Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Michael Herger
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_2092 - كينيا
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 4 سبتمبر، 2019 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 22 فبراير، 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 11 يوليو، 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 3 سبتمبر، 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 4 أكتوبر، 2018 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 2 نوفمبر، 2021 (inactive)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 2 نوفمبر، 2021 (public)
- Il Ngwesi Group Ranch Grazing with Holistic Management Principles: 1 فبراير، 2018 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Leresi Patrick
+254721153572
ilngwesi@nrt-kenya.org
Il Ngwesi Group Ranch
Mukogodo Division, Laikipia North District, PO Box 263, 1042 Timau, Kenya
كينيا
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
22/01/2017
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Yes and no, only time will tell here.
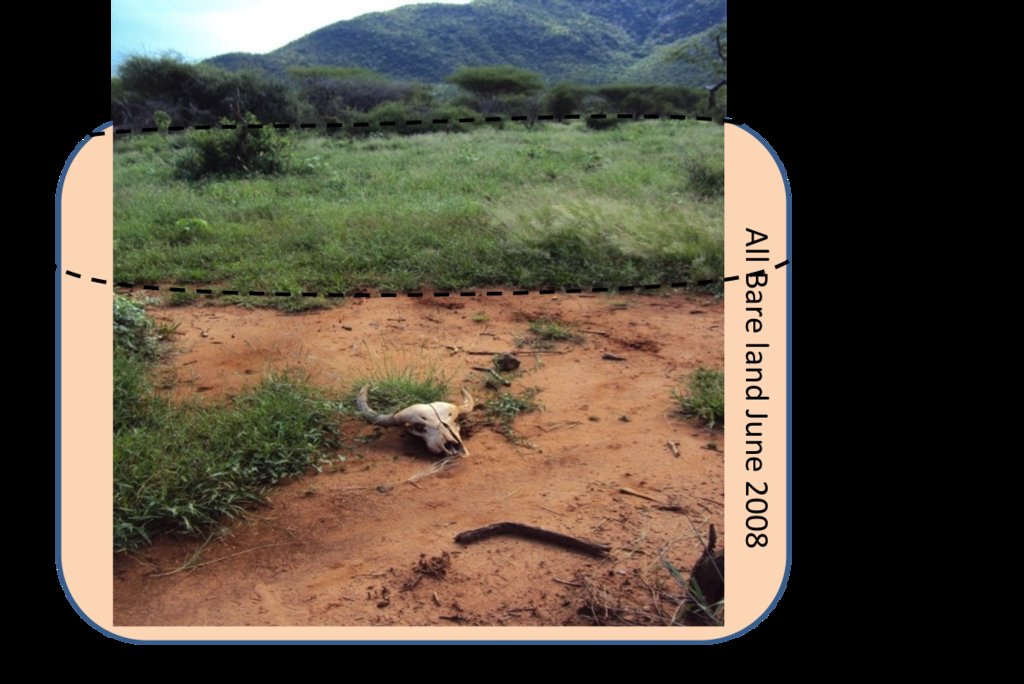
Grazing principles and management (with partly applied Holistic Managment) of Il Ngwesi Group Ranch are said to be exemplary for group ranches in the area. In evaluation processes since the introduction of the new principles and also in reports, they were rated as "best practice". Land recovery is according to these reports in full swing. However, in the field the picture looks partially different. The land is in large areas (still) heavily degraded. Data suggests that vegetation and soil is in a rather bad condition - many erosion features characterize the land. Nevertheless, according to land users, land coverage has significantly improved since the introduction of the new technologies.
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
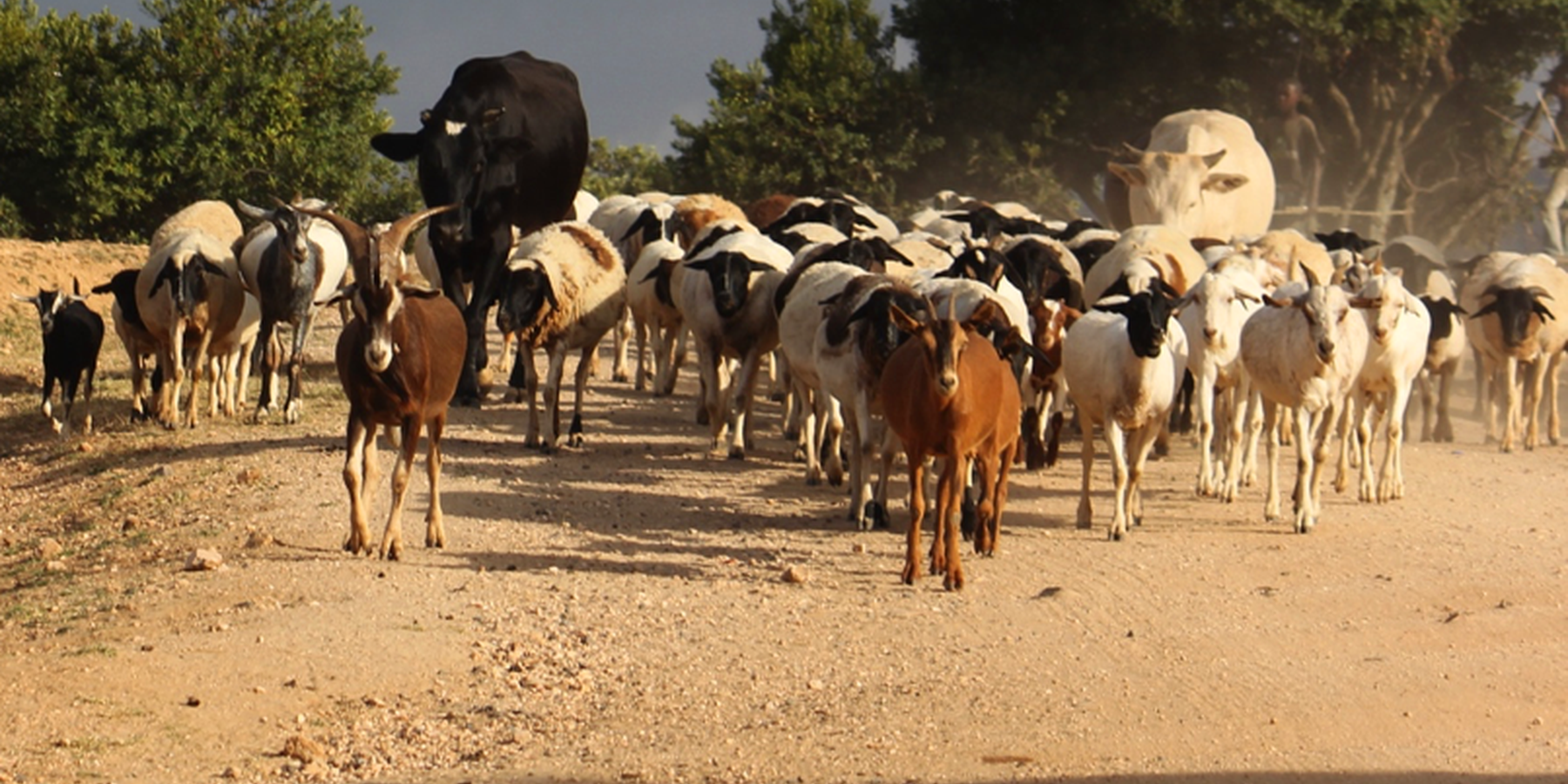
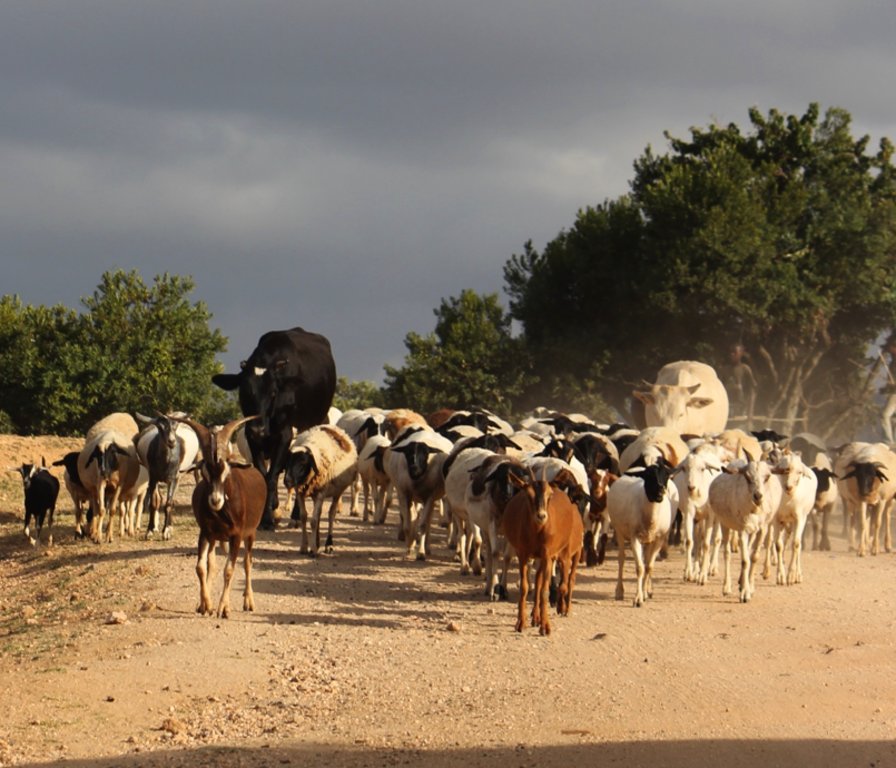
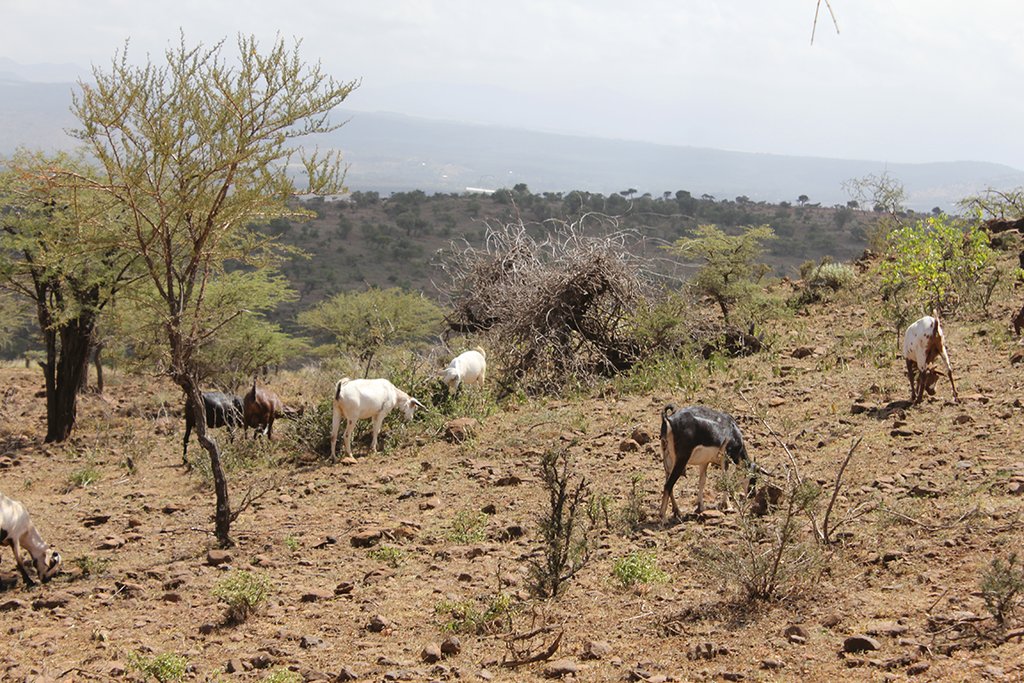
A group ranch belonging to the Masai (traditionally, nomad pastoralists) has applied "Holistic Management" grazing principles. The principles consist of separate, planned grazing in villages during the rains, then “bunching” and moving of all animals in herds during the dry season. Denuded land is recovered by a "Boma” technology: i.e. strategic corralling of animals overnight, and reseeding.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
On Il Ngwesi Masai Group Ranch, livestock production management is a combination of traditional livestock keeping and holistic grazing management principles which were introduced in 2007. Livestock production at Il Ngwesi is for subsistence and sales - and has very high cultural significance. 80% of the land is used for conservation, where wildlife and their habitat are protected. The vision is to integrate community development and sustainable environmental management.
Holistic Management (HM) was originally conceived by Allan Savory (1988), and is facilitated by the Laikipia Wildlife Forum. It integrates decision-making, planning, and livestock keeping. On the land, this means bunching of all livestock close together (in order to act as a "bulldozer" and break the soil to allow seeds, nutrients, and water to infiltrate) resulting in better plant growth. By moving the animals together from block to block, HM aims at managing high numbers of livestock while restoring degraded land. Instead of individual livestock-owning families herding and trekking their own animals, consolidated herds are now managed and moved together, and overseen by herders and supervisors. This allows intensive grazing in restricted areas while resting the remaining land - instead of continuous open grazing. However, Holistic Management principles are still a matter of controversy.
The group ranch land consists of a settlement and a conservation area. The conservation area is further subdivided into a small core zone, measuring 500 hectares and a larger buffer zone of 6,000 hectares. Within this buffer zone, pastoralists are permitted to graze livestock during the dry season.
Besides these two main grazing areas in their group ranch, they use additional grazing areas outside their territory such as pasture in forests. In one forest - Mukogodo - they have settled officially; in Ngare Ngare and on Mount Kenya, on the other hand, it is more of an informal agreement. In Il Ngwesi, HM principles are very strictly applied in the conservation area; elsewhere only partly or not at all. During the movements to the forest glades and Mount Kenya, HM principles are maintained as far as possible.
This documentation describes the combined grazing management system. During the rains, the grazing system is largely by traditional management: animals remain in and around villages managed individually by households. During the dry season, all livestock are bunched together and managed as one herd.
During the wet season, grazing at Il Ngwesi Group Ranch is organized by elders within their seven villages. HM principles are only partly applied. During the dry season, once all the grazing land is eaten, livestock are bunched together and managed by a few herders and overseers. The block system rotation starts. To seek new pasture and water, cattle and smallstock are led to forest glades, and then to the Il Ngwesi conservation area. As soon as the forest pasture is gone, they move on to the conservation area. Usually, this movement of livestock to forests and conservation area starts in February; then they return to the villages in April; and then back to the forests and conservation area until the next rains in November.
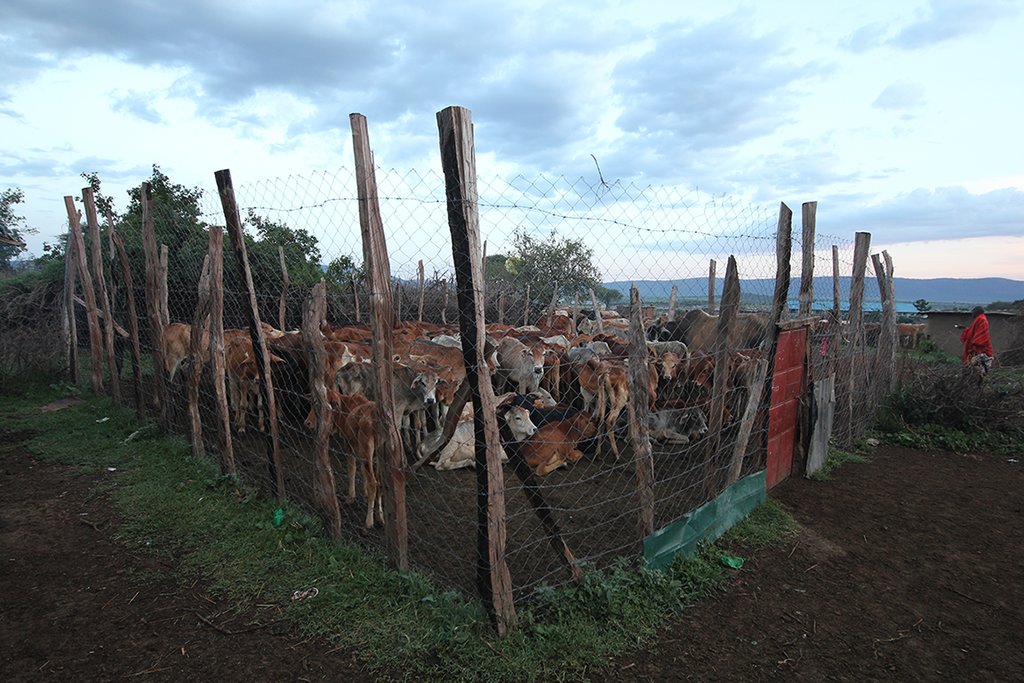
Whilst the livestock are bunched together, large bomas (corrals in Kiswahili) are constructed for overnight enclosure. Bomas are sited on bare land where dung accumulation and crust breaking by hooves helps rehabilitate land. Every year the boma sites are shifted slightly according to a plan. The total area that can be restored per year is almost 1% of the area of Il Ngwesi.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Laikipia
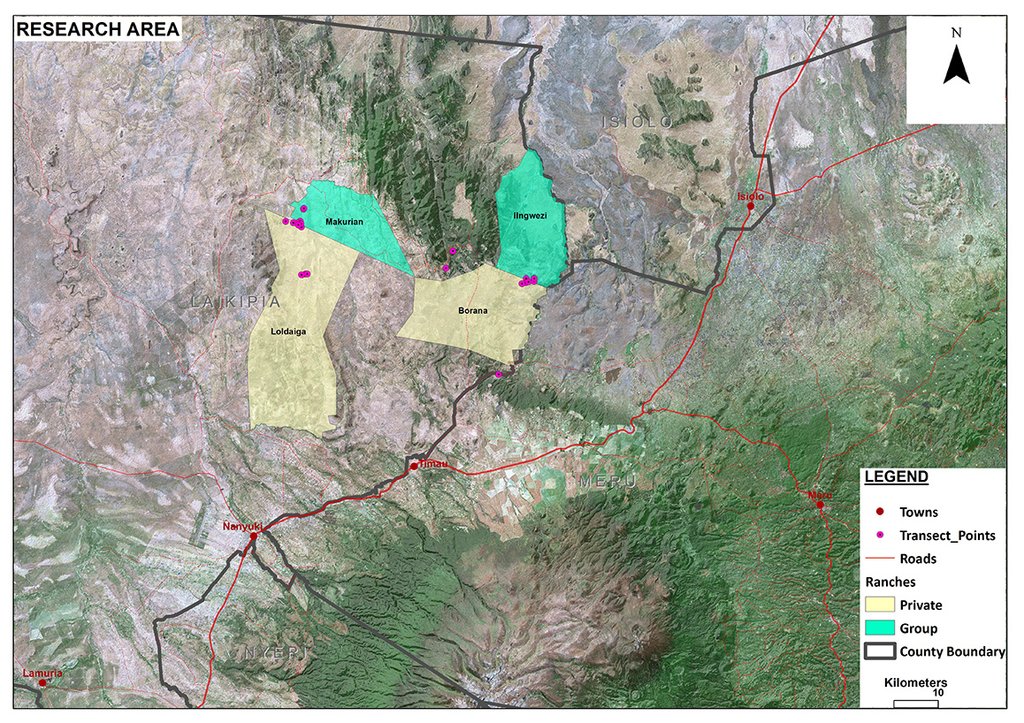
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Mukogodo Divison
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2007
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Holistic Management approach by Allan Savory.
In Laikipia, it was introduced by Richard Hartfield, Laikipia Wildlife Forum and funded by Laikipia Wildlife Forum (LWF), Lewa Conservancy and Northern Rangeland Trust (NRT) (approximately 50% of all additional costs of Il Ngwesi since the implementation were covered by funding). Agreement with elders was reached first, then the community was trained.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
Livestock: Cattle, goats, sheep, donkeys, camels
Meat and milk production (also blood) and as a bank/ value asset. Mainly subsistence and local production.
Livestock: 4’800 TLU; Stocking rate: 3.3 ha/TLU (calculated with the total affected land by livestock: 157km2)
Pressure on land including wildlife: 3.3 ha/TLU (stays the same, calculated with wildlife biomass density estimated by Georgiadis et al. 2007).
Livestock numbers:
Lower Il Ngwesi: 4000 cattle, 20'000 shoats, 50 donkeys, 100 camels.
Sanga: 700 cattle, 2000 shoats, 20 donkeys.
Mukogodo: 1500 cattle, 5000 shoats, 20 donkeys
Livestock fluctuations (per year): -10% sales, -5% loss due to drought/diseases, -5% slaughtered,
+30% natural breeding, new purchase and deaths are mutually offsetting.
Steers are for fattening on private ranches and during droughts other livestock can be moved to private ranches (up to 3000).
Wildlife: elephant, antelope/ gazelle (like gerenuk, impala, Thomson's gazelle, dik-dik), hares, predators and more.

المستوطنات والبنية التحتية
- المستوطنات والمباني
ملاحظات:
Villages, bomas, manyattas.
8'000 inhabitans.
Lodge for Tourism.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Short rains in November and December. Long rains in April and May. Rains from (October) November to December are usually better in this area. Rainfalls with strong local variations and changing regimes.
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
4’800 TLU; Stocking rate: 3.3 ha/TLU. Pressure on land: 3.3 ha/TLU
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 100-10 كم2
التعليقات:
Il Ngwesi has an area size of 87 km2. However, the total affected land by livestock is 157km2. The technology is also applied on other ranches (mainly private ranches, see the documentation for neighboring "Borana") in Mukogodo division.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
- M4: تغيير كبير في توقيت الأنشطة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية
- انسداد مسام التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة
التعليقات:
Across the grasslands and rangelands an increase in bare land and bush has been a clear trend all over Laikipia for many years, both on community-owned lands and private ranches. Major identified ecological problems (partly) caused by livestock production are: bare ground, low contents of soil organic carbon and plant-available nutrients, soil erosion (sealing, crusting, rills and gullies, water flow patterns, sheet erosion, pedestals), poor soil properties, undesirable species, and (increasing) woody and invasive species. However, Il Ngwesi is not affected by the invasive species Opuntia stricta. For more information on rangeland health see Herger (2018). The technology aims at improving vegetation cover of the land and thereby reducing further degradation and restoring degraded land.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
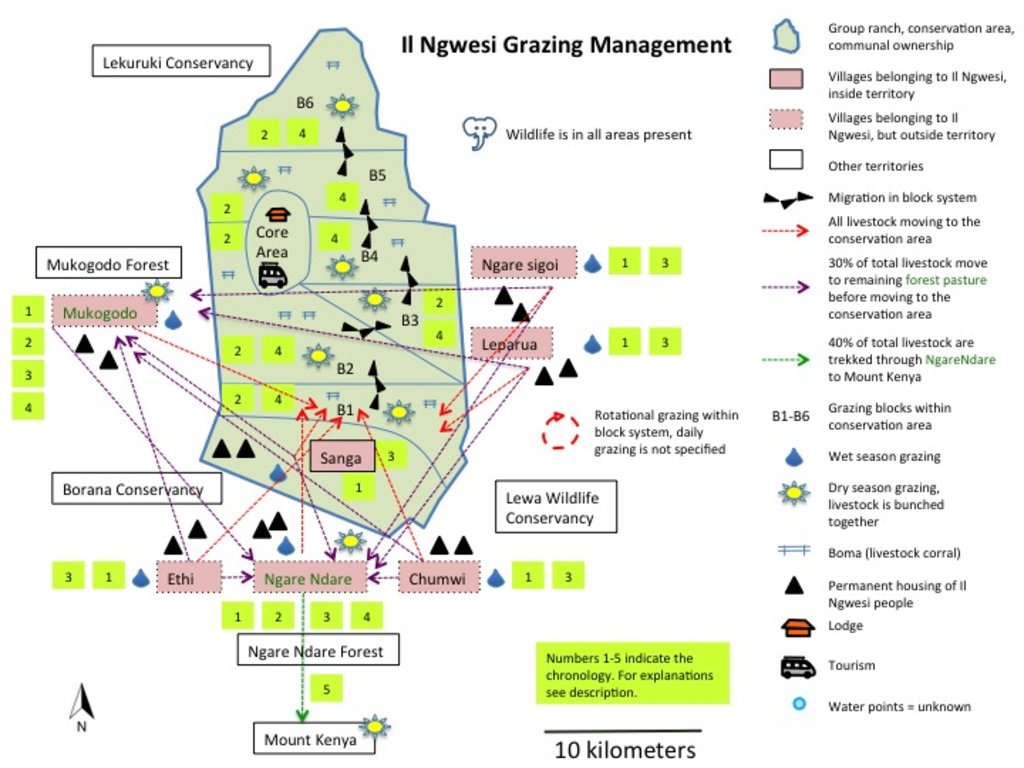
Grazing map of Il Ngwesi in Mukogodo Division
Grazing Principles:
- Rotational, planned grazing
- Bunching
- Resting periods for pasture
- Bomas for bare patches (night corrals)
Value Chain:
• Natural Breeding/buying (Ranches & individually)
• Grazing
o Settlement area (in red, during the wet season, until pasture is gone, organised by elders, bunching of all animals as soon as it gets dry)
o Mukogodo Forest / Ngare Ndare Forest (30% of total livestock, remainder to conservation area for grazing directly)
o Conservation area (6 blocks)
o Mukogodo Forest/Ngare Ndare Forest/Mount Kenya (Ngare Ndare Forest as corridor to Mount Kenya, about 40% of total livestock goes to Mount Kenya)
• Need-driven sales to local butcheries/NRT/Ranches
Il Ngwesi Masai also started to buy land outside their Group Ranch.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
Herders, animals treatment. For the whole area affected by livestock (157 km2)
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
USD 2.5
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Training of elders and community by project leaders | إدارية | |
| 2. | Grazing planning for bunched animals (livestock from all households) | إدارية | |
| 3. | Hiring herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | إدارية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Costs for establishment unknown |
التعليقات:
Trainings were funded by NRT, LWF and Lewa Conservancy. No figures on this.
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herders, supervisors, watchmen etc | إدارية | |
| 2. | Animal treatments (vaccination, spraying, injections) | زراعية | |
| 3. | Planning activites | إدارية | |
| 4. | Boma Management (mainly movement of Bomas) | إدارية |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Herders, watchmen | Person-days | 250,0 | 540,0 | 135000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Supervisors | Person-days | 3,0 | 720,0 | 2160,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Planning activities, management | Person-days | 20,0 | 1500,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Livestock-owning families (for wet season, no wages paid, livelihood) | Person-days | 8000,0 | 300,0 | 2400000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Boma Movement | |||||
| غير ذلك | Animals treatments (spraying against ticks) | Per livestock unit | 5000,0 | 5,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Injections, vaccine | Per livestock unit | 5000,0 | 3,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 2607160,0 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Overall additional costs since introduction of new technology are estimated at 20% higher than before. 50% are covered by project funding (LWF, NRT, Lewa Conservancy)
التعليقات:
Costs per unit are multiplied by days.
According to the interviewed manager, total costs are only USD 18'000 (without herders). However, the listing of all costs results in much higher total costs. Total animal treatment costs for Makurian Group Ranch in comparison are USD 428'000 (labor USD 380'000, animal treatment USD 48'000, without livestock-owning families).
Also, people living in the area (population of 8'000 inhabitants) are involved in livestock keeping and are included here in calcuations as labor (for 3 months, wet season, 10% of total population).
Cost/benefit is currently negative for livestock keeping. Income due to livestock sales is roughly estimated USD 340'000 (price for cattle on average USD 400 per unit, sales around 500 p.a., price for goats and sheep each USD 40 per unit, sales around 2'000 p.a., slaughtered units (for subsistence use) cattle: 50, shoats: 1'000 - detailed figures available Herger 2018)
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
- Managing of one big herd, many supervisors needed.
- Movement of bomas
- Livestock-owning families (although they obviously don't receive any salary): this is simultaneously their livelihood and used for subsistence. But once all their livestock is bunched in a big herd, they lose their nutritional source (milk, blood) and livelihood (sometimes they keep back a few units for this reason).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
500,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Rainfall gauge Borana HQ average from 2013-2016 (neighboring ranch). Strong local (and temporal) variation, changing rainfall regimes. Il Ngwesi is generally drier than Borana. Grazing areas are on different altitudes with different rainfall amounts. While Il Ngwesi Sanga (as one of the villages) is at almost 1700 m a.s.l. with similar rainfall like Borana HQ, Il Ngwesi Conservation area is at 1220 m a.s.l. with significantly lower precipitation (no rainfall gauge). Grazing glades in Mukgodo Forest are at 1850 m a.s.l. and in Ngare Ndare Forest at almost 2100 m a.s.l. (no rainfall measurements available, higher rainfall amounts) and varying heights with much higher precipitation on Mount Kenya (no defined areas).
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Rainfall gauge Borana HQ
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Hilly areas (e.g. Sanga village) and flat areas in lower altitude (conservation area).
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Red and brown sandy soils. Black cotton soil. Luvisol, Regosol, Vertisol
SOC 1.1-1.4 %
pH: 6.3
Clay: 12%
Silt: 53%
Sand: 35%
More information in Herger (2018)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Few springs, Ngare Ndare river, no boreholes. Source is Mount Kenya
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Grassed acacia bushland. Bare land up to 70% during the dry season. Loss of (native) vegetation. Invasive species coming in. Dominant grasses: Eragrostis species, Cynadon species, Hyparrhenia species, Kelenger species. Dominant shrubs: Solyneum inconum, Ipomea hildebranditi, Lyceum europaeum, Barleria acuthodies. Dominant trees: Acacia tortilis, Acacia mellifera, Acacia nilotica, Acacia etbaica, Boscia angustifolia. Detailed list of all species (also wildlife) available (see Herger 2018).
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Masai people. 8'000 Masai living in Il Ngwesi. Traditional lifestyle. Livestock with very high cultural value. About 10% subsistence use, 90% is sold for local and national markets (mainly local).
Very little agriculture; tourism (award-winning eco-lodge in conservation area); people start to diversify. Schooling of children has a high importance today (e.g. smallstock is sold for school fees). Children and young warriors are traditionally herders, however, it is shifting towards hiring herders and sending children to school.
Have been historically "squeezed" from all sides into smaller areas for livestock keeping. Future of pastoralism is in question.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Applies for one household. Herders on the other hand trek livestock over an area of more than 10'000 ha.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
إنتاج حيواني
إدارة الأراضي
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
توافر المياه للماشية
الدخل والتكاليف
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
20-30% above normal (supervision, watchmen, moving big bomas). Previously, every household managed their livestock individually
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
استخدام الأراضي / حقوق المياه
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
External! Better land cover attracts invaders (Invasion from northern tribes), envy
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
Poorest livestock-owning families are better off now since their livestock are also bunched together with all the others. For instance, before they couldn't afford to trek their 5 cows to Mount Kenya for pasture, now their livestock are trekked with all the others - all have the same opportunities. Other households are complaining about this since they can't decide on their own anymore where they want to bring their livestock for grazing.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
less runoff, more water stored in the soil.
الجريان السطحي
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التنوع النباتي
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Il Ngwesi is not affected by the huge invasion of the exotic cactus, Opuntia stricta. However, there are some other invasives like Lantana in the area, but not as problematic as Opuntia. According to land users, native vegetation cover has improved, which results in fewer invasive species.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
More stored in the soil. According to the land users, no measurements conducted.
تعليقات بشأن تقييم الأثر:
All listed impacts are as perceived by land users according to Patrick Leseri, Conservation Manager. In his opinion, vegetation cover has thanks to the new technologies improved. Planning activities significantly increased and therefore also socio-economic and ecological conditions improved. Results from a rangeland health assessment (only ecological conditions) show on the other hand partly heavily degraded ecological conditions (poor soil and vegetation, erosions features, inability of producing annual grasses after rains etc) (Herger 2018). Land users and experts are aware that the ecological conditions of this Group Ranch are still far from optimal, but do see good progress and exemplary management as well as slightly better conditions than on other Group Ranches.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| تغير مناخ تدريجي آخر | Greater variation of seasonal rainfall, higher intensity of rainfall events, change in rainfall regimes in general (see Schmocker 2013 and Imfeld 2016). | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة حر | جيدا |
التعليقات:
Improved rangeland health, better internal organization, and cooperations make them less vulnerable to climate change impacts.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 50-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، وضح الظروف المتغيرة التي تم تكييفها معها:
- تغير المناخ / التطرف
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
Masai people have changed their livestock composition towards owning more smallstock (goats and sheep) than cattle. Goats are tolerant of drought, and as browsers, they don't need any grass. Also, they can be turned into money much quicker than a cow in times of need and because of their more rapid reproductive cycle. They can also recover number more quickly after livestock losses through drought
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Proper utilisation of pasture – controlled usage/grazing |
| Land recovery (more cover, more water, more fodder, less erosion) |
| Carrying capacity increased |
| Traditional knowledge is still used |
| More dialogue in community: brings everyone in the community together – they have a common point – everyone has the same interest |
| Improving breeds is easier (because all are bunched together) |
| Easy vaccination of all livestock at once |
| Approving cultural lifestyle of Masai: the higher the livestock numbers – the better for the land |
| Better for disadvantaged community members: for instance for those who could not afford to move their livestock to Mt Kenya on their own before |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The listed advantages from Patrick Leseri, the land user, are for the most part shared share with the compiler's view. Improved planning of livestock production with planned grazing and long resting periods, improved dialogue in the community, and the named advantages of a big herd (like easy vaccination etc) are important advantages. Regarding Holistic Management (HM) principles, there remains uncertainty about land recovery. On the one hand, it is generally questionable to state as in HM: “the more animals the better” (as long as they are managed properly they can even recover degraded land), which seems dangerous in areas with such high livestock numbers and cultural value of livestock keeping - without scientific proof of the principles in similar ecological conditions. We have witnessed rather poor condition of the land, and the much-vaunted good land was difficult to find. Favourable descriptions might also be related to funding of the project. Results from a rangeland health assessment show (partly) heavily degraded ecological conditions (bare ground, poor soil and vegetation, erosion features, partly an inability of producing perennial and annual grasses after rains etc) (see Herger 2018). However, an evaluation of change over time is impossible to assess. Further monitoring is necessary. Land users and experts are aware that the ecological conditions of this Group Ranch are still far from optimal, but do see good progress and exemplary management as well as slightly better conditions than on other Group Ranches. However, the efforts towards good management and a sense of community was not difficult to notice. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Higher costs. Above 20% more than normal costs. NRT, Laikipia Wildlife Forum and Lewa conservancy as main funders for applying holisitc management principles. Since 2007 they covered about 50% of all costs.. | |
| More labour intensive. 20-30% above normal (supervision, watchmen, moving big bomas) | |
| Challenge to bring people together (and their livestock) and agree on a joint management | |
| Some families still prefer to manage their livestock on their own and make their own decisions. There are no individual decisions anymore: principles apply to everyone | |
| Breeding can also be a problem – those with good genetic material (better livestock) may lose and those with poor may win by mixing | |
| Conflicts among animals; bulls fight a lot. No separation of heifers, cows, steers and bulls | |
| Management of high numbers of big herds is a challenge | |
| Diseases are easily transmitted | |
| Once livestock is collected to big herds, individual families lose their nutritional basis (milk, blood). However, some also keep a few livestock units back. | |
| Sometimes trees are cut for bomas |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
4 field visits with included "rangeland health assessment" in different parts of Il Ngwesi (mostly in Sanga village though) where I could see the condition of the land as well as several other visits of the area.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Several meetings with the grazing coordinator, conservation manager, chief, elders, and other resource people of Il Ngwesi over half a year.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Truman Young
Dan Rubenstein
Dino Martins
John Letai
Samali Letai
Peter Hetz
Dominic Maringa
Joseph Putunoi
Patrick Ekodere
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Scientific papers, LWF reports etc.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Herger, M.B. (2018). Environmental Impacts of Red Meat Production. MSc Thesis. University of Bern.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
University of Bern
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Modeling Seasonal and Annual Precipitation using long-term Climate Records and Topography. Master’s Thesis. Noemi Imfeld (2016).
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
University of Bern
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Savory, A (1988). Holistic Resource Management. Gilmour Publishing, Harare, Zimbabwe
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Online
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية