Vegetated earth-banked terraces [إسبانيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Joris De Vente
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Deborah Niggli
Terrazas de tierra vegetadas (Spanish)
technologies_1516 - إسبانيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
López Carratala Jorge
+34.950.281045
carratala@cebas.csic.es
Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Estación Experimental de Zonas Áridas (EEZA-CSIC)
General Segura 1, 04001; Almeria; Spain
إسبانيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
EEZA-CSIC (EEZA-CSIC) - إسبانيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
05/04/2011
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Regional rural development programme [إسبانيا]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- جامع المعلومات: Joris De Vente
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
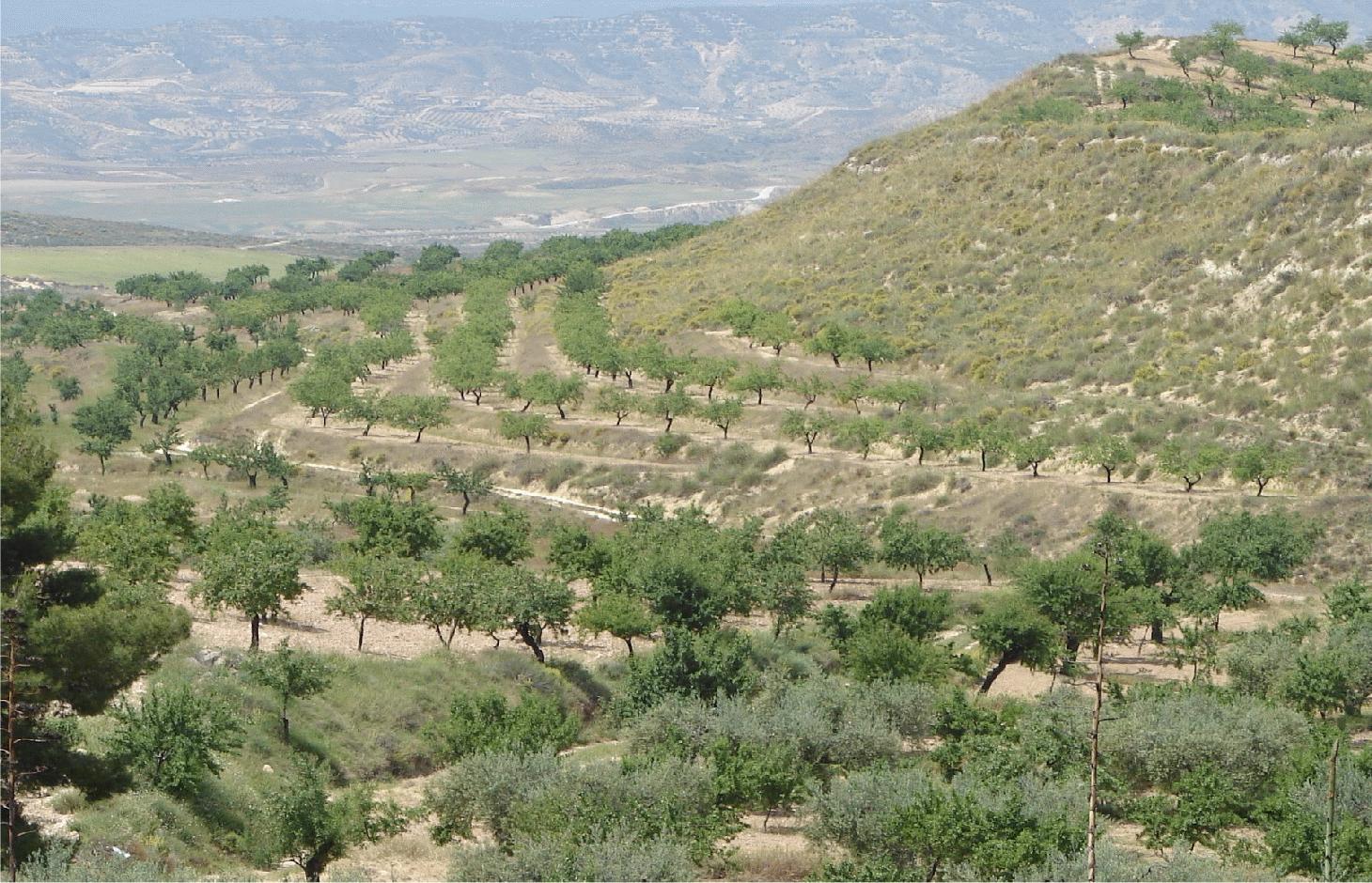
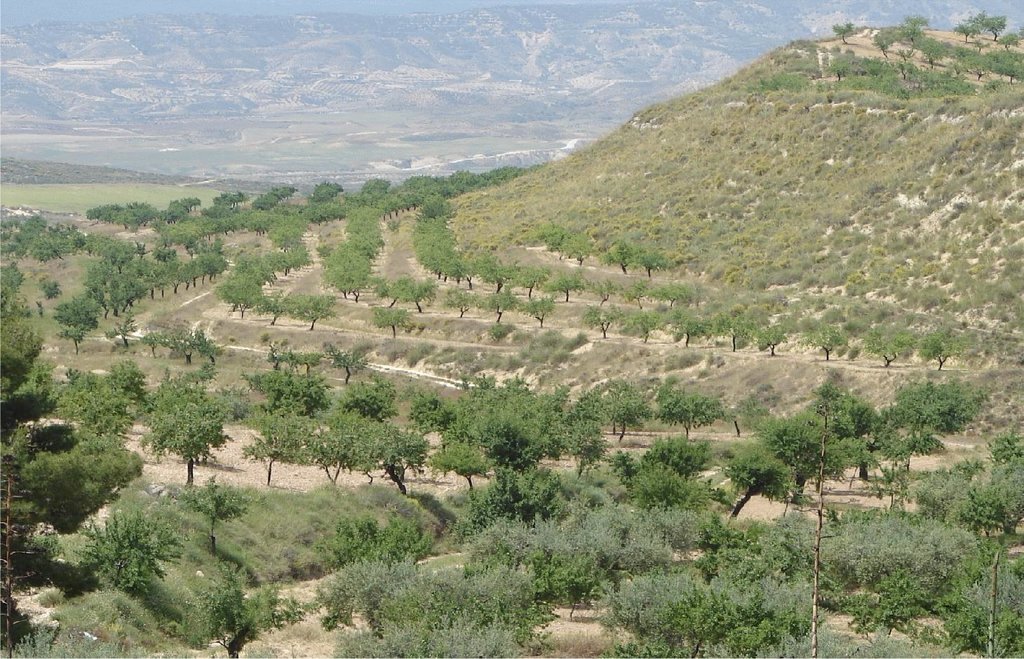
Earth-banked terraces in cereal and almond cropland covered with drought-resistant shrubs.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
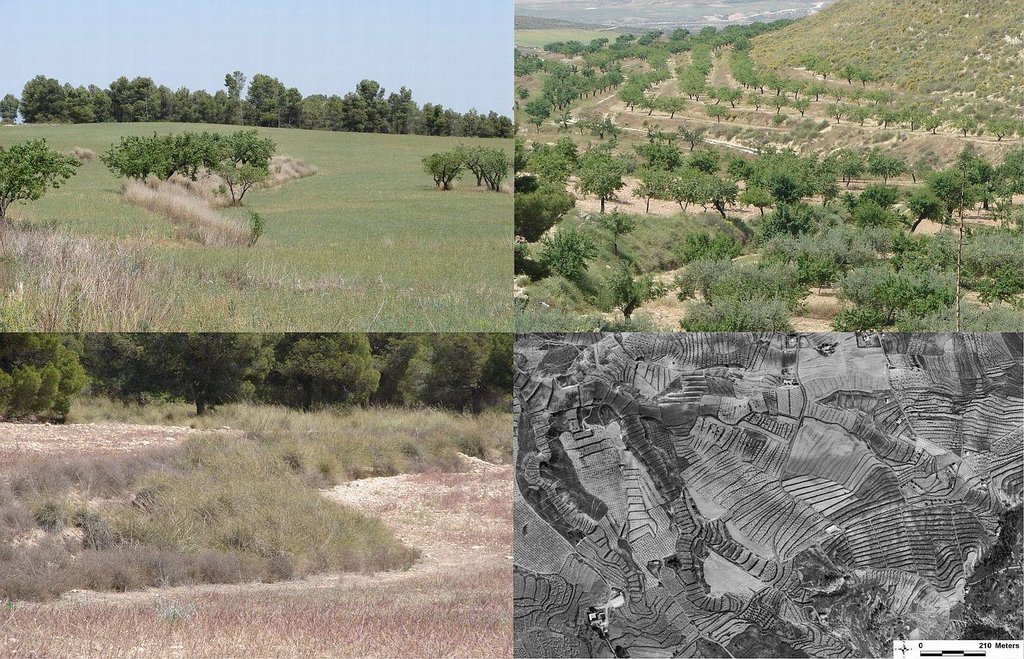
Earth-banked terraces are constructed by carefully removing a superficial soil layer (~10-20 cm) from one part of a field, concentrating it on the lower end of that field in order to reduce slope gradient and length. Another terrace is created directly downslope to form a cascade of terraces. Terrace risers have to be of restricted height (~50-150 cm) to prevent steep and unstable terraces. Stones from the fields can be used to reinforce the terrace ridge. After terrace construction, fields should be gently sloping (<3%) in the direction of the main slope. The distance between terraces must be enough to allow tractor movement during normal cultivation activities and it depends also on the slope gradient. The steeper the slope, the shorter is the distance between terraces. Terraces reduce the formation of gullies and retain water from upslope. The terraces are made with locally available machinery (tractor, small bulldozer). The terrace ridges are optimal locations to plant olives, almonds or fruit trees. Moreover, to be most effective, the terrace ridges are vegetated with shrubs adapted to semi-arid conditions and with a good surface cover (>~30%) throughout the year (e.g. Stipa tenacisima, Rosmarinus officinalis, Thymus vulgaris, Ulex parviflorus, Rhamnus lycioides, Pistacia lentiscus). Natural regeneration of vegetation is allowed without limitation on the terrace ridges, so no herbicide application or burning are carried out to remove weeds. Where possible, regeneration should be stimulated by planting the same adapted species in at least 25% of the terrace ridge. Optionally, in the other 75% of the terrace ridge, cereals or other leguminous species can be sown, but should not be harvested or used for grazing.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology reduces flooding, damage to infrastructure and siltation of water reservoirs, while maintaining (or slightly increasing) crop productivity. This is achieved by reducing runoff, soil erosion and hydraulic connectivity through a decreased slope gradient and an increased vegetation cover. The terrace ridge functions as a sink for runoff within fields and reduces runoff velocity. The vegetation leads to increased soil organic matter content below plants, producing an improved soil structure and a higher infiltration capacity. The use of stones from the fields to reinforce the terraces is optional, but facilitates crop production in the fields and makes the ridges more resistant to higher runoff velocities. The technology requires an initial investment in the construction of the terraces. Terraces can best be located on thalwegs and on areas where gully formation is often observed. Maintenance consists of filling up possible bank gullies developed in the terraces after important rainfall events and, if needed, substitute decayed shrubs with new ones.
Natural / human environment: The technology is generally applied on soils of shallow to medium depth (20 – 60 cm), and slopes are gentle to moderate (5-15%). The climate is semi-arid with a mean annual rainfall around 300 mm. Droughts, peaking in summer commonly last for more than 4-5 months. Annual potential evapotranspiration rates larger than 1000 mm are common. The production system is highly mechanized and market-oriented but depends strongly on agricultural subsidies. All cropland is privately-owned.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
إسبانيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Murcia
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Guadalentin catchment
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Most of the earthen terraces are already much older than 50 years. Recently, the regional administration is promoting clearly defined vegetated strips with minimum dimensions in order to apply for subsidies.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الحراجة الزراعية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): A lack of water availability seriously limits the production potential of the soil and results in a low vegetation/crop cover. The relatively high soil erosion rates cause various off-site related problems (i.e. flooding, reservoir siltation) and on-site problems (i.e. gully formation and loss of soil depth).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water for irrigation of crops limiting the crop types that can be planted as well as the crop yield of dryland farming.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: November to June
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 100-10 كم2
التعليقات:
The exact area is not known, but the technology is widely applied throughout the province of Murcia and the district of the upper Guadalentin.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Almond and cereal fields often have a relatively low surface cover by vegetation during long periods of the year, leaving the soil unprotected against raindrop impact and rill or gully formation), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Reduced infiltration capacity causing runoff and soil erosion), other human induced causes (specify) (Cropping of relatively steep slopes sensitive to erosion because of slope gradient), governance / institutional (spatial planning of land use results in formation of too large fields without field boundaries)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (High intensity erosive rainfall is common), droughts (Dry periods and dry years require higher water availability)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
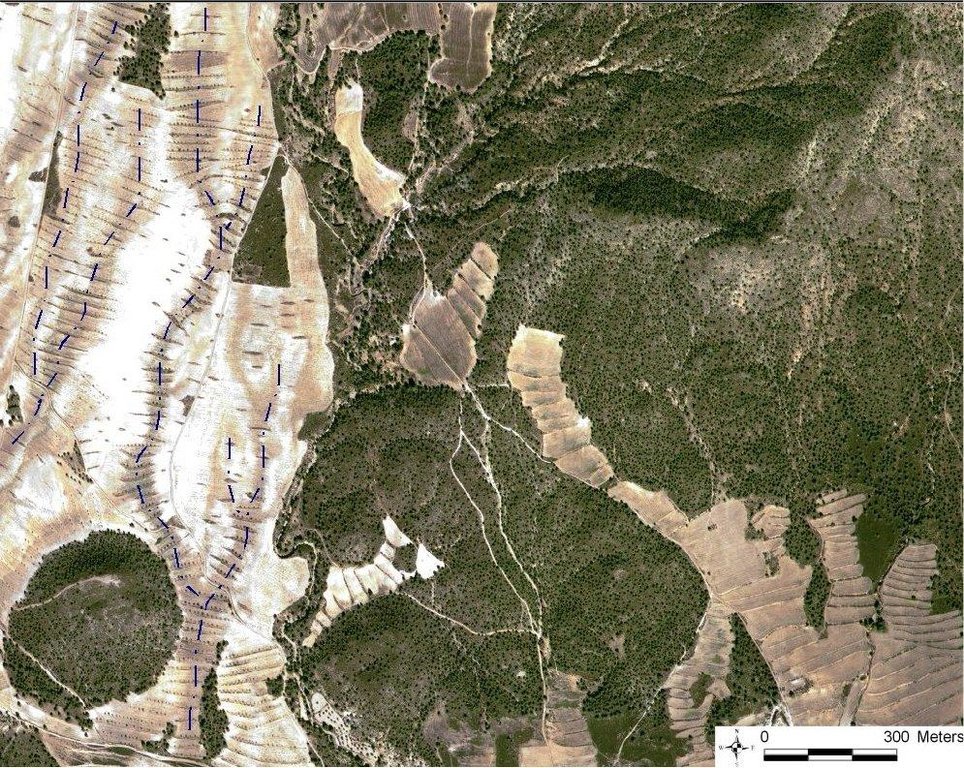
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Quickbird satellite image showing the concentration of terraces along natural drainage lines (thalwegs) where runoff concentrates. Drainage lines are indicated with dotted lines.
Location: Torrealvillla. Murcia
Date: Satellite image 2003
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Design of the terraces and selection of the location requires some technical knowledge.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Practical implementation of the terraces does not require a high level of knowledge)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 42
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 30-100
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-7
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: alligned: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): >30% cover
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 30-100
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Fruit trees / shrubs species: natural regeneration of shrubs with possible additional plantation of almond trees and/or woody shru
Grass species: Natural regeneration assisted by seeding of legiminous species and cereals
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 30-100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-200
Construction material (stone): Only when many stones are present in the fields
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-15%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: <3%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
EURO
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,63
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
79.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plantation of shrubs and cereals or Leguminous species (optional) | نباتية | Autumn - winter |
| 2. | Construction of terraces | بنيوية أو هيكلية | autumn or winter |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 270,0 | 270,0 | 10,0 |
| معدات | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 428,0 | 428,0 | 12,0 |
| المواد النباتية | shrub seedlings and seeds | ha | 1,0 | 218,0 | 218,0 | 10,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 916,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replace died shrubs (optional) | نباتية | autumn-winter |
| 2. | Filling up bank gullies in terraces | بنيوية أو هيكلية | twice a year or after heavy rainstorms |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 28,0 | 28,0 | 10,0 |
| معدات | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 24,0 | 24,0 | 10,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Shrub seedlings and seeds | ha | 1,0 | 22,0 | 22,0 | 10,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 74,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: For initial construction a large tractor or small bulldozer is required. For maintanance a normal tractor can be used.
The costs were indicated assuming a distance between terraces of 50 meter, meaning two terraces of 100 meter long per hectare. Prices are for spring 2008. Subsidies are foreseen for the installation of the vegetated terraces and for maintenance during at least 4 years if all requirements are fullfilled that are described in the regional development programme.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Price of fuel and labour are the most important determinants of the costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
300,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Dry period in summer during 3-4 months (June – August/September)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate. The higher parts are generally somewhat colder
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Hill slopes-footslopes (mostly on concave slope segments)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: >50m (There is a lowering of groundwater table due to overexploitation for irrigation purposes)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (excess: sporadically there are flash floods during extreme rainfall events)
Water quality (untreated): For agricultural use only (irrigation) (groundwater)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Traditionally most agriculture is done by men in this region.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is no difference in the ones who apply the technology and those who don’t. Most farmers do have an off-farm income for example from hunting, work in a factory, or office.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- فردي
التعليقات:
All cropland is privately owned. Some shrubland or forest is state property. Water use is organised by permits to water extraction from aquifers on individual basis. Water rights are provided and controlled by the Water authority of the Segura river basin (CHS).
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Depending on local conditions yield may be the same or increase slightly
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Field paths become shorter, so more tractor movement is required (not more kilometres!)
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Implementation of terraces is considered relatively expensive
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Depends on crop yield.
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less damage to fields due to less gully formation
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less damage to neighbours fields by gullies and flooding
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
There is less damage to fields and to infrastructure due to gully formation and flooding.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
On the long term higher infiltration capacity of the soil
الجريان السطحي
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation on the terraces increases vegetation cover
فقدان التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Provided by the vegetation on the terraces
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Provided by the vegetation on the terraces
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Terraces provide corridors connecting fields and provide shelter
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
The crop type is sensitive to changes in water availability under the semi arid conditions
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
التعليقات:
Implementation of the terraces is relatively expensive. Additionally planting of shrubs is also relatively expensive and requires a subsidy. Once installed, maintenance is not expensive and pays off because of less damage to fields and infrastructure.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
التعليقات:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Terraces are traditionally widespread in the region. Most of them were installed without external support. Nowadays there are subsidies for construction and maintenance of vegetated strips and terraces.
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is acceptance, but it is not growing. In some parts terraces are removed to make larger fields, and some new ones are also constructed. Recently installed subsidies may change this
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
The terraces prevent gully formation and damage to the fields and to their neighbours How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance is needed and should be promoted. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
This technology is very effective at reducing surface runoff and erosion by reducing slope gradients and connectivity. In addition, it has a water harvesting effect. So it reduces on-site and off-site erosion problems and potentially increases water retention in the fields. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology can be enhanced by providing more info and publicity so that existing terraces are maintained. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| It is considered relatively expensive to implement and particularly the optional planting of woody species is considered complicated in dry years | Subsidies for terrace construction and planting of woody species as well as cooperation between farmers to reduce costs of maintenance when subsidies stop. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The technology does not significantly improve farm income and has a significant implementation cost. | Provide information on all the advantages that include many costs for society (including floods, reservoir siltation etc.). The subsidy for implementation already solves the problem of implementation costs. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Garcia-Fayos, P. and Gasque, M., 2002. Consequences of a severe drought on spatial patterns of woody plants in a two-phase mosaic steppe of Stipa tenacissima L. Journal of Arid Environments, 52(2): 199-208.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
internet
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Hooke, J.M., 2006. Human impacts on fluvial systems in the Mediterranean region. Geomorphology, 79(3-4): 311-335.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
internet
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kirkby, M.J., Bracken, L.J. and Shannon, J., 2005. The influence of rainfall distribution and morphological factors on runoff delivery from dryland catchments in SE Spain. CATENA, 62(2-3): 136-156.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
internet
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
CARM 2008. Programa de Desarrollo Rural de la Región de Murcia 2007-2013 Tomo I. 508pp
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.carm.es/neweb2/servlet/integra.servlets.ControlPublico?IDCONTENIDO=4689&IDTIPO=100&RASTRO=c431$m1219
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Regional rural development programme [إسبانيا]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- جامع المعلومات: Joris De Vente
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية