Enhanced mulching in banana and coffee plantation [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Iwona Piechowiak
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Okwalila ebinyasi omukibanja
technologies_1184 - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
Government:
Government:
Mashauri Babylus
Bukoba District Council
P.O Box 491 Bukoba
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
Government:
Rutatinisibwa Dominick
Bukoba District Council
P.O Box 491 Bukoba
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
Government:
Rwezahura Raphael
Bukoba District Council
P.O Box 491 Bukoba
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Kaihura Fidelis
+255 754273849
Fidelis.kaihura@fao.org
K-TAMP
P.O.Box 127 Bukoba
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
25/05/2012
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Indigenous knowledge transfer [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
Indigenous knowledge transfer, is a common phenomena in farming societies whereby elders taught younger generations the practical aspects in production and emphasizes the norms and proms in folk story tales.
- جامع المعلومات: Godfrey Baraba
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
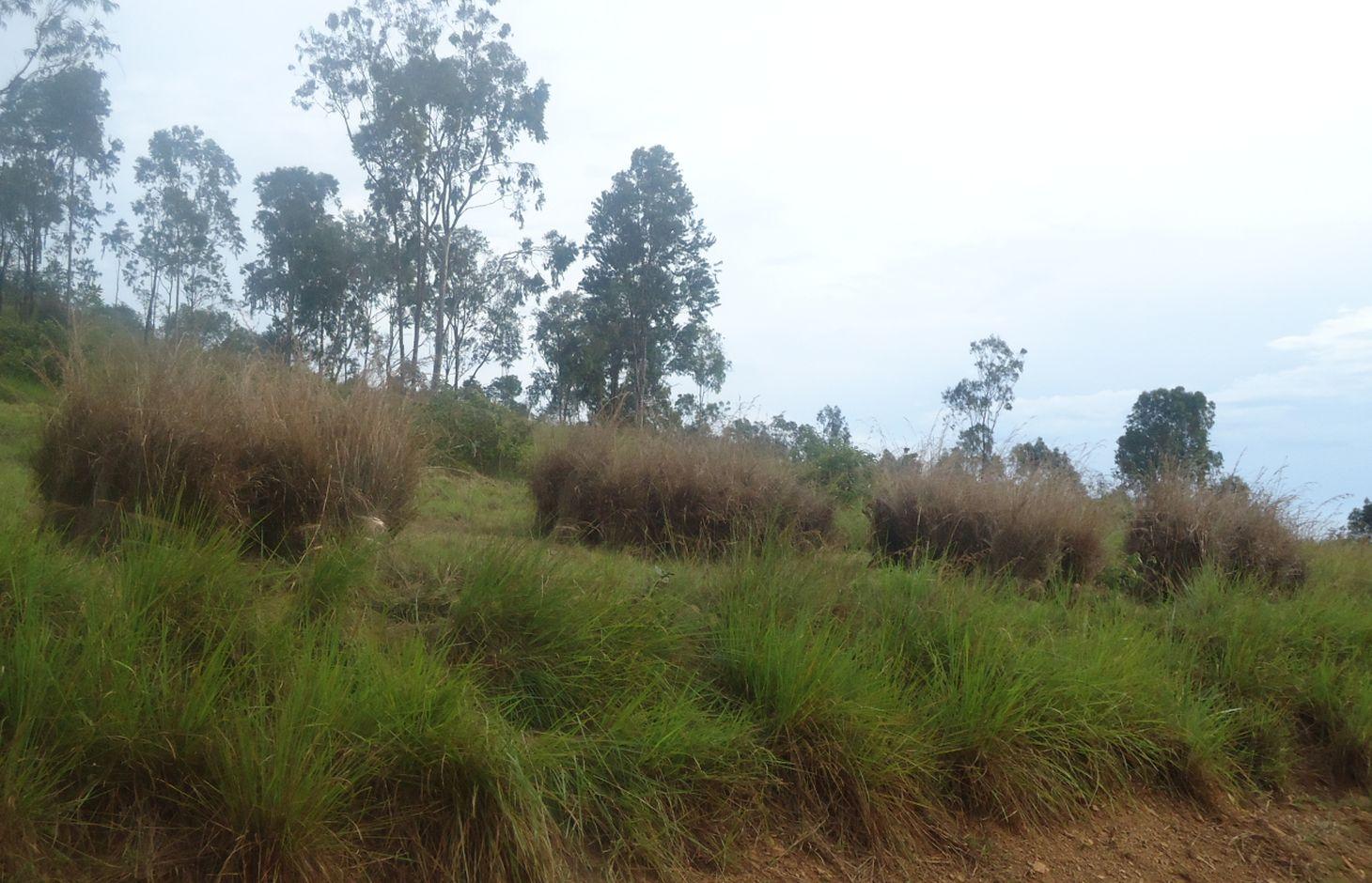
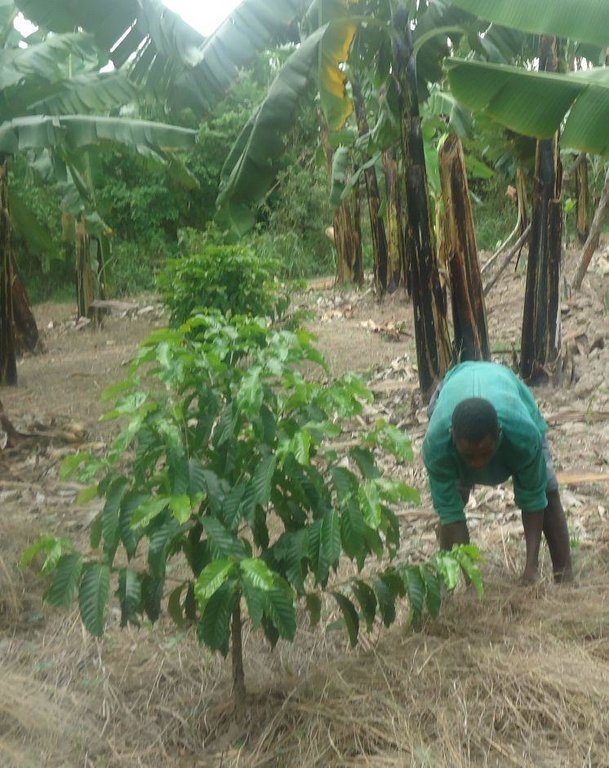
Application of Thatch and Hyperrhenia Rufa grass mulch in banana and coffee plantation to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility and moisture and ensure high productivity
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The technology is applied in coffee and banana fields in the sub humid climate. The technology objective is prevention of land degradation specifically nutrient improvement, erosion control, soil moisture and soil health (soil's living organisms) improvement. The materials applied are very variable perennial grass from 60-240 cm high. Panicle loose and narrow up to 50 cm long, with slightly spreading or contiguous racemes with shortly hairy or nearly glabrous spikelets 3.5-5 mm long. The materials are spreaded to 15cm thickness, manually across the slpoe, once per year, at the beginig of short rains.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to retain moisture content in soil by promoting water infiltration during and after the rains, promoting water holding capacity through decay and formation of organic matter. Grass mulch control soil erosion by intercepting raindrops (splash erosion) that detach soil particles. Grass mulch technology improves soil nutrient through grass decomposition.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There is no establishment activities for the technology only maintenance activities (operational activities) are required once a year.
Maintenance activities include collection of mulching grasses -The grass is cut and collected by household or hired labor. The quantity of grass required per hectar is 1,500 cubic metre equivalent to 375 bundles.
To spread/apply mulching grasses -Grass is spread manually across the slope preferably to 15cm thickness. Dry grasses are spread across the slope with thickness of maximum 15cm. It is recommended to apply mulch grass around 15cm from the banana trunks.This is done once annually before the onset of short rains (during Augost and September)
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied on coffee/banaana fields. The Rainfall is 1000-1500mm, the subhumid climate (temp 26 -30 degree centigrade) and two growing seasons. The technology is meant for soil water evaporation contol and is tolerant in dry spell season while sensitive to excessive rains.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tanzania
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Bukoba District (Karong village)
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
major cash crop: Maize, coffee and Maesopsis
major food crop: Cassava, banana and avocado
other: Beans, yams and mangoes
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, excessive soil water evaporation, fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Excessive weed invasions and reduced productivity
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: September (mid)- January (mid); Second longest growing period in days: 65; Second longest growing period from month to month: March-May
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Only one farmstead considered
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A6:أخرى
التعليقات:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Grass mulching
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Cultivation along the slope), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure (few farmers own grassland), poverty / wealth (Peasants are not able to purchase grass mulch)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Poor soil cover), droughts (There is soil water evaporation)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
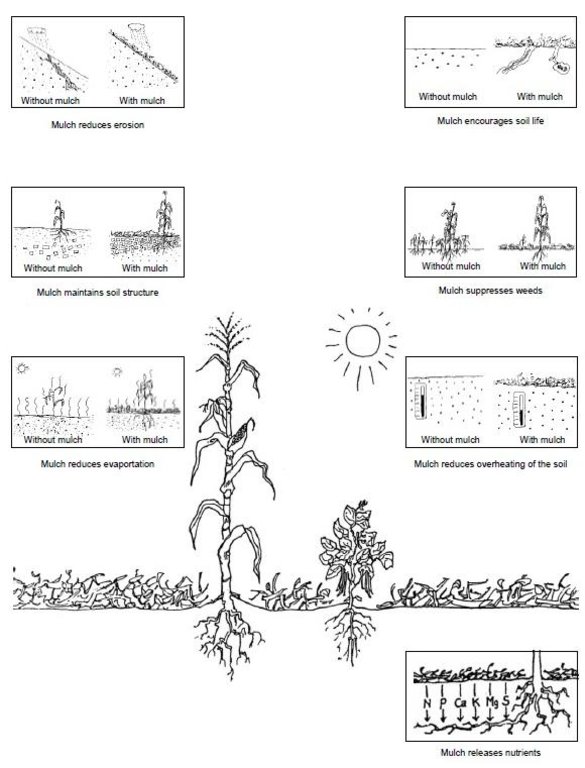
What is the use of mulching?; Source: Müller-Sämann and Kotschi (1994)
Location: Karonge Village. Bukoba District Council
Date: 26 Feb 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Mulching
Material/ species: Dried grasses (Thatch and Hyperrhenia Rufa grass )
Quantity/ density: 1500m3/ha
Remarks: Spreading across the slope
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1.25
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of mulching materials | زراعية | May-June |
| 2. | Application of mulching materials (spreading) | زراعية | June-August |
| 3. | Weeding | زراعية | July and January |
| 4. | De trashing | زراعية | February and September |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Collection and Apllication of mulching materials | persons/day/ha | 16,0 | 1,5625 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Mulch | ha | 1,0 | 117,0 | 117,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 142,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
per hectar of land protected; cost of purchasing 375 bundles of grass and their spread to be $0.3 per bundle and 20 mandays at $ 1.2
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Cost of purchasing mulch grass is the most determinate factor. Mostly due to long distance to fetch the grass and the scatered nature due to degradation and encroachment by tree planting.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Short rains Sept-November, long rains March-May,length of dry period 180 days
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات محدبة أو نتؤات
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average: 6.25%
Altitudinal zone: 1194 m a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: De trashing commonly done by men, collection and application of mulch commonly done by women
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
20% of the land users are rich and own 40% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: Coffee is purely for commercial while banana is for both subsistance and commercial
Level of mechanization: Cultivation is done at establishment phase, another farming systems limits mechanization
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
The technology is highly adopted by well to do farmers, either having off farm source of income or old farmer after achieving reasonable savings. This is because the communal range land has encroached by protected forest.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
Church:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Hyperrhamia rufa is un palatable, hence its dominance implies reduced fodder quality.
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Unpalatability of Hyperrhamia rufa implies reduced nutrient intake, hence animal production is reduced.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
135
التعليقات/ حدد:
Purchase of mulch grass, without transport and labor for spreading mulch.
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased banana productivity, labores earn income for purchasing food
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Practiced farmers respected as inovators as well as progressive farmers
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0 mandays
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10 mandays
التعليقات/ حدد:
Cutting mulching grasses are income generating activities for young men and women.
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved coffee/banana mulching increases farm income. Additional revenue is spent for child’s education and health services
Working in distant unconducive environment
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
تراص التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soil's living organisms
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
التعليقات/ حدد:
Surface water run-off is combated in the area, hence neighbor's fields face only rain direct rain drops.
Nutrient transfer from grassland to crop land
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
| غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
No establishment costs, recurrent costs for mulching Technology for three years consecutively, can increase productivity in two folds and be maintained for more than ten years.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
1766 households (68 percent of land users in stated area)
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
1766 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There are farmers who apply dried banana leaves and pseudo stem as mulch.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The adoption is moderate simply because of increasing cost of mulching grasses compared to produce farm gate price increase. Furthermore the labour force is dominated by the elderly.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Increase in soil moisture especially during the dry season How can they be sustained / enhanced? Perform regularly maintenance activities |
|
Reduced weeds How can they be sustained / enhanced? Apply mulch grasses at the depth of 15 cm twice a year for the first 3 years consecutively |
|
Fertility increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? Soft loan of livestock to be provided to farmers |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Esy to implement and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote extended use of the technology (knowledge sharing) |
|
Multiple ecological benefits: improved soil organic matter, soil moisture and soil biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Educate farmers on diversified mulching materials and systems e.g. intercropping, cover crops, minimum tillage |
|
Prevent soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine other conservation technologies e.g. contour construction with mulching. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Does not stay longer, it can persist for one season, hence requires twice application | Apply the correct quality and quantity material. |
| Not readily available to all farmers simply because range land has been allocated to well to do farmers. |
Land tenure system and land use planning should be revisited |
| Increased manual labour (cutting, transportation spreading) | Plant grasses like vertiva |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Grass mulch available only to farmers with grassland | Other measures should be encouraged (use of chopped banana,pseudo stem, leaves and sheaths) |
| Degradation of grassland | Promotion of SLM Technologies for grassland conservation |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Kagera TAMP project website
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Indigenous knowledge transfer [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
Indigenous knowledge transfer, is a common phenomena in farming societies whereby elders taught younger generations the practical aspects in production and emphasizes the norms and proms in folk story tales.
- جامع المعلومات: Godfrey Baraba
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية