Ecosystem-wide seasonal grazing management in community land [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Peter Tyrrell
- المحررون: Lance W. Robinson, Enoch Mobisa
- المُراجع: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_3372 - كينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/01/2017
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Livestock movements are managed through community governance systems to maintain spatial and temporal heterogeneity of pasture, creating a gradient of quality and quantity of pasture across the landscape. This is achieved through clearly designated seasonal grazing areas for livestock and tight controls on settlement areas, grazing patterns and water points. In addition, at the individual herder level, traditional ecological knowledge plays a strong role in the decisions made to improve livestock production
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
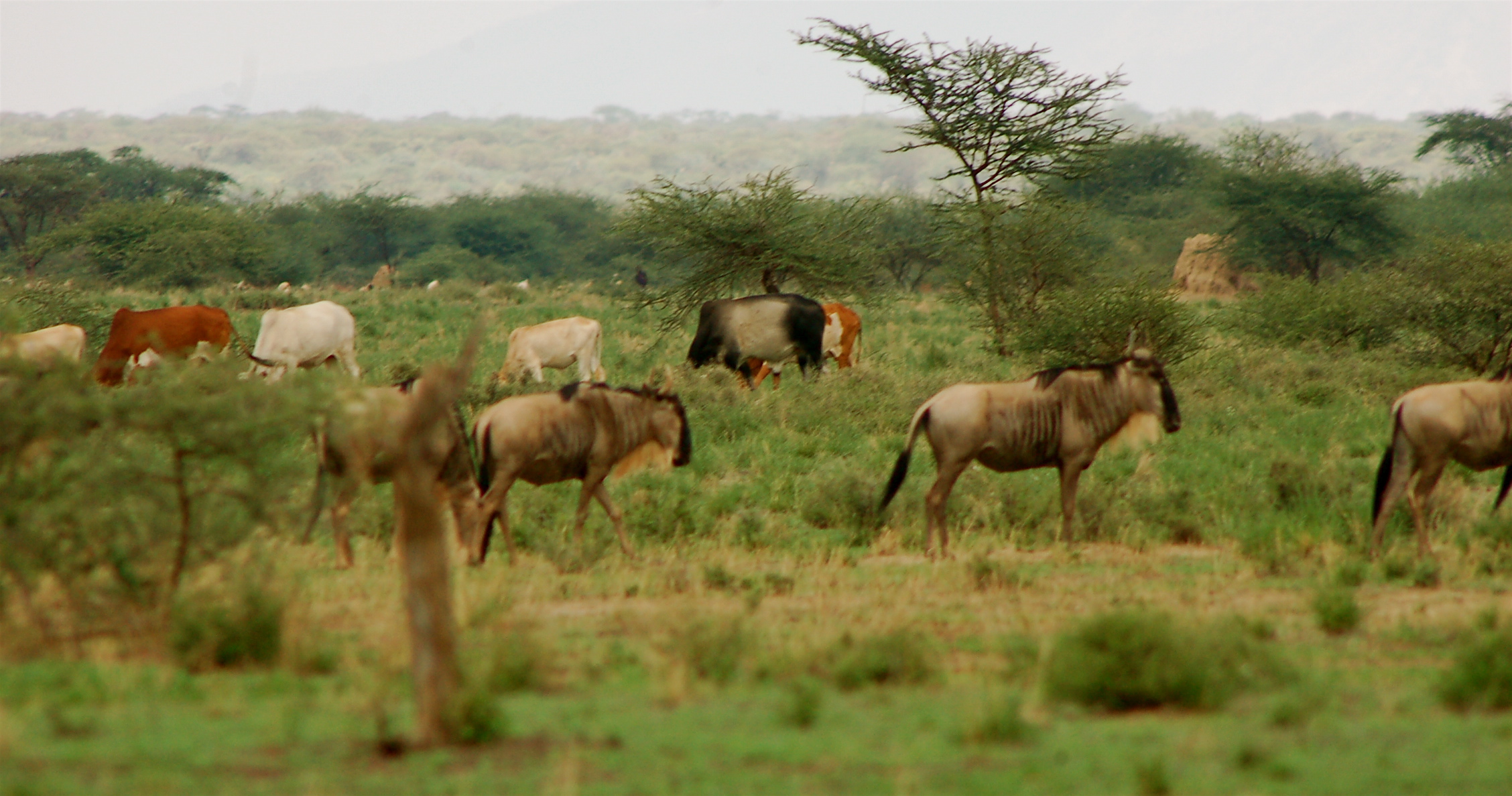
This technology is applied in the South Rift Valley, Kenya, across a semi-arid landscape, with erratic rainfall averaging 400-600 mm per annum. Water availability is an issue. The perennial Ewaso Ngiro South river flows through the Shompole swamp, a vital drought refuge for livestock and wildlife, before ending up in Lake Natron. The area, roughly 1000 km2, is covered by two group ranches, Olkiramatian and Shompole, which are managed as a single ecological unit. A group ranch is a jointly owned freehold land title given to the customary occupants of communal lands. The total number of occupants of both ranches number roughly 20,000 people, with the majority belonging to the Maasai ethnic group. The ranches have not been subdivided and are not fully sedentary, unlike many other areas of southern Kenya.
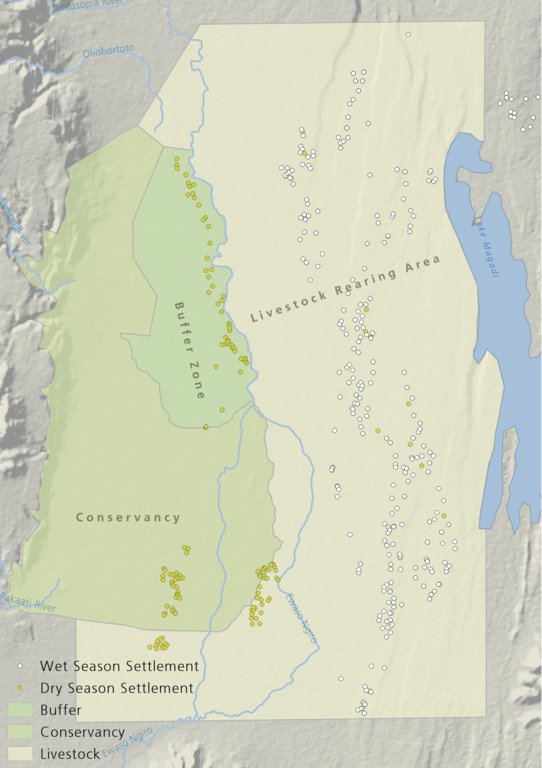
There is a long history of co-existence of wildlife and livestock in Maasialand. In Olkiramatian and Shompole seasonal livestock movements and herding practices are formalized by group ranch grazing plans governed by local committees. The wet season grazing areas are termed “livestock rearing zones”. The dry season grazing areas have been retained as “grass banks” for livestock, and since the early 2000s, have been used additionally as wildlife conservancies for ecotourism (see figure below). Livestock rearing occurs to the east of the Ewaso Ngiro river; grass banks and the wildlife conservancy to the west. Grazing committees from both group ranches manage livestock access to certain areas, with the conservancy (grass bank) rested during the wet season of up to six months. When grazing is permitted in the conservancy, as the dry season progresses, temporary settlements are limited to an area called the “buffer zone”. Livestock must then move into the conservancy from the buffer zones to access this late season grazing. The “livestock rearing zone” is permanently settled and grazed year-round. Within each zone there are small “Olopololis” (grass banks of a few hectares), situated near individual settlements and used to maintain higher quality pasture for weak and young animals. This management strategy ensures that the dry season grazing area is rested during the rains, and it helps to maintain consistently higher biomass and taller grass than that of the wet season grazing area. The higher biomass also corresponds to a rainfall gradient running from the Nguruman Escarpment edge in the western extremity of the group ranches to the dry central rift valley floor in the east. The biomass in the dry season area is used by both livestock and wildlife grazers during the late dry season and in droughts. The grass bank is only grazed out during prolonged dry periods. The Maasai employ a strategy of using the shorter milk-producing grasses of the livestock areas during the rains and the coarser grasses in the grass banks for the dry seasons. The shorter wet season pastures have a higher nutrient content and greater digestibility than the grass bank: this is very important for lactating females. The grass is kept short from both grazing by livestock during the growing seasons and due to intrinsic differences caused by shallower soils and lower rainfall in these grazing areas.
Within this broader governance framework and control of grazing areas, individual decision making is also permitted within these controlled areas. This allows herders to manage livestock to improve production in relation to each herd. For example, individuals might split the herd to take advantage of different energy and nutrient requirements of lactating females, bulls, and calves.
This maintenance and exploitation of forage heterogeneity is vital to the productivity and resilience of the landscape, and this heterogeneity exists at multiple scales, with the major differences existing between the grazing areas, but also smaller difference within them. Resource heterogeneity facilitates wildlife-livestock coexistence. This heterogeneity creates a matrix of varying quality and quantity of forage. Wildlife species have different metabolic requirements and diets, and this varied base ensures that a diverse wild ungulate population is maintained year-round. Late season forage boosts the resilience of wildlife during extreme events. This technology requires a governance structure that is both responsive to the changing ecological conditions and able to build consensus and enforce grazing management
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kajiado
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Olkiramatian
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2004
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The grazing management system is adapted from traditional grazing management of Maasai pastoralists.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
The area is semi-arid and receives rainfall erratically, both in space and time, in a bi-modal pattern.
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Long rains fall between April - June; Short rains fall between October - December.
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
Cattle 6.2 / km2; Shoats 52.2 / km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
التعليقات:
The technology formerly worked across the entirety of Maasailand (50,000 km2). However, breakdowns in social structures, culture, and governance arrangements have led to wide-scale losses in traditional grazing management. Olkiramtian and its neighbor Shompole, are two of the few communities managing to graze in such a way to maintain and capitalize on the spatial-temporal heterogeneity of forage resources through merging traditional and modern institutions.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
- M3: التخطيط وفقا للبيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
- M4: تغيير كبير في توقيت الأنشطة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Although in general, this technology aims to prevent land degradation through the maintenance of forage cover; localized degradation does occur across different locations within the landscape, especially in areas of highest livestock impact, such as water points and settlement areas.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
The drawing shows the management units used in this seasonally structured grazing management system. The livestock rearing zone, to the east of the Ewaso Nyiro river, is permanently settled and is grazed heavily during the wet season (April - July). During this time herders utilize the short, nutritious grasses in this low biomass area. As forage biomass begins to reduce the community grazing committees meet to discuss the opening of settlements to the west of the Ewaso Nyiro river. This decision is made using traditional ecological knowledge, comparing available forage biomass and the numbers of livestock to previous years and past experiences. Once the grazing has been opened to the west of the river people may settle within the buffer zone. This limits direct access to the higher biomass areas within the conservancy and grass banks, and increases the length of travel for each herd every day, in an effort to preserve forage for longer. Once forage has been depleted in the buffer zones and the periphery of the conservancies, the committees meet and allow access for herders into the conservation areas, which have tall, high biomass, but low-quality grazing. Often access to this area requires considerable distances to be walked by livestock. In recent years, adaptive management systems have led to the settlements within the south of the conservation area to be closed to preserve forage biomass within the swamp and conservation area for a longer period of time; and allow for recovery of partially degraded land.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
The two group ranches
حدد الحجم والطول وما إلى ذلك (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
Approximately 1000km2
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
4
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
التعليقات:
No activities were required to establish this practice as it has been ongoing and builds on traditional management structures.
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
N/A
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Management meetings | إدارية | Seasonally |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
The only real costs of this technology, which is different to any other form of grazing system, would be the cost of management through meetings. Otherwise the costs are just that of any other livestock production enterprise.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
There are no or little costs to this technology, as it builds off structures of management which are already in place and work organically within the area.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
400,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Highly variable rainfall both spatially and temporally. Annual average rainfall has a 33%CV.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Lale'enok Resource Centre
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
- قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
This area lies at the bottom of the rift valley, with the Nguruman Escarpment and Loita Hills towering up to the west. This change in elevation ensures that there is fresh water reaching the area year round and that there is very late season forage available at higher altitudes if required.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Seasonal floods down the Ewaso Nyiro river provide an important water source for the Shompole Swamp. This swamp acts as an import drought refuge for livestock.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
تنوع الموائل:
- مرتفع
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
The area has an intact community of large herbivores, 21 species of carnivore and a growing population of elephants. This in part due to the habitat diversity and heterogeneity that has been maintained. Habitat diversity is facilitated by elevation changes up the Nguruman Escarpment, a variable rainfall gradient from East to West, the presence of Soda lakes, and the presence of perennial rivers. The area is also an Important Bird Area and is home to two community conservation areas. It holds some of the largest numbers of large mammals outside of government protected areas in Kenya.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
All ages are involved in this practice and all genders. It is a way of live using this management.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
This land is managed under two community land titles. The management is at an intermediate scale as it does not address grazing management beyond the ecosystem boundary and across the greater landscape. This larger-scale approach is, however, a critical component of a larger landscape management system which was previously governed under Maasai culture.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- Traditional methods of water management through comittees exists in some areas. In other area the creation of Water Resource Users Associations has begun to manage water.
التعليقات:
The land is owned under two community titles. The land-use is restricted to members of the group ranches, who may allow for reciprocal grazing rights to be exchanged with neighbouring communities.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
This is in contrast to areas without seasonal grazing management.
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
This management system works best to preserve lower quality higher biomass fodder. Quality may not increase dramatically, but the creation of short areas of well-fertilized grass near settlements may increase the local quality of fodder during the wet season.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
In comparison to other systems the preservation of late season grazing is crucial in preventing complete losses of livestock during droughts.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الفرص الثقافية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Management of land in this manner relies on traditional ecological knowledge for both individual and community decision making. This is dependent on cultural values and understanding, and underpins grazing management in Maasai society.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
This method increase vegetation cover by maintaining heterogeneity of forage resources across the landscape, and resting pasture seasonally to allow for vegetation regrowth.
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Late season forage available. Recovery and rest allows for greater productivity and rainfall use efficiency.
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Maintenance of spatial and temporal heterogeneity of forage resources ensures that wildlife species have access to the variable resources that they require over time.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | انخفاض | باعتدال |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
No costs to establish and low direct cost of management actions.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
This system is adopted by most land-users because of the governance systems in place. There are some individuals who may not choose to abide by the rules set out by the committees, but a combination of peer pressure; traditional curses; and fines usually prevent this.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، وضح الظروف المتغيرة التي تم تكييفها معها:
- تغير المناخ / التطرف
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
The management is constantly being adapted based on the prevailing ecological conditions. In 2015, over fifty settlements were closed by the community grazing and group ranch committee within the dry season grazing area to allow for pasture regeneration and to consolidate preservation of the dry season grass bank.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| This technology stems from a community based and is not imposed from a top-down perspective, and tries to create consensus among resource users. |
| Allows individual flexibility within the broader grazing structure so that people can manage livestock within their own objectives. |
| This technology provides forage for livestock into the dry season and drought. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Management in this way also replicates the methodologies used for land management for thousands of years by pastoral people and helps to generate an enabling environment for the coexistence of wildlife, domestic livestock, and people. |
| Ensures that pasture is rested during the growing season within the dry season grazing areas, so that root mass can be established and to ensure grass seed production. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Exploitation of the system by elites in charge of management decisions, allowing their livestock to access preferential grazing, which may not represent the needs of all groups. | Ensure credible management structures in place; with the new community land act, this should encourage greater equity in decision making. |
| Preventing settlement in areas of traditional occupation by certain households. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Lack of focus on a production based system and income generation through livestock sales. | Create and enabling environment for change, through market improvement and learning exchanges. |
| Lack of resting and recovery of forage in the wet season grazing area. | Rotate and rest wet season pasture for a few weeks during the growing period, potentially through grazing in the dry season reserve for a longer period. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Living in the area for the last four years.
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Seasonal movements of wildlife and livestock in a heterogeneous pastoral landscape: Implications for coexistence and community based conservation
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2351989417301075
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية