Planting pits and stone lines [النيجر]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Charles Bielders
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Tassa avec cordon pierreux (french)
technologies_1100 - النيجر
- Planting pits and stone lines: 6 يونيو، 2019 (public)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 4 إبريل، 2018 (inactive)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 4 إبريل، 2018 (inactive)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 4 مايو، 2017 (inactive)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 28 إبريل، 2017 (inactive)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 28 إبريل، 2017 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Oudou Noufou Amadou
PDRT
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Projet de développement rural de Tahoua, Niger (PDRT)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Université catholique de Louvain (Université catholique de Louvain) - بلجيكااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Centre for Agriculture in the Tropics and Subtropics (Centre for Agriculture in the Tropics and Subtropics) - ألمانيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/08/1999
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
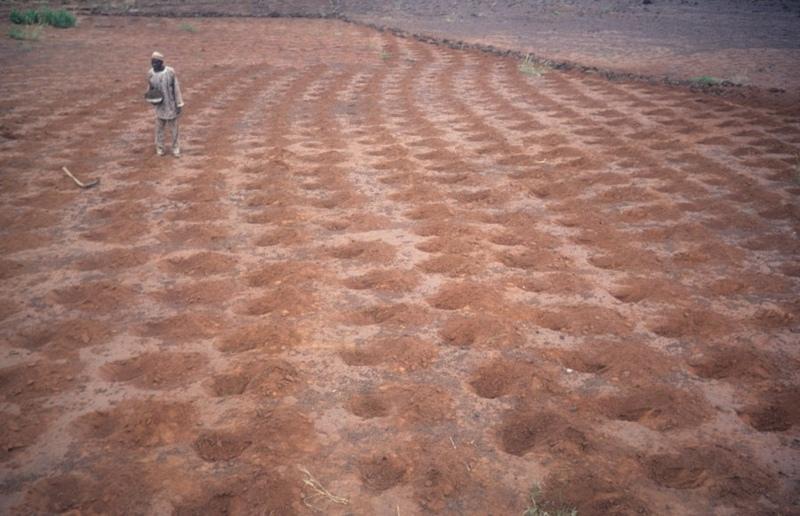
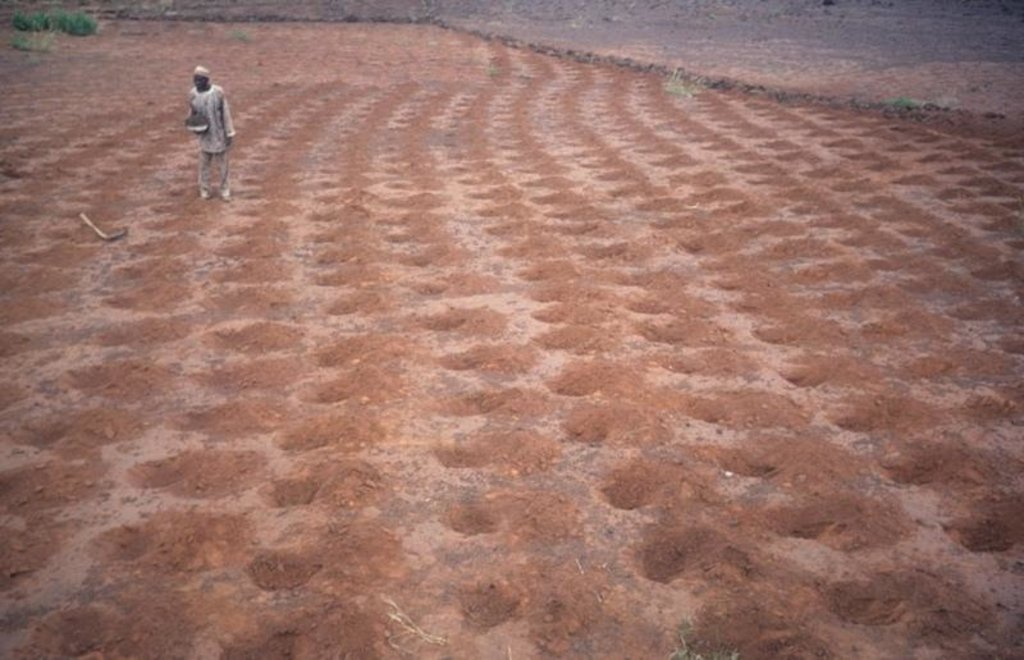
Rehabilitation of degraded land through manured planting pits, in combination with contour stone lines. The planting pits are used for millet and sorghum production on gentle slopes.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The combination of planting pits (tassa) with stone lines is used for the rehabilitation of degraded, crusted land. This technology is mainly applied in semi-arid areas on sandy/loamy plains, often covered with a hard pan, and with slopes below 5%. These denuded plains are brought into crop cultivation by the combination of tassa and stone lines. Planting pits are holes of 20-30 cm diameter and 20-25 cm depth, spaced about 1 m apart in each direction. The excavated earth is formed into a small ridge downslope of the pit. Manure is added to each pit, but its availability is sometimes a problem. At the start of the rainy season, millet or sorghum is sown in these pits. The overall aim of the system is to capture and hold
rainfall and runoff, and thereby improve water infiltration, while increasing nutrient availability.
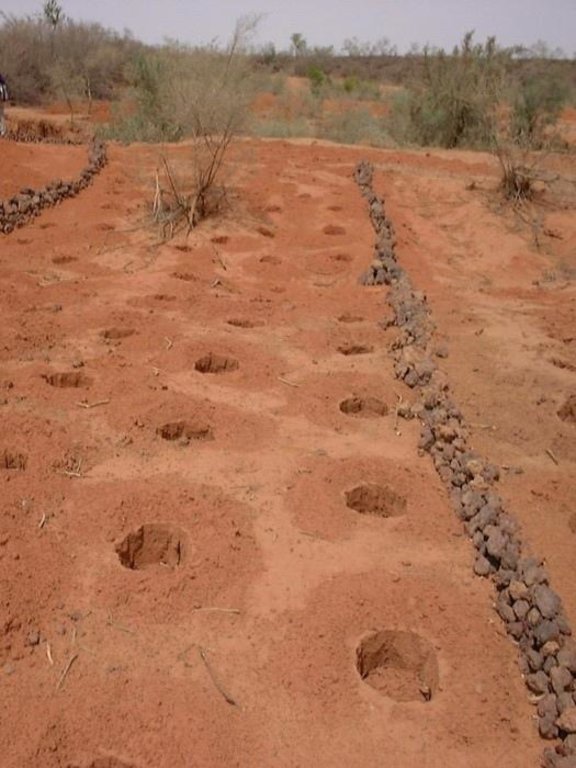
Stone lines are small structures, at most three stones wide and sometimes only one stone high. The distance between the lines is a function of the slope and availability of stone. Typically they are sited 25-50 m apart on 2-5% slopes. Stones are usually collected from nearby sites - though sometimes up to 5-10 km away and brought to the fields by donkey carts or lorries (when a project is involved). They are positioned manually, along the contour. Stone lines are intended to slow down runoff. They thereby increase the rate of infiltration, while simultaneously protecting the planting pits from sedimentation.
Often grass establishes between the stones, which helps increase infiltration further and accelerates the accumulation of fertile sediment. Wind-blown particles may also build up along the stone lines due to a local reduction in wind velocity. The accumulation of sediment along the stone lines in turn favours water infiltration on the upslope side. This then improves plant growth, which further enhances the effect of the system. Construction does not require heavy machinery (unless the stones need to be brought from afar by lorry).
The technique is therefore favourable to spontaneous adoption. Stone lines may need to be repaired annually, especially if heavy rains have occurred. Manure is placed every second (or third) year into the previously dug pits and sand is removed annually: normally the highest plant production is during the second year after manure application.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيجر
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Niger, Tahoua
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
major food crop: Millet and sorghum
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil fertility decline is the basic problem: this is due to degradation and nutrient mining. Loss of limited rainwater by runoff and loss of soil cover result in low crop production and food insufficiency. This occurs in combination with lack of pasture, resulting in shortage of manure.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 40 km2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A6:أخرى

التدابير البنيوية
- S11: غير ذلك
التعليقات:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Manure application (supplementary)
Specification of other structural measures: stone lines, planting pits
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
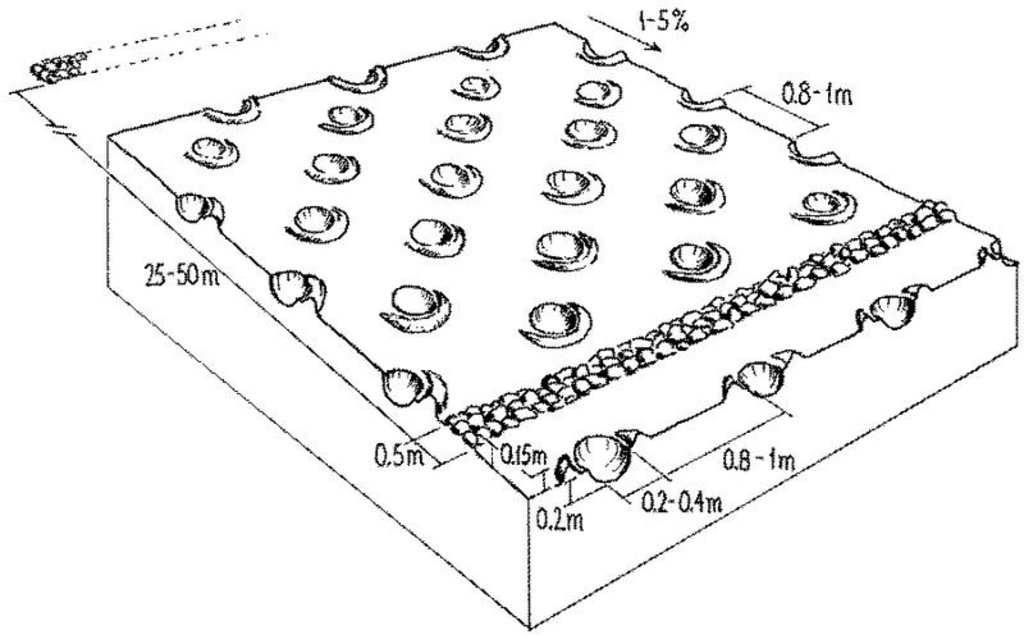
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Planting pits (tassa) capture rainfall runoff for cultivation of annual crops, and the stone lines - spaced at 25-50 metres apart - help hold back moisture and eroded soil.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase in soil fertility, increases natural regeneration of trees
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, improvement of soil structure
Manure / compost / residues
Quantity/ density: 2.5 t/ha
Structural measure: stone lines
Spacing between structures (m): 25-50planting pits
Structural measure: planting pits
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 1
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2-0.25
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2-0.3
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): <5%
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging pits (tassa): the excavated earth | بنيوية أو هيكلية | dry season (November to May) |
| 2. | Digging out stones from nearby sites | بنيوية أو هيكلية | dry season (November to May) |
| 3. | Transporting stones | بنيوية أو هيكلية | dry season (November to May) |
| 4. | Aligning the stones along the contour with the help of a ‘water tube | بنيوية أو هيكلية | dry season (November to May) |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Digging tassa | persons/day/ha | 100,0 | 1,5 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Building stone lines | persons/day/ha | 26,666 | 1,5 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools for tassa | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools for stone lines | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 75,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Transporting stones with lorri | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 245,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Manuring the pits with approx 250 g per pit | زراعية | dry season (November to May) / initial establishment |
| 2. | Manuring the pits with about 250 g per pit (2.5 t/ha) | زراعية | October/November or March-May / every second year |
| 3. | Removing sand from the tassa | بنيوية أو هيكلية | March-May/annual |
| 4. | Check and repair stone lines | بنيوية أو هيكلية | annually and after heavy rains. |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | persons/day/ha | 21,0 | 1,5 | 31,5 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools for tassa | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 35,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, pick-axe, shovel, donkey cart, (lorries)
The costs are based on 300 m of stone lines per hectare (on a 3-4% slope). Maintenance costs refer to removing
sand from the pits from the second year onwards, and to the application of manure every second year (costs are spread on an annual basis). If applicable, costs for transporting the manure need to be added. The general assumption in these calculations is that adequate manure is readily available close by. The availability of stones is the main factor in determining costs - though labour availability can affect prices also. If stones are not available in the field or nearby (from where they can be transported by donkey cart), they have to be carried by lorries, which is much more expensive. The costs here refer to fuel costs only, paid by a project: they do not include depreciation of lorries.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Also deep
Soil fertility is low - very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good, though infiltration is low where there is a crust
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Off-farm income specification: remittances from out-migration of labour, commerce and crafts
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
input contstraints
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Through mutual aid in technology implementation
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Land use rights conflicts of rehabilitated land and conflicts between farmers and pastoralists, because pasture land is being turned into cultivated fields
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التربة
رطوبة التربة
فقدان التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
soil fertility
long-term soil cover
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is moderate growing spontaneous adoption (for rehabilitation of the plains), but there are no estimates available regarding the extent.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Simple technology, individually applicable in the dry season, requiring only very little training/knowledge and no special equipment. |
| Making best use of manure, which is a limiting resource. |
| Increase in agricultural production. |
| Rehabilitation of degraded and denuded land: bringing back into production formerly uncultivated land; extension of farm land to the plateaus. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Labour demanding technology for implementation and maintenance | Mechanisation of tasks: transportation of stones and manure. However, this would raise the cost. |
| Instability of planting pits in loose soil, increased erosion on steeper slopes and with heavier rains |
Avoid loose sandy soils and steep slopes. |
|
The effectiveness can be compromised if the various geo-morphological units (plateaus, slopes) are not treated simultaneously |
Catchment area approach if downstream flooding is an issue. |
|
Possibility of land use conflicts concerning rehabilitated land, in particular with pastoralists |
Better coordination/consultation before implementing the technology in an area. |
| Implementation constraint: availability of manure and/or stones and transporting manure/stones to the plateaus and slopes |
Subsidise transport means (or supply donkey carts) or/and apply stone lines only in areas where there are stones available close to the fields. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Bety A, Boubacar A, Frölich W, Garba A, Kriegl M, Mabrouk A, Noufou O, Thienel M and Wincker H: Gestion durable desressources naturelles. Leçons tirées du savoir des paysans de l’Adar. Ministère de l’agriculture et de l’élevage, Niamey, 142 pp.. 19
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Hassane A, Martin Pand Reij C:Water harvesting, land rehabilitation and household food security in Niger: IFAD’s Soil and Water Conservation Project in IllelaDistrict. IFAD, Rome, 51 pp.. 2000.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Mabrouk A, Tielkes E and Kriegl M: Conservation des eaux et des sols: Leçons des connaissances traditionnelles de la région de Tahoua, Niger. In: Renard, G., Neef, A,. Becker, K. and Von Oppen, M. (eds). de la région de Tahoua, Niger. 1998.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية