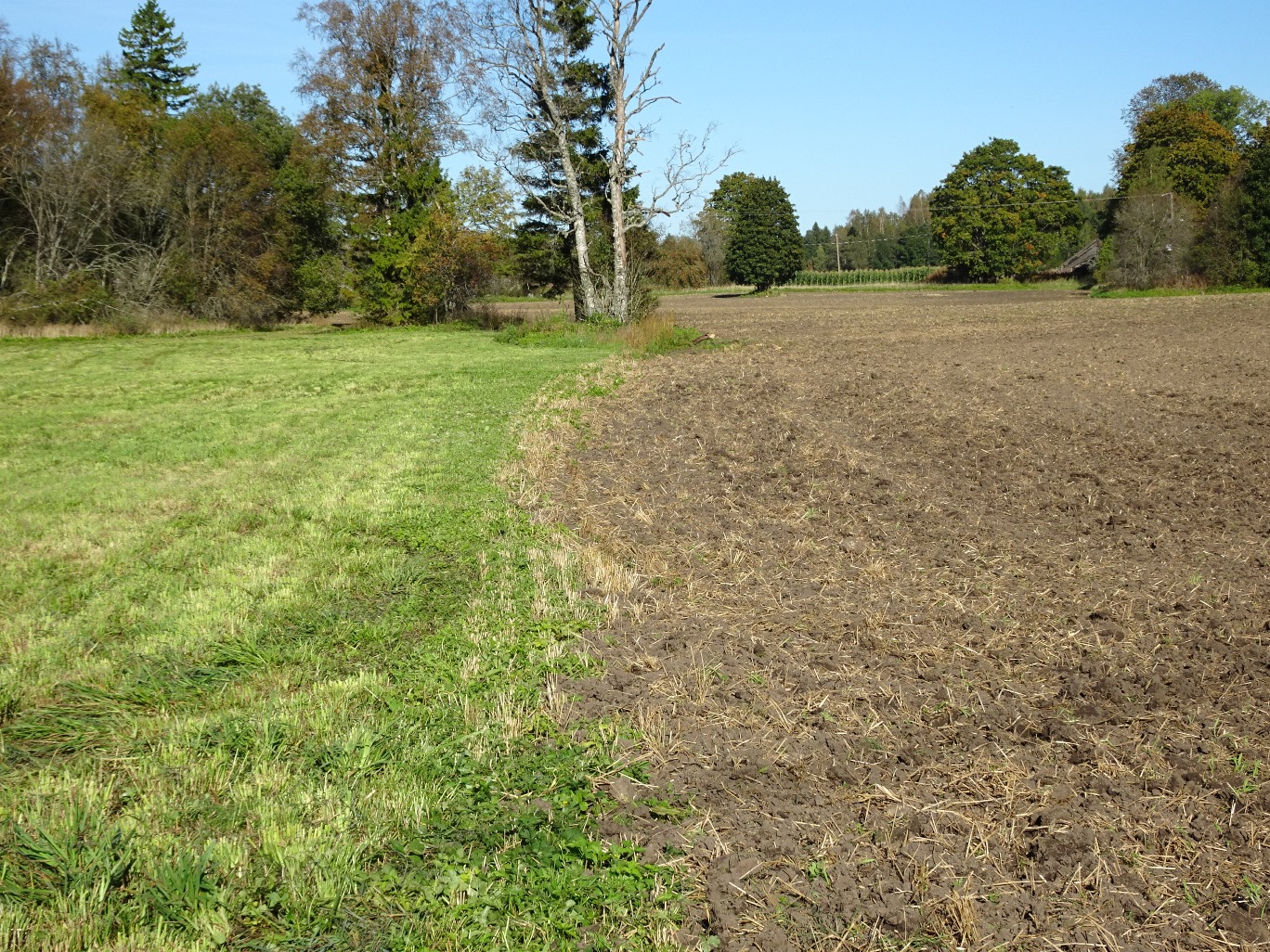
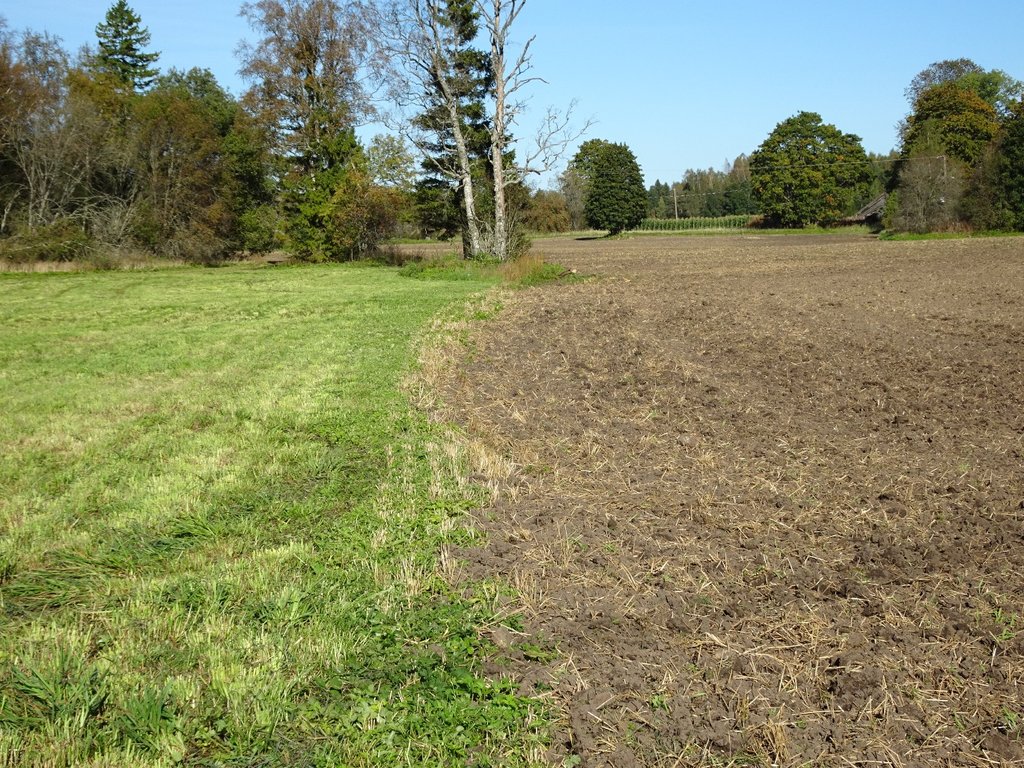
Permanent grassland on peaty and eroded soils [استونيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Endla Reintam
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch
Püsirohumaa turvas- ja erodeeritud muldadel
technologies_3113 - استونيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
مستخدم الأرض:
Selge Are
+37257863250
are.selge@emu.ee
Hummuli Agro
Tiigi 3b, Hummuli, 68410 Valga maakond
استونيا
researcher:
Penu Priit
+3725156165
priit.penu@pmk.agri.ee
Agricultural Research Centre
Teaduse 4/6, 75501 Saku, Harjumaa
استونيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences (IAES/EMÜ) - استونيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
04/06/2017
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
A permanent plant cover is maintained or established to protect soil against erosion or peat decomposition.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
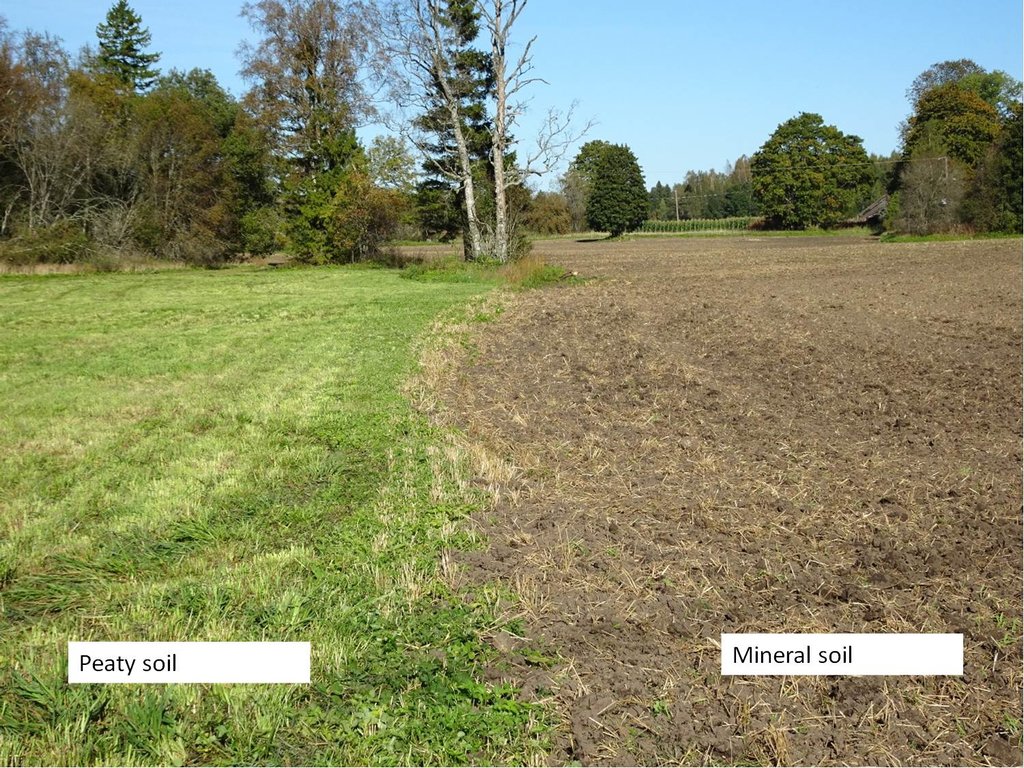
The technology is applied in sub-humid climate with an average of 696 mm of precipitations per year, from which more comes from July to October and less in March and April. Average annual temperature is +4 C, length of the growing period is 180-195 days. The territory is mostly flat to slopes of 6-10%. Average altitude from the sea level is 50 m. About half of the Estonian territory is above 50 m and half is below it. Soils are from very shallow (less than 0.1 m) inthe north to very deep (> 120m ) in the south. Soil cover is very variable. The peat cover of peatlands varies from 0.3 m to more than 10 m from well decomposed to poorly decomposed peat. On hilly areas the soils are medium textured with low (< 1%) organic matter in topsoil. Groundwater in near the surface in peatlands and deep in hilly areas. Biodiversity of these areas is medium. Market orientation of production system is mixed and off-farm income less than 10%. Relative level of wealth is average from individual households to cooperatives. Soil management is mechanized. Land belongs to land users but is leased also in case of bigger farms (over 1000 ha).
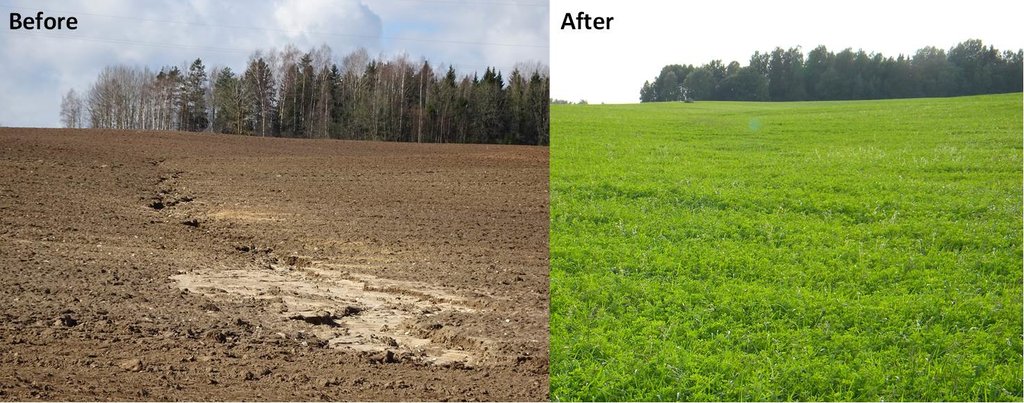
In the agricultural land the area will be excluded from intensive tillage by establishing a permanent plant cover, mainly with grass. The aim is to protect the slopes over 10% against erosion and peaty soils from further intensive decomposition of organic matter and with that the reduction of CO2 emission. The farmers should maintain permanent plant cover in the areas mentioned, or establish permanent plant cover. Renewing of the grassland is allowed from the top (without ploughing) once in a 5 year period. Government pays support of 50 EUR/ha if the area is bigger than 0.3 ha. The technology reduces intensively tilled area and thus the possibility to grow cash crops and/or reduces the yield from grassland. On the other hand it allows to still use wet areas for agriculture (i.e. fodder production).
The rules of the technology are fixed with the Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014-2020 under activity "Support for regional soil protection" (https://www.agri.ee/et/eesmargid-tegevused/eesti-maaelu-arengukava-mak-2014-2020) related to the reguation of the European Parliment and of the Council 1305/2013, article 28. The regulation is relevant more to the South-Estonia in case to reduce erosion, as the landscape is more hilly there. The exclusion of peatlands from agricultural use is relevant more in West-Estonia where the share of peatlands of the total area is the highest. However, it can be applied in whole Estonia if the area of peatland is bigger than 0.3 ha.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
استونيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
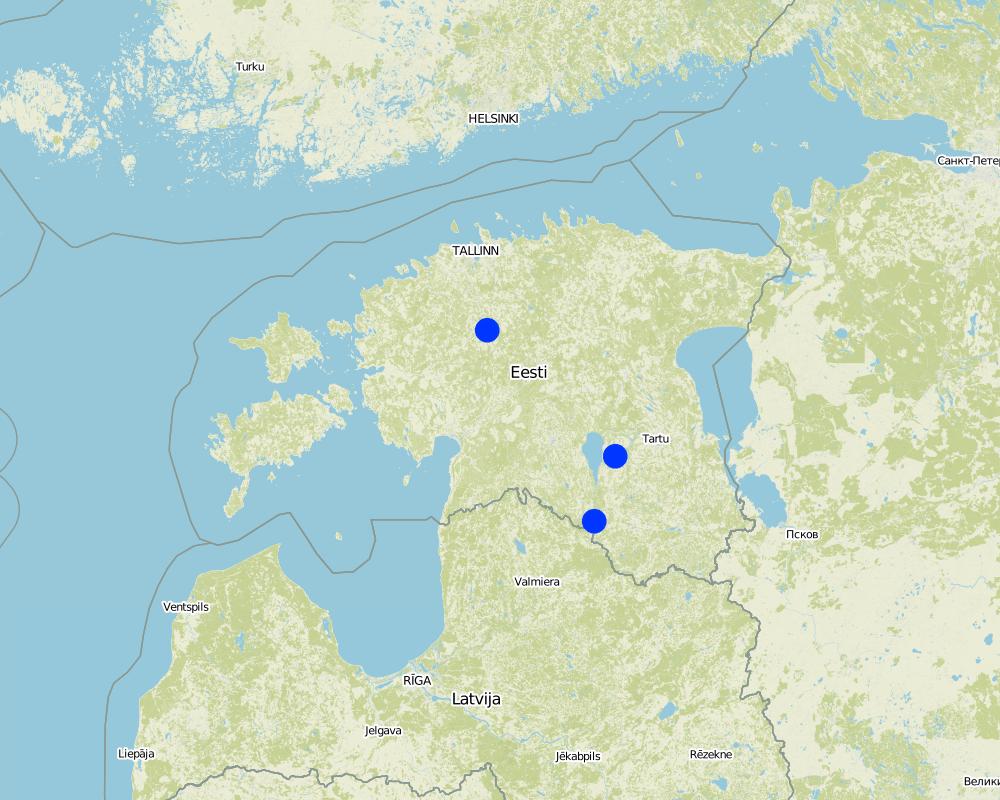
One site at Rapla, second at Tartu, third at Valga (erosion)
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
One site: Rapla county, Pae; second site Tartu county, Annikoru, third site Valga county, Hummuli
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
- Governmental tool
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The tool is a part of Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020 for soil fertility.
The survey was done by the Soil Survey Bureau of the Estonian Agricultural Research Centre (http://pmk.agri.ee/). The results presented here are partly from this survey and from the work done by the project iSQAPER.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
barley, wheat, rye, oat, oilseed rape, pea, bean, corn for silage, vegetables - potato, carrot, cabbage

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- مربى ماشية محدد
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- مراعي محسنة
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
Species: cattle, beef cattle, sheep,
Products: milk, beef, lamb
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Usually before the implementation of the technology the land was intensively tilled and used for annual crop plantation. After implementation the grasslands can be used for cutting and grazing.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
On Histosols the groundwater is close to the surface.
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
For the cereals one harvest per year, for grasslands 1-4 cuts per year. For hay 1 cut, for silage 2-4 cuts depending on the year
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
التعليقات:
To get the governmental support the area should be larger than 0.3 ha. Othervise the size is not important, depending on the area covered by hilly area or wet soils in the landscape.
In 2016 it was 10554 ha Histosols and only 40 ha of eroded soils covered with this technology in Estonia. This area excludes grasslands on another soil types. On specific sites: in Rapla county in Pae the size of the field is ca 3.2 ha, at Tartu county, Annikoru 2.8 ha.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
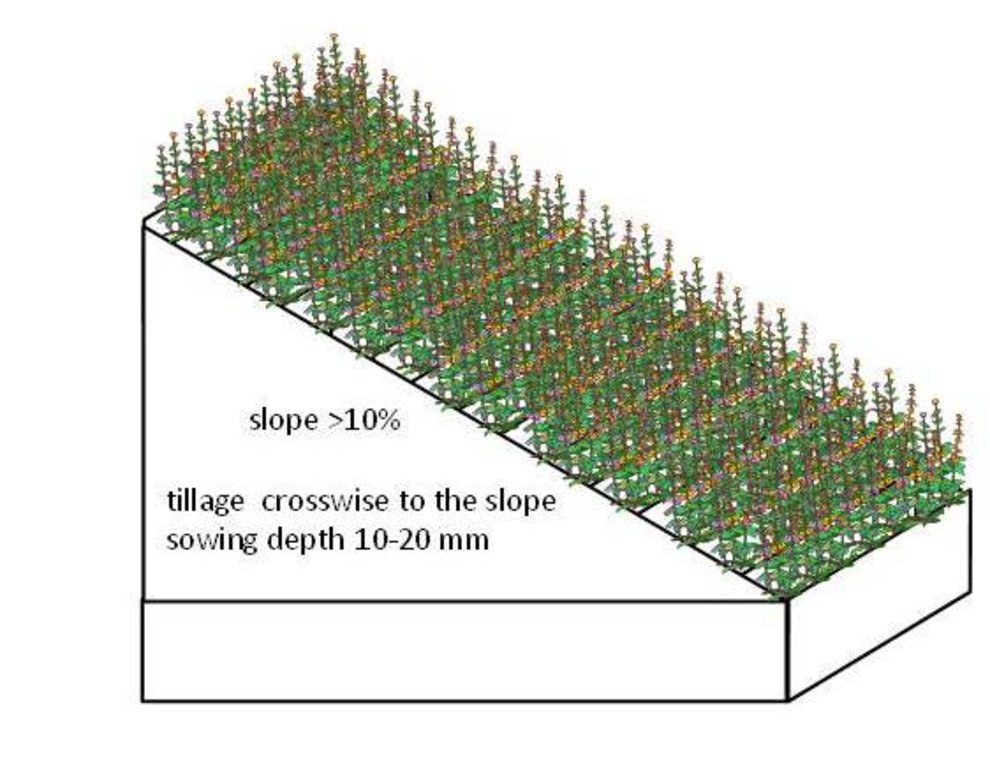
The requirements to create a permanent grassland depends on soil type.
Species mixture suitable for the permanent grassland on wet soils (Histosols): Bromus sitchensis 30%, Phalaris arundinacea 45%, Phleum pratense 20%, Poa pratensis 5%. Sowing rate 20 kg/ha.
For the drier areas (eroded soils) the next mixture is suitable: Dactylis glomerata 65%, Phleum pratense 26%, Poa pratensis 9%. Sowing rate 23 kg/ha.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
per hectar
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
EUR
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
1,18
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
36-40 EUR/day + taxes
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage (ploughing, cultivation) | زراعية | in spring |
| 2. | Collecting stones, slip (by demand) | إدارية | in spring |
| 3. | Fertilization | زراعية | in spring complex fertilizer |
| 4. | Sowing | زراعية | in spring |
| 5. | Rolling | زراعية | in spring |
| 6. | Cutting the weeds | زراعية | during growth (summer) |
| 7. | Fertilization during growth period | زراعية | after every cut of grass, if cutted grassland, N-fertilizer |
التعليقات:
If renewing the grassland, there will be no ploughing, collecting the stones and sliping. Only chisel plowing and/or sowing with fertilization. If the grassland will be use for grazing, no need for fertilization during growth period.
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Driver (machinery work) | person day | 0,5 | 36,0 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Equipment (machinery) cost on establishment year | year | 1,0 | 207,0 | 207,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | kg | 22,0 | 2,47 | 54,34 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Complex fertilizer | kg | 500,0 | 0,42 | 210,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 100,0 | 0,33 | 33,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 522,34 | |||||
التعليقات:
For tillage and other operations it is calculated 14-18 EUR/ha.
If to hire equipment the labour costs should be included to the machinery costs - for cutted grassland 225 EUR/ha, for grazed grassland 162 EUR/ha
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting or grazing the grass | نباتية | 1-4 times per vegetation period |
| 2. | Fertilization | زراعية | in spring in the beginning of season and after every cut N-fertilizer, after each second year complex fertilizer |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | Grasslands for cutting - machinery costs | year | 1,0 | 141,0 | 141,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 200,0 | 0,33 | 66,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Complex fertilizer | kg | 200,0 | 0,42 | 84,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Materials for hay making | year | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 306,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
The governmental support to establish and to maintain the grassland is 50 EUR/ha.
If to use the land for the grazing, the machinery cost per year is 38 EUR/ha.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Fuel price.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
696,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Average 696 mm, almost equally spread over the year, more from July to October, less in March and April
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Tartu Tõravere
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
LGP 180-195 days
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات محدبة أو نتؤات
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Eutric Histosol, well decomposed peat, drained area.N 2.32%; C32.89%; C/N14.20%; P2,62 mg/100g; K 13.73 mg/100g; Ca 1762.32 mg/100g; Mg 166.98mg/100g
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Histosols biodiversity depends on the base saturation and level of groundwater (degree of drainage). Diversity is higher at higher pH and better drainage.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- تعاونية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
There are also small-scale and medium-scale farms applying the technology. At Pae, the farm have 4900 ha of land, from which 1800 are grasslands, at Annikoru the farm have 2320 ha of land from which 390.5 ha are grasslands.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
- individual/open access
التعليقات:
Groundwater belongs to the state. Smaller water bodies can be in individual use, larger are usually open access
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The area will be excluded from crop production and it means no cash crops can be cultivated on this area. Instead of crops hay or silage is possible to sell.
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
As it is not allowed to renew these grasslands intensively, the quantity of grass will drop. For short term clover+grasses mixture the average yield is 16 tons/ha per year, for long-term grass mixtures 5.2 tons/ha per year.
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to the change of species in the mixture, the protein level will drop. Instead of red clover grasses will be used in the mixture of long-term grasslands.
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to the changes in silage/hay quality (protein) there can be reduction of milk and meat production if the differences will not be covered with other fodder.
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
In case of crop orientation, there are new products to sell - grass, hay, silage, or grasslands to rent.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Depending on the farm it can be simplified or hindered. If focus was on crops, then new machinery is needed to manage grasslands (for cutting, hay or silage making).
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
As renewing of grassland is after every 5 years, there is no need to buy seeds every year, as well as pesticides and to till the soil.
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to the reduction of the inputs costs, the income my increase. Also the government pays support 50 EUR/ha for the land under these measures.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Next to the yield (grass, silage, hay) the support from the government (50 EUR/ha)
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
It may decrease due to no need of every year tillage and sowing and due to the change from 2 year short-term grasslands to the permanent grasslands. However, if not managed grasslands earlier it may increase the workload as cutting and collecting the grass is needed.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
More land under grasslands than under crops. Grasses are suitable for animals feeding, not for human direct consumption.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
If land was eroded before and soil was on the road, everybody can see the differences after establishment of the grasslands. It is not so severe in case of peatlands, however, less tractors will stuck in to the mud on rainy period.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
In case of erosion, no soil will be washed down to the hill as plant cover protects soil surface and increases infiltration. In case of peatlands, grass cover creates better structure and increases water infiltration thus decreases surface runoff during heavy rainfall.
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Grass creates protection to the soil surface and raindrops can't destroy the soil structure any more. Also grass roots create better porosity and structure in the soil leading to better water drainage.
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The difference in soil moisture between mineral and organic soils under cereals and under grassland was ca 5% and 25%, respectively, in favour to the grasslands in autumn 2016.
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under spring cereals soil is covered only 4-5 months per year, under grasses soil is covered 100% of the year.
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
On the slopes depending o the crop and the amount of precipitations, the loss varied from 3 to 60 tons/ha, under permanent grass cover it is less than 0.05 tons/ha per year. Without every year tillage there is no intensive decomposition of the peat, as well as no wind erosion.
تراكم التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under grasses we can increase the soil organic matter content by 0.35 t/ha in 5 year period in peatlands. In eroded soils we can increase 0.02% per year.
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
As plants protect soil surface, raindrops can't destroy the soil structure and there will be no crust formation
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under the grasslands the bulk density was lower by 0.1-0.2 g/cm3 compared to tilled soil.
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the intensive decomposition of the peat stops or there will not be any leaching by water, more nutrients remain in the soil. Also the permanent plant cover during the whole year stops nutrient leaching.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under permanent grasslands the Corg increases by 0.35 t/ha per 5 year period.
الحموضة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Without periodic liming the acidity of peatlands starts to increase. If no CaCO3 in mineral part, also pH of previously eroded soils starts to decrease slowly, as organic acids form during decomposition process.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Thanks to the permanent plant cover there is no period of the year without vegetation.
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
If previously the plant residues were mixed with the soil by tillage, now there will always some extent of plant mass be left above ground (5-10 cm), even if the most is removed for hay or silage.
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Long-term grassland includes at least 4 species in the mixture, short-term mixtures 2-3 species. However, compared with the cereals, the annual weeds will disappear and the diversity may decline.
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
There are more spiders, ants, beets.
الأنواع المفيدة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2 species of earthworms
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3-4 species of earthworms
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under grasslands were 1-2 more earthworm species than under tilled management. More spiders and ground beetles were found there compared to the tilled soil.
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Grasslands create untilled patterns to the landscape.
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
Grasses surpress many soil born crops diseases and pests, also annual and perennial weeds.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Grass roots go to the deeper soil and they are not so sensitive to the drought.
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
خطر الحريق
التعليقات/ حدد:
If the grass will not be cutted before winter, the dry grass has the risk of higher landscape fires in the spring.
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
التعليقات/ حدد:
The changes of soil temperature as well as moisture content are smaller under permanent grass cover than under tillage.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
التعليقات/ حدد:
All year plant cover helps to bind nutrients and stop their leaching from the soil. Higher amount of organic matter in the soil increases water holding capacity.
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Organic peat particles are light and are easy subject of wind erosion in dry conditions by tillage. Permanent plant cover stops such kind of erosion
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
التعليقات/ حدد:
On hilly landscape no extra soil is flushed to neighbours fields. In case of peatlands no dust is carried around.
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
التعليقات/ حدد:
In case of erosion, no soil is carried by water or wind to the ditches and on the roads.
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الشتاء | زيادة | باعتدال |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الربيع | زيادة | باعتدال |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | زيادة | غير معروف | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الشتاء | زيادة | غير معروف |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الخريف | زيادة | غير معروف |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | باعتدال |
| عاصفة رعدية محلية | غير معروف |
| عاصفةبَرَد محلية | غير معروف |
| عاصفة ثلجية محلية | باعتدال |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة باردة | غير معروف |
| ظروف شتاء قاسية | باعتدال |
| جفاف | باعتدال |
| حريق الأرض | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | باعتدال |
| هبوب العواصف / الفيضانات الساحلية | باعتدال |
| الانزلاق الأرضي | جيدا |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| أمراض وبائية | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
In 2016 two hundred four households got the governmental support, in total 10554 ha
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
التعليقات:
Anyway, the use of Histosols and Gleysols is limited due to their properties and regular use of these soils is for grazing or grass cutting.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Better soil protection |
| Possibility to earn money in unsuitable soil conditions. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Reduces soil erosion on hilly landscape |
| Reduces the decomposition of peat on Histosol |
| Reduces CO2 emission from agricultural land. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Loss of income | Governmental support (50 EUR/ha) |
| Problems with the grass (farms without animals) | Cooperation with neighbours, selling the hay for energy production |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Farmers don't want to use the technology | More effective lobbying |
| Wrong declaration of the land under the technology | Better advisory system and improvement of electronic databases |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
5 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
10 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
8
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Bender, A. (koostaja) 2006. Eritüübiliste rohumaade rajamine ja kasutamine. I. ja II. osa. Jõgeva
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Bender, A. 2010. Heintaimede sordiaretus ja seemnekasvatus. Jõgeva Sordiaretuse Instituut
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Older, H. 2011. Kohalikud söödad. Eesti Rohumaade Ühing.
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.agri.ee/en/objectives-activities/estonian-rural-development-plan-erdp-2014-2020
العنوان/الوصف:
Kattetulu arvestused taime- ja loomakasvatuses 2016. Koost: Marju Aamisepp, Helle Persitski. Maamajanduse infokeskus. 2017.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.maainfo.ee/data/trykis/kattetulu/KATTETULU2016.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
Statistics Estonia
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.stat.ee/en
العنوان/الوصف:
Eesti maaelu arengukava 2007-2013 2. telje ning Eesti maaelu arengukava 2014-2020 4. ja 5. prioriteedi püsihindamiseks 2016. aastal läbiviidud uuringute aruanne. Põllumajandusuuringute keskus. Saku 2016.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://pmk.agri.ee/mak/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/09/aruanne_uuringud_2015.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
Eesti tuleviku kliimastsenaariumid aastani 2100
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/kliimastsenaariumid_kaur_aruanne_ver190815.pdf
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية