No Till [الاتحاد الروسي]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Peter Liebelt
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, David Streiff
Нулевая обработка
technologies_1319 - الاتحاد الروسي
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Sustainable land management in the Russian steppes (KULUNDA / GLUES)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
No tillage is based on direct seeding with the innovative/ modern direct seeder Condor and works without any kind of soil disturbance.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
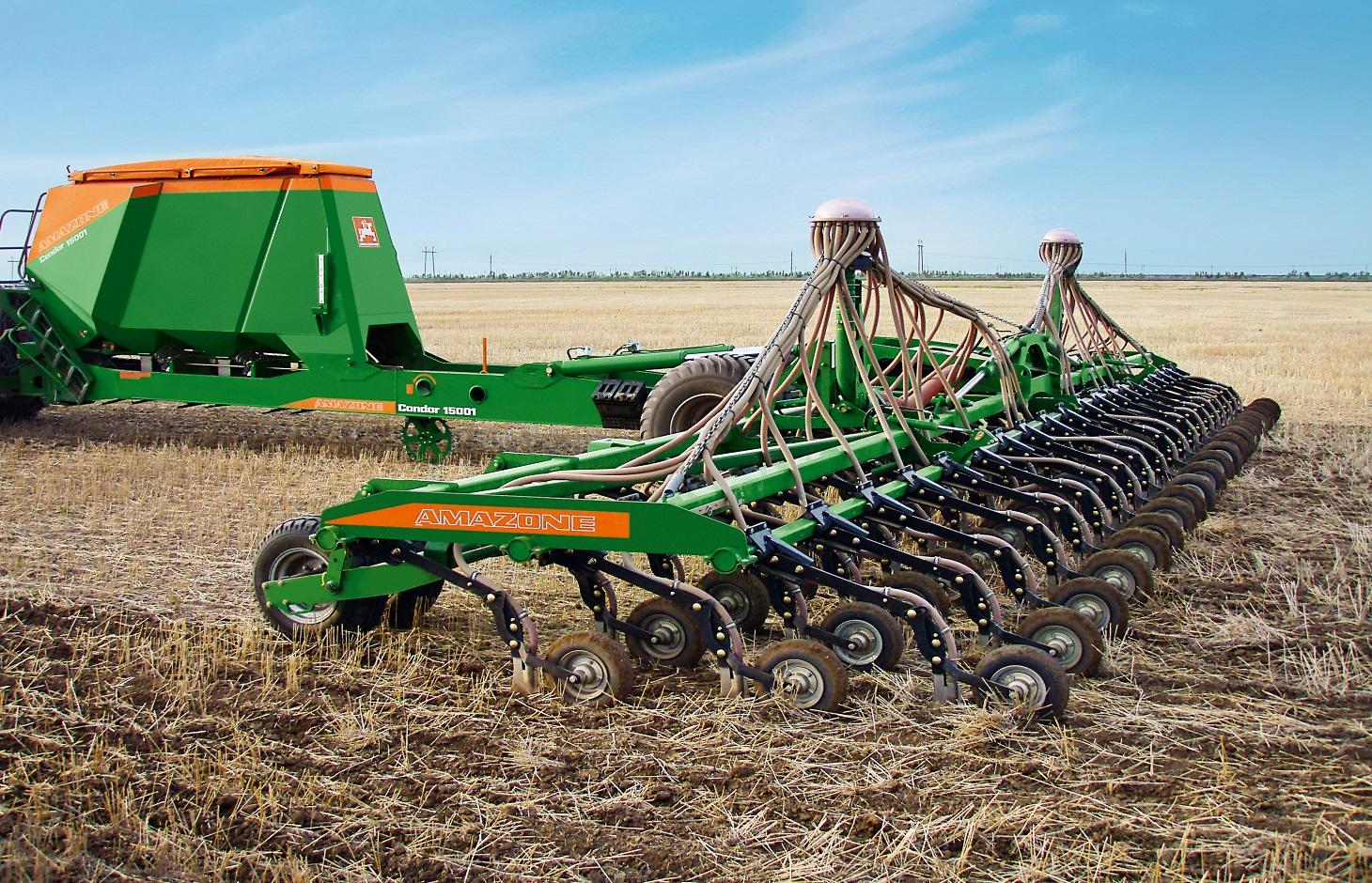
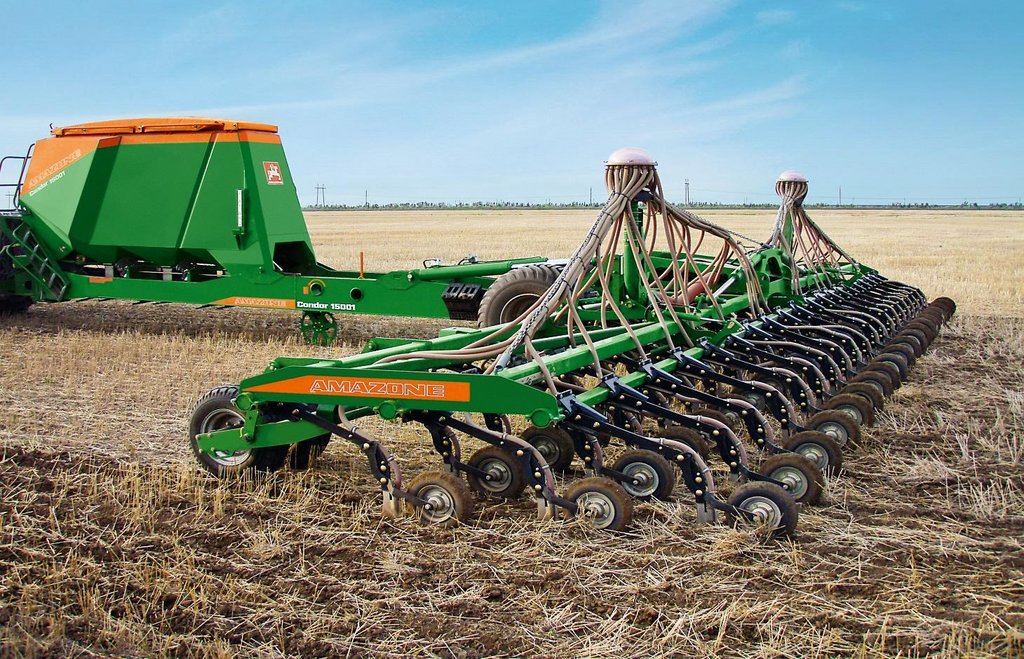
"No-Till" is a key element of the ‘modern cropping system/ Canadian System’ in the Kulunda steppe. In contrast to minimum tillage an innovative modern direct seeding machine is used. The successful implementation of “No-Till” requires an adaptation of the whole cropping system including crop rotation. Rotation includes a succession of cereal crops (e.g. spring wheat), legumes (peas), and oil seed crops. In the study area predominantly spring cereals are grown. The direct seeder ‘Condor tine seeder’ (Amazone) was used for direct seeding. In contrast to the SZS 2.1 seeder used for minimum tillage it has flexible, individually depth-guided tine coulters, which ensure a high precision of seed placement. When opening the seed furrow, the narrow coulter moves little soil, so that the valuable soil moisture remains in the soil, and there is sufficient fine soil to ensure the optimum seed/ soil contact. Straw is safely cleared from the seed furrow, preventing the "hairpinning-effect" which is the pressing of straw by the coulter into the sowing slit. During the sowing period fertilizers are applied and broad spectrum herbicide in autumn and selective pesticides in the growing season are sprayed which help to increase yield.
No-till works without intensive primary tillage and stubble cultivation that saves time, fuel and reduces soil water evaporation. No-till increases soil aggregate stability, helps to reduce the risk of soil erosion, leads to a higher soil fertility and reduces soil water losses. Weed control through crop rotation and herbicide application allows to omit mechanical weeding and thus to protect the soil against fertility decline and soil water loss. Fertilization becomes more important, because of the decreased mineralization rate under no soil tillage, especially at the beginning of the conversion of the cropping system and until soil organic matter could build up in the soil.
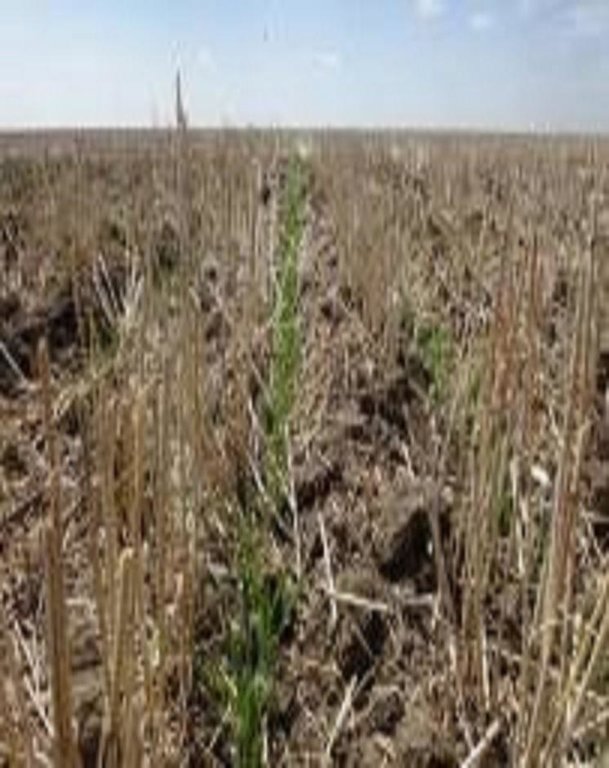
The Technology including crop rotation was tested in the field in 4 test plots with 4 repetitions at the test site in Poluyamki. Results showed that the intensity of soil tillage and seeding methods used had a great influence on crop establishment and expected yields. It was demonstrated that no tillage leads to higher water use efficiency and highest yields. Positive effects were also observed regarding soil structure and soil fertility already after 3 years. Positive effects were also observed regarding soil structure and soil fertility already after 3 years. Minimized soil disturbance led to higher aggregate stability, which leads to a lower risk of wind erosion, increased soil organic carbon storage and soil fertility as well as available soil water content. The Modern Canadian system caused fixed production costs in form of annual depreciation and also additional costs due to the application of fertilizers and pesticides, the prices of which increased in the last four years. Due to not finalised land rights reforms, uncertain credits and harvest insurance farmers are reluctant to invest in new machines.
The test site in Poluyamki is located in the dry steppe of the border region next to Kazakhstan, where, due to the climatic conditions, no natural afforestation occurs, and the planted windbreaks don’t grow vigorously due to the prevailing aridity. The annual precipitation is under 300 mm a year. Probably the greatest climatic influence factor is the precipitation - in terms of quantity and space/ time distribution and, due to high summer temperatures, the high rates of evapotranspiration. The total yearly precipitation rate is the primary yield-limiting factor in all steppe regions. The ratio between precipitation and evaporation is negative. In the late weeks of spring, prolonged droughts must be expected in 5-year cycles, limiting germination and crop establishment. The soils are classed among those of cool-tempered grasslands. Due to their physical and chemical characteristics, these soils (Chernozems and Kastanozems) have high agronomic potential.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الاتحاد الروسي
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Russian Federation/Altai Krai
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Mikhaylovski district (Pavlovski district, Mamontovski district)
التعليقات:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Centre latitude: _52° 4'3.00"N Centre longitude: 79°54'26.16"E Test site Poluyamki
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Since the collapse of the Soviet Union increasingly innovative conservation technologies that are being developed in research experiments are implemented in practice. But the no technology of "No-till" as the most extreme form of conservation tillage is rarely applied in the study area. Thus the tested no-system is highly innovative for the Kulunda steppe.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): It's the decrease of soil organic carbon content in the soils, topsoil thickness through deflation and soil compaction, which lead to a decrease of soil fertility. Additionally, the negative soil water balance due to the high summer temperatures and evaporation and in addition the high spatial and temporal variability of precipitation as a serious problem relating to the lack of soil water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land user that we work with and that implement the our new farming practices have a similar opinion relating the land use problems like the research staff of the project. But there are still a lot of farmer, that underestimate the ecological risks of soil degradation resulting from traditional soil management.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 110, Longest growing period from month to month: May-October
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.13 m2.
The total investigation area of the SLM Technology “Minimum Tillage” refers to our test site areas: 1. Poluyamki, Mikhaylovskiy Rayon: 13ha managed by Minimum Tillage; 2. Pervomayskiy, Mamontovskiy Rayon: 10ha managed by Minimum Tillage; 3. Komsomolskiy, Pavlovskiy Rayon: 3ha.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
التعليقات:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mulching, green manure, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية
- (Ed): الانكماش والترسب
- (Eo): تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Conventional soil tillage by ploughing), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Bare fallow without vegetation cover), Capital for investments (Lack of capital for investment in modern adapted agricultural technologies)
Secondary causes of degradation: wind storms / dust storms (Strong winds and storms - Sukhoveijs - from the southwestern central-Asiatic semi-desert regions cause a higher risk of wind erosion especially on traditional cultivated cropland without plant cover), droughts (The frequently occurring early-summer drought periods are particularly problematic for agricultural production), education, access to knowledge and support services (Need for better know how how to manage no-till systems. Need for more effective measures for knowledge transfer and capacity building.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
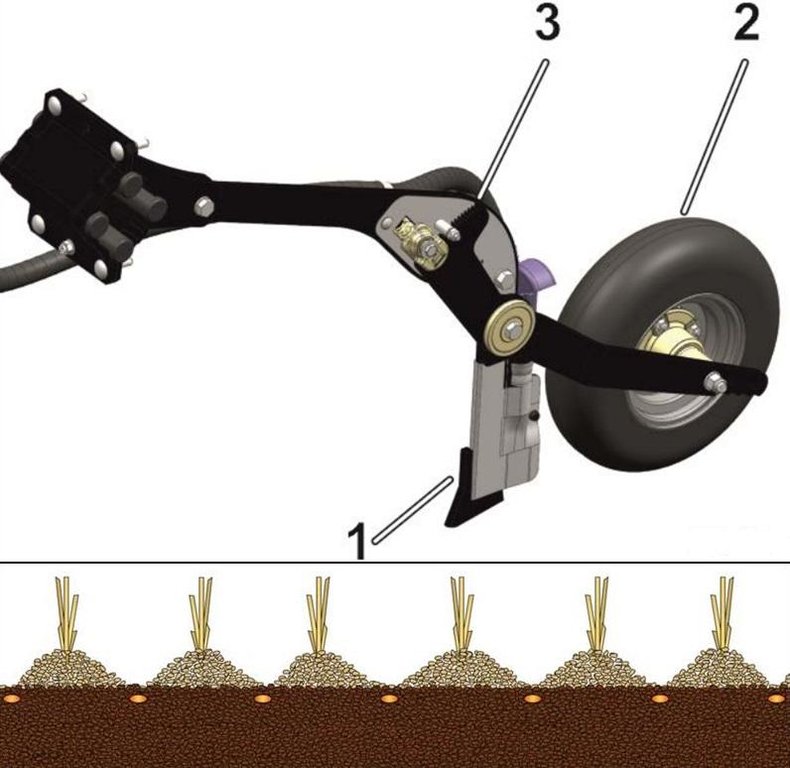
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
The coulter system of the direct seeder Condor based on an individually depth guided tine coulter. When opening the seed furrow, the narrow coulter moves little soil, so that the soil moisture remains in the soil. The accurate depth control and the packer wheel lead to an optimum contact between seed an soil, which is very important especially in dry regions like the Kulunda dry steppe in Poluyamki. 1-Chisel coulter 2- Packer wheel 3-Air diffuser. Illustration: seed grains placed between the former sowing rows
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Crop rotation without bare fallow
Green manure
Material/ species: Pea (once in a rotation)
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: with calcium ammonium nitrate
Quantity/ density: yearly
Remarks: 100kg/ha (spring wheat and rape), 50kg/ha (pea)
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: wheat-pea-wheat-rape
Quantity/ density: 4 years
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: Direct seeder Condor (Amazone company)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Direct seeding | زراعية | Late april/ early may |
| 2. | Fertilizer application | زراعية | |
| 3. | Pest management | زراعية | period of vegetation |
| 4. | Harvest | زراعية | september |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,12 | 4,12 | |
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 15,96 | 15,96 | |
| معدات | fuel | ha | 1,0 | 25,49 | 25,49 | |
| المواد النباتية | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 19,37 | 19,37 | |
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 30,83 | 30,83 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 9,42 | 9,42 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 105,19 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor MTS 1221, Tractor Kirovets K 701, Harvester Don 1500, Direct seeder Condor 15001, Sprayer UX 5200
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
High initial investment in new machines. Compared to the Traditional Soviet System with conventional deep ploughing without fertilizer application fertilizer and pesticides are the main additional cost factors.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري جدا
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- موظف (شركة، حكومة)
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: There are generally less woman than men in rural regions caused by rural-urban migration. Furthermore, jobs in the in the field of crop production are not so attractive for woman. Traditionally, much more women work in the field of livestock farming.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- مؤجر
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
state: 45%, the data refer to the Altai Krai
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
In the first years after the change of the cropping system, there is an increased risk of crop losses due not correct/suitable management of the new cropping system
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Initial costs, first years for herbicides
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
but increase of costs for pesticides and fertilizer, decrease for fuel and labor
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
in general yes, but food security is not a problem in this region
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
contribution to human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors, like precipitation or the economic situation and financial power of the farmers
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
There is a lower risk for compaction damage than under under traditional ploughing
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الأنواع المفيدة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
سرعة الرياح
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
use of herbicide application
التعليقات/ حدد:
The no-till system works without mechanical weed control, therefore it must be a chemical weed control especially in the first years of no-till system.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
higher content of soil moisture
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The 3 farms where we have tested the technology of minimum tillage will partly apply this technology on their farming land. But it must be considered that the test farms of the KULUNDA project were interested in conservation technologies already at the beginning at the project and they are able to invest in new machinery to implement the tested SLM technology, that is not representative for the whole Kulunda-region.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
There is a trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors like the precipitation or conditions an economic situation of the financial power of the farms. For example the drier the conditions, the more sense is to minimize the tillage. But there is a need to invest in new machinery. In contrast to the Adapted cropping system (with minimum tillage) the modern Canadian system require new seeding machinery that that means high establishment cost. Therefore the implementation growth is not so significant compared to the adapted system that use already existing Soviet seeding machinery.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Increase of soil aggregate stability and improved soil structure thus better erosion control and protection of soil organic matter will improve soil fertility and water holding capacity |
| Minimization of evaporation losses through better soil cover |
| Lower input costs (materials, fuel, labour, time) and quicker field operations |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Application of chemical herbicides leads to higher costs and possible ecological risks. | Selective spraying using the “Amaspot” system that is based on infrared detection of weeds. |
| Higher requirements for fertilizers, especially at the beginning, due to lower mineralization rates and less nutrient availability compared to conventional cultivation. | Higher fertilizer application in the first years after conversion. |
| High initial investment costs for buying direct seeders | share machine and costs with other land users. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية