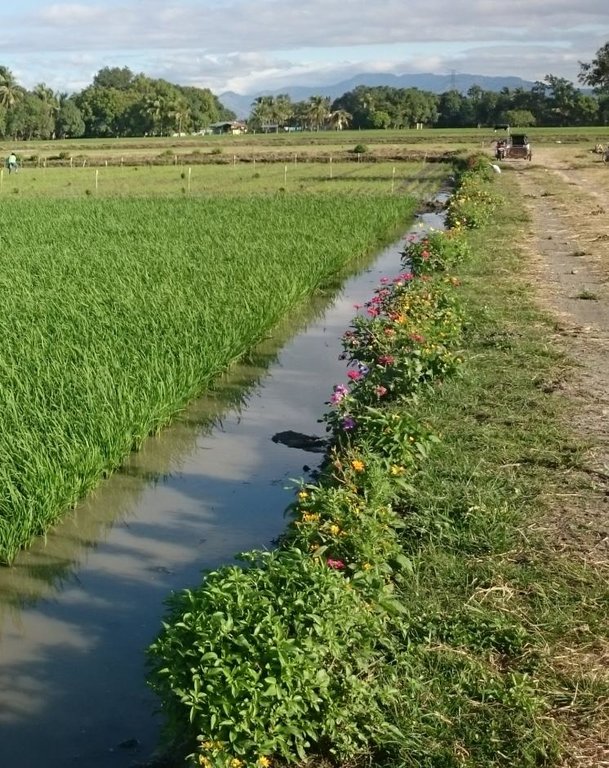
Ecological engineering in lowland rice agroecosystems by planting of flower strips in rice fields as habitats for beneficial arthropods which control pests.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
To counteract the negative impact of agricultural intensification, in particular the loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services, more sustainable management for crop land and surrounding habitats is required. ‘Ecological engineering’, in this case meaning the provision of habitats for beneficial arthropods, has recently gained considerable attention as a method of reducing pesticide input, through stimulating biological pest control by natural enemies.
Purpose of the Technology: The concept of ecological engineering is aimed primarily at the regulation of pest species, through the provision of habitats for their natural enemies. However, other ecosystem services, such as pollination and cultural services, may simultaneously be enhanced by using the same measures. One such measure, which is popular and effective in temperate countries where agro-environmental schemes are implemented, is the planting of flower strips as habitats.
In intensively managed tropical rice production systems, biological pest control, pollination services and landscape aesthetics could also benefit from the establishment of flower strips on the bunds within irrigated fields. The specific aim of the technology featured here is to increase biodiversity in rice fields and provide habitats for beneficial organisms such as predators of rice pests (e.g. spiders) or parasitoids (e.g. hymenopteran parasites), which in turn will help to minimize the use of pesticides. An additional benefit is landscape beautification.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The process comprises collecting seeds of flowering plants (e.g. flowering annuals such as Melampodium divaricatum) and planting them in a nursery. After a month or so they can be transplanted into rice fields on bunds, with a strip size of 0.25 x 5 metres, and a distance between strips of 5 metres (to enable access for farm operations such as fertilizer application). Farmers are requested not to spray insecticides when they test this system. The flowering plants should be pruned during the fallow period in the wet season; and they will require watering during the dry season when rice is cropped. The flower strips will need to be replanted after the rice crop is harvested, if an annual species are chosen.
Natural / human environment: While this SLM technology is for an irrigated rice ecosystem in the center of the island of Luzon in the Philippines, it has already been applied in other rice producing areas – for example in Vietnam and, with some adaptations, should be applicable to irrigated lowland rice production systems throughout Southeast Asia.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الفيليبين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Nueva Ecija
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Muñoz
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
major cash crop: vegetables
major food crop: rice
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): pest outbreaks; low population of natural enemies; loss of biodiversity and health hazards to farmers. High levels of pesticide use leading to insect resistance. Complete loss of forest leading to degraded watersheds and sedimentation of dams, soil erosion, and temperatures rising as a result of climate change. Intensive agriculture causing degraded soil conditions and compromising the sustainability of productive lands. Intensive agriculture also means increased use of water resources, more chemical inputs and more pest pressure.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Pest problems
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: vegetables are planted between rice cropping seasons
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- ري كامل
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: January to AprilSecond longest growing period in days: 120Second longest growing period from month to month: June to September
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة للآفات والأمراض (بما في ذلك الزراعة العضوية)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V5: أخرى
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Specification of other vegetative measures: Annual flower strips
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bp): زيادة الآفات/الأمراض، وفقدان الحيوانات المفترسة
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Complete deforestation), population pressure (Growing population)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (intensive lowland rice production)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
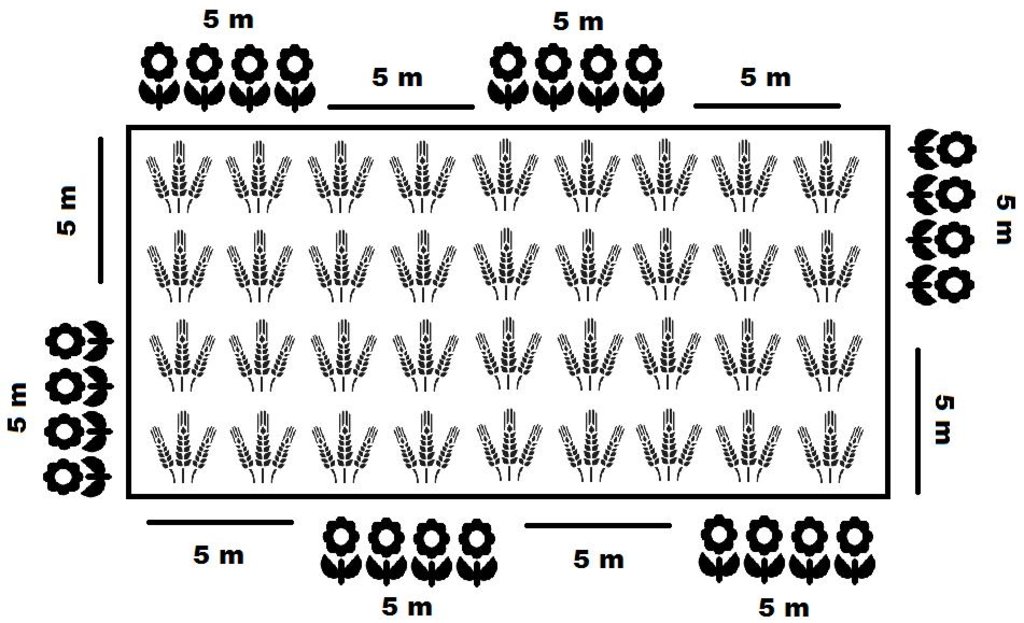
Flowering plants planted around rice field (e.g. annuals such as Melampodium divaricatum)
Location: Maligaya. Muñoz, Nueva Ecija, Philippines
Date: 14 March 2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: Biological pest control reduces pollution by agro-chemicals
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 800
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Other species: annual flowers, e.g. Melampodium divaricatum
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
7
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Flowering plant seed collection | نباتية | Fallow period |
| 2. | Flowering plant nursery establishment | نباتية | Fallow period |
| 3. | Transplanting flowering plants | نباتية | vegetative stage of rice |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Flowering plant/ nursery / transplanting | Person/day | 13,0 | 7,0 | 91,0 | |
| العمالة | Trasnportation | - | 1,0 | 41,5 | 41,5 | |
| معدات | plastic bags / plot | - | 1,0 | 19,0 | 19,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost | kg | 250,0 | 0,12 | 30,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | kg | 4,0 | 1,0 | 4,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 185,5 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
NA
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Flowering plant maintenance, i.e. trimming, removal of volunteer seedlings out of the strips and thinning during cropping season. Watering and replacement in times of long drought fallow period | نباتية | rice cropping season |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Flowering plant maintenance | Person/day | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 40,0 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
NA
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Costs are given for the first year of testing. If flower strips with annual flowering plants will be planted recurrently, then ‘establishment’ costs will be the same each year.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
rainy season May - November; dry season January - April
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth: plow layer of paddy soil
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farming
Manual labour: Transplanting, fertilizer application, pesticide application and other maintenance activities
Mechanised: land preparation and harvesting
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إدارة الأراضي
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
About 0 since labour constrains increased and workload decreased
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الوضع الصحي
الفرص الترفيهية
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
70 familes (90 percent of the area)
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
التعليقات:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
70 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: adaptation for now is mainly by the project farmer cooperators and technicians (for demonstration)
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Farmers save money by reducing pesticide use How can they be sustained / enhanced? Present research study results to farmers |
|
Ceasing or reducing pesticide use improves farmers' health How can they be sustained / enhanced? Educate farmers in the harmful effects of pesticide use |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Enhances biodiversity in rice ecosystem How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue demonstration |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Additional work for farmers | Incorporate activities in traditional rice growing activities |
| To achieve maximum impact, neighboring farmers and fields should also reduce the use of pesticides and agro-chemicals | A management plan for the whole area needs to be developed |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Does not solve all problems with pests, i.e. pest outbreaks are still possible | Develop integrated pest management, e.g. use pesticides only in emergencies, and/or develop an insurance system for farmers. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Westphal, C. et al. (2015) Promoting multiple ecosystem services with flower strips and participatory approaches in rice production landscapes
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1016/j.baae.2015.10.004
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
LEGATO website
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://legato-project.net/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية